Financial Distress Drives Health System Mergers Kaufman Halls Role
Financial distress drives health system merger acquisition Kaufman Hall, a statement that’s become increasingly relevant in today’s healthcare landscape. The rising costs of care, coupled with shrinking reimbursements, have pushed many hospitals and health systems to the brink. This precarious financial situation is forcing them to consider drastic measures, with mergers and acquisitions emerging as a potential lifeline. But navigating this complex process requires expert guidance, and that’s where firms like Kaufman Hall come in, offering their expertise in financial advisory and strategic planning to help these organizations survive and thrive.
This post dives into the critical role Kaufman Hall plays in facilitating these mergers and acquisitions, examining the strategies employed and the long-term implications for both the merging entities and the patients they serve.
We’ll explore the various factors contributing to financial distress in healthcare, from the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic to the persistent challenges of managing escalating operating costs. We’ll also analyze the different merger and acquisition strategies, examining their potential benefits and drawbacks. Finally, we’ll delve into the critical issue of long-term financial sustainability post-merger, highlighting the importance of effective planning and management to ensure the success of these combined entities.
Financial Distress in Healthcare Systems
The healthcare industry, while vital, is increasingly facing significant financial pressures. These pressures are forcing many systems to consider mergers and acquisitions as a survival strategy. Understanding the root causes of this financial distress is crucial for developing effective solutions and ensuring the long-term viability of healthcare providers.
Declining Reimbursements and Increasing Operating Costs
Healthcare systems are squeezed between decreasing reimbursements from payers (like Medicare and Medicaid) and escalating operating costs. Reimbursement rates often lag behind the actual cost of providing care, creating a significant revenue shortfall. Simultaneously, expenses related to staffing (salaries, benefits, and recruitment), pharmaceuticals, technology upgrades, and regulatory compliance continue to climb. This widening gap between revenue and expenses is a primary driver of financial instability.
For example, a hospital might see a decrease in Medicare reimbursement for a specific procedure while simultaneously facing increased labor costs due to a nursing shortage, leading to a significant loss in profitability.
The Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic dramatically exacerbated the existing financial challenges within the healthcare sector. Hospitals faced surges in patient volumes requiring intensive care, leading to increased expenses for staffing, personal protective equipment (PPE), and treatments. At the same time, elective procedures were often postponed, resulting in a significant drop in revenue. The pandemic also highlighted existing vulnerabilities in the healthcare system, such as staffing shortages and supply chain disruptions, further compounding financial strain.
Many healthcare systems experienced unprecedented losses during this period, impacting their long-term financial stability. For example, smaller rural hospitals, already operating on thin margins, were particularly vulnerable and some were forced to close their doors permanently.
Financial Indicators of Distress
The following table Artikels key financial indicators that signal distress in a healthcare system. Monitoring these metrics is crucial for proactive management and intervention.
| Indicator Name | Description | Impact | Mitigation Strategy |
|---|---|---|---|
| Operating Margin | Net income divided by operating revenue; reflects profitability of core operations. | Low or negative operating margin indicates financial instability. | Improve revenue cycle management, reduce operating costs, increase efficiency. |
| Days Cash on Hand | Number of days a healthcare system can operate using its current cash reserves. | Low days cash on hand indicates limited liquidity and vulnerability to unexpected expenses. | Improve cash flow management, explore financing options, reduce expenses. |
| Debt-to-Equity Ratio | Measures the proportion of debt financing compared to equity financing. | High debt-to-equity ratio signifies high financial risk. | Reduce debt levels, explore refinancing options, improve profitability to increase equity. |
| Patient Days/Occupancy Rate | Measures the average number of days patients stay in a facility or the percentage of beds occupied. | Decreased patient days/occupancy rates indicate reduced demand and potential revenue loss. | Expand services, enhance marketing and outreach, improve patient satisfaction. |
The Role of Kaufman Hall in M&A Activity
Kaufman Hall is a leading healthcare consulting firm that plays a significant role in the mergers and acquisitions (M&A) activity within the healthcare industry. Their expertise in financial advisory and strategic planning makes them invaluable partners for healthcare systems, particularly those navigating financial distress. They provide a wide range of services designed to help organizations make informed decisions, optimize operations, and achieve sustainable growth through strategic partnerships or acquisitions.Kaufman Hall’s Expertise in Healthcare Financial Advisory and M&A InvolvementKaufman Hall possesses deep expertise in healthcare finance, operations, and strategy.
This allows them to provide comprehensive advisory services throughout the M&A process. Their consultants understand the intricacies of healthcare reimbursement, regulatory compliance, and market dynamics, enabling them to develop tailored strategies that address the unique challenges faced by each client. Their involvement extends from initial feasibility assessments and due diligence to post-merger integration and performance improvement.
Services Provided to Financially Distressed Healthcare Systems
Kaufman Hall offers a suite of services specifically designed for healthcare systems facing financial distress. These services often include financial restructuring, operational improvement plans, and strategic planning to guide mergers or acquisitions. They might assess a system’s financial health, identify areas for cost reduction, and develop strategies to improve revenue cycle management. Furthermore, they assist in negotiations with creditors and stakeholders, helping to secure favorable terms and navigate complex financial situations.
Their goal is to stabilize the system’s finances and create a path toward long-term sustainability, often through strategic partnerships or acquisitions.
Examples of Successful Mergers and Acquisitions Facilitated by Kaufman Hall
While specific details of client engagements are often confidential, Kaufman Hall’s website and industry publications frequently highlight successful case studies demonstrating their impact. These case studies often showcase how their strategic guidance led to improved financial performance, enhanced operational efficiency, and increased market share for their clients following mergers or acquisitions. For example, they might describe how their analysis identified synergies between merging organizations, resulting in significant cost savings and revenue growth.
They may also illustrate how their expertise in regulatory compliance helped navigate the complex approval processes associated with hospital mergers. A successful case might highlight a struggling rural hospital that, through Kaufman Hall’s guidance, successfully merged with a larger, more financially stable system, ultimately ensuring continued service to the community.
Kaufman Hall’s Contribution to M&A Decision-Making
Kaufman Hall’s insights are crucial to the decision-making process during M&A transactions. Their financial modeling and valuation expertise provide a clear picture of the financial implications of potential mergers or acquisitions. They analyze market trends, competitive landscapes, and regulatory environments to assess the strategic fit and long-term viability of proposed transactions. This data-driven approach helps healthcare systems make informed decisions, minimizing risk and maximizing the potential for success.
Their analysis may include detailed projections of cost savings, revenue enhancements, and overall financial performance following a merger or acquisition, providing a robust foundation for the decision-making process. This reduces uncertainty and allows for a more confident approach to potentially transformative transactions.
Merger and Acquisition Strategies in Response to Financial Distress
Financial distress in the healthcare sector often necessitates strategic mergers and acquisitions (M&A) to ensure survival and long-term viability. The choice of M&A strategy is complex, depending on numerous factors specific to each system’s unique circumstances. Understanding these strategies and their implications is crucial for both the acquiring and acquired entities.
Comparison of Merger and Acquisition Strategies
Financially distressed healthcare systems employ various M&A strategies, each with its own set of advantages and disadvantages. These strategies broadly fall into categories such as acquisitions by larger, financially stable systems, mergers of equals facing similar challenges, or strategic partnerships focusing on specific services or geographic areas. Acquisitions often involve a larger system absorbing a smaller, struggling one, while mergers of equals imply a more collaborative approach where both organizations contribute equally to the new entity.
Strategic partnerships offer a less encompassing integration, focusing on shared resources or services without complete organizational merging. The choice hinges on the specific needs and circumstances of the involved parties.
Factors Influencing M&A Strategy Selection
Several key factors significantly influence the selection of an appropriate M&A strategy. The size of the organization plays a crucial role; smaller, financially distressed hospitals may be more easily absorbed by larger systems, while larger systems might pursue mergers of equals or strategic partnerships to address their specific challenges. Geographic location is another important factor, with proximity often facilitating operational integration and cost savings.
Kaufman Hall’s reports highlight how financial distress is pushing many health systems towards mergers and acquisitions. This pressure to consolidate is further complicated by the need to adopt cutting-edge technology, like the generative AI solutions discussed by Amy Waldron at Google Cloud Healthcare, as seen in this insightful article: google cloud healthcare amy waldron generative AI. Ultimately, the financial pressures driving these mergers often necessitate investments in tech like this to improve efficiency and boost revenue streams.
The type of healthcare system (e.g., hospital, physician group, long-term care facility) also impacts the strategy; a hospital facing financial difficulties might merge with another hospital or be acquired by a larger health system, while a physician group might seek a strategic partnership with a hospital to improve its referral network and financial stability.
Kaufman Hall’s report highlights how financial distress is pushing many health systems towards mergers and acquisitions. It’s a tough climate, and the news that NextGen Healthcare is exploring a sale, as reported by Reuters here , perfectly illustrates this trend. This pressure to consolidate is only expected to increase as healthcare providers grapple with rising costs and shrinking margins.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Various M&A Strategies
For acquiring entities, M&A strategies offer potential benefits such as increased market share, access to new technologies and expertise, and economies of scale leading to cost reductions. However, there are also drawbacks, including integration challenges, potential cultural clashes, and the risk of financial burdens associated with absorbing a financially distressed entity. For acquired entities, the benefits include improved financial stability, access to resources and capital, and the potential for enhanced service offerings.
Drawbacks can include the loss of autonomy, potential job losses due to restructuring, and the need to adapt to a new organizational culture.
Hypothetical Scenario: Financial Distress and Merger Options
Let’s consider a hypothetical scenario: “City General Hospital” is facing significant financial distress due to declining patient volumes and increasing operational costs.
Kaufman Hall’s reports highlight how financial distress is pushing hospitals towards mergers and acquisitions. This pressure is intensified by factors like staffing shortages, as seen in the recent new york state nurse strike montefiore richmond university deals , where labor disputes add to already strained budgets. Ultimately, these financial challenges are a major driver behind the consolidation we’re seeing in the healthcare industry.
- Option 1: Acquisition by “Regional Health System”: Regional Health System, a large and financially stable organization, offers to acquire City General. This offers City General immediate financial stability but might lead to job losses and a loss of local control. Outcome: Increased financial stability for City General, but potential loss of local identity and jobs.
- Option 2: Merger with “County Medical Center”: County Medical Center, a similarly sized hospital facing similar financial challenges, proposes a merger. This creates a larger entity with greater bargaining power but requires significant restructuring and integration efforts. Outcome: Potential for improved financial stability and market share, but increased risk and complexity of integration.
- Option 3: Strategic Partnership with “University Medical Group”: City General forms a strategic partnership with University Medical Group, focusing on shared services and improved referral networks. This minimizes disruption but might not fully address the financial challenges. Outcome: Improved efficiency and potentially increased patient volume, but less immediate financial relief.
Impact of Mergers and Acquisitions on Healthcare Services

Source: narasinara.id
Mergers and acquisitions (M&A) in the healthcare industry are complex events with far-reaching consequences. While often driven by financial necessity or strategic goals, their impact on the quality of patient care, access to services, and the healthcare workforce is significant and multifaceted. Understanding these impacts is crucial for policymakers, healthcare providers, and patients alike.
Impact on Patient Care Quality, Financial distress drives health system merger acquisition kaufman hall
The effect of M&A on patient care quality is a subject of ongoing debate. While some mergers lead to improved efficiency and resource allocation, potentially enhancing care, others can result in decreased quality due to disruptions in established processes and staff turnover. Factors influencing the outcome include the integration strategies employed, the cultural fit between merging organizations, and the level of investment in technology and staff training.
A successful integration prioritizes maintaining or improving existing quality metrics, such as patient satisfaction scores, readmission rates, and infection control measures. Conversely, a poorly managed merger can lead to decreased quality due to staff shortages, system failures, and a decline in patient experience.
Effects on Access to Care in Underserved Communities
Mergers and acquisitions can significantly impact access to care, particularly in underserved communities. While some M&A activity aims to expand services into these areas, others can lead to the closure of facilities or reduction of services due to cost-cutting measures or strategic realignment. The resulting impact on access can be substantial, disproportionately affecting vulnerable populations who rely on these facilities.
For example, a hospital merger resulting in the closure of a rural emergency room could significantly increase travel times and decrease access to timely care for residents in that area. Conversely, a successful merger could lead to improved access through expanded service offerings or the introduction of telehealth initiatives.
Implications for the Healthcare Workforce
M&A activity often results in significant changes to the healthcare workforce. Job losses due to redundancies are a common concern, potentially impacting morale and expertise within the remaining staff. Conversely, mergers can also create new job opportunities, particularly in administrative and management roles. However, the overall impact on employment depends on the integration strategy and the extent of workforce restructuring.
Successful integration requires careful planning and communication to minimize job losses and maintain staff morale, often involving retraining and upskilling initiatives. Failure to address workforce concerns can lead to decreased productivity, increased turnover, and a decline in overall care quality.
Examples of Successful and Unsuccessful M&A Integrations
Successful Integration: The merger of two large health systems, resulting in the creation of a comprehensive network offering a wider range of specialized services and improved access to care in underserved areas. This was achieved through a well-defined integration plan, significant investment in technology and staff training, and a focus on maintaining a positive work environment. Patient satisfaction scores increased following the merger, indicating improved quality of care.
Unsuccessful Integration: The merger of two competing hospitals, resulting in significant staff layoffs, reduced services, and decreased patient satisfaction. The lack of a clear integration plan, coupled with poor communication and inadequate investment in technology and staff training, contributed to the failure. The merger ultimately resulted in a decline in the quality of care and reduced access to services in the affected communities.
Long-Term Financial Sustainability Post-Merger: Financial Distress Drives Health System Merger Acquisition Kaufman Hall
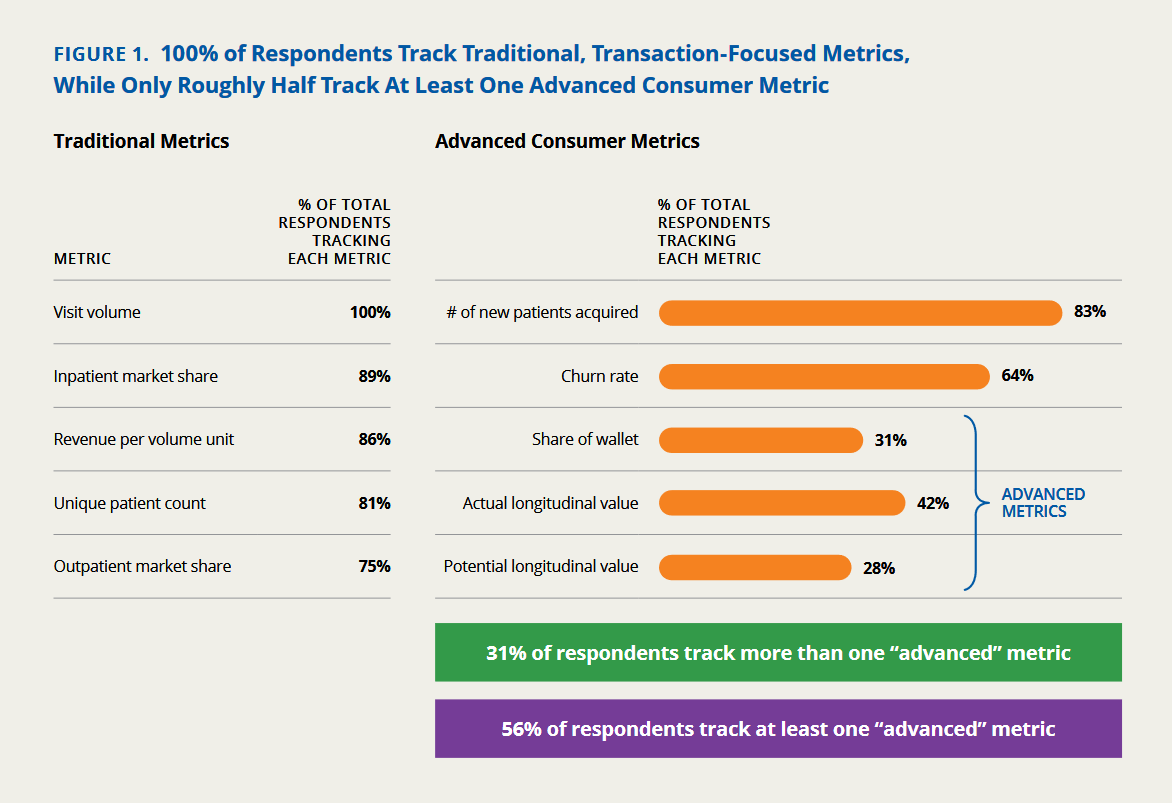
Source: healthpopuli.com
Successfully navigating a healthcare system merger or acquisition requires a long-term perspective that extends far beyond the closing date. Achieving sustainable financial health post-merger demands proactive strategies, meticulous planning, and a commitment to continuous improvement. This involves not only integrating disparate systems and operations but also fostering a culture of financial responsibility and innovation.
Strategies for achieving long-term financial sustainability after a merger hinge on a multifaceted approach encompassing cost optimization, revenue enhancement, and efficient financial management. A successful integration relies on careful planning, effective communication, and a clear understanding of the financial implications of each decision. Without a robust plan, even the most promising mergers can falter, leading to financial instability and jeopardizing the quality of patient care.
Successful Integration Strategies Leading to Improved Financial Performance
Successful integration strategies often involve a phased approach, starting with a comprehensive due diligence process to identify potential synergies and challenges. This is followed by the development of a detailed integration plan that addresses key areas such as clinical integration, operational efficiency, and financial management. For example, Cleveland Clinic’s acquisition strategy has consistently focused on identifying organizations with complementary strengths and a strong cultural alignment.
This approach minimizes disruption and maximizes the potential for financial gains. Their focus on shared services and technology platforms also contributes significantly to cost savings and improved operational efficiency. Another example is the Mayo Clinic, known for its highly integrated system and strong financial performance. Their success is partly attributed to a culture of continuous improvement and a commitment to efficient resource allocation.
Post-Merger Cost Optimization and Revenue Enhancement Initiatives
Cost optimization is a critical element of long-term financial sustainability. This involves identifying and eliminating redundancies in administrative functions, supply chain management, and clinical operations. Revenue enhancement initiatives, on the other hand, focus on expanding service offerings, improving pricing strategies, and strengthening payer relationships. For instance, a merged system might leverage its expanded network to negotiate better rates with insurance providers, or it might invest in new technologies or service lines to attract more patients.
These initiatives are often intertwined; cost savings can free up resources for investment in revenue-generating activities.
Effective Financial Planning and Management Contributing to Long-Term Success
Effective financial planning and management are paramount for the long-term success of a merged entity. This includes developing a comprehensive financial model that projects revenue, expenses, and cash flow over a multi-year period. The model should account for various scenarios, including optimistic and pessimistic forecasts. Regular monitoring and reporting are essential to track progress, identify potential problems, and make necessary adjustments.
A strong internal control system is also critical to ensure the accuracy and reliability of financial information.
Illustrative Example of a Successful Post-Merger Financial Plan
Imagine a hypothetical financial plan for a merged healthcare system. The plan would begin with a detailed assessment of the pre-merger financial performance of both entities, identifying areas of strength and weakness. This would be followed by a comprehensive integration plan outlining specific targets for cost reduction (e.g., 10% reduction in administrative expenses within two years) and revenue growth (e.g., 5% increase in outpatient revenue within three years).
The plan would also detail specific initiatives to achieve these targets, including streamlining supply chain management, implementing new revenue cycle management technologies, and expanding into new service areas. Key performance indicators (KPIs) would be established to track progress toward these targets, and regular reporting mechanisms would be put in place to monitor performance and make adjustments as needed.
The plan would also include contingency plans to address unexpected challenges, such as changes in regulatory environment or economic downturns. This comprehensive approach, focusing on both short-term and long-term goals, ensures a sustainable financial future for the merged entity.
Outcome Summary
The increasing financial pressure on healthcare systems is undeniable, and the resulting surge in mergers and acquisitions is reshaping the industry. Kaufman Hall’s significant role in this transformation underscores the need for strategic guidance and financial expertise during these complex transactions. While mergers and acquisitions offer a path to stability and potentially improved efficiency, the success hinges on careful planning, effective integration, and a long-term focus on financial sustainability.
The future of healthcare may well depend on the careful navigation of these turbulent financial waters, with the right expertise proving essential for successful outcomes.
FAQ Summary
What are some common reasons for unsuccessful health system mergers?
Unsuccessful mergers often stem from poor cultural integration, inadequate due diligence, unrealistic financial projections, and a lack of clear strategic planning post-merger.
How does Kaufman Hall assess the financial health of a healthcare system?
Kaufman Hall uses a variety of financial indicators, including operating margins, debt levels, days cash on hand, and patient revenue trends, to assess a system’s financial health. They also consider qualitative factors such as market position and leadership capabilities.
What are the potential downsides of a health system merger for patients?
Potential downsides include reduced access to care in certain areas, higher costs (if not managed effectively), and disruptions to established patient-physician relationships during the integration process.
What role does regulatory approval play in health system mergers?
Regulatory approval from bodies like the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) and state health departments is crucial for any health system merger, and this process can be lengthy and complex, often involving antitrust reviews.