Healthcare Leaders Struggle with Inefficient Data Reporting
Majority of healthcare leaders struggle with inefficient data report intelligent medical objects – it’s a harsh reality. We’re drowning in data, yet so often lack the tools and processes to transform that raw information into actionable insights. This impacts everything from patient care and operational efficiency to financial stability. Imagine trying to navigate a complex medical system with a blurry map – that’s the daily struggle for many healthcare professionals.
This post dives into the core issues, explores potential solutions, and offers a glimpse into a future where data empowers, rather than overwhelms.
The problem isn’t a lack of data; it’s a lack of efficient ways to collect, analyze, and interpret it. Inefficient reporting leads to delayed decision-making, missed opportunities for improvement, and ultimately, poorer patient outcomes. The cost is significant, both financially and in terms of human well-being. This is particularly true when it comes to Intelligent Medical Objects (IMOs), powerful tools that are hampered by the very data they need to thrive.
The Problem

Source: knowi.com
Let’s face it: many healthcare leaders are drowning in data, yet starved for actionable insights. The current state of data reporting in healthcare is often characterized by inefficiency, hindering effective decision-making and ultimately impacting patient care. The sheer volume of data, coupled with its fragmented nature and lack of standardization, creates a significant hurdle for those responsible for steering healthcare organizations towards success.The current system often relies on disparate, siloed systems, leading to data residing in numerous locations, making a holistic view incredibly difficult to achieve.
Reports are frequently delayed, incomplete, or presented in formats that are challenging to interpret, requiring significant time and effort for analysis. This inefficient data landscape is a major obstacle to progress, impacting everything from strategic planning to operational efficiency.
Impact on Decision-Making
Inefficient data reporting directly undermines the ability of healthcare leaders to make informed decisions. For instance, delays in receiving accurate patient readmission data can hinder the implementation of effective interventions to improve patient outcomes and reduce healthcare costs. Similarly, incomplete or inaccurate data on staffing levels can lead to poor resource allocation, resulting in burnout among staff and potentially compromised patient safety.
Without timely and reliable data, strategic decisions regarding investments in new technologies, expansion plans, or even basic resource allocation become mere educated guesses, rather than informed choices based on solid evidence. A hospital system might, for example, invest heavily in a new cardiac unit based on outdated or incomplete data regarding regional demand, leading to underutilization and financial losses.
Challenges in Data Access and Interpretation
Accessing and interpreting relevant data presents a significant challenge for healthcare leaders. The sheer volume of data generated daily, combined with its complexity and the lack of standardization across different systems, often requires specialized skills and expensive software to effectively manage and analyze. Furthermore, many healthcare professionals lack the necessary data literacy skills to interpret complex data sets, requiring investment in training and development.
This often creates a dependency on specialized data analysts, which can be both costly and time-consuming, creating bottlenecks in the decision-making process. Imagine a situation where a hospital administrator needs to understand the effectiveness of a new diabetes management program. Without easy access to consolidated patient data, including blood glucose levels, medication adherence, and hospital readmissions, making an informed assessment becomes virtually impossible.
So many healthcare leaders are drowning in inefficient data, struggling to make sense of their intelligent medical objects. It’s a huge problem, and I was really interested to read about how Google Cloud Healthcare, with Amy Waldron at the helm, is leveraging generative AI to tackle these issues – check out this article: google cloud healthcare amy waldron generative AI.
Hopefully, solutions like this can help streamline data reporting and finally give healthcare professionals the insights they need to improve patient care. The current struggle with inefficient data reporting is simply unacceptable.
Financial Consequences of Inefficient Data Reporting
The financial consequences of inefficient data reporting are substantial. Delayed or inaccurate data can lead to increased operational costs, reduced revenue, and even financial penalties from regulatory bodies. For example, inefficient reporting on billing processes can lead to delayed payments from insurance companies, impacting cash flow and potentially harming the financial stability of the organization. Similarly, inaccurate data on medication usage can lead to overspending on unnecessary drugs, or worse, under-prescription of essential medications, leading to increased patient complications and higher costs down the line.
A lack of comprehensive data on patient flow and resource utilization can lead to inefficient scheduling and staffing, resulting in increased overtime costs and decreased productivity. These financial impacts ripple throughout the organization, impacting profitability and the ability to invest in improvements in patient care.
Impact of Inefficient Data on Intelligent Medical Objects (IMOs)
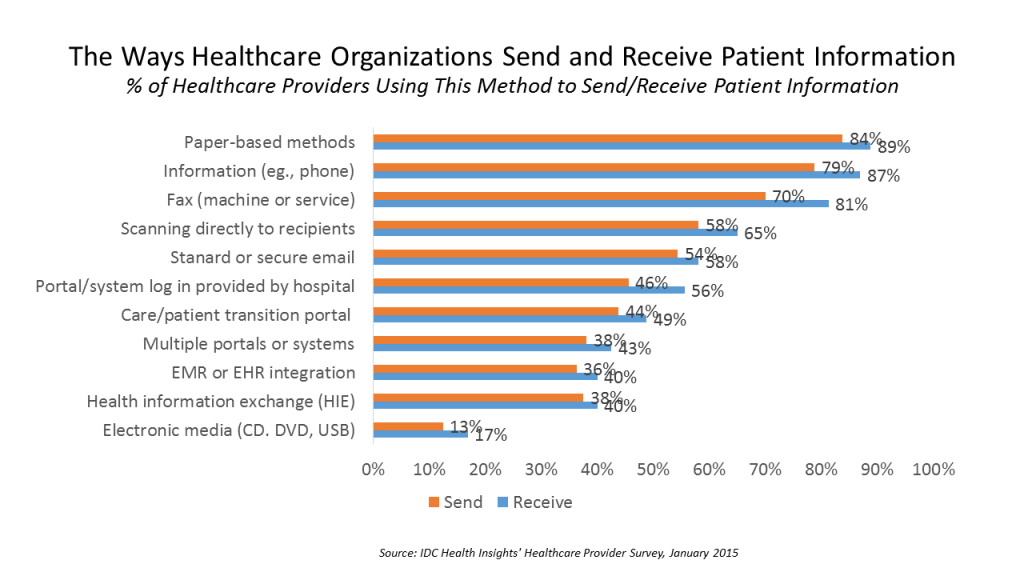
Source: healthpopuli.com
The promise of Intelligent Medical Objects (IMOs) – self-contained, reusable data structures representing medical concepts – is immense. They offer the potential to streamline healthcare processes, improve data interoperability, and ultimately enhance patient care. However, the reality is that many healthcare organizations struggle to fully realize this potential due to a pervasive problem: inefficient data reporting. The quality and consistency of the data feeding these intelligent systems directly impacts their effectiveness, creating a significant bottleneck in the path to realizing the benefits of IMOs.Inefficient data reporting significantly hinders the effective use of IMOs by creating a foundation of flawed information.
IMOs rely on accurate, complete, and consistently formatted data to function correctly. Inconsistent coding, missing values, and data entry errors all lead to inaccurate or incomplete representations within the IMO, diminishing its reliability and utility. For example, an IMO designed to track patient allergies might fail to alert a clinician to a critical allergy if the allergy information is inconsistently recorded across different systems or is missing altogether.
This not only undermines the intended functionality of the IMO but also poses significant risks to patient safety.
Data Quality and IMO Performance, Majority of healthcare leaders struggle with inefficient data report intelligent medical objects
The relationship between data quality and IMO performance is directly proportional. High-quality data, characterized by accuracy, completeness, timeliness, and consistency, leads to robust and reliable IMO functionality. Conversely, poor data quality results in unreliable IMOs, leading to inaccurate analyses, flawed decision-support, and potentially harmful consequences for patient care. Imagine an IMO used for predicting patient readmission risk. If the underlying data contains inaccuracies regarding patient diagnoses, medications, or social determinants of health, the IMO’s predictive capabilities will be severely compromised, potentially leading to misallocation of resources and suboptimal patient management.
IMO Potential vs. Data Limitations
The potential benefits of IMOs are substantial: improved clinical decision-making, enhanced interoperability between healthcare systems, more efficient workflows, and better patient outcomes. However, the realities of current data limitations often fall short of these ideals. Many healthcare systems still rely on disparate, legacy systems that lack interoperability, resulting in data silos and fragmented information. This fragmented data makes it extremely challenging to create and maintain accurate and consistent IMOs.
Furthermore, the lack of standardized data formats and terminologies further complicates data integration and IMO development. The result is a significant gap between the theoretical potential of IMOs and their practical application in many real-world settings.
Enhancing IMO Functionality Through Improved Data Reporting
Improved data reporting is crucial for maximizing IMO functionality. Several key improvements can significantly enhance the performance and reliability of IMOs. These include implementing standardized data entry protocols, investing in data quality tools and techniques, ensuring data governance and validation processes, and promoting interoperability between healthcare systems. For instance, the adoption of standardized terminologies like SNOMED CT and LOINC ensures that data is consistently represented across different systems, improving the accuracy and reliability of IMOs.
Furthermore, the use of data quality tools can help identify and correct errors in the data before they impact the performance of IMOs. By addressing these data quality issues, healthcare organizations can unlock the full potential of IMOs and realize the substantial benefits they offer.
Technological Solutions for Improved Data Reporting
The struggle with inefficient data reporting in healthcare is real, and it’s impacting the effectiveness of Intelligent Medical Objects (IMOs). Fortunately, technological solutions offer a path to streamlined data collection, aggregation, and insightful analysis. By implementing the right systems and strategies, healthcare leaders can transform raw data into actionable intelligence, leading to better patient care and improved operational efficiency.
Addressing this challenge requires a multifaceted approach, focusing on both the technological infrastructure and the processes for utilizing the data generated. This involves selecting appropriate tools, designing effective data pipelines, and establishing clear visualization strategies to communicate complex information concisely and effectively.
Streamlined Data Collection and Aggregation System Design
A successful system prioritizes interoperability and standardization. It should integrate seamlessly with existing Electronic Health Records (EHRs), Picture Archiving and Communication Systems (PACS), and other relevant healthcare information systems. Data should be collected in a standardized format, using common data models like HL7 FHIR, to ensure consistency and ease of analysis. The system should also incorporate automated data cleaning and validation processes to minimize errors and ensure data quality.
Consider a centralized data warehouse or a cloud-based solution for efficient data storage and retrieval. This approach allows for scalable storage and easy access for authorized personnel. For example, a hospital system could implement a cloud-based data lake to store all its data from various sources, allowing for a unified view and advanced analytics.
Transforming Raw Data into Actionable Insights
A step-by-step process for transforming raw data into actionable insights involves several key stages. First, data cleaning and preprocessing are crucial to remove inconsistencies and errors. Next, data aggregation and transformation involve summarizing and restructuring the data into a format suitable for analysis. This might involve calculating key performance indicators (KPIs), such as average length of stay or readmission rates.
Then, advanced analytics techniques, such as predictive modeling and machine learning, can be applied to identify trends and patterns. Finally, the insights derived from the analysis should be clearly communicated to healthcare leaders through visualizations and reports. For instance, predicting patient readmission risk allows for proactive interventions, reducing healthcare costs and improving patient outcomes.
Successful Data Visualization Techniques
Effective data visualization is essential for communicating complex healthcare data clearly and concisely. Dashboards are useful for presenting key metrics at a glance, providing a high-level overview of performance. Interactive charts and graphs allow for deeper exploration of the data, enabling users to drill down into specific areas of interest. Geographic maps can be used to visualize the distribution of diseases or healthcare resources.
For example, a heatmap showing the geographic distribution of influenza cases can help public health officials allocate resources effectively. Similarly, a dashboard showing key metrics like patient satisfaction scores, wait times, and readmission rates provides a comprehensive view of hospital performance.
Comparison of Data Analytics Tools
| Tool Name | Key Features | Cost | Integration Capabilities |
|---|---|---|---|
| Microsoft Power BI | Data visualization, dashboards, reporting, AI-powered insights | Subscription-based, varying costs | Integrates with various data sources, including EHRs and other healthcare systems |
| Tableau | Data visualization, dashboards, analytics, data preparation | Subscription-based, varying costs | Integrates with a wide range of data sources, including cloud-based and on-premise systems |
| Qlik Sense | Data visualization, dashboards, self-service analytics, associative data exploration | Subscription-based, varying costs | Integrates with various data sources, including EHRs and other healthcare systems |
| R/Python | Statistical computing, machine learning, data mining | Open-source, free | Requires custom integration with healthcare systems |
Strategies for Data Governance and Management

Source: 4imag.com
Efficient data reporting is the backbone of effective healthcare. Without a robust data governance framework, intelligent medical objects (IMOs) remain underutilized, hindering advancements in patient care and operational efficiency. This section details key strategies for establishing and maintaining a data governance system that ensures data quality, security, and usability.
A comprehensive data governance framework requires a multi-faceted approach, addressing data quality, security, standardization, and user training. This framework isn’t a one-time project; it’s an ongoing process of improvement and adaptation to meet evolving needs and regulatory changes. Successful implementation necessitates buy-in from all levels of the organization, from clinicians to administrators.
Developing a Comprehensive Data Governance Framework
A robust data governance framework establishes clear roles, responsibilities, and processes for managing healthcare data throughout its lifecycle. This includes defining data ownership, establishing data quality standards, and implementing procedures for data collection, storage, and access. For example, a hospital might assign a data governance committee composed of representatives from various departments (IT, clinical, administration) to oversee the framework’s implementation and ongoing maintenance.
This committee would be responsible for setting data quality standards, approving data sharing agreements, and resolving data-related disputes. Regular audits and reviews are essential to ensure the framework remains effective and aligned with organizational goals.
Robust Data Security Protocols for Sensitive Patient Information
Protecting patient data is paramount. Robust data security protocols are crucial, encompassing technical safeguards like encryption, access controls, and intrusion detection systems, as well as administrative controls such as data loss prevention policies and employee training programs on data privacy and security best practices. Compliance with regulations like HIPAA in the US or GDPR in Europe is essential.
For instance, implementing strong password policies, multi-factor authentication, and regular security audits can significantly reduce the risk of data breaches. Data anonymization and de-identification techniques can also facilitate data sharing for research and analysis while protecting patient privacy.
The Role of Data Standardization in Efficient Data Reporting and Analysis
Data standardization is critical for efficient data reporting and analysis. Standardized data formats and terminologies (e.g., LOINC, SNOMED CT) ensure interoperability between different systems and facilitate accurate data aggregation and analysis. Without standardization, data from various sources may be incompatible, leading to inconsistencies and inaccuracies in reports. For example, using a standardized code for a specific diagnosis across all hospital systems allows for accurate tracking of disease prevalence and treatment outcomes.
Implementing standardized data dictionaries and ontologies helps to eliminate ambiguity and ensure data consistency across the organization.
Training Program for Healthcare Professionals on Data Literacy and Effective Data Utilization
Effective data utilization requires a data-literate workforce. A comprehensive training program should equip healthcare professionals with the skills to understand, interpret, and utilize data effectively. This program should cover topics such as data analysis techniques, data visualization, and the ethical considerations of data use. For example, training could include workshops on using data analytics tools to identify trends in patient outcomes or using data visualization techniques to communicate findings effectively to colleagues and stakeholders.
Ongoing professional development opportunities should be provided to keep healthcare professionals abreast of the latest data management techniques and technologies.
Case Studies
Let’s delve into real-world examples of healthcare organizations that have successfully navigated the challenges of inefficient data reporting and implemented effective solutions. These case studies illustrate the tangible benefits of improved data management and highlight best practices for others to emulate. They demonstrate that a commitment to data-driven decision-making can lead to significant improvements in patient care and operational efficiency.
Honestly, it’s a huge headache for most healthcare leaders – wrestling with clunky, inefficient data reports when trying to make sense of intelligent medical objects. The sheer volume of information is overwhelming. But I recently read a fascinating study widespread digital twins healthcare , which suggests a potential solution. Maybe digital twins could streamline data analysis, helping leaders finally get a grip on those overflowing reports and make better, faster decisions.
It’s a hopeful sign in the ongoing battle against data overload.
Successful Data Reporting at Memorial Healthcare System
Memorial Healthcare System (MHS), a large public healthcare system in South Florida, faced challenges with data silos and inconsistent reporting methods across its numerous facilities. This hindered their ability to track key performance indicators (KPIs) and make data-driven decisions regarding resource allocation and quality improvement. To address this, MHS implemented a comprehensive data warehousing and business intelligence solution.
This involved consolidating data from various sources into a centralized repository, standardizing data definitions, and developing a suite of interactive dashboards and reports. The system utilized a combination of SQL databases, ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) processes, and a user-friendly business intelligence platform. The result was a significant improvement in data accessibility and the ability to generate timely, accurate reports on a wide range of metrics, including patient satisfaction, readmission rates, and operational efficiency.
Challenges included overcoming resistance to change from some staff members and ensuring data quality throughout the integration process. However, the improved data visibility led to better resource allocation, reduced costs, and demonstrably improved patient outcomes.
It’s a real headache for most healthcare leaders – wrangling inefficient data and making sense of intelligent medical objects. This struggle to effectively utilize data is highlighted by the recent news that Walgreens is raising its healthcare segment outlook following the Summit acquisition, walgreens raises healthcare segment outlook summit acquisition. This suggests a potential path forward, showing how leveraging data effectively can translate to significant improvements, but many organizations still need to bridge that gap in efficient data reporting.
Improved Patient Outcomes Through Enhanced Data Reporting at Northwest Regional Hospital
Northwest Regional Hospital, a mid-sized hospital in the Pacific Northwest, focused on improving patient outcomes by leveraging enhanced data reporting. They identified a need for more accurate and timely tracking of patient data related to specific conditions, such as heart failure and pneumonia. By implementing a real-time data monitoring system integrated with their electronic health record (EHR), they could track key clinical indicators and identify patients at high risk of complications.
This allowed for proactive interventions, such as earlier discharge planning and more frequent follow-up appointments. The system used predictive analytics to flag patients who might require additional attention, based on historical data and current trends. This resulted in a noticeable reduction in hospital readmissions and improved patient satisfaction scores. The hospital also saw increased operational efficiency due to more streamlined workflows and better resource allocation.
The initial investment in the new system and the training required for staff were significant challenges. However, the return on investment was considerable, with demonstrably improved patient outcomes and reduced healthcare costs.
Key Takeaways from Case Studies
The following points summarize the key lessons learned from the case studies presented above:
The successful implementation of efficient data reporting requires a multi-faceted approach involving:
- Data Consolidation and Standardization: Establishing a centralized data repository and standardizing data definitions are crucial for ensuring data accuracy and consistency.
- Investment in Technology: Modern data warehousing and business intelligence tools are essential for effective data analysis and reporting.
- Change Management: Overcoming resistance to change and ensuring staff buy-in are vital for successful implementation.
- Data Governance and Security: Robust data governance policies and security measures are essential to protect patient data and maintain data integrity.
- Focus on Measurable Outcomes: Defining clear objectives and tracking key performance indicators (KPIs) are essential for demonstrating the value of improved data reporting.
Future Trends in Healthcare Data Reporting
The healthcare industry is on the cusp of a data revolution. The sheer volume of data generated daily – from electronic health records (EHRs) to wearable sensors – presents both immense challenges and unprecedented opportunities. Efficiently harnessing this data to improve patient care, streamline operations, and drive better decision-making is paramount, and emerging technologies are poised to play a pivotal role in this transformation.The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) is reshaping how healthcare data is reported and analyzed.
These technologies are not merely automating existing processes; they are fundamentally changing our approach to data interpretation and predictive modeling.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning in Data Analysis
AI and ML algorithms can sift through vast datasets to identify patterns and insights that would be impossible for humans to detect manually. For instance, ML models can predict patient readmission rates based on historical data, allowing hospitals to proactively intervene and improve patient outcomes. AI can also automate the generation of reports, flagging potential anomalies or areas of concern for clinicians.
This frees up valuable time for healthcare professionals to focus on direct patient care. Imagine an AI system analyzing thousands of patient records to identify subtle correlations between genetic markers and disease progression, leading to earlier and more effective interventions. This level of analysis is simply not feasible with traditional methods.
Challenges and Opportunities of Advanced Technologies
The adoption of AI and ML in healthcare data reporting is not without its challenges. Data privacy and security are paramount concerns. Robust safeguards are needed to protect sensitive patient information. Furthermore, the development and implementation of these sophisticated technologies require significant investment in infrastructure, training, and expertise. However, the potential benefits are substantial.
Improved accuracy in diagnosis, personalized treatment plans, and more efficient resource allocation are just a few examples of the positive impact these technologies can have. The challenge lies in navigating the ethical and practical considerations to unlock their full potential responsibly.
Impact on Healthcare Leaders and Decision-Making
The shift towards AI-driven data reporting will fundamentally alter the role of healthcare leaders. Decision-making will become increasingly data-driven, relying on insights generated by AI and ML algorithms. Leaders will need to develop new skills to interpret and utilize these insights effectively. This means investing in data literacy training for their teams and fostering a culture of data-driven decision-making throughout the organization.
Furthermore, they will need to grapple with the ethical implications of AI and ensure that these technologies are used responsibly and equitably. For example, leaders will need to address potential biases in algorithms and ensure that AI-driven decisions are transparent and explainable.
Improved Integration and Utilization of IMOs
AI and ML can significantly enhance the integration and utilization of Intelligent Medical Objects (IMOs). These technologies can automate the process of extracting relevant information from IMOs, streamlining data analysis and reporting. AI can also assist in the creation and maintenance of IMOs by identifying gaps in information and suggesting improvements to their structure and content. This will lead to a more efficient and effective use of IMOs, ultimately improving patient care and decision-making.
For example, an AI system could automatically update IMOs with the latest research findings, ensuring that clinicians have access to the most current and relevant information.
Outcome Summary: Majority Of Healthcare Leaders Struggle With Inefficient Data Report Intelligent Medical Objects
The challenges of inefficient data reporting in healthcare are significant, but not insurmountable. By embracing new technologies, implementing robust data governance frameworks, and fostering a culture of data literacy, we can pave the way for a more efficient and effective healthcare system. The journey towards data-driven decision-making is ongoing, but the potential rewards – improved patient care, enhanced operational efficiency, and significant cost savings – make the effort more than worthwhile.
Let’s work together to unlock the power of data and build a healthier future.
Question & Answer Hub
What are Intelligent Medical Objects (IMOs)?
IMOs are reusable, standardized components of medical information that can be easily shared and integrated across different healthcare systems. They improve data interoperability.
How can improved data reporting reduce healthcare costs?
Efficient reporting can identify areas of waste, optimize resource allocation, and prevent costly errors, leading to significant cost savings.
What role does data security play in efficient data reporting?
Robust security protocols are crucial to protect sensitive patient information while ensuring data can be shared effectively and ethically.
What are some examples of successful data visualization techniques in healthcare?
Dashboards, interactive charts, and geographical maps are commonly used to present complex healthcare data in a clear and understandable way.