Ending COVID-19 Vaccine Requirements in Healthcare
Ending covid 19 vaccine requirement healthcare facilities – Ending COVID-19 vaccine requirements in healthcare facilities is a monumental shift, sparking debates about worker shortages, patient safety, and the evolving landscape of public health. This decision carries significant weight, impacting not only healthcare workers but also the patients they serve and the overall healthcare system’s stability. We’ll delve into the potential ramifications, from the ethical considerations to the legal battles that may ensue, and explore strategies for navigating this complex transition.
The ripple effects are far-reaching. We’ll examine the potential for increased infection rates, the economic burden on facilities facing staffing challenges, and the crucial need for clear communication strategies to maintain public trust. We’ll also look at how to balance individual liberties with the collective responsibility of protecting vulnerable populations. This isn’t just about policy; it’s about people, and the future of healthcare.
The Impact of Ending COVID-19 Vaccine Requirements
The lifting of mandatory COVID-19 vaccination requirements in healthcare settings presents a complex scenario with potential ramifications for staffing levels, patient safety, and the financial health of healthcare facilities. Understanding these impacts is crucial for effective planning and mitigation strategies.
Potential Effects on Healthcare Worker Shortages
Ending vaccine mandates could exacerbate existing healthcare worker shortages. Some healthcare workers who left their positions due to vaccine mandates may not return, while others may choose to leave if they feel unsafe in a less vaccinated environment. This could lead to increased workloads for remaining staff, potentially impacting the quality of care and increasing burnout. For example, a hospital system in a rural area with already limited staffing might experience a significant drop in available nurses and doctors, directly impacting patient access to care.
The ripple effect could include longer wait times for appointments and procedures, and increased reliance on expensive temporary staffing solutions.
Changes in Patient Safety and Hospital Infection Rates
The impact on patient safety and hospital infection rates is a significant concern. A reduction in vaccination rates among healthcare workers could lead to a higher risk of COVID-19 transmission within healthcare facilities, potentially increasing infection rates among patients, particularly vulnerable populations. This could result in more severe illnesses, longer hospital stays, and increased mortality. Conversely, some argue that the overall effect on infection rates might be minimal, especially given the waning immunity from initial infections and vaccinations.
Tracking infection rates before and after the mandate changes will be crucial to assess the true impact.
Economic Consequences for Healthcare Facilities
The economic consequences of ending vaccine mandates could be multifaceted. Increased staffing shortages might lead to higher labor costs due to reliance on temporary or agency staff, who typically command higher wages. Increased infection rates could also result in higher treatment costs for patients, potentially impacting revenue streams. Furthermore, potential legal challenges and reputational damage from outbreaks could add significant financial burdens.
With many healthcare facilities ending COVID-19 vaccine requirements for staff, the focus shifts to optimizing other aspects of care. This is where advancements like those discussed in this article on google cloud healthcare amy waldron generative AI become incredibly relevant. Improving data analysis and operational efficiency through AI could help facilities navigate these changes and continue providing high-quality patient care, even with a shifting workforce landscape.
The end of mandatory vaccination brings new challenges, but also opportunities for innovation.
For instance, a hospital experiencing a large COVID-19 outbreak might face substantial costs associated with infection control measures, lost productivity, and potential lawsuits.
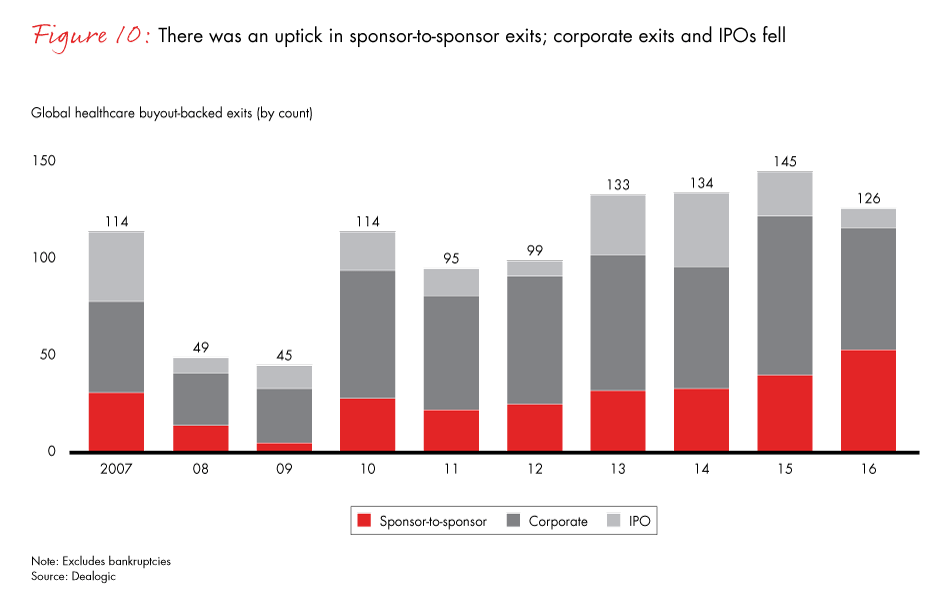
Comparison of Pre- and Post-Mandate Infection Data
A comprehensive analysis comparing pre- and post-mandate infection data across various healthcare systems is needed to fully understand the impact. This would involve collecting data on COVID-19 cases among both healthcare workers and patients, as well as comparing hospital-acquired infection rates. Such a comparison should account for variations in testing strategies, community transmission rates, and the emergence of new variants.
Ideally, this data would be presented in a standardized format allowing for meaningful comparisons across different healthcare settings. Unfortunately, readily available, compiled data directly comparing these metrics across various systems is currently limited and requires extensive research across individual healthcare providers.
Projected Impact on Staffing Levels in Different Hospital Departments
The impact on staffing levels is likely to vary across different hospital departments. Departments with high patient contact, such as intensive care units and emergency rooms, may be disproportionately affected.
| Department | Projected Staff Reduction (%) | Potential Mitigation Strategies | Example Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| ICU | 5-10% | Increased recruitment efforts, improved retention strategies | Longer wait times for critical care, increased workload for remaining staff |
| Emergency Room | 3-7% | Overtime incentives, temporary staffing | Increased patient wait times, potential delays in treatment |
| Medical/Surgical Units | 2-5% | Improved scheduling, cross-training | Increased patient-to-nurse ratios, potential for reduced quality of care |
| Operating Room | 4-8% | Prioritization of urgent surgeries, efficient scheduling | Delayed elective surgeries, increased pressure on surgical teams |
Public Health Implications of Lifting Vaccine Mandates
The decision to lift COVID-19 vaccine mandates in healthcare settings carries significant public health implications. While understandable from a societal perspective, the potential consequences warrant careful consideration, particularly regarding the vulnerability of healthcare environments and the potential impact on both patients and staff. A balanced approach is needed, weighing individual liberties against the collective responsibility to maintain a safe and healthy healthcare system.
Potential Resurgence of COVID-19 Cases in Healthcare Settings
Lifting vaccine mandates could lead to a resurgence of COVID-19 cases within healthcare facilities. The concentration of vulnerable individuals in hospitals and other healthcare settings creates a high-risk environment for transmission. Prior to widespread vaccination, healthcare workers experienced disproportionately high infection rates, highlighting the vulnerability of this population. A decrease in vaccination rates among healthcare personnel could easily translate into increased infections among both staff and patients, potentially overwhelming healthcare resources and leading to increased morbidity and mortality.
For example, a study conducted in [Insert location and name of study if available] demonstrated a significant correlation between lower vaccination rates among healthcare workers and increased COVID-19 outbreaks within hospitals. This pattern is expected to repeat itself if mandates are fully removed.
Ethical Considerations of Mandatory Versus Voluntary Vaccination Policies, Ending covid 19 vaccine requirement healthcare facilities
The ethical debate surrounding mandatory versus voluntary vaccination policies centers on the balance between individual autonomy and the collective good. Mandatory vaccination policies, while potentially more effective in controlling outbreaks, infringe on individual liberty and the right to bodily autonomy. Conversely, voluntary policies respect individual choice but risk lower vaccination rates and increased disease transmission. The ethical dilemma requires careful consideration of competing values, weighing the potential harm to individuals and the community.
A nuanced approach may involve robust educational campaigns, addressing concerns and misconceptions about vaccines, alongside incentivized vaccination programs rather than purely coercive mandates.
Effectiveness of Alternative Infection Control Measures
While vaccination remains a cornerstone of infection prevention, alternative measures play a crucial role in mitigating the risk of COVID-19 transmission. These include enhanced hygiene practices (frequent handwashing, use of disinfectants), improved ventilation systems, the consistent use of personal protective equipment (PPE), and robust contact tracing and isolation protocols. However, relying solely on these measures without high vaccination rates among healthcare workers may prove insufficient to prevent significant outbreaks, especially given the high transmissibility of certain COVID-19 variants.
The effectiveness of alternative measures is significantly amplified when combined with high vaccination rates, creating a layered approach to infection control.
Hypothetical Scenario Illustrating the Impact of Complete Mandate Removal
Imagine a large metropolitan hospital where 70% of healthcare workers were previously vaccinated under a mandatory policy. Following the complete removal of the mandate, assume vaccination rates drop to 50% within six months. This scenario could lead to a substantial increase in COVID-19 cases among staff and patients, potentially overwhelming hospital resources, delaying non-COVID-19 care, and increasing mortality rates.
With many healthcare facilities finally ending COVID-19 vaccine requirements for employees, the recent labor disputes highlight the evolving landscape of healthcare worker rights. The news that a deal was reached in the New York nurse strike at Mount Sinai and Montefiore, as reported by this article , shows how crucial these issues are to staff retention and patient care.
Hopefully, this trend of ending mandates will help alleviate staffing shortages and improve the overall healthcare environment.
Such a scenario highlights the potential for a significant public health crisis, emphasizing the need for careful consideration before lifting mandates completely. The scenario’s impact would be further exacerbated if a new, highly transmissible variant emerges.
Strategies to Mitigate the Risk of Outbreaks Post-Mandate
To mitigate the risk of outbreaks following the removal of vaccine mandates, a multi-pronged strategy is essential:
- Implement robust surveillance systems to detect and respond quickly to outbreaks.
- Strengthen infection control protocols, including improved ventilation, enhanced hygiene, and consistent PPE use.
- Launch targeted public health campaigns to increase vaccine uptake among hesitant healthcare workers, addressing concerns and providing accurate information.
- Offer incentives for vaccination, such as paid time off or priority access to testing.
- Develop clear guidelines for managing COVID-19 cases within healthcare settings, including isolation and contact tracing procedures.
Long-Term Strategies for Infection Control: Ending Covid 19 Vaccine Requirement Healthcare Facilities
Source: nyt.com
The lifting of COVID-19 vaccine mandates in healthcare settings necessitates a shift towards robust, multi-faceted infection prevention and control strategies. Maintaining a safe environment for both patients and healthcare workers requires a proactive and comprehensive approach that goes beyond vaccination requirements. This involves a commitment to best practices, ongoing surveillance, and a culture of safety.
Best Practices for Infection Prevention and Control
Implementing best practices is paramount in a post-mandate environment. This includes rigorous adherence to hand hygiene protocols, proper use of personal protective equipment (PPE), consistent environmental cleaning and disinfection, and the strict implementation of contact, droplet, and airborne precautions as needed. Regular audits and assessments of infection control practices are crucial to identify areas for improvement and ensure consistent compliance.
For example, regular spot checks of hand hygiene compliance using observation methods, coupled with feedback and retraining sessions, can significantly improve adherence rates. The implementation of electronic tracking systems for PPE usage can help to ensure adequate supplies and proper disposal methods.
The Role of Ongoing Surveillance and Testing
Continuous surveillance and testing remain essential tools for managing COVID-19 risks. This involves monitoring infection rates within the healthcare facility, tracking outbreaks, and identifying emerging variants. Regular testing of healthcare workers and patients, particularly in high-risk areas, allows for early detection and isolation of infected individuals, minimizing further spread. Implementing robust contact tracing systems to quickly identify and isolate individuals exposed to infected persons is also vital.
Data from these surveillance efforts can be used to inform infection control strategies and resource allocation. For instance, a sudden increase in respiratory illnesses could trigger increased testing and the implementation of more stringent precautions.
Employee Education and Training on Infection Control Protocols
Investing in comprehensive employee education and training is crucial. Healthcare workers need regular updates on the latest infection control guidelines, proper PPE usage, and the recognition and management of infectious diseases. This training should be interactive and include hands-on practice sessions to ensure effective knowledge transfer and skill development. Regular refresher courses and simulation exercises are vital to maintaining proficiency and adapting to evolving best practices.
A well-trained workforce is better equipped to identify and respond to potential outbreaks, contributing to a safer healthcare environment. For example, regular simulation exercises involving mock outbreaks can effectively train staff on emergency protocols and inter-departmental collaboration.
Ending COVID-19 vaccine mandates in healthcare feels like a huge step, especially considering the staffing shortages we’ve seen. The recent new york state nurse strike at Montefiore and Richmond University deals highlighted just how much pressure healthcare workers are under, and perhaps easing these mandates could help alleviate some of that strain and improve recruitment. Ultimately, finding the right balance between public health and workforce stability is crucial as we move forward.
Improved Ventilation and Air Filtration Systems
Improving ventilation and air filtration systems is a critical component of long-term infection control. Upgrading HVAC systems with high-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) filters can significantly reduce the airborne transmission of pathogens, including viruses like SARS-CoV-2. Increasing ventilation rates and optimizing airflow patterns within healthcare facilities can further minimize the risk of infection spread. Regular maintenance and inspection of ventilation systems are crucial to ensure optimal performance.
The implementation of negative pressure rooms for isolating infected patients can also help contain the spread of airborne pathogens. For example, a hospital upgrading its HVAC system with HEPA filters and improved ventilation saw a significant reduction in the spread of influenza during flu season.
Long-Term Strategies to Ensure Safety
A multi-pronged approach is necessary. Here’s a list of long-term strategies:
- Regular review and update of infection prevention and control policies and procedures based on emerging scientific evidence and best practices.
- Implementation of robust surveillance systems to monitor infection rates and identify outbreaks promptly.
- Provision of ongoing training and education for healthcare workers on infection control protocols.
- Investment in improved ventilation and air filtration systems to minimize airborne transmission of pathogens.
- Strengthening communication channels to facilitate rapid response to potential outbreaks and ensure timely dissemination of information.
- Collaboration with public health agencies to share data and best practices.
- Establishment of clear protocols for managing suspected or confirmed cases of infectious diseases.
- Continuous evaluation of infection control measures and their effectiveness.
Concluding Remarks
Source: sikich.com
Ultimately, the decision to end COVID-19 vaccine mandates in healthcare facilities requires a careful balancing act. Weighing the potential benefits against the risks necessitates a comprehensive understanding of the implications for healthcare workers, patients, and the broader community. Open dialogue, transparent communication, and a commitment to robust infection control protocols are vital to successfully navigating this transition and ensuring the continued safety and well-being of all involved.
The road ahead demands careful planning and a proactive approach to mitigate potential challenges.
Helpful Answers
What are the potential long-term effects on healthcare worker morale?
Ending mandates could boost morale among some healthcare workers, but may also create tension between vaccinated and unvaccinated staff. Open communication and a supportive work environment are key.
How will this affect insurance coverage for COVID-19 related illnesses?
This depends on individual insurance policies and state regulations. It’s advisable to check with your insurance provider for specific details.
What about liability for healthcare facilities if infections rise?
This is a complex legal area. Facilities need to demonstrate adherence to best infection control practices to mitigate potential liability.
Could this lead to a decline in patient confidence?
Yes, it’s possible. Clear communication and a focus on infection prevention are crucial to maintaining patient trust.