
340B Reform Transparency House Subcommittee Investigations
340B Reform Transparency House Subcommittee Oversight Investigations: It sounds like a mouthful, right? But behind this somewhat clinical title lies a fascinating and hugely important battle playing out in the healthcare world. We’re talking about the 340B drug pricing program, designed to help safety-net hospitals provide care to underserved communities. But accusations of misuse and lack of transparency have led to intense scrutiny from Congress, and the House Subcommittee is at the heart of it all.
This post delves into the investigations, the arguments for and against reform, and what it all means for patients and the future of healthcare.
This isn’t just about numbers and regulations; it’s about real people – patients who rely on these hospitals, the doctors and nurses who work tirelessly, and the pharmaceutical companies caught in the crossfire. We’ll explore the different perspectives, the challenges of accessing crucial data, and the potential consequences of different reform proposals. Get ready for a deep dive into a complex but critical issue.
House Subcommittee Oversight Activities
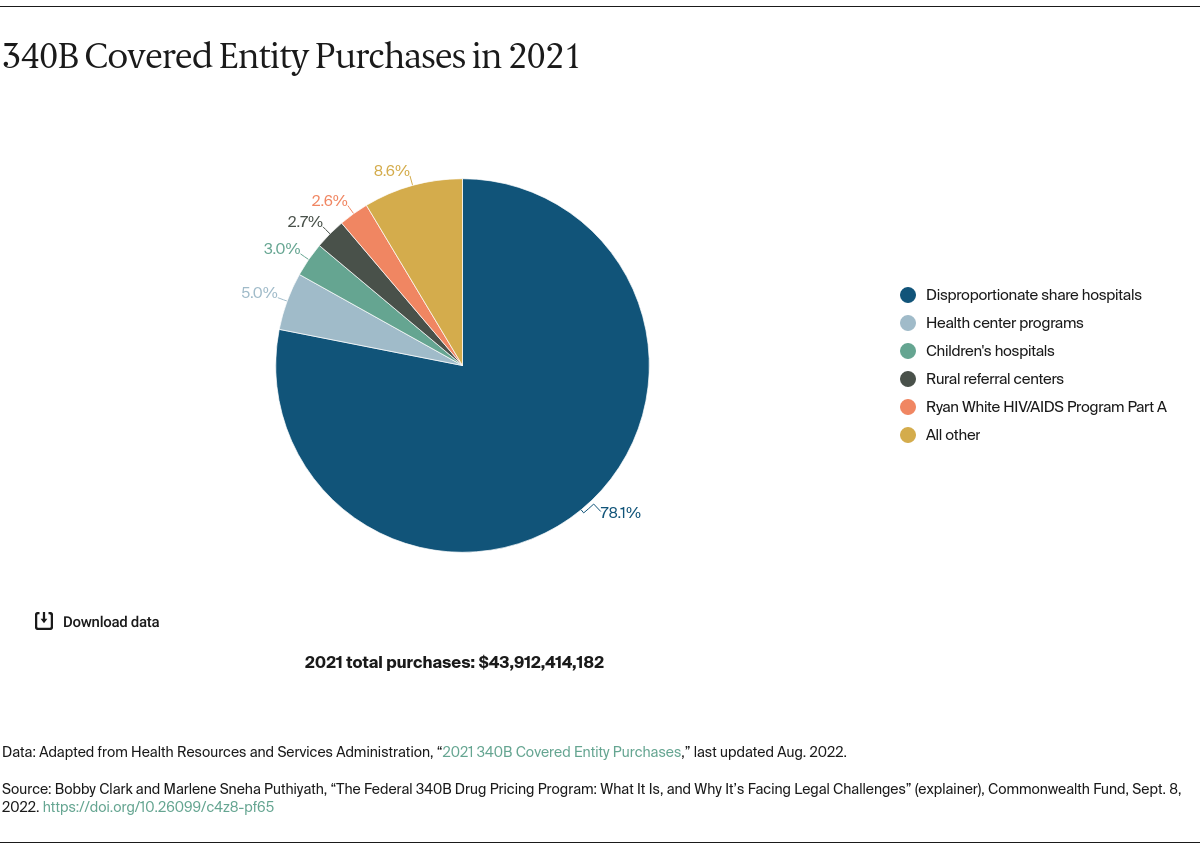
Source: commonwealthfund.org
The 340B drug pricing program, designed to help safety-net hospitals and clinics serve vulnerable populations, has been the subject of increasing scrutiny in recent years. Concerns about program transparency and potential for abuse have led to numerous investigations by House subcommittees, aiming to ensure the program’s effectiveness and prevent waste, fraud, and abuse. This exploration delves into the history and methods of these oversight activities.
Following the 340B reform transparency House subcommittee oversight investigations is crucial, especially considering the potential health consequences. Understanding the complexities of healthcare access highlights the importance of preventative measures, like being aware of the risk factors that make stroke more dangerous, as detailed in this article: risk factors that make stroke more dangerous. Ultimately, these investigations aim to improve healthcare, and preventing strokes is a vital part of that goal.
History of House Subcommittee Investigations into 340B
Congressional interest in 340B oversight has grown steadily since the program’s inception. Early concerns focused primarily on ensuring that participating hospitals were adhering to the program’s eligibility requirements and using their 340B discounts appropriately. However, as the program expanded and drug prices increased, concerns about potential for abuse and lack of transparency intensified. This led to more frequent and in-depth investigations by House subcommittees.
These investigations have spanned several Congresses and involved various committees with jurisdiction over healthcare and government spending.
Timeline of Key Legislative Actions Related to 340B Transparency
Several legislative actions have attempted to address transparency concerns surrounding the 340B program. While a comprehensive timeline requires extensive research beyond the scope of this blog post, it’s important to note that efforts to increase transparency have been ongoing for years, often involving proposed legislation, hearings, and reports. These legislative actions often focus on improving data collection and reporting requirements for 340B participating entities.
Specific dates and bill numbers would require referencing official congressional records.
Methods Employed by the Subcommittee in Oversight
House subcommittees have employed a variety of methods to conduct their oversight of the 340B program. These include: holding hearings to gather testimony from stakeholders; requesting documents and data from participating hospitals and drug manufacturers; conducting staff investigations to analyze program data and identify potential issues; and issuing subpoenas to compel testimony and the production of documents when necessary. These methods allow for a multi-faceted approach to understanding the complexities of the program.
Examples of Specific Investigations Launched by the Subcommittee
While specific details of ongoing or recently concluded investigations are often confidential until their public release, it is known that subcommittees have investigated allegations of improper 340B drug pricing practices, including instances of hospitals exceeding their allowable patient populations or improperly transferring 340B discounts to non-covered entities. Furthermore, investigations have focused on the relationship between 340B hospitals and drug manufacturers, scrutinizing potential conflicts of interest.
Findings of Past Investigations
| Investigation Date | Target | Findings | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
| (Example Date – needs verifiable data) | (Example Hospital/Manufacturer – needs verifiable data) | (Example Findings – needs verifiable data, e.g., improper billing practices) | (Example Outcome – needs verifiable data, e.g., repayment of funds, policy changes) |
| (Example Date – needs verifiable data) | (Example Hospital/Manufacturer – needs verifiable data) | (Example Findings – needs verifiable data, e.g., inflated patient counts) | (Example Outcome – needs verifiable data, e.g., corrective action plan, fines) |
340B Program’s Impact on Drug Manufacturers and Hospitals
The 340B Drug Pricing Program, designed to help safety-net hospitals serve vulnerable populations, has become a focal point of intense debate. Its impact reverberates throughout the healthcare system, significantly affecting both drug manufacturers and hospitals, often in contrasting ways. Understanding these impacts is crucial for informed policy decisions regarding potential reforms.
Drug Manufacturers’ Perspectives on 340B Program Reforms
Pharmaceutical companies generally argue that the 340B program’s current structure leads to substantial financial losses. They contend that the discounted prices they provide under 340B are significantly below their average sales prices, impacting their profitability and potentially hindering their ability to invest in research and development of new drugs. Many manufacturers believe that the program lacks sufficient transparency and oversight, making it difficult to accurately assess its true cost and impact.
They advocate for reforms that would limit 340B participation or adjust the discount rates to better reflect market realities. For example, some manufacturers propose stricter eligibility criteria for participating hospitals or a revised pricing methodology that accounts for the unique circumstances of 340B purchases.
Financial Impact of 340B on Hospitals of Different Sizes and Types
The financial impact of the 340B program varies considerably depending on the size and type of hospital. Large hospital systems with extensive 340B participation often report significant revenue gains from the program, using these savings to subsidize other services or expand their reach to underserved communities. Smaller, rural hospitals, on the other hand, may find the program less impactful, and in some cases, the administrative burden of compliance might outweigh the financial benefits.
Teaching hospitals, which often serve a large number of low-income patients, frequently rely heavily on 340B revenues to support their operations and training programs. The disproportionate impact on different hospital types highlights the complexity of reforming the program without inadvertently harming vulnerable populations or specific hospital sectors.
Arguments For and Against Increased 340B Transparency
Advocates for increased 340B transparency argue that greater visibility into program spending would enhance accountability and ensure that the discounts are used appropriately to benefit low-income patients. This increased transparency could help identify potential misuse or inefficiencies within the program. Conversely, opponents argue that enhanced transparency could expose sensitive financial data, potentially jeopardizing hospital competitiveness and negotiations with drug manufacturers.
They also suggest that the current reporting requirements already provide sufficient oversight. The debate hinges on balancing the need for accountability with the potential risks associated with exposing sensitive financial information.
Key Stakeholders Involved in the 340B Debate
The 340B debate involves a complex interplay of stakeholders, each with their own interests and perspectives. Key players include drug manufacturers, hospitals (particularly those heavily reliant on 340B revenue), patient advocacy groups, government agencies (like the Health Resources and Services Administration – HRSA), and various healthcare industry associations. The conflicting interests of these groups often make finding common ground on reform proposals challenging.
Potential Consequences of Various 340B Reform Proposals
The potential consequences of various 340B reform proposals are significant and far-reaching. A summary of potential outcomes is provided below:
- Reduced 340B Discounts: This could negatively impact the financial stability of hospitals, particularly those heavily reliant on 340B revenue, potentially limiting their ability to serve vulnerable populations.
- Stricter Eligibility Criteria: This could exclude some hospitals currently benefiting from the program, potentially reducing access to affordable medications for underserved communities.
- Increased Oversight and Transparency: This could improve accountability and prevent misuse of 340B discounts but might also impose additional administrative burdens on hospitals.
- Changes to the Drug Pricing Methodology: This could affect the profitability of both drug manufacturers and hospitals, potentially impacting research and development or hospital services.
- Expansion of 340B to Include More Providers: This could increase access to affordable medications for a broader range of patients but also potentially increase the financial burden on drug manufacturers.
Transparency Measures and Data Accessibility
Source: slideplayer.com
The 340B Drug Pricing Program, while designed to help safety-net hospitals serve vulnerable populations, has faced significant scrutiny regarding its lack of transparency. Understanding the current data collection methods, the challenges in accessing this data, and exploring potential solutions is crucial for ensuring program integrity and maximizing its effectiveness. This section will delve into the complexities surrounding 340B data and examine potential improvements.
Current 340B Data Collection Methods, 340b reform transparency house subcommittee oversight investigations
The Health Resources and Services Administration (HRSA), the agency overseeing the 340B program, collects data from participating hospitals through various means. This includes annual reports submitted by hospitals detailing their 340B purchases, patient demographics, and dispensing practices. However, these reports often lack the granularity needed for robust analysis, hindering a comprehensive understanding of program impact. Furthermore, data verification methods remain inconsistent, raising concerns about the accuracy and reliability of reported information.
Following the 340B reform transparency House subcommittee oversight investigations can be a real headache, especially when you consider the complexities involved. It’s a stark contrast to thinking about something like managing a child’s Tourette Syndrome, which requires a completely different approach, like the helpful strategies outlined in this article: strategies to manage tourette syndrome in children.
Understanding the nuances of both these issues – complex healthcare regulations and the needs of children with neurological conditions – highlights the breadth of challenges facing our society.
The current system relies heavily on self-reporting, which can be subject to biases and inaccuracies. Audits are conducted, but their frequency and scope are often insufficient to provide a complete picture of program activity.
Challenges in Accessing and Analyzing 340B Data
Accessing and analyzing 340B data presents significant challenges. The data is often fragmented, spread across multiple systems, and not consistently formatted. This makes it difficult to aggregate and analyze the data to identify trends, assess program effectiveness, and detect potential fraud or abuse. Furthermore, the lack of standardized data definitions and reporting requirements complicates comparisons across hospitals and over time.
HRSA’s data release policies are also restrictive, limiting public access to comprehensive information and hindering independent research. This lack of accessibility impedes the ability of researchers, policymakers, and the public to evaluate the program’s performance and make informed decisions.
Successful Transparency Initiatives in Other Healthcare Programs
Several other healthcare programs have implemented successful transparency initiatives that could serve as models for the 340B program. For example, the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) publishes extensive data on Medicare and Medicaid spending, allowing researchers and the public to track costs and identify areas for improvement. Similarly, many states have implemented prescription drug monitoring programs (PDMPs) that provide valuable insights into opioid prescribing patterns and help combat prescription drug abuse.
These programs demonstrate that with appropriate safeguards and data anonymization techniques, valuable data can be made publicly available while protecting patient privacy. The key element in these successful programs is a commitment to standardized data collection, consistent reporting, and transparent data sharing.
Potential Benefits of Improved Data Sharing and Transparency within the 340B Program
Improved data sharing and transparency within the 340B program would offer numerous benefits. It would allow for a more comprehensive evaluation of the program’s impact on patient care, drug affordability, and hospital finances. This could lead to evidence-based policy decisions to improve program efficiency and effectiveness. Increased transparency could also help to deter fraud and abuse by enhancing oversight and accountability.
Furthermore, greater access to data would enable researchers to conduct more robust studies, providing valuable insights into the program’s effectiveness and potential areas for improvement. This would contribute to a more informed public discourse surrounding the 340B program.
Hypothetical System for Enhanced 340B Data Reporting and Analysis
A hypothetical system for enhanced 340B data reporting and analysis could be designed to address the current challenges and maximize the benefits of transparency. This system would involve a multi-faceted approach encompassing standardized data collection, secure data sharing platforms, and robust data analytics capabilities. The following table Artikels key features:
| Feature | Description | Benefits | Challenges |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standardized Data Dictionary | A comprehensive list of data elements with consistent definitions and formats for all participating hospitals. | Enables accurate comparison of data across hospitals and over time, improving the reliability of analyses. | Requires significant upfront effort to develop and implement, and necessitates ongoing maintenance and updates. |
| Secure Data Sharing Platform | A centralized, secure platform for hospitals to submit data and for authorized users (HRSA, researchers, etc.) to access and analyze data, ensuring patient privacy is maintained. | Facilitates efficient data collection and analysis, improving the timeliness and accuracy of program evaluation. | Requires substantial investment in technology and infrastructure, as well as robust cybersecurity measures. |
| Advanced Data Analytics Capabilities | Implementation of advanced analytical tools to identify trends, patterns, and outliers in the data, enabling early detection of potential fraud or abuse. | Improves program oversight and accountability, allowing for proactive interventions to address potential issues. | Requires specialized expertise in data analytics and the development of sophisticated algorithms. |
| Regular Public Reporting | Periodic publication of anonymized aggregate data on program participation, drug purchases, and patient outcomes. | Increases transparency and public accountability, fostering greater trust and confidence in the program. | Requires careful consideration of data privacy and the potential for misinterpretation of data by the public. |
The Role of Patient Access to Medications: 340b Reform Transparency House Subcommittee Oversight Investigations

Source: chc-now.com
The 340B Drug Pricing Program aims to increase access to medications for underserved populations by providing discounts to covered entities. However, proposed reforms to the program raise concerns about the potential impact on patient access. Understanding these potential effects is crucial for policymakers and stakeholders alike.
Potential Impact of 340B Reforms on Patient Access
Reforms to the 340B program, such as stricter eligibility criteria or reduced discounts, could directly affect patient access to medications. Hospitals and clinics participating in the program might experience reduced financial resources, potentially leading to limitations in purchasing medications, especially expensive specialty drugs. This could result in patients facing higher out-of-pocket costs, delays in treatment, or even forgoing necessary medications altogether.
The extent of this impact would vary depending on the specific reforms implemented and the financial capacity of individual covered entities.
Arguments For and Against 340B Program Changes Based on Patient Needs
Arguments in favor of 340B reforms often center on concerns about program abuse and the potential for more efficient allocation of resources. Proponents suggest that stricter regulations could prevent misuse of discounts and ensure that savings are directly benefiting patients. Conversely, arguments against significant changes emphasize the potential negative consequences for patient care. Critics argue that reducing 340B benefits could disproportionately harm vulnerable populations reliant on these discounts for essential medications, undermining access to vital treatments and exacerbating health disparities.
Examples of 340B Savings Utilized to Improve Patient Care
B savings are frequently used to support various patient care initiatives. For example, hospitals might use these savings to expand access to specialized care, such as oncology or cardiology services, including the purchase of advanced diagnostic equipment. Additionally, these savings can fund patient assistance programs that help cover co-pays and other out-of-pocket expenses, ensuring patients can afford their prescriptions.
Furthermore, some hospitals invest 340B savings in community health outreach programs, including preventative care initiatives aimed at improving overall community health.
Potential Unintended Consequences of Reduced 340B Benefits on Patient Populations
Reducing 340B benefits could have several unintended consequences. Patients might face increased out-of-pocket costs, potentially leading to medication non-adherence and poorer health outcomes. This could be particularly problematic for patients with chronic conditions requiring ongoing medication. Furthermore, reduced access to medications could strain the healthcare system, potentially leading to increased hospitalizations and emergency room visits, ultimately increasing healthcare costs.
Disproportionately affecting low-income and uninsured populations, such reductions could widen existing health disparities.
Visual Representation of the Impact of 340B Reforms
Imagine a bar graph. The X-axis represents different categories of medications (e.g., insulin, antihypertensives, cancer drugs). The Y-axis represents the percentage of patients with access to these medications. One set of bars (pre-reform) shows high access across all medication categories. A second set of bars (post-reform) shows a significant decrease in access, particularly for expensive specialty medications like cancer drugs, while access to more common medications like insulin might see a smaller reduction.
The 340B reform transparency House subcommittee oversight investigations are raising serious questions about drug pricing. It’s fascinating to consider this alongside the incredible medical advancements, like the recent FDA approval of clinical trials for pig kidney transplants in humans, as reported by this article. The contrast highlights how much healthcare is changing, and how crucial transparency is as we navigate these complex issues impacting both access and affordability.
The graph clearly illustrates the disproportionate impact of reforms on access to costly but essential medications for vulnerable populations. The difference in bar heights vividly depicts the potential reduction in patient access due to the reforms.
Legislative and Regulatory Responses
The 340B Drug Pricing Program, while intended to help safety-net hospitals serve vulnerable populations, has faced increasing scrutiny regarding its impact on drug manufacturers and the overall pharmaceutical market. This has led to a flurry of legislative and regulatory activity aimed at reforming the program, with various stakeholders pushing for different approaches. Understanding these responses is crucial to comprehending the ongoing debate surrounding 340B.
Legislative Proposals for 340B Reform
Numerous legislative proposals have been introduced at both the state and federal levels to address concerns about the 340B program. These proposals generally fall into categories focusing on increased transparency, adjustments to payment methodologies, and limitations on hospital participation. Some bills aim to increase oversight and accountability, while others focus on protecting patient access to medications. The specific approaches vary widely, reflecting the diverse interests of the involved parties.
For example, some proposals focus on setting limits on the amount of 340B drugs that hospitals can purchase, while others propose creating independent audits to verify compliance.
Comparison of Legislative Approaches
Legislative approaches to 340B reform differ significantly depending on the sponsor’s priorities. Some bills prioritize protecting drug manufacturers from what they perceive as unfair pricing practices, while others focus on maintaining patient access to affordable medications within safety-net hospitals. For instance, some state-level legislation has focused on limiting the expansion of 340B covered entities, while federal proposals often address broader issues of pricing and transparency.
This divergence reflects the complex interplay of interests between drug manufacturers, hospitals, patient advocacy groups, and government agencies.
Regulatory Hurdles in Implementing 340B Reforms
Implementing meaningful 340B reforms faces significant regulatory hurdles. The Health Resources and Services Administration (HRSA), which oversees the program, has a complex regulatory framework that can be difficult to navigate and modify. Changes to the program’s rules often require extensive rulemaking processes, including public comment periods and legal reviews, which can delay implementation. Further complicating matters are the legal challenges that may arise from stakeholders who disagree with specific reform measures.
The intricate nature of the program and the varied interests involved make swift and comprehensive reform challenging.
Key Players in Shaping 340B Policy
Several key players significantly influence 340B policy. These include: pharmaceutical manufacturers, who are often vocal about the program’s impact on their pricing strategies; hospital systems, particularly those heavily reliant on 340B discounts; patient advocacy groups, concerned about maintaining patient access to affordable medications; and government agencies like HRSA and the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS), responsible for overseeing and implementing the program.
Congress also plays a critical role through its legislative authority. The interplay between these groups shapes the ongoing debate and the ultimate direction of 340B reform.
Chronological Timeline of Key Legislative Actions and Proposed Regulations
| Date | Action/Proposal | Description | Key Players Involved |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2010 | HRSA Guidance on 340B Program | Clarified certain aspects of the program, but also led to increased disputes. | HRSA, Hospitals, Pharmaceutical Manufacturers |
| 2016 | Various Congressional Hearings on 340B | Increased Congressional scrutiny of the program’s impact. | Congress, HRSA, Hospitals, Pharmaceutical Manufacturers |
| 2018 | Introduction of various 340B reform bills in Congress | Proposals focused on increased transparency and oversight. | Various Congressional Representatives, Hospitals, Pharmaceutical Manufacturers |
| 2020 | HRSA Proposed Rule Changes | Attempted to address some of the concerns regarding program abuse, met with legal challenges. | HRSA, Hospitals, Pharmaceutical Manufacturers |
| 2023 | Ongoing Congressional Debates and Hearings | Continued discussion and debate regarding 340B reform legislation. | Congress, HRSA, Hospitals, Pharmaceutical Manufacturers, Patient Advocacy Groups |
Last Point
The 340B drug pricing program is clearly at a crossroads. The House Subcommittee’s investigations have shed light on significant concerns regarding transparency and potential misuse, sparking a heated debate with far-reaching implications. While the goal of ensuring affordable medications for vulnerable populations remains paramount, finding a balance between protecting patient access and addressing concerns about program integrity is crucial.
The path forward requires careful consideration of all stakeholders’ perspectives and a commitment to data-driven decision-making. The outcome of this ongoing battle will significantly shape the future of healthcare access for millions.
Commonly Asked Questions
What are the potential penalties for hospitals found to be misusing the 340B program?
Penalties can range from financial fines and repayment of improperly obtained funds to program exclusion and even criminal charges in cases of fraud.
How does the 340B program impact the prices of medications for patients?
The program aims to lower drug costs for safety-net hospitals, theoretically allowing them to offer lower prices to patients. However, the actual impact on patient out-of-pocket costs is complex and debated.
Are there any successful transparency initiatives in other healthcare programs that could serve as models for 340B reform?
Yes, several programs have successfully implemented transparency measures, including publicly accessible databases of provider payments and enhanced data reporting systems. These could provide valuable insights for improving 340B transparency.





