CMS Tougher Medicare Advantage Jon Blum, NAACOS
Cms tougher medicare advantage jon blum naacos – CMS Tougher Medicare Advantage: Jon Blum, NAACOS – the very phrase sparks debate! This post dives into the complex world of Medicare Advantage regulations, examining the influential role of Jon Blum at NAACOS and the ongoing tension between tighter CMS oversight and the needs of beneficiaries and providers. We’ll unpack the arguments, explore the potential consequences, and consider what the future might hold for this crucial aspect of healthcare.
NAACOS, the National Association of ACOs, represents a powerful voice in the Medicare Advantage landscape. Jon Blum, a key figure within NAACOS, has actively shaped the organization’s response to increasingly stringent CMS regulations. His public statements and advocacy efforts have played a significant role in the ongoing dialogue surrounding access to care, cost containment, and the overall health of the Medicare Advantage system.
We’ll analyze his position, comparing it to other industry leaders and exploring the nuances of this critical debate.
Jon Blum’s Role in NAACOS and Medicare Advantage
Jon Blum’s influence on the Medicare Advantage landscape is significant, primarily through his leadership role at the National Association of ACOs (NAACOS). His position allows him to shape the organization’s advocacy efforts and significantly impact the ongoing dialogue surrounding Medicare Advantage policy and regulations. Understanding his role within NAACOS and his public pronouncements provides crucial insight into the future trajectory of this vital component of the US healthcare system.Jon Blum serves as the President and CEO of NAACOS.
This position places him at the forefront of representing Accountable Care Organizations (ACOs), many of which participate in Medicare Advantage programs. His influence extends to shaping NAACOS’s policy positions, lobbying efforts, and public communications regarding Medicare Advantage. His expertise and experience are frequently sought out by policymakers and industry stakeholders.
Blum’s Public Statements on Medicare Advantage
Blum’s public statements consistently emphasize the value of Medicare Advantage in providing seniors with comprehensive and affordable healthcare options. He frequently highlights the positive outcomes achieved by ACOs participating in Medicare Advantage, such as improved quality of care and reduced costs. For example, he often cites data showing lower hospitalization rates and improved patient satisfaction among Medicare Advantage beneficiaries served by ACOs.
These statements are often made in the context of advocating for policies that support the continued growth and success of Medicare Advantage. He frequently uses his platform to counter negative narratives surrounding the program, emphasizing the positive contributions it makes to the healthcare system.
Blum’s Advocacy Efforts Concerning Medicare Advantage Regulations
NAACOS, under Blum’s leadership, actively engages in advocacy efforts related to Medicare Advantage regulations. They work to influence the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) rulemaking process, advocating for policies that are favorable to ACOs and their beneficiaries. This includes advocating for regulatory changes that promote value-based care, streamline administrative processes, and ensure adequate reimbursement rates. A specific example of Blum’s advocacy could involve lobbying efforts to prevent or modify regulations that he believes would unduly restrict ACOs’ ability to innovate and improve the quality of care.
The CMS tightening its grip on Medicare Advantage, as Jon Blum from NAACOS highlighted, presents real challenges for providers. But improving patient care isn’t just about regulations; it’s about connection. That’s why I found this article on enhanced human potential how customer service technology increases empathy so interesting – better tech can actually boost empathy, leading to better patient experiences, which is crucial when navigating these stricter CMS guidelines.
Ultimately, improving the human side of healthcare will help us navigate the complexities of the CMS and NAACOS’s concerns.
This often involves close collaboration with other healthcare industry groups and stakeholders.
Jon Blum’s recent NAACOS comments on CMS tightening Medicare Advantage regulations got me thinking about the bigger picture of primary care. It seems like a direct response to the increasing pressure on the system, and it makes the news that CMS launched a new primary care model ACO, which you can read about here: cms launches primary care medicare model aco , even more significant.
Ultimately, these changes, both the stricter regulations and the new ACO model, aim to improve care and cost-effectiveness within Medicare Advantage.
Comparison of Blum’s Stance with Other Industry Leaders
While specific comparisons require a detailed analysis of statements from multiple leaders, Blum generally aligns with other industry leaders in supporting the continued growth of Medicare Advantage. However, nuances exist in their approaches. Some might focus more on specific aspects of the program, such as risk adjustment methodologies or network adequacy, while Blum’s advocacy tends to be broader, emphasizing the overall value proposition of Medicare Advantage and the role of ACOs in delivering high-quality, cost-effective care.
Differences might also arise in the specific policy proposals each leader champions. The consensus, however, centers around the belief that Medicare Advantage plays a crucial role in providing healthcare coverage to seniors.
NAACOS’s Position on CMS Medicare Advantage Regulations

Source: medpagetoday.net
NAACOS, the National Association of ACOs, plays a significant role in shaping the landscape of Medicare Advantage. Their position on CMS regulations is multifaceted, advocating for policies that they believe will enhance the quality of care and expand access for beneficiaries while also ensuring the financial viability of Medicare Advantage plans. This often involves a delicate balancing act, navigating the competing interests of beneficiaries, providers, and the government.NAACOS’s official stance on current CMS regulations for Medicare Advantage generally centers on promoting responsible growth and innovation within the program.
They consistently argue against overly restrictive regulations that they believe stifle innovation and limit access to care for seniors. Their approach is typically one of engagement and collaboration, working with CMS to find solutions that address concerns while avoiding overly burdensome restrictions.
NAACOS Lobbying Efforts
NAACOS employs various lobbying strategies to influence Medicare Advantage regulations. This includes direct engagement with CMS officials, participation in rulemaking processes through formal comments and submissions, and advocacy through publications and public statements. For example, NAACOS actively participated in the debates surrounding the risk adjustment methodology, advocating for a system that accurately reflects the health status of beneficiaries without unduly penalizing plans that serve sicker populations.
They also frequently lobby for increased flexibility in plan design, arguing that this allows plans to better tailor benefits to the specific needs of their beneficiaries. Their efforts often involve providing data and analysis to support their claims and demonstrate the potential consequences of different regulatory approaches.
Key Arguments Used by NAACOS
NAACOS consistently emphasizes several key arguments in its advocacy efforts. They highlight the importance of Medicare Advantage in providing seniors with access to comprehensive and affordable healthcare. They argue that the program offers significant value for taxpayers and that burdensome regulations could jeopardize its success. Specifically, they contend that excessive scrutiny and restrictions on plan operations can lead to reduced provider participation, limit benefit offerings, and ultimately harm beneficiaries.
They often cite data demonstrating the positive outcomes achieved by Medicare Advantage plans, including higher patient satisfaction and improved health outcomes in certain areas.
Potential Consequences of Stricter CMS Regulations
NAACOS warns that overly stringent CMS regulations could have several detrimental consequences. One major concern is the potential for reduced competition among Medicare Advantage plans. If regulations become too complex or costly to comply with, smaller plans may be forced to exit the market, leaving beneficiaries with fewer choices. This could lead to higher premiums and reduced access to care, particularly in underserved areas.
Furthermore, stricter regulations could discourage innovation in plan design and benefit offerings, limiting the ability of plans to adapt to the evolving needs of the aging population. For example, increased scrutiny on risk adjustment could lead to plans reducing enrollment of higher-risk beneficiaries, potentially exacerbating health disparities. This could also impact the financial stability of plans, potentially leading to higher premiums or reduced benefits.
Impact of “Tougher” CMS Regulations on Medicare Advantage Plans
The recent tightening of CMS regulations on Medicare Advantage (MA) plans has sent ripples throughout the healthcare industry. These changes, driven by concerns about potential overpayments and inadequate care, are poised to significantly impact MA plans, providers, and beneficiaries alike. The extent of these impacts remains to be seen, but the potential consequences are substantial and far-reaching.
Effects on Medicare Advantage Plan Enrollment
Increased scrutiny from CMS could lead to a decrease in MA plan enrollment. If plans are forced to tighten their benefits or increase premiums to meet stricter regulatory requirements, some beneficiaries might find themselves opting for Original Medicare instead. This shift could be particularly pronounced among those with lower incomes or those who are less familiar with the complexities of navigating the healthcare system.
The potential for increased administrative burdens and audits could also deter some plans from actively marketing their services, further impacting enrollment. For example, if a plan is penalized for coding errors, they may be less inclined to actively recruit new members.
Financial Implications for Medicare Advantage Providers
Stricter regulations translate directly into increased costs for MA providers. Compliance with more stringent documentation requirements, intensified audits, and potential penalties for non-compliance all place a strain on financial resources. This could lead to reduced profitability for some plans, potentially forcing mergers, acquisitions, or even plan closures in the long run. The increased administrative burden also demands additional staffing and technology investments, further impacting the bottom line.
A real-world example could be a plan facing substantial fines due to inaccurate risk adjustment coding, significantly affecting their operating budget.
Impact on Beneficiary Access to Care
While the goal of stricter regulations is to improve the quality of care, the unintended consequence could be reduced access to care for some beneficiaries. If plans become less profitable due to increased regulatory burdens, they may reduce their provider networks, leading to longer wait times for appointments and reduced choice of specialists. Furthermore, plans might become more selective in accepting new enrollees, potentially excluding those with complex health needs.
The CMS’s tougher stance on Medicare Advantage, as highlighted by Jon Blum at NAACOS, raises concerns about access to crucial preventative care. This is especially relevant considering advancements like the Google iCAD AI mammography expansion , which could improve early detection rates. Ultimately, balancing cost-containment with access to innovative technologies like AI-powered diagnostics remains a key challenge for the CMS and its ongoing negotiations with providers.
This could disproportionately affect vulnerable populations, creating significant disparities in access to quality healthcare. For instance, a plan might limit its network of specialists to reduce costs, making it harder for beneficiaries with specialized needs to find appropriate care.
Stakeholder Impact Comparison
| Stakeholder | Benefits of Stricter Regulations | Drawbacks of Stricter Regulations |
|---|---|---|
| Beneficiaries | Potentially higher quality of care, reduced fraud and abuse. | Reduced choice of plans, potential increase in premiums, decreased access to care in some cases. |
| Providers | Improved accuracy in coding and billing practices, potentially leading to more efficient operations in the long run. | Increased administrative burden, reduced profitability, potential for penalties and fines. |
| Government | Reduced Medicare spending, improved program integrity, increased accountability for MA plans. | Increased administrative costs associated with oversight and enforcement, potential negative impact on beneficiary access to care. |
Specific Examples of “Tougher” CMS Regulations

Source: ascendintegrated.com
The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) has implemented several recent regulations aimed at increasing oversight and accountability within the Medicare Advantage (MA) program. These changes reflect a growing concern about potential overpayments, inappropriate coding practices, and variations in quality of care across different MA plans. The rationale behind these stricter regulations is multifaceted, focusing on protecting beneficiaries, ensuring fair payment to plans, and promoting transparency and efficiency within the system.
Changes to Risk Adjustment Methodology
CMS has made significant adjustments to the risk adjustment methodology used to determine payments to MA plans. This methodology calculates payments based on the health status of the enrolled beneficiaries. The changes aim to reduce potential gaming of the system, where plans might exaggerate beneficiary health conditions to receive higher payments. These revisions include more precise diagnostic coding requirements, enhanced data validation techniques, and adjustments to the model itself to better reflect actual healthcare costs.
Key changes include stricter auditing of diagnosis codes submitted by plans, implementation of new statistical models to detect outliers and anomalies, and increased penalties for inaccurate reporting. The impact on plan operations includes a need for more robust data management systems, stricter internal coding protocols, and potentially lower payments for plans that previously benefited from less accurate risk adjustment.
Increased Scrutiny of Star Ratings
The Medicare Star Ratings system plays a significant role in consumer choice and plan performance. CMS has increased the rigor of the Star Ratings calculation, focusing on the accuracy and validity of the data used in the process. This includes stricter standards for data collection, more robust auditing procedures, and increased penalties for plans with inaccurate reporting. The rationale is to provide beneficiaries with more reliable information to compare plans and to incentivize MA plans to focus on delivering higher quality care.
Key changes include the addition of new quality measures, increased weight given to certain measures reflecting patient experience, and stricter penalties for plans with low star ratings. The impact on plan operations includes a greater emphasis on data integrity, improved quality control procedures, and a need to prioritize patient satisfaction and health outcomes. For example, a plan might invest more in patient education programs or implement new care coordination models to improve their ratings.
Enhanced Audits and Enforcement, Cms tougher medicare advantage jon blum naacos
CMS has significantly increased the frequency and intensity of audits on MA plans. These audits examine a wide range of plan activities, including coding practices, beneficiary enrollment processes, and compliance with various regulations. The rationale is to deter fraudulent activities and ensure plans are operating within the guidelines. The increased scrutiny aims to reduce overpayments and ensure beneficiaries are receiving appropriate care.
Key changes include more frequent audits, more rigorous review of medical records, and increased penalties for non-compliance. The impact on plan operations includes increased administrative burden, a need for more robust compliance programs, and potentially significant financial penalties for plans found to be non-compliant. This increased oversight might lead to a greater focus on internal controls and compliance training within MA organizations.
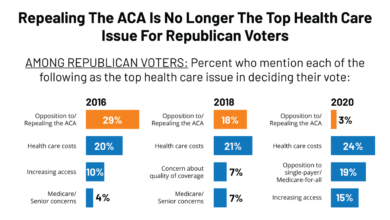
Public Perception and Media Coverage of Medicare Advantage
Medicare Advantage (MA) plans, while offering supplemental coverage beyond traditional Medicare, often face a complex public perception shaped significantly by media portrayals. Understanding this dynamic is crucial for both the plans themselves and policymakers aiming to ensure a robust and accessible healthcare system for seniors.Public perception of Medicare Advantage is often mixed, ranging from positive experiences reported by some beneficiaries to significant concerns highlighted by others and amplified by the media.
Many seniors appreciate the added benefits, such as vision, dental, and hearing coverage, along with lower out-of-pocket costs in some cases. However, a significant portion harbors skepticism due to concerns about network restrictions, limited provider choices, and potentially confusing plan structures.
Media Coverage and Concerns about Medicare Advantage
Media outlets frequently report on investigations and audits revealing issues within the MA system. These reports often focus on concerns regarding the financial incentives driving enrollment practices, potential conflicts of interest, and accusations of misleading marketing. For example, news articles have highlighted instances of plans actively discouraging beneficiaries from switching to more affordable options or delaying necessary care to maximize profits.
Other reports focus on denials of coverage for medically necessary services, leading to increased financial burdens and health complications for beneficiaries. These reports, often appearing in reputable publications and news broadcasts, significantly influence public opinion.
Impact of Media Portrayals on Public Opinion
The cumulative effect of negative media coverage can create a climate of distrust and apprehension surrounding Medicare Advantage. Even if only a small percentage of plans engage in questionable practices, the negative stories gain traction, overshadowing the positive experiences of many satisfied beneficiaries. This creates a narrative that paints the entire system with a broad brush, leading to widespread skepticism.
Furthermore, the complexity of MA plans themselves can make it difficult for seniors and their families to navigate the system and make informed decisions, exacerbating the negative impact of negative press.
Hypothetical Scenario Illustrating Negative Media Impact
Imagine a hypothetical scenario where a major news network publishes an investigative report detailing how a prominent Medicare Advantage plan systematically denied coverage for a specific, widely used cancer treatment, leading to several patient deaths. The report meticulously details internal emails and financial documents that show a conscious effort to limit payouts, prioritizing profits over patient care. Following the report’s airing, public outcry is immediate and intense.
The plan in question experiences a significant drop in enrollment as potential beneficiaries, swayed by the negative publicity, opt for traditional Medicare or alternative MA plans. The company’s stock price plummets, and investigations by state and federal authorities are launched. This scenario illustrates how even a single negative story, if credible and well-publicized, can have devastating consequences for a Medicare Advantage plan’s reputation and financial stability.
Potential Future Changes in Medicare Advantage Regulations: Cms Tougher Medicare Advantage Jon Blum Naacos
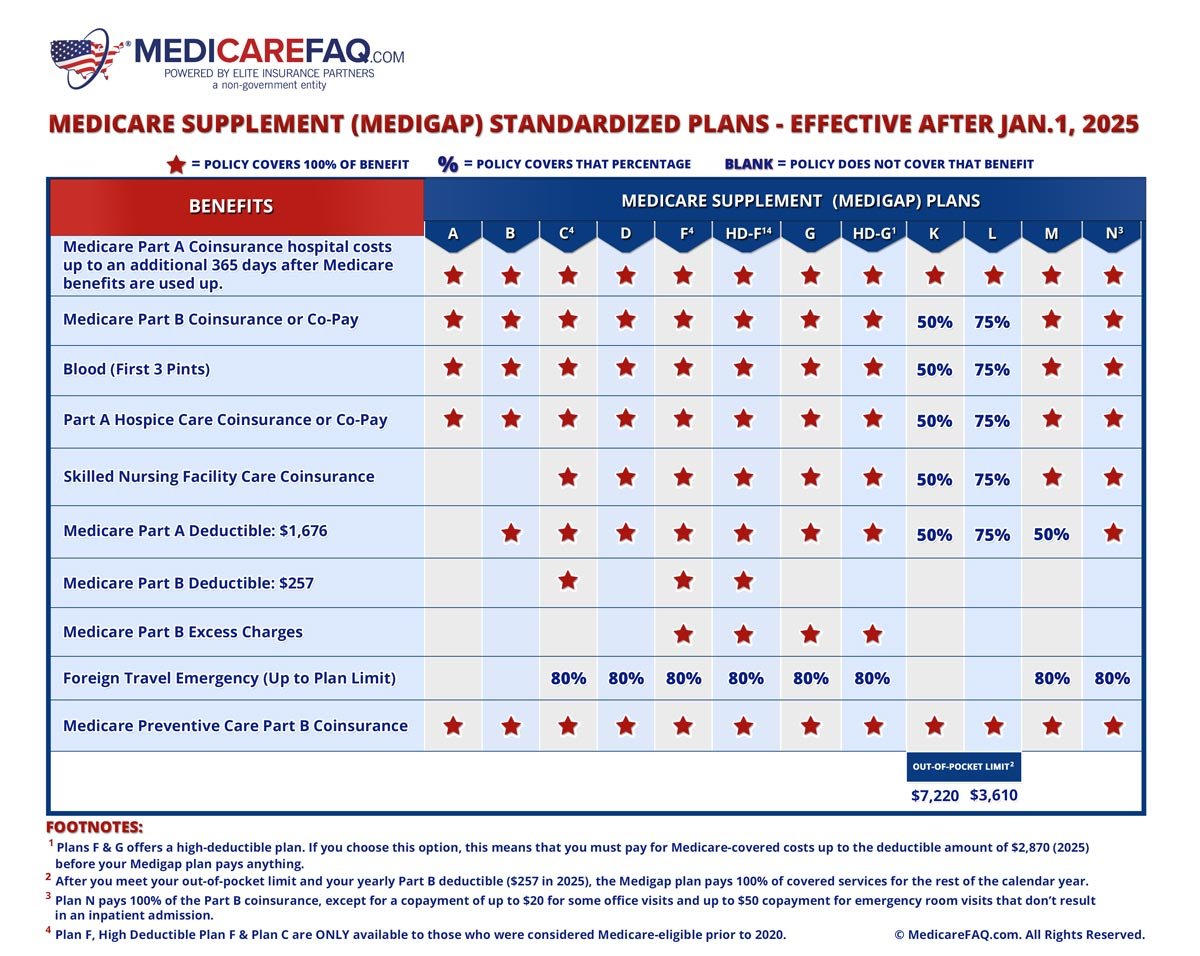
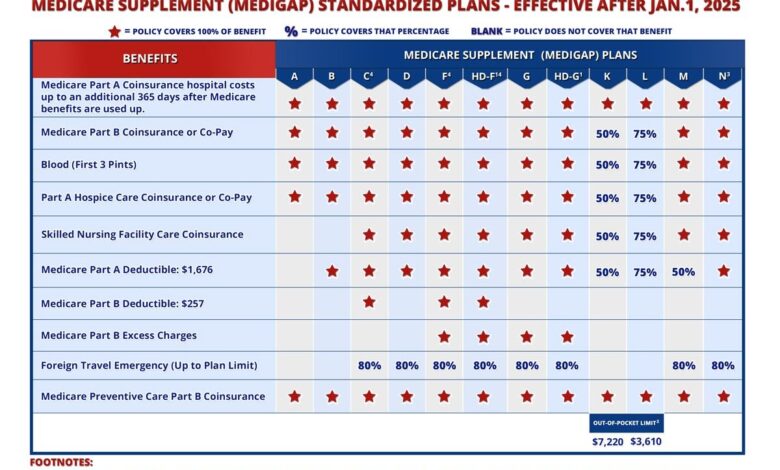
Source: medicarefaq.com
The future of Medicare Advantage (MA) hinges on several converging factors: the ongoing debate about cost containment, the persistent need to improve quality of care, and the evolving technological landscape of healthcare delivery. Current trends suggest significant regulatory shifts are likely in the coming years, impacting both MA plans and beneficiaries.
Several key areas are ripe for regulatory change. The increasing scrutiny of MA plan marketing practices, driven by concerns about misleading advertising and enrollment processes, will likely lead to stricter oversight and enforcement. Furthermore, the persistent disparity in quality of care between MA plans and traditional Medicare is likely to prompt regulators to implement more robust quality metrics and performance-based payment models.
Finally, the potential for increased integration of technology, such as telehealth and remote patient monitoring, within MA plans will necessitate the development of new regulatory frameworks to ensure patient safety and data privacy.
Increased Transparency and Accountability in Marketing Practices
The CMS is likely to implement stricter rules regarding MA plan marketing materials and enrollment processes. This could include more stringent requirements for transparency in plan benefits, cost-sharing, and network adequacy. Increased oversight and penalties for deceptive marketing practices are also anticipated. For example, we might see regulations requiring plans to provide standardized comparison tools that make it easier for beneficiaries to compare plans side-by-side, based on objective metrics.
This increased transparency should help beneficiaries make more informed choices and reduce confusion around plan options.
Enhanced Quality Measurement and Performance-Based Payment
Future regulations will likely place greater emphasis on quality metrics and performance-based payment models. This means MA plans will be increasingly held accountable for the quality of care they provide, with financial incentives tied to achieving specific quality targets. For instance, we could see a shift towards value-based payment models that reward plans for improving patient outcomes and reducing healthcare costs.
This could involve a more nuanced scoring system that accounts for factors beyond simply the number of patients seen or procedures performed, but instead weighs factors like patient satisfaction and preventative care adherence. This approach mirrors the broader shift towards value-based care in the healthcare industry as a whole.
Adaptation of Regulatory Frameworks to Technological Advancements
The integration of telehealth and remote patient monitoring technologies into MA plans presents both opportunities and challenges. Future regulations will need to address issues such as data security, patient privacy, and the appropriate use of these technologies. For example, regulations may need to define standards for telehealth platforms used by MA plans, ensuring interoperability and data security. They might also need to establish guidelines for remote patient monitoring programs, ensuring that they are clinically appropriate and do not compromise patient safety.
This proactive regulatory approach will be crucial to harness the potential of these technologies while mitigating risks.
A Hypothetical Policy Proposal: Strengthening Medicare Advantage Through Value-Based Payment and Consumer Protection
This proposal aims to improve the MA system by enhancing value-based payment models and strengthening consumer protections. It would implement a tiered payment system rewarding plans that consistently demonstrate high quality of care, as measured by a comprehensive set of metrics including patient experience, preventative care adherence, and chronic disease management outcomes. Simultaneously, it would increase penalties for plans that fail to meet quality targets or engage in deceptive marketing practices.
The increased financial incentives for high-quality care, coupled with strong penalties for poor performance and unethical practices, would create a more robust and equitable MA system. This model would incentivize plans to prioritize patient well-being while ensuring cost-effectiveness. Independent audits of plan performance would be regularly conducted to ensure accountability and transparency. This multifaceted approach would address both cost and quality concerns, promoting a more efficient and effective Medicare Advantage system.
Ending Remarks
The debate surrounding stricter CMS regulations on Medicare Advantage is far from over. The interplay between NAACOS, Jon Blum’s influence, and the CMS’s regulatory power will continue to shape the future of this vital program. Understanding the perspectives of all stakeholders – beneficiaries, providers, and the government – is crucial for navigating this complex landscape and ensuring that Medicare Advantage continues to provide accessible and high-quality care for millions of Americans.
The coming years will undoubtedly bring further changes, making ongoing vigilance and informed discussion essential.
General Inquiries
What specific concerns do beneficiaries have about stricter Medicare Advantage regulations?
Beneficiaries worry about reduced choice of plans, limited access to preferred doctors, and potential increases in out-of-pocket costs.
How might stricter regulations impact innovation within the Medicare Advantage system?
Increased scrutiny could stifle innovation by making it more difficult for plans to implement new programs and technologies.
What role does public opinion play in shaping Medicare Advantage regulations?
Public perception, often influenced by media coverage, significantly impacts political pressure on policymakers to adjust regulations.
Are there any examples of successful collaborations between CMS and Medicare Advantage plans?
Yes, several successful initiatives demonstrate how collaboration can improve care quality and cost efficiency. These often involve data sharing and performance-based incentives.