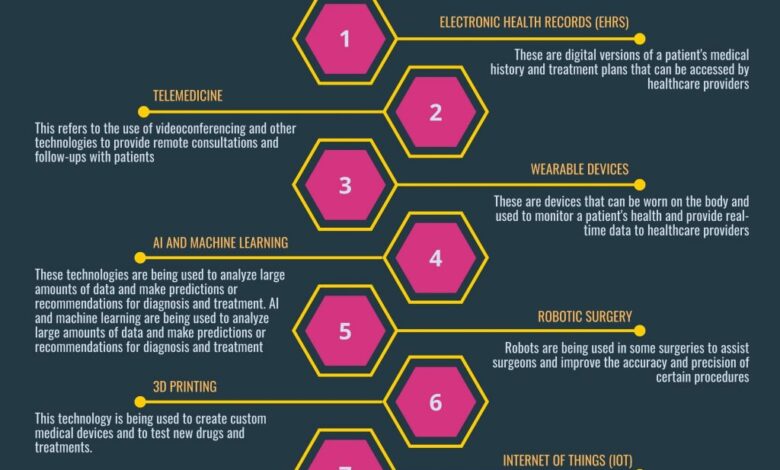
5 Dynamics Shaping Healthcares Digital Evolution
5 dynamics shaping healthcares digital evolution – 5 Dynamics Shaping Healthcare’s Digital Evolution sets the stage for a fascinating journey into the rapidly transforming world of medicine. We’re diving deep into the forces reshaping how we access, receive, and experience healthcare, from the rise of telehealth and the power of AI to the crucial role of cybersecurity and the increasing empowerment of patients. Get ready for a look at the digital revolution that’s changing healthcare as we know it!
This post explores five key trends dramatically altering the healthcare landscape. We’ll examine the impact of telehealth on accessibility and delivery models, the transformative potential of artificial intelligence in diagnostics and treatment, the power of big data analytics in improving population health, the critical need for robust cybersecurity measures, and the growing importance of patient engagement and empowerment. Each dynamic presents both opportunities and challenges, and we’ll delve into the complexities of each to provide a comprehensive overview of this exciting and rapidly evolving field.
The Rise of Telehealth

Source: gartsolutions.com
The digital transformation of healthcare is rapidly reshaping how medical services are delivered, and at the forefront of this revolution is telehealth. Telehealth, encompassing remote patient monitoring, virtual consultations, and online education, has emerged as a powerful tool for expanding access to care, improving efficiency, and enhancing the overall patient experience. Its impact is felt across various demographics and healthcare settings, promising a more convenient and accessible healthcare system for all.Telehealth’s impact on patient access and healthcare delivery models is profound.
It breaks down geographical barriers, making specialized care accessible to patients in rural or underserved areas. It also offers increased convenience, allowing patients to receive care from the comfort of their homes, eliminating travel time and costs. This increased accessibility has the potential to improve health outcomes, particularly for chronic conditions requiring frequent monitoring. The shift towards telehealth also necessitates a change in healthcare delivery models, with a greater emphasis on remote monitoring and virtual interactions.
This evolution necessitates a robust technological infrastructure and a skilled workforce capable of delivering care effectively through digital channels.
Telehealth Compared to In-Person Visits
The following table compares in-person and telehealth visits across key metrics. While effectiveness can vary depending on the condition and the type of telehealth interaction, the overall trend indicates that telehealth offers significant advantages in terms of convenience and cost, often without compromising significantly on effectiveness for many conditions. Note that these are general comparisons and individual experiences may vary.
| Metric | In-Person Visit | Telehealth Visit |
|---|---|---|
| Cost | Higher (travel, parking, time off work) | Lower (no travel costs, potentially lower consultation fees) |
| Convenience | Lower (requires travel, scheduling around appointments) | Higher (can be accessed from anywhere with internet access, flexible scheduling) |
| Effectiveness | Generally high for physical examinations and complex procedures | High for many conditions, particularly chronic disease management and mental health; effectiveness can be lower for conditions requiring physical examination. |
| Accessibility | Limited by geographical location and availability of specialists | Increased accessibility for patients in remote areas or with mobility issues |
Technological Advancements Driving Telehealth Expansion
The rapid expansion of telehealth is fueled by significant advancements in both infrastructure and software. High-speed internet access, particularly broadband and 5G, is crucial for supporting high-quality video conferencing and data transmission. Improved mobile device capabilities, such as better cameras and microphones, enhance the user experience. On the software side, user-friendly telehealth platforms offer secure video conferencing, electronic health record (EHR) integration, and remote patient monitoring tools.
For example, platforms like Teladoc and MDLive provide secure, HIPAA-compliant video conferencing, allowing patients to consult with physicians remotely. The development of AI-powered diagnostic tools also promises to further enhance the capabilities of telehealth, enabling faster and more accurate diagnoses in certain cases.
So, I’ve been diving into the five dynamics shaping healthcare’s digital evolution – AI, telehealth, data analytics, cybersecurity, and patient engagement. It’s fascinating to see how these are playing out in real-world scenarios, like the recent news about HSHS Prevea closing some Wisconsin hospitals and health centers – you can read more about it here: hshs prevea close wisconsin hospitals health centers.
This kind of restructuring highlights the need for adaptable digital strategies in a changing healthcare landscape, further emphasizing the importance of those five key dynamics.
Regulatory and Reimbursement Challenges of Telehealth
Despite its benefits, the widespread adoption of telehealth faces significant regulatory and reimbursement hurdles. Varying state licensing requirements can complicate the provision of telehealth services across state lines. Reimbursement policies from insurance providers often lag behind technological advancements, creating uncertainty about the financial viability of telehealth services for healthcare providers. For instance, some insurance plans may not cover telehealth visits for certain conditions or specialists, limiting patient access to this convenient form of care.
Furthermore, ensuring data privacy and security within telehealth platforms is crucial, necessitating robust cybersecurity measures and adherence to regulations like HIPAA. Addressing these challenges through clear guidelines, consistent reimbursement policies, and robust security protocols is essential for realizing the full potential of telehealth.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Healthcare
The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) is rapidly transforming healthcare, promising a future where diagnoses are faster, treatments are more personalized, and overall patient outcomes are significantly improved. AI algorithms, fueled by vast datasets of medical information, are already demonstrating their ability to analyze complex patterns and provide insights that would be impossible for humans to achieve alone. This revolution is impacting various aspects of healthcare, from early disease detection to drug discovery.AI algorithms are enhancing diagnostic accuracy and personalizing treatment plans through sophisticated machine learning techniques.
These algorithms learn from massive amounts of patient data, including medical images, electronic health records, and genetic information. This learning allows them to identify subtle patterns and anomalies that might be missed by human clinicians, leading to earlier and more accurate diagnoses. For instance, AI-powered image analysis tools can detect cancerous lesions in mammograms with higher accuracy than human radiologists in some cases.
Furthermore, AI can analyze patient data to predict the likelihood of developing certain diseases, enabling proactive interventions and preventative care. Personalized treatment plans are also becoming a reality, with AI helping to select the most effective therapies based on a patient’s unique genetic makeup and medical history.
AI Applications Across Medical Specialties
AI’s impact spans numerous medical specialties. In radiology, AI algorithms analyze medical images (X-rays, CT scans, MRIs) to detect abnormalities like tumors, fractures, and other pathologies. In oncology, AI assists in cancer diagnosis, treatment planning (radiation therapy optimization), and predicting treatment response. In cardiology, AI algorithms analyze electrocardiograms (ECGs) to detect arrhythmias and predict the risk of heart attacks.
Pathology benefits from AI’s ability to analyze microscopic images of tissue samples to identify cancerous cells or other abnormalities. In ophthalmology, AI can detect diabetic retinopathy from retinal images, potentially preventing blindness. These are just a few examples of how AI is improving the accuracy and efficiency of medical diagnoses and treatments.
Ethical Considerations of AI in Healthcare
The widespread adoption of AI in healthcare necessitates careful consideration of ethical implications. The potential benefits are substantial, but responsible implementation requires addressing several key concerns.
The following points highlight crucial ethical considerations:
- Data Privacy and Security: AI algorithms rely on vast amounts of sensitive patient data. Robust security measures are essential to prevent data breaches and protect patient confidentiality. Strict adherence to data privacy regulations (like HIPAA in the US) is paramount.
- Algorithmic Bias: AI algorithms are trained on data, and if that data reflects existing biases (e.g., racial, socioeconomic), the algorithms may perpetuate and even amplify those biases in their predictions and recommendations. Careful attention must be paid to data quality and algorithm fairness to mitigate this risk.
- Transparency and Explainability: Understanding how an AI algorithm arrives at a particular diagnosis or treatment recommendation is crucial for building trust and ensuring accountability. “Black box” algorithms, where the decision-making process is opaque, can raise concerns about transparency and potential errors.
- Responsibility and Liability: Determining liability in cases where an AI system makes an incorrect diagnosis or recommendation is a complex legal and ethical challenge. Clear guidelines and frameworks are needed to address potential malpractice issues.
- Access and Equity: The benefits of AI in healthcare should be accessible to all patients, regardless of their socioeconomic status or geographic location. Efforts must be made to prevent AI-driven healthcare from exacerbating existing health disparities.
AI Revolutionizing Drug Discovery
Imagine a scenario where AI significantly accelerates the drug discovery process. Currently, developing a new drug can take years and cost billions of dollars. AI could revolutionize this by analyzing vast datasets of molecular structures, genetic information, and clinical trial data to identify potential drug candidates and predict their efficacy and safety. For example, an AI system could analyze millions of molecules to identify those most likely to bind to a specific target protein involved in a disease, significantly reducing the time and cost required for preclinical testing.
Furthermore, AI could analyze patient data to identify subgroups who are most likely to respond to a particular drug, enabling personalized medicine approaches. This hypothetical scenario illustrates how AI could dramatically shorten the drug development timeline, leading to faster availability of life-saving medications. Real-world examples already exist where AI is assisting in identifying promising drug candidates and optimizing clinical trial designs, although the full potential is still being realized.
Big Data and Analytics in Healthcare: 5 Dynamics Shaping Healthcares Digital Evolution
The sheer volume of data generated within the healthcare industry – from electronic health records (EHRs) and medical imaging to wearable sensor data and genomic information – presents both unprecedented challenges and incredible opportunities. Big data analytics provides the tools to unlock the potential of this data, transforming how we understand, treat, and prevent disease. By analyzing these massive datasets, we can identify previously unseen patterns, predict health risks, and personalize treatments, ultimately leading to improved patient outcomes and a more efficient healthcare system.Big data analysis is revolutionizing healthcare through the identification of trends, improvement of population health management, and enhancement of public health initiatives.
So, I’ve been diving into the five dynamics shaping healthcare’s digital evolution – telehealth, AI, data analytics, patient portals, and remote monitoring. A perfect example of this shift is the innovative approach taken by humana centerwell primary care centers walmart , which cleverly integrates technology into accessible primary care. This partnership highlights how these five dynamics are converging to create a more efficient and patient-centric healthcare system.
It’s fascinating to see how these forces are reshaping the industry.
This involves sophisticated techniques that go beyond simple descriptive statistics to uncover complex relationships and make predictive models.
Examples of Big Data Analysis in Healthcare
Big data analytics is already being used in numerous ways to improve healthcare. For instance, analyzing patient data from EHRs can identify high-risk patients who are likely to be readmitted to the hospital after discharge, allowing for proactive interventions to prevent readmission. Similarly, analyzing claims data can reveal patterns of disease outbreaks, helping public health officials to quickly implement preventative measures.
Pharmaceutical companies use big data to analyze clinical trial results more efficiently, accelerating the development of new drugs and treatments. Analysis of genomic data is leading to the development of personalized medicine, tailoring treatments to individual patients based on their unique genetic makeup. Finally, analyzing data from wearable fitness trackers can provide insights into individual health behaviors, empowering individuals to make healthier choices.
Data Analytics Techniques in Healthcare
Several data analytics techniques are employed in healthcare, each with its strengths and limitations. Predictive modeling, for example, uses historical data to predict future outcomes, such as the likelihood of a patient developing a specific disease. While powerful in identifying at-risk populations, predictive models can be limited by the quality and completeness of the input data. Machine learning algorithms, which can identify patterns in data without explicit programming, are increasingly used for tasks like image analysis in radiology and natural language processing of clinical notes.
However, the “black box” nature of some machine learning models can make it difficult to understand how they arrive at their conclusions. Finally, network analysis can reveal connections between different diseases or risk factors, providing a holistic view of patient health. However, network analysis requires careful consideration of confounding factors to ensure accurate interpretation.
Data Flow in a Healthcare Setting
Imagine a visual representation: Data originates from diverse sources – EHRs, medical devices, wearable sensors, claims databases, and public health registries. This data is then cleaned, standardized, and integrated into a central repository. From this repository, data is extracted and analyzed using various techniques (as described above). The results of this analysis – insights, predictions, and recommendations – are then fed back into the healthcare system, informing clinical decision-making, public health interventions, and the development of new treatments and technologies.
For example, insights from analyzing patient data might lead to changes in clinical protocols, while predictions of disease outbreaks might lead to targeted public health campaigns. This iterative process of data collection, analysis, and application continuously improves the quality and efficiency of healthcare.
The Growing Importance of Cybersecurity
Source: slideteam.net
So, I’ve been diving deep into the five dynamics shaping healthcare’s digital evolution – AI, telehealth, data security, interoperability, and patient engagement. It’s fascinating how these are all interconnected, and the implications are huge, especially considering recent news like Robert F. Kennedy Jr. clearing a key hurdle in his bid for HHS Secretary, as reported here: rfk jr clears key hurdle on path to hhs secretary.
His potential influence on these digital transformations will be something to watch closely as we consider the future of healthcare tech.
The digital transformation of healthcare has undeniably improved patient care and operational efficiency. However, this interconnectedness also exposes the industry to a growing number of cybersecurity threats. Protecting sensitive patient data and maintaining the integrity of healthcare systems is no longer a luxury; it’s a critical necessity. The consequences of a breach can be devastating, impacting patient safety, financial stability, and the reputation of the healthcare provider.The increasing reliance on electronic health records (EHRs), connected medical devices, and cloud-based services creates a vast attack surface for malicious actors.
These actors are constantly evolving their tactics, making it crucial for healthcare organizations to proactively adapt their security measures.
Major Cybersecurity Threats Facing Healthcare
The healthcare industry faces a unique set of cybersecurity threats due to the sensitive nature of the data it handles and the often-complex technological infrastructure it relies on. These threats can lead to significant financial losses, reputational damage, legal repercussions, and most importantly, harm to patients.
- Phishing and Social Engineering: These attacks exploit human vulnerabilities by tricking individuals into revealing sensitive information or granting access to systems. Sophisticated phishing emails mimicking legitimate sources are common, targeting employees with access to sensitive data.
- Malware and Ransomware: Malware can disrupt operations, steal data, and compromise system integrity. Ransomware attacks encrypt data and demand payment for its release, potentially halting critical services like patient care.
- Data Breaches: These incidents involve unauthorized access to and disclosure of protected health information (PHI), violating privacy regulations and potentially exposing patients to identity theft and financial fraud. The consequences can include hefty fines and lawsuits.
- Insider Threats: Malicious or negligent insiders, such as employees or contractors, can pose a significant risk by intentionally or unintentionally compromising data or systems. This can range from accidental data leaks to deliberate sabotage.
- Medical Device Vulnerabilities: Connected medical devices, while offering significant benefits, can be vulnerable to hacking, potentially compromising patient safety and data integrity. Attacks could manipulate device settings or even directly harm patients.
Strategies and Technologies for Protecting Patient Data, 5 dynamics shaping healthcares digital evolution
Healthcare providers are increasingly adopting a multi-layered approach to cybersecurity, combining preventative measures, detection systems, and incident response plans. This approach is essential to mitigate the risks associated with the various threats Artikeld above.
- Robust Access Control: Implementing strong password policies, multi-factor authentication, and role-based access control limits unauthorized access to sensitive systems and data.
- Data Encryption: Encrypting data both in transit and at rest protects it from unauthorized access even if a breach occurs. This is especially critical for PHI.
- Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDPS): These systems monitor network traffic and systems for suspicious activity, alerting administrators to potential threats and automatically blocking malicious attempts.
- Security Information and Event Management (SIEM): SIEM solutions collect and analyze security logs from various sources, providing a comprehensive view of security events and facilitating threat detection and response.
- Regular Security Audits and Penetration Testing: Proactive security assessments identify vulnerabilities and weaknesses before they can be exploited by malicious actors. Penetration testing simulates real-world attacks to evaluate the effectiveness of security controls.
Cybersecurity Awareness Training: A Hypothetical Case Study
Consider a hypothetical scenario: Sarah, a medical receptionist at a small clinic, receives an email appearing to be from the IT department, requesting her password to address a system issue. Unbeknownst to Sarah, this is a phishing attempt. Without adequate cybersecurity awareness training, Sarah might inadvertently provide her credentials, granting attackers access to the clinic’s network and patient data.However, if Sarah had received comprehensive training on recognizing phishing emails, she would have identified the suspicious email address, the lack of formal communication, and the request for sensitive information.
This training would have enabled her to report the email to the IT department instead of falling victim to the attack. This illustrates the critical role of cybersecurity awareness training in preventing breaches and protecting patient data. Regular, engaging training programs that simulate real-world scenarios are essential for building a strong security culture within healthcare organizations.
Patient Empowerment and Engagement
The digital revolution is fundamentally reshaping the patient experience, shifting the power dynamic from a solely provider-centric model to one that actively involves patients in their own healthcare journey. This empowerment is driven by increased access to information, personalized care options, and tools that facilitate proactive health management. The result is a more engaged and informed patient population, leading to improved health outcomes and a more efficient healthcare system.Patient portals and mobile health (mHealth) apps are at the forefront of this transformation.
These digital tools provide patients with unprecedented access to their medical records, appointment scheduling capabilities, secure messaging with their healthcare providers, and educational resources tailored to their specific conditions. This readily available information allows patients to become active participants in their care, fostering a stronger patient-provider relationship built on trust and shared decision-making.
The Role of Patient Portals and Mobile Health Apps
Patient portals offer a centralized hub for managing healthcare information. Patients can view test results, medication lists, and appointment summaries, eliminating the need for time-consuming phone calls or office visits. Many portals also include educational materials, allowing patients to learn more about their conditions and treatment options. mHealth apps extend this functionality to mobile devices, offering features such as medication reminders, symptom trackers, and even remote monitoring capabilities.
For example, a patient with diabetes might use an app to track their blood sugar levels, share the data with their doctor, and receive personalized feedback and adjustments to their treatment plan. Similarly, a patient recovering from surgery might use a physical therapy app to guide their rehabilitation exercises and monitor their progress. The convenience and accessibility of these tools significantly improve patient engagement and adherence to treatment plans.
Examples of Patient Empowerment in Practice
Several innovative approaches demonstrate how healthcare providers are using technology to empower patients. One example is the use of telehealth platforms for remote consultations. These platforms allow patients to connect with their doctors virtually, eliminating the need for travel and reducing healthcare costs. This is particularly beneficial for patients in rural areas or those with mobility limitations.
Another example is the use of wearable technology, such as smartwatches and fitness trackers, to monitor patients’ vital signs and activity levels. This data can provide valuable insights into a patient’s health and can be used to identify potential problems early on. For instance, a smartwatch might detect an irregular heartbeat, prompting the patient to seek medical attention.
Furthermore, personalized medicine initiatives are leveraging patient data and genetic information to tailor treatment plans to individual needs, leading to more effective and targeted interventions.
Comparing Approaches to Patient Education and Engagement
Various digital tools offer different approaches to patient education and engagement. While patient portals provide a comprehensive overview of medical information, mHealth apps offer personalized and targeted interventions. Educational videos and interactive simulations can enhance understanding of complex medical concepts. Gamification techniques, such as incorporating points and rewards systems into health tracking apps, can incentivize patient engagement and adherence to treatment plans.
The effectiveness of these tools depends on several factors, including the design of the interface, the accessibility of the information, and the level of support provided to patients. Studies have shown that user-friendly interfaces and personalized content significantly improve patient engagement and satisfaction. For instance, an app that simplifies complex medical jargon and uses clear visual aids will be more effective than one that relies on technical terminology and dense text.
Similarly, providing ongoing support and guidance through in-app messaging or telehealth consultations can help patients overcome challenges and stay motivated.
Outcome Summary
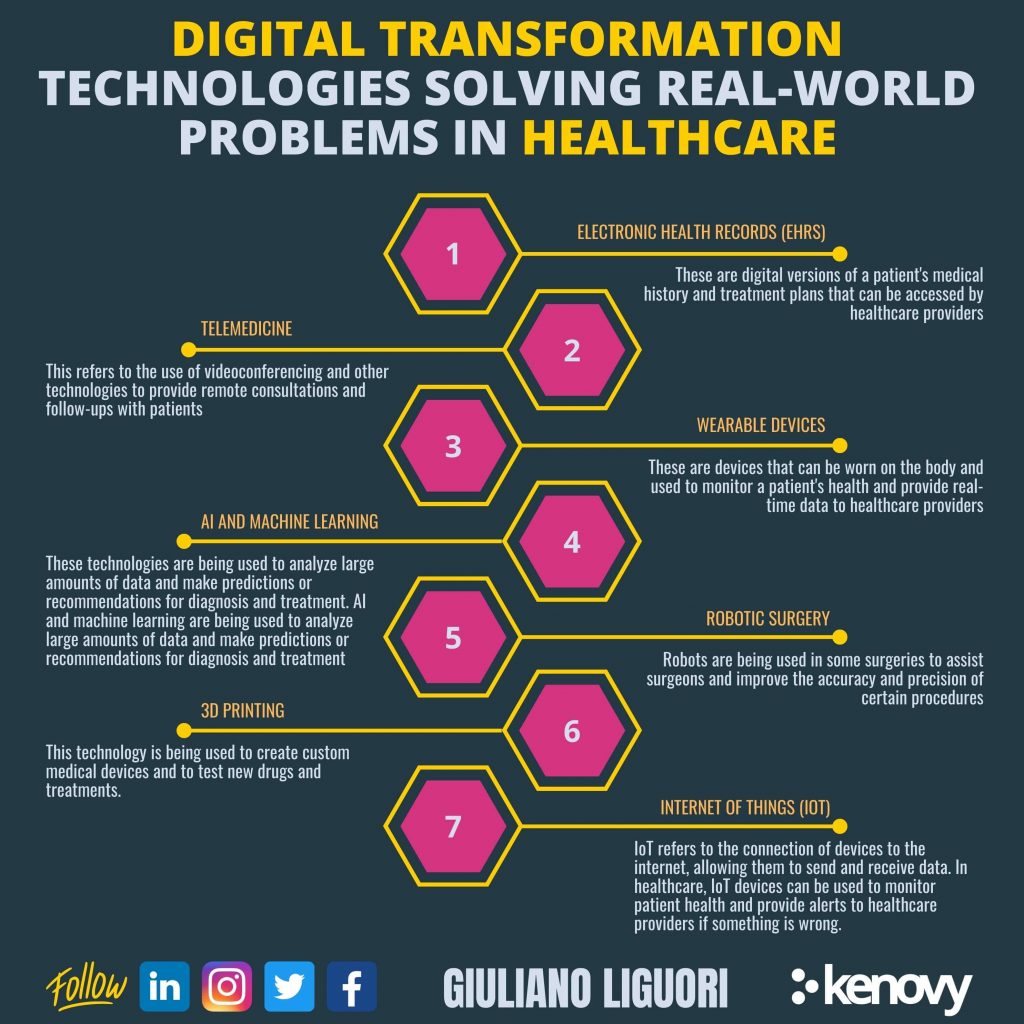
Source: kenovy.com
The digital transformation of healthcare is undeniably underway, driven by these five powerful dynamics. While challenges remain – from regulatory hurdles to ethical considerations – the potential benefits for patients and providers are immense. From improved access and personalized care to more efficient operations and proactive health management, the future of healthcare is undeniably digital. Staying informed about these trends is key to navigating this evolving landscape and embracing the opportunities it presents for a healthier future for all.
Key Questions Answered
What are the biggest risks associated with AI bias in healthcare?
AI bias can lead to inaccurate diagnoses, inappropriate treatment plans, and health disparities, particularly affecting marginalized communities. Algorithmic bias reflects and amplifies existing societal biases in the data used to train the AI.
How can patients protect their data in the age of digital healthcare?
Patients should choose reputable healthcare providers with strong cybersecurity practices, be cautious about sharing personal information online, use strong passwords, and regularly review their online accounts for suspicious activity. Understanding your rights regarding your health data is also crucial.
What are some examples of successful patient engagement strategies using technology?
Successful strategies include user-friendly patient portals, personalized health reminders via mobile apps, interactive educational materials, and opportunities for virtual consultations and remote monitoring.





