US Reaches Record Low Uninsured Rate Before Medicaid Redetermination
Us reaches record low uninsured rate just prior to medicaid redeterminatio – US Reaches Record Low Uninsured Rate Before Medicaid Redetermination: It’s a headline that’s both celebratory and slightly unsettling. We’ve hit a historic low in uninsured Americans, but the looming shadow of Medicaid redetermination casts a long, uncertain future. This means millions could potentially lose coverage, throwing a wrench into this impressive achievement. Let’s dive into the numbers, the potential pitfalls, and what this all means for the future of healthcare access in the US.
The recent data showing a record low uninsured rate is undeniably positive. However, the upcoming wave of Medicaid eligibility checks, known as redetermination, presents a significant threat to this progress. Millions of individuals currently enrolled in Medicaid could lose their coverage if they no longer meet the eligibility requirements. This potential loss of coverage disproportionately impacts vulnerable populations, raising serious concerns about access to essential healthcare services.
Understanding the interplay between these two factors—the record low and the looming redetermination—is crucial for comprehending the current state of healthcare in America.
The Record Low Uninsured Rate
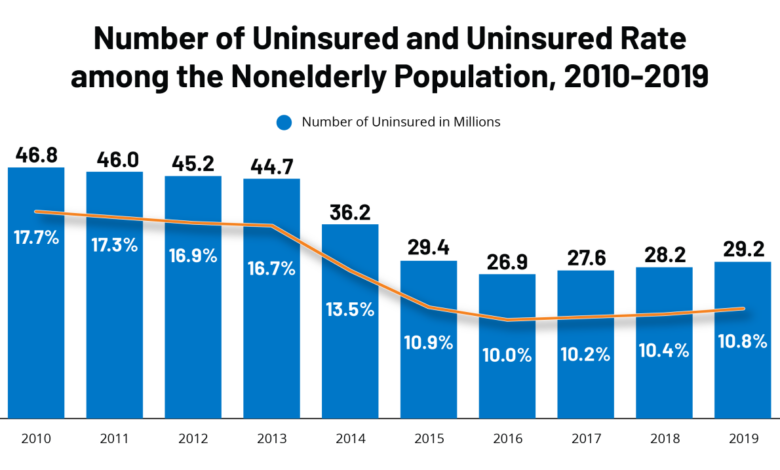
Source: kff.org
The United States recently achieved a record low uninsured rate, a significant milestone in the ongoing effort to expand healthcare access. This achievement, however, comes just before a crucial period of Medicaid redeterminations, which could potentially impact the sustainability of this progress. Understanding the context of this record low rate is crucial to anticipating future trends and ensuring continued progress towards universal healthcare coverage.The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) reported a significant drop in the uninsured rate, reaching its lowest point on record.
The US hitting a record low uninsured rate right before Medicaid redeterminations is pretty wild, especially considering the potential upheaval. It’ll be interesting to see how this plays out, especially given that Robert F. Kennedy Jr. cleared a key hurdle in his bid to become HHS Secretary, as reported here. His potential policies could significantly impact those newly insured and the overall trajectory of healthcare access in the US, making this a pivotal moment for the future of health coverage.
While the exact figure fluctuates slightly depending on the data source and methodology, the trend is undeniable. Numerous factors contributed to this reduction, including expanded access through the Affordable Care Act (ACA) marketplaces and state-level initiatives. However, the long-term implications remain uncertain, especially given the upcoming wave of Medicaid eligibility reviews.
Demographic Breakdown of the Insured and Uninsured Populations
Analyzing the uninsured rate requires a deeper dive into the demographics. The uninsured population is not uniformly distributed across the population. Disparities persist based on factors like race, ethnicity, age, income, and geographic location. For example, while overall uninsured rates have fallen, minority groups and those in lower-income brackets often experience disproportionately higher rates of uninsurance.
Understanding these disparities is essential for targeted interventions and policies aimed at improving equity in healthcare access. Data from the U.S. Census Bureau and the National Health Interview Survey (NHIS) provide detailed breakdowns of these demographic trends, highlighting the specific populations requiring focused attention.
Historical Trends in the Uninsured Rate
Examining the historical trends in the uninsured rate provides valuable context for understanding the recent record low. The following table offers a simplified view of the uninsured rate over the past decade, highlighting contributing factors and significant policy changes. Note that precise figures may vary depending on the source and methodology used.
| Year | Uninsured Rate | Contributing Factors | Policy Changes |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2013 | 14.5% (estimated) | Implementation of the ACA, economic recovery | ACA Marketplace expansion, Medicaid expansion in some states |
| 2016 | 8.6% (estimated) | Continued ACA enrollment, improving economy | Continued ACA implementation, some state-level initiatives |
| 2019 | 8.5% (estimated) | Stable ACA enrollment, economic growth | Limited policy changes at the federal level |
| 2022 | 7.9% (estimated) | Increased ACA enrollment due to pandemic relief, expanded Medicaid in some states | COVID-19 relief measures, continued state-level efforts |
| 2023 | 7.5% (estimated) | Continued economic recovery, expanded access through ACA and state initiatives | Continued state-level efforts, ongoing efforts to improve ACA enrollment |
*Note: These figures are estimates and may vary slightly depending on the data source and methodology used. Data sources include the U.S. Census Bureau, the National Health Interview Survey (NHIS), and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).*
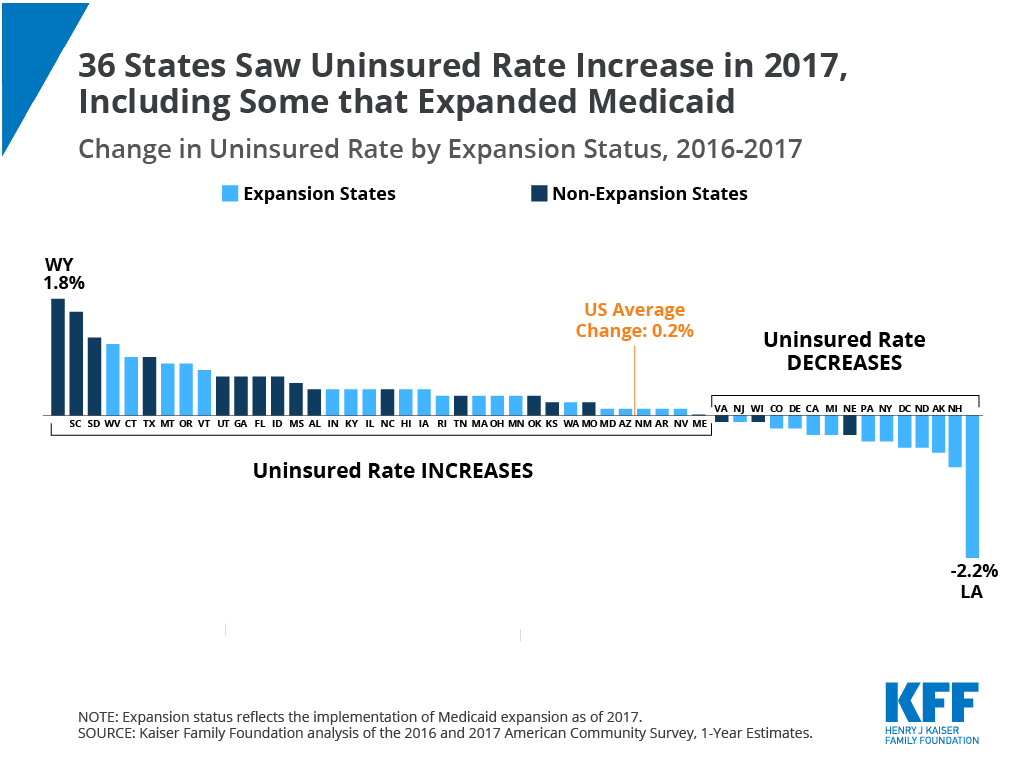
Medicaid Redetermination and its Potential Impact
The recent record low uninsured rate is undeniably positive news, but the upcoming wave of Medicaid redeterminations casts a shadow on its longevity. This process, designed to ensure individuals still qualify for Medicaid benefits, could significantly impact the number of insured Americans. Understanding the mechanics and potential consequences of this redetermination is crucial to anticipating its effects on healthcare access and the overall uninsured rate.The process of Medicaid redetermination involves a review of each recipient’s eligibility for continued coverage.
States are responsible for conducting these reviews, typically requiring individuals to submit updated information on income, household size, and other relevant factors. The timeline for these redeterminations varies by state, but the federal government initially set a deadline of December 2023 to complete the process, which has been extended for many states. This process, however, is extensive and presents logistical challenges, potentially leading to delays and administrative backlogs.
Medicaid Redetermination Process and Timeline
The redetermination process begins with a notification sent to Medicaid recipients, outlining the required documentation and deadlines for resubmission. Recipients then have a specific timeframe to provide the necessary information, often involving income verification, proof of residency, and other supporting documents. Failure to submit the required information within the given timeframe can lead to the termination of Medicaid benefits.
States are responsible for establishing their own timelines and procedures, leading to some variation across the country. For instance, some states may offer extensions or provide additional support to recipients facing difficulties in the documentation process, while others may have stricter enforcement procedures. This variation in state-level implementation could contribute to disparities in the impact of redeterminations across different regions.
Potential Consequences of Redetermination on the Uninsured Rate
The large-scale nature of Medicaid redeterminations poses a significant risk of increasing the uninsured rate. Millions of individuals could lose coverage due to procedural complexities, administrative delays, or changes in their circumstances. This is particularly concerning given the already existing challenges in accessing affordable healthcare, especially for vulnerable populations. A substantial increase in the uninsured population could lead to delayed or forgone care, resulting in worse health outcomes and increased healthcare costs in the long run.
For example, a study by the Kaiser Family Foundation projected a potential increase of several million uninsured individuals as a result of the redeterminations. These projections highlight the potential severity of the situation and underscore the need for proactive measures to mitigate the impact.
The US hitting a record low uninsured rate right before Medicaid redeterminations is pretty wild, especially considering the potential impact on access to healthcare. It makes you wonder about overall health and well-being, and how nutrition plays a role. This ties into the fascinating question of dietary differences between the sexes, as explored in this article: are women and men receptive of different types of food and game changing superfoods for women.
Ultimately, ensuring access to both healthcare and healthy food is crucial for a thriving population, regardless of the upcoming Medicaid changes.
Differential Impact of Redetermination Across Demographics
The impact of Medicaid redeterminations is unlikely to be uniform across all demographics. Certain groups are expected to be disproportionately affected. For instance, low-income families, individuals with disabilities, and people of color may face greater challenges in navigating the redetermination process due to limited resources, language barriers, or lack of access to technology. These individuals may be less equipped to gather and submit the required documentation on time, increasing their risk of losing coverage.
The US just hit a record low uninsured rate, which is amazing news, especially right before the Medicaid redetermination process kicks in. This progress is further bolstered by initiatives like the new CMS program; check out the details on this exciting development at cms launches primary care medicare model aco. Hopefully, these combined efforts will ensure continued access to healthcare for everyone, even as the redetermination process unfolds.
Similarly, individuals experiencing homelessness or those with unstable housing situations may face significant obstacles in providing accurate and timely information. The potential for unequal impacts emphasizes the need for targeted outreach and support programs to assist vulnerable populations in successfully completing the redetermination process and retaining their healthcare coverage.
Factors Contributing to the Record Low Rate: Us Reaches Record Low Uninsured Rate Just Prior To Medicaid Redeterminatio
The unprecedented drop in the uninsured rate is a complex phenomenon, resulting from a confluence of economic, policy, and public health factors. Understanding these contributing elements is crucial for maintaining this progress and ensuring continued access to healthcare for all. While the recent Medicaid redetermination process presents potential challenges, analyzing the factors behind this achievement offers valuable insight into effective strategies for healthcare access.
Several interconnected forces have driven this remarkable decline in the uninsured population. These factors can be broadly categorized into economic improvements, impactful policy changes, and successful public health initiatives. The interplay between these categories is significant, with each factor often reinforcing the effects of others, creating a synergistic impact on insurance coverage.
Economic Factors
Economic conditions play a significant role in healthcare access. Improved economic circumstances, such as increased employment and higher wages, directly translate to greater affordability of health insurance, both employer-sponsored and individual market plans. The expansion of the economy also leads to increased tax revenue, which can be allocated to support government-funded healthcare programs.
- Increased Employment and Wages: A robust economy with plentiful job opportunities and rising wages enables more individuals to afford employer-sponsored health insurance, a major source of coverage for many Americans. This is especially true for those previously employed in low-wage jobs with limited or no benefits.
- Economic Growth and Tax Revenue: Economic growth generates increased tax revenue, allowing governments to allocate more funds to programs such as Medicaid and the Affordable Care Act (ACA) marketplaces, expanding coverage to those who qualify.
Policy Changes
Policy decisions have a direct and substantial impact on the insured rate. The Affordable Care Act (ACA), despite ongoing debates, has played a pivotal role, particularly through its expansion of Medicaid eligibility in many states and the establishment of health insurance marketplaces.
- Affordable Care Act (ACA) Marketplaces: The ACA marketplaces offer subsidized health insurance plans to individuals and families who meet specific income requirements. These subsidies make health insurance more affordable for many, driving enrollment and reducing the uninsured rate.
- Medicaid Expansion: The ACA’s Medicaid expansion, adopted by many states, broadened eligibility criteria, resulting in significantly increased coverage for low-income adults. This expansion has been a major driver of the decline in the uninsured rate in participating states.
Public Health Initiatives
Public health initiatives, while not directly related to insurance coverage, can indirectly influence the uninsured rate. Improved public health outcomes reduce the demand for expensive healthcare services, making healthcare more affordable for both individuals and the system as a whole. Furthermore, initiatives promoting health literacy and preventative care can lead to better health outcomes and reduce the need for costly interventions later in life.
- Increased Access to Preventative Care: Improved access to preventative care, such as vaccinations and screenings, helps prevent serious health issues, reducing the overall cost of healthcare and making it more manageable for individuals.
- Public Health Campaigns: Public health campaigns focused on healthy lifestyles, such as promoting healthy eating and exercise, can lead to improved population health and reduced healthcare costs.
Illustrative Interplay of Factors
Imagine a Venn diagram with three overlapping circles representing Economic Factors, Policy Changes, and Public Health Initiatives. The area where all three circles overlap represents the synergistic effect of these factors on the uninsured rate. For instance, economic growth (circle 1) increases tax revenue, allowing for greater government funding of healthcare programs (overlap with circle 2, Policy Changes).
Simultaneously, a strong economy leads to more job opportunities and higher wages, enabling individuals to afford insurance (overlap with circle 3, Public Health Initiatives). Improved public health (circle 3) reduces healthcare costs, freeing up resources for other programs or lowering individual burdens, further reinforcing the impact of economic factors and policy changes. The larger the overlapping areas, the more pronounced the effect on the reduction of the uninsured rate.
The size of each circle represents the relative contribution of each factor, with the overlaps representing the compounding effect of their combined influence. This visual representation illustrates how these factors work together, rather than in isolation, to produce the record low uninsured rate.
Potential Challenges and Uncertainties
Maintaining the recently achieved record low uninsured rate presents significant challenges, particularly in the wake of upcoming Medicaid redeterminations. The process of reassessing eligibility for millions of individuals enrolled in Medicaid could lead to a substantial increase in the number of uninsured Americans, reversing recent progress and exacerbating existing healthcare disparities. Several factors contribute to this uncertainty, demanding proactive strategies to mitigate potential negative outcomes.The primary concern revolves around the logistical complexities and potential bureaucratic hurdles associated with the redetermination process.
Millions of individuals will need to navigate a potentially confusing and time-consuming application process, requiring documentation and information that may not be readily available. Furthermore, changes in eligibility criteria, even minor ones, could result in unexpected disenrollment for many individuals who previously qualified. This process, particularly for vulnerable populations with limited resources or technological access, risks leaving many uninsured.
Obstacles to Continued Healthcare Coverage Access
Several obstacles threaten continued access to healthcare coverage. Firstly, the sheer volume of individuals requiring redetermination presents a massive administrative challenge for state agencies. Delays in processing applications and communication breakdowns could lead to significant gaps in coverage, leaving individuals without insurance during critical periods. Secondly, many individuals who lose Medicaid coverage may not be eligible for other affordable coverage options, such as subsidized marketplace plans through the Affordable Care Act (ACA).
This is particularly true for those who fall into the coverage gap, earning too much to qualify for Medicaid but too little to afford ACA subsidies. Finally, a lack of awareness about the redetermination process and available resources could lead to significant numbers of individuals failing to re-enroll, even if they remain eligible.
Hypothetical Scenario: Increased Uninsured Rate Post-Redetermination, Us reaches record low uninsured rate just prior to medicaid redeterminatio
Imagine a state with 1 million Medicaid recipients undergoing redetermination. Let’s assume that due to administrative delays, 10% of applications are processed late, resulting in a temporary lapse in coverage for 100,000 individuals. Simultaneously, due to stricter eligibility criteria and increased documentation requirements, 5% of previously eligible individuals (50,000) are disenrolled. Furthermore, a significant portion of those losing Medicaid coverage, say 40% (200,000 from the initial 500,000 disenrolled), are unable to afford or qualify for ACA marketplace plans due to the coverage gap.
In this scenario, the state could experience an increase of 350,000 uninsured individuals—a 35% jump in the uninsured population from the initial 1 million Medicaid recipients. This hypothetical scenario highlights the potential for a significant increase in the uninsured rate, illustrating the cascade effect of administrative challenges, eligibility changes, and the limitations of alternative coverage options. This increase wouldn’t just be limited to one state; a similar pattern across multiple states could result in a substantial national impact.
Policy Implications and Future Outlook
The achievement of a record low uninsured rate presents a significant opportunity to reshape healthcare policy in the United States. However, the looming Medicaid redetermination process casts a shadow on this progress, demanding proactive policy adjustments to mitigate potential setbacks and ensure sustained access to care. Understanding the implications of this dual reality is crucial for crafting effective strategies moving forward.The current low uninsured rate, while celebratory, doesn’t necessarily translate to universal access to quality care.
Many individuals might remain underinsured, facing high out-of-pocket costs that effectively limit their access to needed services. The upcoming wave of Medicaid redeterminations risks exacerbating this issue, potentially pushing millions back into the ranks of the uninsured. This necessitates a proactive approach that focuses not just on maintaining coverage, but on enhancing affordability and accessibility of healthcare services.
Maintaining Healthcare Coverage
Sustaining the recent progress requires a multi-pronged strategy. Simply maintaining the status quo is insufficient given the anticipated impact of Medicaid redeterminations. Targeted outreach programs, simplifying the enrollment process, and leveraging technology for streamlined applications are essential. Furthermore, exploring options for expanding affordable coverage options, such as strengthening the Affordable Care Act marketplaces and exploring public option programs, should be considered.
These strategies aim to ensure a seamless transition for those at risk of losing coverage and actively promote enrollment for those currently uninsured. The success of such initiatives will depend on sufficient funding and effective coordination across federal and state agencies. For example, the state of California’s successful expansion of Medi-Cal coverage could serve as a model for other states grappling with similar challenges.
Their use of streamlined enrollment and robust outreach campaigns effectively increased coverage and reduced the uninsured rate.
Mitigating the Impact of Medicaid Redetermination
The upcoming Medicaid redeterminations pose a significant challenge. Millions of individuals risk losing coverage due to administrative hurdles, changes in income, or failure to update their information. To mitigate this, proactive measures are necessary. This includes simplifying the renewal process, providing clear and accessible information to beneficiaries, and offering robust assistance programs to navigate the complexities of the system.
States can also consider extending grace periods for renewal and implementing strategies to proactively identify individuals at risk of losing coverage. For instance, implementing automatic renewal processes for those who meet eligibility criteria could significantly reduce the number of individuals losing coverage due to administrative errors. Furthermore, allocating sufficient resources for caseworkers to handle the anticipated surge in applications is crucial for successful redetermination.
The experience of states that have already undergone partial redeterminations offers valuable lessons and data to inform policy adjustments.
Improving Affordability and Access
Beyond simply maintaining coverage, policy should address the affordability and accessibility of healthcare services. This includes measures to control healthcare costs, such as negotiating drug prices and strengthening regulations on surprise medical billing. Expanding access to affordable primary care and preventative services is also vital in improving overall health outcomes and reducing the burden on the healthcare system.
Investing in community health centers and expanding telehealth options can increase access to care, particularly in underserved areas. For example, the expansion of telehealth during the COVID-19 pandemic demonstrated its potential to improve access to care for individuals in rural or remote areas. The lessons learned during this period can be applied to further integrate telehealth into the healthcare system.
Last Recap
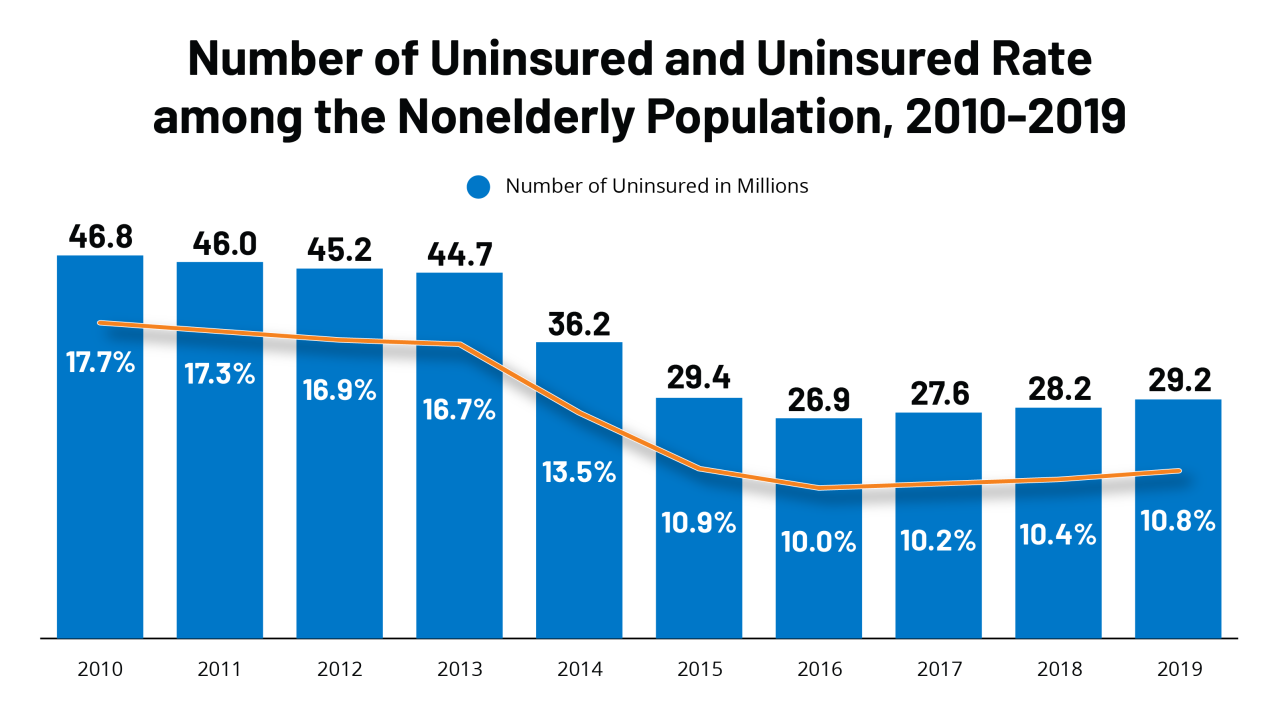
Source: kff.org
The record low uninsured rate is a significant accomplishment, a testament to years of policy changes and improved access. But the upcoming Medicaid redeterminations are a major hurdle. The potential for a surge in the uninsured population is real, and the consequences could be devastating for many. While the current numbers are encouraging, we need proactive policies and a keen eye on the coming months to ensure we don’t undo the progress we’ve made.
The focus now should be on mitigating the potential negative impacts of redetermination and preserving this hard-won progress towards universal healthcare access. This requires a multifaceted approach involving not only policy changes but also public awareness campaigns and increased support for vulnerable communities.
Questions and Answers
What is Medicaid redetermination?
It’s the process where states periodically review the eligibility of individuals enrolled in Medicaid to ensure they still meet the program’s requirements. This involves checking income, household size, and other factors.
How will redetermination affect different demographics?
The impact will vary. Low-income families, children, and people of color are likely to be disproportionately affected, potentially facing significant disruptions to their healthcare access.
What are some potential solutions to mitigate the impact of redetermination?
Streamlining the redetermination process, providing more robust outreach and assistance to those at risk of losing coverage, and potentially expanding eligibility criteria could all help lessen the negative effects.
What role does the Affordable Care Act (ACA) play in all this?
The ACA significantly expanded Medicaid coverage, and its continued success is intertwined with the outcomes of the redetermination process. Losing coverage could lead to increased reliance on the ACA marketplaces, potentially impacting its stability.