
SVB Collapse Healthcares Urgent Crisis
Fall of svb hits healthcare sector as federal regulators step in – SVB Collapse: Healthcare’s Urgent Crisis. The shocking downfall of Silicon Valley Bank (SVB) sent shockwaves through the financial world, but its impact on the healthcare sector is particularly alarming. Venture-backed startups, hospitals relying on SVB for banking services, and even established players found themselves suddenly facing funding disruptions and liquidity issues. The ripple effects are far-reaching, impacting everything from investment in cutting-edge medical technologies to patient care itself.
Federal regulators swiftly stepped in, but the long-term consequences remain uncertain, leaving many in the healthcare industry grappling with the fallout.
This unprecedented event forced a critical examination of healthcare funding models, prompting a search for alternative financing options and raising concerns about the future of innovation in the sector. We’ll delve into the immediate impact, the federal response, and the potential long-term ramifications for healthcare funding, innovation, and patient access.
Immediate Impact on Healthcare Investments: Fall Of Svb Hits Healthcare Sector As Federal Regulators Step In
The collapse of Silicon Valley Bank (SVB) sent shockwaves through the financial world, and the healthcare sector, heavily reliant on venture capital and banking services, felt the impact acutely. The immediate market reaction was a sharp downturn in valuations for many healthcare companies, particularly those with significant deposits or loan facilities with SVB. Uncertainty surrounding funding and liquidity led to a freeze in some investment activity, creating a challenging environment for many organizations.The types of healthcare organizations most immediately affected were those with substantial exposure to SVB.
This included venture-backed startups in the biotech, medical device, and digital health spaces, who often relied on SVB for operational funding and venture capital investments. Hospitals and healthcare systems with significant cash reserves deposited in SVB also faced immediate liquidity challenges. Smaller, regional healthcare providers were potentially more vulnerable due to their limited access to alternative banking options.
Venture-Backed Biotech Startups Facing Funding Disruptions
Many venture-backed biotech startups experienced significant funding disruptions following the SVB collapse. These companies often relied on SVB for bridge loans, venture debt, and other short-term financing crucial for clinical trials and product development. The sudden loss of access to these funds created immediate cash flow problems, potentially delaying crucial research and development initiatives. For example, several early-stage biotech companies focused on oncology and rare diseases reported difficulties securing immediate funding to meet payroll and operational expenses.
Some were forced to cut staff or delay clinical trials, potentially impacting timelines and the overall success of their projects.
Hospitals and Healthcare Systems with SVB Accounts
Hospitals and healthcare systems, especially smaller regional ones, were also affected. Many held operating funds in SVB accounts, relying on these deposits for day-to-day operations. The sudden inability to access these funds created significant liquidity challenges, potentially delaying payments to vendors, impacting staffing decisions, and even disrupting patient care in some cases. While larger hospital systems with diversified banking relationships may have experienced less severe disruptions, the overall impact on the sector’s financial stability was undeniable.
The collapse of SVB sent shockwaves through the healthcare sector, leaving many startups scrambling for funding. This instability highlights the need for robust financial models, especially as we see advancements like those explored in a fascinating new study on study widespread digital twins healthcare , which could potentially revolutionize efficiency and cost-effectiveness. Ultimately, the SVB fallout underscores the fragility of the current system and the importance of innovative solutions for a more resilient healthcare future.
Examples include reports of hospitals needing to scramble to secure emergency lines of credit to cover immediate expenses.
Comparison of SVB Exposure Across Healthcare Sub-Sectors
| Sub-Sector | Estimated Exposure | Impact on Funding | Projected Recovery Time |
|---|---|---|---|
| Biotechnology (Early Stage) | High | Significant disruptions, potential delays in clinical trials | 6-12 months |
| Medical Devices (Startups) | Medium-High | Funding challenges, slowed product development | 3-6 months |
| Digital Health (Venture-backed) | Medium | Reduced investment activity, challenges securing new funding | 6-12 months |
| Hospitals & Healthcare Systems | Low-Medium (variable by size) | Liquidity issues for some, particularly smaller systems | 3-6 months (variable) |
Federal Intervention and its Effects
The collapse of Silicon Valley Bank (SVB) sent shockwaves through the financial system, and its impact on the healthcare sector, heavily reliant on venture capital and investment banking, was immediate and significant. Federal regulators swiftly intervened to prevent a wider crisis, but the long-term consequences of their actions remain to be seen. This section will explore the steps taken by the government, the potential long-term effects on healthcare, and the implications for future investment and lending practices.The federal government’s response involved a multi-pronged approach.
First, the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC) took over SVB, guaranteeing all deposits, a move designed to prevent a bank run and restore confidence in the financial system. This action was crucial for healthcare providers, many of whom held significant deposits at SVB. Secondly, the Federal Reserve implemented measures to improve liquidity in the banking sector, ensuring banks had access to sufficient funds to meet their obligations.
The collapse of SVB sent shockwaves through the healthcare sector, forcing federal regulators to intervene and stabilize the situation. This instability highlights the need for robust, reliable tech solutions, and it makes me wonder how initiatives like Google Cloud Healthcare’s work with Amy Waldron on generative AI, as detailed in this fascinating article google cloud healthcare amy waldron generative AI , could help improve data security and financial resilience within healthcare organizations facing similar crises.
Ultimately, the fallout from SVB underscores the importance of innovative and secure technological solutions in the healthcare industry.
This included expanding access to discount window lending and providing additional liquidity through various facilities. These actions were aimed at preventing a domino effect, where the failure of one bank could trigger the collapse of others. Finally, regulators initiated a review of banking practices, particularly regarding risk management and oversight of banks with concentrated depositor bases, like those heavily invested in the tech sector, including those serving the healthcare industry.
Long-Term Consequences of Government Intervention on Healthcare Financing and Innovation, Fall of svb hits healthcare sector as federal regulators step in
The government’s intervention, while preventing an immediate crisis, could have long-term implications for healthcare financing and innovation. The FDIC’s guarantee of all deposits, while necessary in the short-term, may create moral hazard, encouraging excessive risk-taking by banks in the future. Healthcare startups, accustomed to a readily available source of funding, may find securing capital more challenging as banks become more cautious in their lending practices following increased regulatory scrutiny.
This could stifle innovation and potentially slow the development of new treatments and technologies. For example, the increased cost of capital might delay the development of promising new pharmaceuticals or medical devices, impacting patient care and overall healthcare advancements. The increased regulatory burden could also lead to a reduction in the number of venture capital firms willing to invest in healthcare, further limiting the availability of funding for startups.
Implications of Increased Regulatory Scrutiny on Healthcare Investment and Lending Practices
The SVB collapse has undoubtedly led to increased regulatory scrutiny of investment and lending practices within the healthcare sector. Banks and other financial institutions will likely face stricter oversight, requiring more rigorous risk assessments and more stringent capital requirements. This could make it more difficult and expensive for healthcare companies to secure funding, particularly for smaller firms and startups.
Lenders might prioritize lower-risk investments, potentially reducing the flow of capital to innovative but higher-risk ventures. This could lead to a more conservative investment landscape, potentially hindering the growth of promising healthcare technologies and services. Furthermore, the increased regulatory burden will increase compliance costs for healthcare companies, potentially diverting resources away from research and development.
Potential Benefits and Drawbacks of the Federal Response for Healthcare Providers
The federal response had both positive and negative consequences for healthcare providers.
It’s important to consider the context of these points. The benefits and drawbacks are intertwined and their relative significance will vary depending on the specific circumstances of each healthcare provider.
- Benefit: Prevention of a wider financial crisis, safeguarding deposits and preventing disruptions to healthcare operations.
- Benefit: Increased regulatory oversight could ultimately lead to a more stable and resilient financial system, reducing the risk of future crises.
- Drawback: Increased regulatory scrutiny and stricter lending practices could make it more difficult and expensive for healthcare providers to access capital.
- Drawback: Potential for reduced investment in healthcare innovation due to increased caution by lenders and investors.
- Drawback: Increased compliance costs associated with stricter regulations.
Long-Term Implications for Healthcare Funding
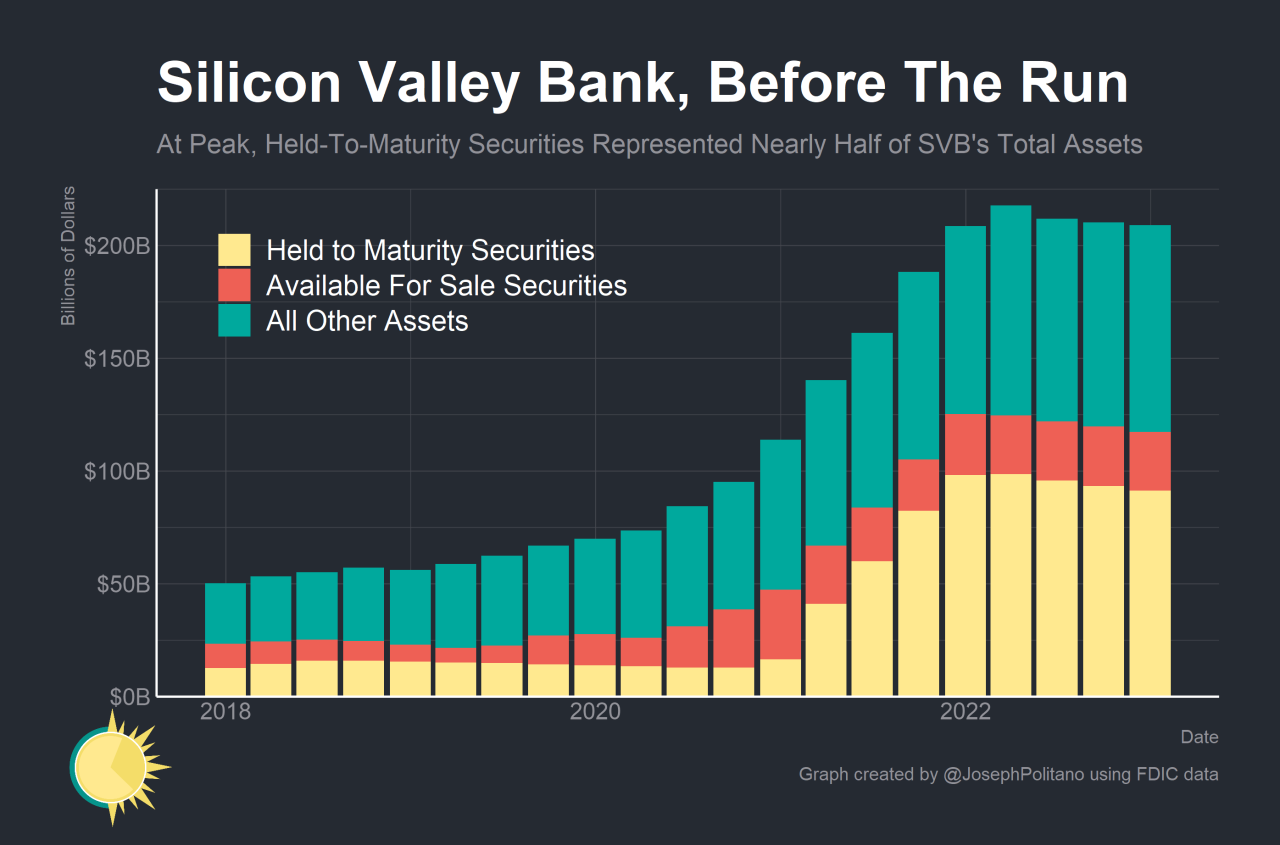
Source: substackcdn.com
The collapse of Silicon Valley Bank (SVB) sent shockwaves through the financial system, and its impact on the healthcare sector, while initially focused on immediate liquidity concerns, promises to reshape healthcare funding models for years to come. The event highlighted the vulnerability of relying heavily on a single funding source, particularly one susceptible to rapid market shifts and regulatory changes.
This necessitates a critical re-evaluation of healthcare financing strategies and a diversification of funding streams to enhance resilience.The SVB failure exposed the interconnectedness of the financial system and its profound influence on healthcare. Many healthcare organizations, particularly venture-backed startups and smaller hospitals, held significant deposits in SVB, relying on those funds for operations and investments. The sudden loss of access to these funds created immediate crises, but the longer-term consequences may be even more significant, prompting a reassessment of risk management and a search for more stable and diversified funding sources.
Potential Shifts in Healthcare Funding Models
The SVB crisis will likely accelerate the adoption of more diversified funding models within the healthcare sector. Traditional reliance on venture capital, private equity, and bank loans will likely decrease as organizations seek to mitigate the risks associated with concentrated funding sources. This will involve a shift towards a more balanced approach, incorporating a wider range of funding sources to reduce dependence on any single entity.
For example, we might see a rise in public-private partnerships, increased reliance on government grants and subsidies, and a greater exploration of alternative financing mechanisms such as crowdfunding and philanthropic donations. The need for more robust risk management strategies, including diversification of financial assets and improved due diligence processes, will also be paramount.
Alternative Funding Sources for Healthcare Organizations
Healthcare organizations are already exploring and implementing alternative funding sources to enhance their financial resilience. These include increased focus on government grants targeted at specific healthcare initiatives, exploring philanthropic avenues for capital investment, and the development of innovative revenue streams such as value-based care models and telehealth services. The growth of impact investing, which focuses on both financial returns and social impact, presents another viable option, attracting investors seeking both profit and positive social outcomes.
Furthermore, strategic partnerships with other healthcare providers or technology companies can provide access to new funding opportunities and resources.
Comparison of Traditional and Alternative Financing Options
Traditional funding models, such as bank loans and venture capital, offer significant capital but often come with stringent requirements and potentially high interest rates. Venture capital, for example, often demands significant equity in exchange for funding, potentially diluting the ownership of the healthcare organization. Alternative funding options, on the other hand, may offer smaller amounts of capital but with greater flexibility and potentially lower risk.
Government grants, for instance, may come with specific conditions but offer stability and support for specific healthcare initiatives. Philanthropic donations, while unpredictable, can provide crucial funding for critical projects or programs. The optimal approach will involve a strategic blend of traditional and alternative funding, carefully tailored to the specific needs and risk tolerance of each healthcare organization.
A Potential Future for Healthcare Funding
Considering the lessons learned from the SVB collapse, a potential future for healthcare funding could involve a more decentralized and diversified approach. We might see a rise in regional or community-based funding initiatives, fostering greater resilience at a local level. Technological advancements, such as blockchain technology, could play a significant role in improving transparency and efficiency in healthcare funding processes.
Furthermore, a stronger emphasis on risk management and financial literacy within healthcare organizations will be crucial in navigating future economic uncertainties. For instance, a large hospital system might diversify its funding sources across several banks, government grants, philanthropic endowments, and revenue generated from its own value-based care programs. This would create a more resilient and less vulnerable financial structure compared to a model heavily reliant on a single bank like SVB.
Impact on Healthcare Innovation and Technology

Source: tavaga.com
The collapse of Silicon Valley Bank (SVB) and the subsequent regulatory intervention sent shockwaves through the financial system, with significant ramifications for the healthcare sector. Beyond the immediate impact on funding and investments, the crisis poses a serious threat to the development and adoption of innovative healthcare technologies. Reduced access to capital could stifle progress in areas crucial to improving patient care and outcomes.The ripple effects of the SVB failure are likely to be felt most acutely by early-stage healthcare companies and those heavily reliant on venture capital funding.
These companies, often developing cutting-edge technologies, are particularly vulnerable to funding disruptions, potentially delaying or even halting promising projects. This has the potential to slow down the already complex and expensive process of bringing new medical technologies to market.
Impact on Funding for Healthcare Technology Development
The SVB crisis highlights the precarious nature of funding for healthcare innovation. Many startups in the sector rely on venture capital, and the instability in the banking sector can severely restrict their access to crucial capital. This decreased funding directly impacts the ability of these companies to conduct research and development, hire skilled personnel, and navigate the complex regulatory pathways necessary for product approval.
For example, a promising biotech firm developing a novel cancer treatment might find its clinical trials delayed or even cancelled due to a lack of funding, directly impacting patient access to potentially life-saving therapies.
Specific Technologies Vulnerable to Funding Disruptions
Several healthcare technology sectors are particularly vulnerable to funding disruptions caused by the SVB crisis. Artificial intelligence (AI) in healthcare, for instance, requires significant investment in data acquisition, algorithm development, and validation. Similarly, the development and deployment of advanced medical devices, such as robotic surgery systems or sophisticated diagnostic tools, demand substantial capital. Telehealth platforms, while showing rapid growth, may also experience setbacks as funding dries up, hindering expansion and improvements to service delivery.
Companies focused on genomic sequencing and personalized medicine, which often involve high upfront costs and long development timelines, are also particularly susceptible.
Potential Acceleration or Hindrance of Technological Advancements
The impact of the SVB crisis on the pace of technological advancements in healthcare is complex and multifaceted. While it undeniably poses a significant challenge to many companies, it could also inadvertently accelerate certain trends. For example, the crisis may force companies to become more efficient and strategic in their resource allocation, leading to a more focused and effective approach to innovation.
Furthermore, it might spur increased collaboration and consolidation within the industry, potentially leading to the development of more robust and sustainable business models. However, the risk of significant delays and even project cancellations remains substantial, potentially hindering progress in vital areas of healthcare innovation.
Impact Across Various Healthcare Technology Sectors
| Technology Sector | Potential Impact on Funding | Impact on Development | Potential Long-Term Consequences |
|---|---|---|---|
| Telehealth | Reduced investment in platform expansion and improvement | Slower adoption rates, limited access in underserved areas | Increased healthcare disparities, hindered remote patient monitoring |
| Medical Devices | Delayed clinical trials, reduced production capacity | Slower innovation, limited availability of advanced devices | Compromised patient care, higher healthcare costs |
| AI in Healthcare | Reduced funding for algorithm development and data acquisition | Slower progress in diagnostic tools and personalized medicine | Delayed adoption of AI-driven solutions, limited improvements in patient outcomes |
| Genomic Sequencing & Personalized Medicine | Significant delays in research and development | Reduced availability of personalized therapies, slower advancements in precision medicine | Limited access to targeted treatments, slower progress in disease prevention |
Patient Care and Access to Services

Source: nyt.com
The collapse of Silicon Valley Bank (SVB) sent shockwaves through the financial system, and its repercussions extend far beyond the tech sector. The ramifications for the healthcare industry, particularly concerning patient care and access to services, are significant and warrant careful consideration. Reduced investment and potential funding shortfalls stemming from the SVB fallout could lead to a cascade of negative consequences for patients, impacting both the quality and availability of healthcare.The SVB’s failure has already created uncertainty in the financial markets, impacting venture capital funding for healthcare startups and potentially hindering the ability of established healthcare providers to access crucial credit lines.
This decreased access to capital could directly translate to limitations in operational budgets, forcing healthcare institutions to make difficult choices.
Service Cuts and Treatment Delays
Reduced funding inevitably translates into difficult decisions for healthcare providers. Hospitals and clinics might be forced to cut back on services, leading to longer wait times for appointments, diagnostic tests, and procedures. Elective surgeries, often already subject to delays, could be postponed indefinitely, impacting patients’ health and quality of life. For example, a hospital facing a budget shortfall might reduce its operating hours for certain departments, leading to increased wait times in emergency rooms and decreased availability of specialized care.
This scenario is particularly concerning for time-sensitive conditions requiring prompt medical attention.
Impact on Vulnerable Populations
Vulnerable populations, including low-income individuals, the elderly, and those with chronic illnesses, are often the most susceptible to disruptions in healthcare access. Service cuts and delays disproportionately affect these groups, who may lack the resources to navigate complex healthcare systems or afford alternative care options. For instance, a reduction in mental health services could have devastating consequences for individuals already struggling with mental illness, while cuts to transportation assistance could prevent patients in rural areas from accessing necessary care.
The lack of adequate healthcare can exacerbate existing health disparities and lead to worse health outcomes for these vulnerable populations.
The collapse of SVB sent shockwaves through the healthcare sector, leaving many wondering about the future. This instability comes at a terrible time, as healthcare executives are already grappling with a major crisis, as highlighted in this article: healthcare executives say talent acquisition labor shortages business risk. These staffing shortages were a huge concern even before the SVB fallout, now they’re a potentially crippling blow to an already stressed system, further complicated by the federal intervention.
Ripple Effects on Healthcare Staffing and Workforce Stability
The financial instability caused by the SVB collapse could also have a significant impact on healthcare staffing. Hospitals and clinics might be forced to implement hiring freezes or even reduce their workforce to control costs. This could lead to increased workloads for remaining staff, potentially compromising the quality of patient care and contributing to burnout and staff turnover.
A shortage of healthcare professionals, already a significant issue in many areas, could be further exacerbated by the financial difficulties resulting from the SVB failure. The loss of experienced and skilled healthcare workers could have long-term implications for the quality and efficiency of healthcare services.
Wrap-Up
The collapse of SVB serves as a stark reminder of the interconnectedness of the financial system and the vulnerabilities within the healthcare industry. While federal intervention has provided some immediate relief, the long-term implications for healthcare funding, innovation, and patient care are still unfolding. The crisis has highlighted the need for greater diversification of funding sources, more robust risk management strategies, and a deeper understanding of the potential consequences of systemic financial shocks.
The healthcare sector is adapting, exploring alternative funding models and seeking ways to ensure continued access to vital services, but the journey ahead is complex and requires ongoing vigilance.
Question Bank
What types of healthcare organizations were most affected by the SVB collapse?
Venture-backed startups, smaller hospitals, and those heavily reliant on SVB for banking services were most significantly impacted. Larger hospital systems with diversified banking relationships experienced less severe consequences.
How will the SVB collapse impact access to healthcare for patients?
The impact on patient access is indirect but potentially significant. Funding disruptions could lead to reduced services, staffing cuts, and delays in treatment, particularly affecting vulnerable populations.
What alternative funding sources are healthcare organizations exploring?
Organizations are exploring options like private equity, venture debt, government grants, and strategic partnerships to mitigate reliance on traditional banking channels.
What is the long-term outlook for healthcare innovation following the SVB crisis?
The long-term impact is uncertain. While some innovation may be slowed by funding constraints, the crisis could also spur the development of more resilient and diversified funding models for healthcare technologies.




