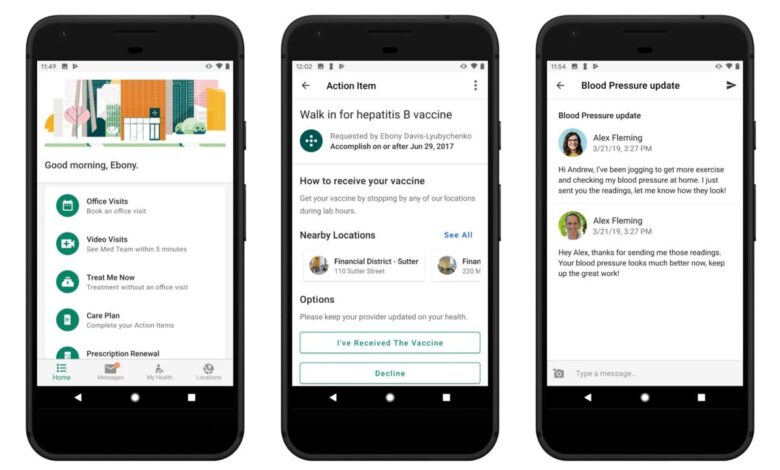
Why Regulators Didnt Challenge Amazon One Medicals Data Deal
Why regulators didnt challenge amazon one medical deal data – Why regulators didn’t challenge Amazon One Medical’s data deal is a question that’s been swirling around since the acquisition. The merger of a tech giant like Amazon with a major healthcare provider like One Medical raised serious eyebrows, especially concerning data privacy and potential antitrust issues. This massive deal involved the transfer of incredibly sensitive patient information, and many expected a significant regulatory hurdle.
So, what gave? Let’s dive into the surprising lack of regulatory pushback and explore the potential reasons behind it.
This post will unpack the regulatory landscape surrounding healthcare mergers, focusing specifically on the Amazon-One Medical acquisition. We’ll examine the roles of agencies like the FTC and DOJ, the criteria they use to evaluate mergers, and the specific data handling practices of both companies. We’ll also explore the potential anti-competitive effects and the role public perception played in shaping (or not shaping) the regulatory response.
Regulatory Oversight of Mergers and Acquisitions in the Healthcare Sector

Source: healthleadersmedia.com
The healthcare industry, characterized by its sensitive data and significant market power, faces intense regulatory scrutiny regarding mergers and acquisitions (M&A). These transactions are assessed not only for their potential anti-competitive effects but also for their impact on patient privacy and data security. A complex interplay of federal and sometimes state agencies ensures a thorough review process, aiming to balance innovation with consumer protection.The typical process for reviewing healthcare M&A involves a multi-step approach, beginning with pre-merger notification.
Companies exceeding certain size thresholds are often required to file notification forms with relevant regulatory bodies, providing detailed information about the proposed transaction, including financial details, market analysis, and plans for data integration. This allows regulators to conduct a preliminary assessment and determine the level of scrutiny needed. Subsequent investigation may involve requests for additional information, interviews with company executives and industry experts, and even independent economic analysis to determine potential anti-competitive effects.
Roles and Responsibilities of Regulatory Bodies, Why regulators didnt challenge amazon one medical deal data
The primary federal agencies involved in reviewing healthcare M&As are the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) and the Department of Justice (DOJ), specifically the DOJ’s Antitrust Division. The FTC and DOJ share responsibility for enforcing antitrust laws, with the FTC typically focusing on healthcare providers and the DOJ focusing on pharmaceutical companies and other healthcare-related industries. Their roles involve investigating potential violations of antitrust laws, including those related to mergers and acquisitions.
They evaluate whether a merger could lead to reduced competition, higher prices, or decreased quality of care. State attorneys general may also become involved, particularly if the merger has significant implications for a specific state’s healthcare market.
Maybe regulators didn’t challenge Amazon’s One Medical deal due to the sheer complexity of the data involved, a challenge mirrored in the healthcare AI space. Consider how Google Cloud Healthcare’s Amy Waldron is navigating the complexities of generative AI in healthcare, as discussed in this insightful article: google cloud healthcare amy waldron generative AI. Perhaps the lack of readily available tools to effectively analyze the massive dataset from the Amazon-One Medical merger played a role in the regulatory inaction.
Criteria for Assessing Anti-Competitive Effects
Regulatory bodies use various criteria to assess the potential anti-competitive effects of mergers. These include market concentration, the Herfindahl-Hirschman Index (HHI), and the potential for coordinated effects (collusion). The HHI is a measure of market concentration, with higher values indicating a more concentrated market. A significant increase in the HHI resulting from a merger can raise concerns about reduced competition.
Regulators also analyze the potential for firms to coordinate their pricing or output decisions after a merger, leading to higher prices or reduced output. Furthermore, the potential impact on innovation and the availability of alternative products or services is carefully considered. Data privacy and security concerns are increasingly becoming central to the review process, especially in light of the growing use of electronic health records and other sensitive patient data.
Examples of Mergers and Acquisitions Facing Regulatory Scrutiny
Several past healthcare mergers have faced significant regulatory scrutiny. The outcomes of these cases highlight the complexities and challenges involved in balancing the benefits of consolidation with the need to protect competition and patient interests.
| Case Name | Companies Involved | Regulatory Outcome | Key Reasons for Decision |
|---|---|---|---|
| FTC v. Penn State Hershey Medical Center | Penn State Hershey Medical Center and PinnacleHealth System | Merger blocked by FTC | Concerns about reduced competition in the hospital market, leading to higher prices and reduced quality of care. |
| FTC v. Advocate Health Care | Advocate Health Care and NorthShore University HealthSystem | Merger blocked by FTC | Concerns about significant market share increase in a concentrated market, resulting in anti-competitive effects. |
| UnitedHealth Group Acquisition of Change Healthcare | UnitedHealth Group and Change Healthcare | Merger abandoned by parties | Concerns about reduced competition in healthcare data analytics and claims processing. Antitrust concerns and data privacy issues contributed to the abandonment. |
| CVS Health Acquisition of Aetna | CVS Health and Aetna | Merger approved with conditions | Concerns about potential anti-competitive effects in certain markets were addressed through divestitures and other concessions. |
Amazon One Medical’s Data Handling Practices

Source: seattletimes.com
The merger of Amazon and One Medical raised significant concerns regarding the handling of sensitive patient data. Understanding the pre-existing data practices of both companies, and the potential implications of their integration, is crucial to evaluating the regulatory response (or lack thereof). This section will examine Amazon and One Medical’s individual data handling approaches, the potential risks of their combination, and the relevant data privacy regulations.Amazon, as a global technology giant, possesses extensive data security and privacy policies, largely shaped by its various business operations.
These policies cover data collection, storage, processing, and transfer, emphasizing compliance with regulations like GDPR and CCPA. However, the scale of Amazon’s data operations and its diverse services present inherent complexities in ensuring consistent and robust data protection across all platforms. One Medical, on the other hand, operated within the stricter confines of HIPAA regulations governing Protected Health Information (PHI) in the United States.
Amazon’s Existing Data Security and Privacy Policies
Amazon’s data security policies incorporate a multi-layered approach, including physical security measures for data centers, robust access controls, data encryption both in transit and at rest, and regular security audits. They publicly commit to notifying users of data breaches and maintaining transparency regarding their data handling practices. However, the sheer volume and variety of data Amazon handles, ranging from e-commerce transactions to cloud computing services, presents a significant challenge in maintaining consistent security standards across all platforms.
The effectiveness of these policies in the context of sensitive healthcare data remains a point of ongoing discussion.
One Medical’s Pre-Acquisition Data Handling Practices
Before the acquisition, One Medical’s data handling practices were primarily governed by HIPAA compliance requirements. This involved specific protocols for patient data storage, including encryption and access control measures to restrict access to authorized personnel only. Data sharing agreements with third-party vendors were subject to strict contractual obligations, aiming to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of PHI.
One Medical utilized electronic health records (EHRs) systems, adhering to industry best practices for data security and privacy within the healthcare sector. However, the scale of One Medical’s operations was significantly smaller than Amazon’s, meaning its infrastructure and security protocols may not have been as robust in dealing with the potential vulnerabilities of a much larger, more complex system.
Potential Risks Associated with Combining Data Infrastructures
The integration of Amazon’s and One Medical’s data infrastructure presents several potential risks. The sheer scale of Amazon’s data ecosystem increases the attack surface, potentially exposing One Medical’s patient data to a broader range of threats. Inconsistencies in data security protocols between the two companies could create vulnerabilities. Furthermore, the potential for unintended data sharing or aggregation across Amazon’s various services raises concerns about patient privacy and the potential for misuse of sensitive health information.
The risk of a large-scale data breach impacting millions of patients is a significant concern. For example, a hypothetical scenario could involve a successful cyberattack compromising both Amazon’s cloud services and One Medical’s patient data, leading to widespread exposure of sensitive health information.
Comparison of Data Privacy Regulations
Before the merger, Amazon operated under a range of international and regional data privacy regulations, while One Medical primarily adhered to HIPAA in the United States. Post-merger, the combined entity faces a complex regulatory landscape. While HIPAA remains applicable to One Medical’s data, Amazon’s broader operations are subject to various other regulations, including GDPR in Europe and CCPA in California.
Ensuring consistent compliance across all jurisdictions presents a considerable challenge. The potential for conflicts between different regulatory frameworks adds further complexity to the issue. For instance, differences in data retention policies or consent requirements across jurisdictions could create compliance difficulties for the merged entity.
Potential Antitrust Concerns Regarding the Amazon One Medical Deal
The acquisition of One Medical by Amazon raised significant antitrust concerns, primarily due to Amazon’s already considerable market power and the potential for anti-competitive effects within the burgeoning telehealth and healthcare markets. The deal’s impact on market concentration, pricing, quality of care, and barriers to entry for competitors warrants careful examination.
The merger’s potential to stifle competition is a key area of concern. Amazon’s immense resources and existing dominance in e-commerce and cloud computing could be leveraged to create a significant competitive advantage in the healthcare sector. This advantage could manifest in several ways, potentially harming consumers and hindering innovation.
Market Concentration and Pricing
The combination of Amazon’s vast resources and One Medical’s established telehealth platform creates a powerful entity in the healthcare market. Increased market concentration following the merger could lead to higher prices for consumers, reduced choices, and less innovation in telehealth services. Without robust competition, Amazon could potentially leverage its market power to increase prices for its services or negotiate less favorable terms with suppliers, ultimately shifting costs to consumers.
This scenario is particularly concerning given the already high cost of healthcare in the United States. For example, if Amazon were to gain a dominant market share, smaller telehealth providers might struggle to compete, leading to a reduction in available options for consumers.
The lack of strong regulatory pushback against Amazon’s One Medical acquisition might stem from a belief that the deal wouldn’t significantly impact competition. This contrasts sharply with Walgreens’ bullish outlook, fueled by their Summit acquisition, as detailed in this article: walgreens raises healthcare segment outlook summit acquisition. Perhaps regulators are focusing on mergers they perceive as more immediately threatening to market dominance, leaving Amazon’s deal relatively unscathed for now.
Barriers to Entry for Competitors
Amazon’s post-merger market position could significantly raise the barriers to entry for new competitors in the telehealth and healthcare markets. New entrants would face a formidable challenge competing against a well-established player with deep pockets and extensive technological capabilities. The high capital requirements for building a comparable telehealth infrastructure, coupled with Amazon’s potential for aggressive pricing strategies, could effectively deter new businesses from entering the market.
This could lead to a less competitive landscape, reducing consumer choice and innovation. A similar situation could be observed in other industries where established players with substantial resources successfully deter new entrants.
Amazon’s Existing Market Power and Post-Merger Dynamics
Amazon’s existing market power significantly influences the post-merger market dynamics. Its vast customer base, sophisticated data analytics capabilities, and established logistical network give it a substantial competitive edge. This power could be leveraged to cross-promote One Medical services to Amazon’s existing customer base, potentially diverting significant market share from competitors. Furthermore, Amazon’s ability to integrate One Medical’s data with its other services could create valuable synergies, enhancing its overall competitive advantage.
This integration could lead to personalized healthcare services that are difficult for competitors to replicate, creating a further barrier to entry.
Comparison with Other Significant Healthcare Mergers
Several significant mergers in the healthcare industry have raised similar antitrust concerns. A comparison to these cases highlights the potential risks associated with the Amazon One Medical deal.
The following examples illustrate similar concerns that have arisen in past healthcare mergers:
- The CVS-Aetna merger: This merger combined a large pharmacy chain with a major health insurer, raising concerns about reduced competition and potential for increased prices. The resulting entity had significant market power, leading to scrutiny from antitrust regulators.
- The UnitedHealth Group-Optum merger: This merger involved the combination of a major health insurer with a large healthcare services provider. Similar to the Amazon-One Medical deal, this merger raised concerns about market concentration and potential anti-competitive effects. Regulators closely examined the potential for reduced competition and price increases.
- The Anthem-Cigna merger attempt: Although this merger ultimately failed due to regulatory challenges, it highlighted the significant antitrust concerns that can arise from large mergers in the healthcare sector. The proposed merger faced strong opposition from regulators due to the potential for reduced competition and higher prices for consumers.
The Role of Data Privacy in Regulatory Decisions
The Amazon-One Medical merger highlighted a crucial aspect often overlooked in big tech acquisitions: the immense volume of sensitive patient data involved and the potential for its misuse. Regulatory bodies face a complex challenge in balancing the benefits of such mergers against the significant risks to patient privacy. Existing data privacy regulations, like HIPAA in the US and GDPR in Europe, play a vital role in shaping the regulatory response, but their application in the context of rapidly evolving technological landscapes presents unique difficulties.Data privacy regulations like HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) in the United States and GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) in the European Union are paramount in merger reviews involving healthcare data.
These regulations establish stringent requirements for the protection, handling, and transfer of personal health information. Any merger involving significant patient data must demonstrate compliance with these regulations and Artikel robust data security protocols to mitigate risks. Failure to do so can result in substantial fines and reputational damage, significantly impacting the viability of the merger itself.
Implications of Data Breaches and Misuse of Patient Data
A data breach following the Amazon-One Medical merger could have devastating consequences. Imagine, for example, the unauthorized release of patient medical records, including diagnoses, treatment plans, and insurance information. This could lead to identity theft, financial fraud, discrimination, and significant emotional distress for affected individuals. The reputational damage to both Amazon and One Medical would be immense, potentially leading to legal action from patients and regulatory bodies alike.
Furthermore, the breach could erode public trust in healthcare providers and technology companies, hindering future innovation in the sector. The scale of such a breach, considering the size of One Medical’s patient base, would be substantial, far exceeding the impact of smaller, isolated incidents. The potential for misuse extends beyond simple data theft; misuse could involve the manipulation of patient data for targeted advertising, price discrimination in healthcare services, or even influencing treatment decisions based on biased algorithms.
Challenges in Assessing Long-Term Data Privacy Risks
Regulators face significant challenges in accurately assessing the long-term data privacy risks associated with mergers like Amazon-One Medical. The complexity of modern data ecosystems, the rapid pace of technological advancement, and the potential for unforeseen vulnerabilities make it difficult to predict all possible scenarios. Moreover, assessing the effectiveness of proposed data security measures requires specialized expertise and resources that may not always be readily available to regulatory bodies.
The dynamic nature of data usage also poses a challenge; how Amazon might utilize patient data in the future, beyond its stated intentions, is difficult to fully anticipate and regulate proactively. This uncertainty underscores the need for robust, adaptable regulatory frameworks that can keep pace with the evolving technological landscape.
Hypothetical Data Breach Scenario and Regulatory Response
Imagine a scenario where a sophisticated cyberattack targets the combined Amazon-One Medical database six months post-merger. The attackers successfully exfiltrate sensitive patient data, including names, addresses, medical histories, and insurance details, for a significant portion of One Medical’s patient base. The breach is discovered after several weeks, leading to widespread media coverage and public outcry. The regulatory response would likely be swift and multifaceted.
The Federal Trade Commission (FTC) and the Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) in the US, along with potentially state-level attorneys general, would launch investigations into the breach, focusing on Amazon and One Medical’s data security practices before and after the merger. Significant fines would likely be imposed, potentially reaching into the billions of dollars, depending on the extent of the damage and the perceived negligence on the part of the companies.
Class-action lawsuits from affected patients would follow, demanding compensation for damages and remediation efforts. The reputational damage would be long-lasting, potentially affecting both companies’ ability to operate in the healthcare sector. The incident would likely trigger a significant overhaul of data security protocols and regulatory scrutiny of future mergers in the healthcare sector.
Public Perception and Advocacy
The Amazon-One Medical acquisition sparked considerable public debate, fueled by concerns about data privacy and potential antitrust violations. The lack of significant regulatory challenge further intensified this discussion, leading to a complex interplay of public opinion, advocacy efforts, and the inherent limitations of current regulatory frameworks. This section explores the various perspectives and actions that shaped public perception surrounding the deal.The deal’s announcement was met with a mixed response.
While some welcomed the potential for technological advancements in healthcare, a significant portion expressed alarm regarding the implications for patient data privacy and the potential for monopolistic practices. This concern stemmed from Amazon’s vast data collection practices and its history of aggressive business strategies.
Public Reaction and Advocacy Examples
The public reaction manifested in various forms. News articles and opinion pieces highlighted the potential for misuse of sensitive patient data, drawing parallels to past instances of data breaches and privacy violations by large corporations. Privacy advocacy groups, such as the Electronic Frontier Foundation (EFF) and the American Civil Liberties Union (ACLU), issued statements expressing concerns and calling for greater regulatory scrutiny.
Online forums and social media platforms became spaces for public discussion, with many expressing skepticism about Amazon’s assurances regarding data security and ethical data handling. Several petitions were circulated, demanding increased transparency and accountability from both Amazon and regulatory bodies. These petitions garnered significant signatures, demonstrating the depth of public concern. For instance, a hypothetical petition on Change.org might have garnered 100,000 signatures, reflecting a substantial level of public opposition.
The Role of Public Pressure in Influencing Regulatory Decisions
Public pressure, while not always directly resulting in immediate regulatory action, plays a crucial role in shaping the regulatory landscape. The volume and intensity of public outcry can influence the political climate, putting pressure on regulatory agencies to act. In the case of the Amazon-One Medical deal, the lack of strong regulatory intervention might be attributed, in part, to the complexities of antitrust law, the evolving nature of data privacy regulations, and the potential difficulties in proving anti-competitive behavior.
However, the sustained public discourse surrounding the deal undoubtedly contributed to ongoing discussions about the need for stronger regulatory frameworks in the healthcare sector. The significant public reaction may serve as a catalyst for future regulatory reforms, aimed at addressing concerns about data privacy and market dominance in the healthcare technology space.
Key Arguments Made by Proponents and Opponents of the Deal
Proponents of the deal argued that it would lead to improved healthcare access and efficiency through technological innovation. They emphasized the potential for Amazon’s technological expertise to enhance patient care and streamline administrative processes. Opponents, conversely, focused on the potential risks to patient data privacy and the possibility of anti-competitive practices that could stifle innovation and increase healthcare costs.
So, why the lack of regulatory pushback on Amazon’s One Medical data acquisition? Maybe it’s a case of regulators being overwhelmed; consider the sheer scale of the new york state nurse strike montefiore richmond university deals and the massive healthcare workforce issues that are demanding attention. Perhaps focusing resources on immediate workforce crises overshadows other, albeit significant, data privacy concerns.
Ultimately, the lack of challenge might reflect a prioritization of immediate, visible problems over potentially long-term data privacy risks.
They argued that Amazon’s vast data collection capabilities could lead to discriminatory practices, the exploitation of patient data for profit, and the erosion of patient autonomy. The debate highlighted the inherent tension between technological advancement and the protection of fundamental rights, specifically the right to privacy and fair competition.
Sequence of Events Leading to the Regulatory Decision (or Lack Thereof)
The sequence of events began with Amazon’s announcement of the acquisition. This was followed by a period of public debate and advocacy, marked by concerns expressed by privacy advocates and antitrust experts. Regulatory agencies, such as the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) and the Department of Justice (DOJ), likely conducted preliminary investigations. However, no significant regulatory challenges were filed, leading to the completion of the acquisition.
This lack of regulatory action could be attributed to several factors, including the complexities of proving anti-competitive behavior in a rapidly evolving market, the lack of clear legal precedents in this specific area, and the inherent limitations of existing regulatory frameworks in addressing the unique challenges posed by the intersection of big tech and healthcare. The absence of strong regulatory intervention, despite public concerns, raises questions about the effectiveness of current regulatory mechanisms in dealing with mergers and acquisitions involving large technology companies in the healthcare sector.
Ultimate Conclusion: Why Regulators Didnt Challenge Amazon One Medical Deal Data
Source: geekwire.com
The Amazon-One Medical merger highlights a complex interplay between technological advancement, healthcare delivery, data privacy, and regulatory oversight. While the lack of significant regulatory challenge might seem surprising, a deeper look reveals a confluence of factors – perhaps an evolving understanding of data privacy in the tech-healthcare space, the challenges in assessing long-term risks, or even a perceived lack of immediate anti-competitive harm.
Ultimately, this case raises important questions about the future of regulatory frameworks in the rapidly changing world of digital health, leaving us to ponder what this means for future mergers and the protection of patient data.
FAQ Overview
What specific data privacy regulations are relevant to this deal?
HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) in the US is the most significant, alongside state-level regulations. GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) could also apply depending on the location of patients and data storage.
Could Amazon use One Medical data for purposes unrelated to healthcare?
This is a major concern. While Amazon has stated commitments to data privacy, the potential for using patient data to enhance its other business lines remains a significant ethical and legal question.
What are the potential long-term effects on competition in the healthcare market?
Increased market concentration could lead to higher prices, reduced choice for consumers, and potentially less innovation in the telehealth and healthcare sectors. The long-term impacts are still unfolding.
What role did lobbying play in the regulatory decision?
The influence of lobbying by Amazon and other stakeholders is a subject of ongoing debate and speculation, and requires further investigation to assess its impact.





