
Advocate Home Care Private Equity Sale
Advocate Home Care Private Equity Sale: The recent sale of Advocate Home Care to a private equity firm highlights a booming trend in the healthcare industry. This isn’t just about money; it’s about the future of elder care, the evolving landscape of healthcare investment, and the complex dance between profit and patient well-being. This post dives deep into the details, exploring the market forces driving this acquisition, the due diligence involved, and what it all means for the future of home healthcare.
We’ll unpack the intricacies of private equity investment in the home care sector, examining the valuation methodologies, integration strategies, and regulatory hurdles involved. We’ll also look at a hypothetical case study to illustrate a successful sale, examining the financial performance, operational efficiency, and post-acquisition strategies that led to success. Get ready for a fascinating look into the world of high-stakes healthcare deals!
Market Overview of Home Care
The home care industry is experiencing a period of significant growth, driven primarily by an aging global population and a shift in preference towards receiving care within the familiar comfort of one’s own home. This presents a compelling investment opportunity for private equity firms, offering both substantial returns and the potential for positive social impact. This overview examines the market dynamics, key trends, and various service models within this expanding sector.
The home care market is vast and multifaceted, encompassing a wide range of services tailored to meet the diverse needs of individuals requiring assistance with daily living activities. This includes personal care, such as bathing and dressing; homemaking services, like meal preparation and cleaning; and skilled medical care, provided by registered nurses or therapists. The market’s size and growth are inextricably linked to demographic shifts, particularly the rapidly expanding elderly population.
The Advocate Home Care private equity sale got me thinking about the future of healthcare. It’s amazing how innovation is impacting various sectors; for example, I just read that the FDA has approved clinical trials for pig kidney transplants in humans – check out this article for details: fda approves clinical trials for pig kidney transplants in humans.
This kind of breakthrough highlights the potential for disruptive change, making the Advocate sale even more significant in the context of evolving healthcare models.
Market Size and Growth Trends
The global home healthcare market is substantial and continues to expand at a healthy pace. While precise figures vary depending on the source and definition of “home care,” reports consistently indicate a multi-billion dollar market with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) exceeding 5% in many developed nations. This growth is fueled by several factors, including increasing life expectancy, rising prevalence of chronic diseases requiring ongoing care, and a growing preference for aging in place.
For example, the U.S. home healthcare market alone is projected to reach hundreds of billions of dollars in the coming years. This significant growth trajectory presents a lucrative opportunity for investors.
Impact of Aging Population
The aging population is the primary driver of home care market expansion. Globally, the number of individuals aged 65 and older is increasing dramatically. In many developed countries, this demographic cohort represents a significant portion of the population, and this proportion is only projected to grow further. This demographic shift directly translates into a higher demand for home care services, as older adults often require assistance with various aspects of daily living.
The increase in the number of people living with chronic conditions like Alzheimer’s disease and dementia further intensifies this demand.
The Advocate Home Care private equity sale got me thinking about the long-term care needs of our aging population. It’s crucial to consider preventative measures, and I recently read a fascinating article on how an eye test might help detect dementia risk in older adults; check it out: can eye test detect dementia risk in older adults.
Early detection could significantly impact the demand for home care services in the future, making the Advocate sale even more significant in the context of healthcare evolution.
Home Care Service Models
Different models exist within the home care industry, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. The choice of model significantly impacts operational efficiency, scalability, and overall profitability.
| Service Model | Ownership/Structure | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Agency-Based | Centralized management, employs caregivers | Consistent quality control, economies of scale | Higher overhead costs, potential for caregiver turnover |
| Franchise | Franchises operate under a parent company’s brand | Brand recognition, established systems and processes | Franchise fees, potential for inconsistencies across franchises |
| Independent | Individual caregivers or small businesses | Flexibility, personalized care | Limited scalability, inconsistent quality control |
Private Equity Investment in Home Care
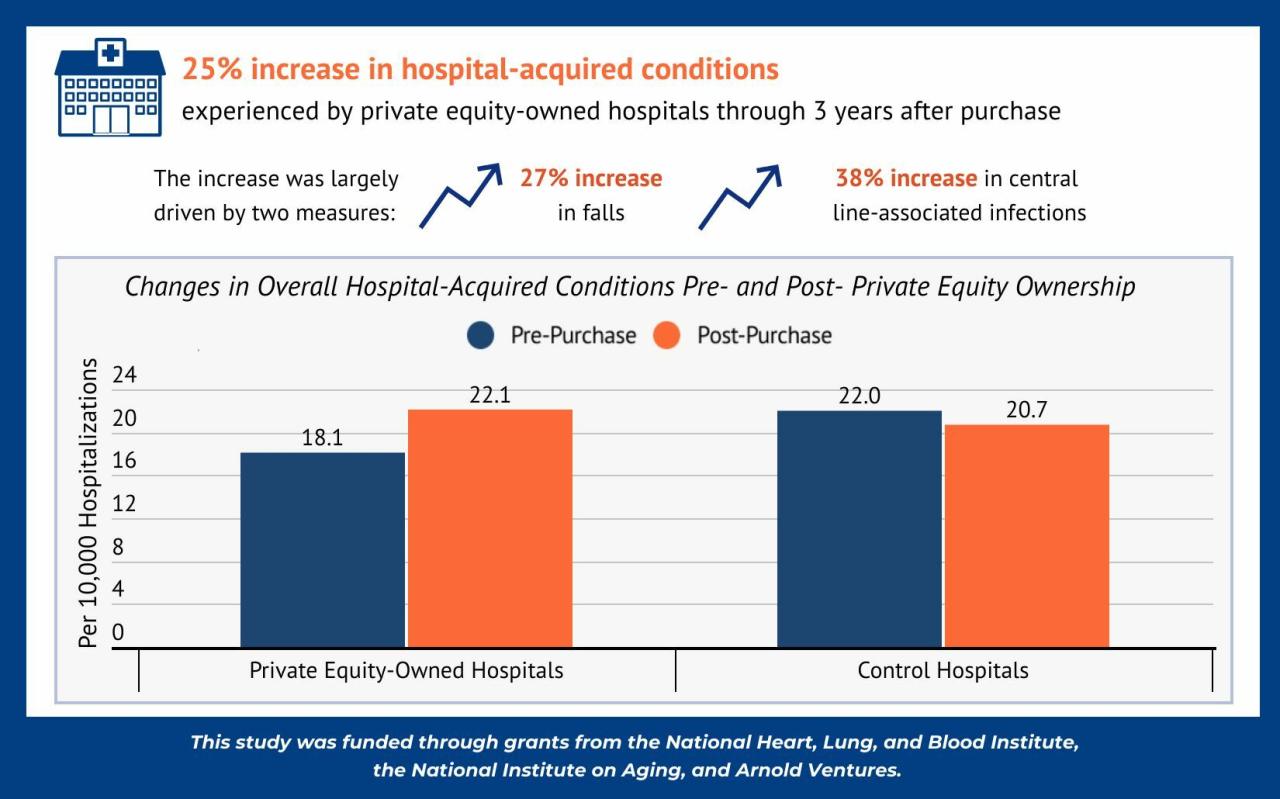
Source: nihcm.org
The home care sector is experiencing a surge in private equity (PE) investment, driven by compelling demographic trends, increasing healthcare costs, and the growing preference for aging-in-place. This influx of capital is reshaping the industry, leading to consolidation, improved operational efficiency, and enhanced service delivery. Understanding the motivations and strategies behind this investment is crucial for stakeholders across the home care landscape.Private equity firms are drawn to the home care sector for several key reasons.
The aging global population is a primary driver, creating a consistently expanding market for home-based care services. This demographic shift, coupled with rising healthcare costs and a preference for community-based care over institutionalization, ensures a robust and sustainable demand for home care services. Furthermore, the industry’s fragmentation presents opportunities for consolidation and operational improvements, offering significant potential for value creation through economies of scale and enhanced efficiency.
Finally, the relatively stable, recurring revenue streams generated by home care businesses appeal to PE firms seeking predictable cash flows and strong returns.
Investment Strategies in Home Care
Private equity firms employ various strategies when investing in home care. A common approach involves acquiring smaller, independent home care agencies and consolidating them into larger, more geographically diverse platforms. This allows for increased bargaining power with suppliers, improved operational efficiencies through shared resources and best practices, and the ability to offer a broader range of services. Another strategy focuses on providing capital for growth and expansion to existing, well-managed home care businesses.
This can involve funding acquisitions of competing agencies, expanding service offerings, or investing in technology and infrastructure improvements to enhance operational capabilities. Some PE firms also invest in developing innovative home care models, such as technology-enabled remote monitoring and telehealth solutions, to capitalize on emerging trends and improve the efficiency and effectiveness of care delivery. For example, a PE firm might invest in a company specializing in using AI-powered tools to monitor patient health remotely, thereby reducing the need for frequent in-person visits and improving overall efficiency.
Key Financial Metrics for Home Care Acquisition
Evaluating the financial health of a home care business is critical for PE firms. Key metrics include revenue growth, profitability (measured by metrics such as EBITDA margin), client retention rates, payer mix (proportion of revenue from different sources like Medicare, Medicaid, and private insurance), and operating efficiency (measured by metrics like cost per visit or administrative expenses as a percentage of revenue).
A strong track record of revenue growth, coupled with healthy margins and high client retention, is highly attractive to potential investors. Analyzing the payer mix is crucial as it indicates the stability and predictability of the revenue stream. A diverse payer mix generally reduces reliance on any single payer, mitigating the risk of reimbursement cuts or policy changes.
Furthermore, efficient operations, reflected in low cost per visit or low administrative expenses, signify a strong management team and opportunities for further cost optimization. For instance, a home care agency demonstrating consistent year-over-year revenue growth of 10% and a stable EBITDA margin of 15% would be considered a strong candidate for acquisition. Conversely, an agency with declining revenue and high administrative expenses would likely be less attractive.
Due Diligence Process for Home Care Acquisitions
Acquiring a home care company is a complex undertaking for private equity firms. A thorough due diligence process is crucial to mitigating risk and ensuring a successful investment. This process involves a systematic investigation of various aspects of the target company, from its financial health to its regulatory compliance. A comprehensive approach significantly improves the chances of a profitable and sustainable investment.
Regulatory Compliance Review
Regulatory compliance is paramount in the home care industry. Failure to meet stringent regulations can lead to significant financial penalties, operational disruptions, and reputational damage. Therefore, a detailed review of the target company’s compliance with all applicable federal, state, and local regulations is essential. This includes examining licensing and certifications, adherence to HIPAA regulations (regarding patient health information), and compliance with labor laws related to employee classification and compensation.
A thorough review of any past or present regulatory actions or investigations is also critical.
Operational Efficiency Assessment
Operational efficiency directly impacts profitability and scalability. Due diligence should assess the target company’s operational processes, including client intake, care delivery, scheduling, billing, and payroll. Key performance indicators (KPIs) such as client satisfaction scores, caregiver turnover rates, and average cost per visit should be analyzed to identify areas for improvement and potential cost savings. This analysis might include reviewing operational manuals, interviewing key personnel, and conducting site visits to observe operations firsthand.
For example, a high caregiver turnover rate could signal underlying issues with compensation, training, or management practices.
Financial Health Analysis
A comprehensive financial review is crucial to understanding the target company’s financial stability and future potential. This includes a detailed analysis of financial statements (income statements, balance sheets, and cash flow statements) for at least the past three years. Key metrics such as revenue growth, profitability margins, and debt levels should be scrutinized. The accuracy and reliability of the financial information should be verified through independent audits and reviews.
Furthermore, the analysis should assess the company’s working capital management, accounts receivable collection efficiency, and inventory management (if applicable). Any significant inconsistencies or anomalies in the financial data require further investigation.
Client and Employee Relationships Evaluation
The success of a home care company hinges on strong relationships with both clients and employees. Due diligence should assess client satisfaction through surveys, reviews, and interviews. Employee morale and retention should also be evaluated through employee surveys, exit interviews, and review of employee records. High employee turnover rates can be costly and disruptive, while low client satisfaction can lead to lost business.
Understanding the dynamics of these relationships provides valuable insights into the company’s overall health and potential for future growth.
Technology and Infrastructure Assessment
The use of technology is increasingly important in the home care industry, impacting efficiency, communication, and data management. Due diligence should assess the target company’s technology infrastructure, including its electronic health record (EHR) system, scheduling software, and communication tools. The security and reliability of these systems are critical for protecting patient data and ensuring operational continuity. The assessment should also consider the company’s ability to adapt to technological advancements and integrate new technologies to improve efficiency and client care.
Legal and Contractual Review, Advocate home care private equity sale
A thorough review of all relevant legal documents and contracts is essential. This includes reviewing contracts with clients, employees, suppliers, and other stakeholders. The review should identify any potential legal risks or liabilities, such as outstanding lawsuits, breach of contract claims, or intellectual property issues. Compliance with all relevant employment laws and regulations should be verified. This review also assesses the terms and conditions of any existing leases, licenses, or permits.
Critical Areas Checklist
The following checklist summarizes the critical areas to investigate during due diligence:
- Regulatory Compliance: Licenses, certifications, HIPAA compliance, labor law compliance, regulatory actions.
- Operational Efficiency: Client intake processes, care delivery methods, scheduling efficiency, billing and payroll processes, KPIs (client satisfaction, caregiver turnover, cost per visit).
- Financial Health: Revenue growth, profitability margins, debt levels, working capital management, accounts receivable, inventory management (if applicable).
- Client and Employee Relationships: Client satisfaction scores, employee retention rates, employee morale.
- Technology and Infrastructure: EHR system, scheduling software, communication tools, data security.
- Legal and Contractual Review: Client contracts, employee contracts, supplier contracts, legal risks, compliance with employment laws.
Valuation of Home Care Businesses
Valuing a home care business for a private equity sale requires a nuanced approach, considering the unique characteristics of the industry. Unlike manufacturing or technology firms, home care businesses are heavily reliant on human capital, client relationships, and regulatory compliance. Several valuation methodologies are employed, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. The selection of the most appropriate method often depends on the specific circumstances of the transaction and the available data.
Valuation Methodologies
Several key methodologies are commonly used to determine the fair market value of a home care business. These include discounted cash flow (DCF) analysis, comparable company analysis, and precedent transactions. Each approach offers a different perspective on value, and a comprehensive valuation often involves a combination of these methods to arrive at a robust estimate.
Discounted Cash Flow (DCF) Analysis
DCF analysis is an intrinsic valuation method that focuses on the present value of future cash flows. It involves projecting the home care company’s future cash flows over a specified period, discounting them back to their present value using a discount rate that reflects the risk associated with the investment. This method requires detailed financial projections, including revenue growth rates, operating margins, and capital expenditures.
The discount rate typically incorporates the company’s weighted average cost of capital (WACC). A crucial element of this process is accurately forecasting the future growth trajectory of the business. For example, if a company is expanding into new geographic markets or introducing new service lines, this would influence future cash flow projections and ultimately, the valuation. A key challenge in applying DCF to home care is accurately predicting client turnover and associated revenue fluctuations.
Comparable Company Analysis
This relative valuation method compares the target home care company to publicly traded or privately held companies with similar characteristics, such as size, service offerings, geographic location, and client demographics. The valuation multiples (e.g., EBITDA multiple, revenue multiple) of the comparable companies are then applied to the target company’s financial metrics to estimate its value. For instance, if comparable companies trade at an average EBITDA multiple of 6x, and the target company’s EBITDA is $1 million, a preliminary valuation could be $6 million.
However, finding truly comparable companies in the fragmented home care market can be difficult, and differences in operational efficiency, client mix, and regulatory environments can significantly affect the accuracy of this method. Furthermore, the availability of reliable comparable company data, especially for privately held firms, can be limited.
Precedent Transactions
This method analyzes the sale prices of similar home care businesses in recent transactions. By comparing the target company’s key financial and operational characteristics to those of companies involved in past acquisitions, a valuation range can be derived. For example, if several comparable home care companies were recently acquired at an average multiple of 5x revenue, this multiple could be applied to the target company’s revenue to estimate its value.
This approach relies heavily on the availability of reliable data on past transactions, which can be challenging to obtain, particularly for private transactions. Differences in transaction structures, market conditions, and the specific circumstances of each deal can also affect the comparability and reliability of this method.
Integration and Post-Acquisition Strategies: Advocate Home Care Private Equity Sale

Source: ytimg.com
Successfully integrating a newly acquired home care company into a larger portfolio is crucial for private equity firms to realize the full potential of their investment. This involves a multifaceted approach encompassing operational, financial, and cultural aspects, all while minimizing disruption to client care and employee morale. Effective integration strategies directly impact the post-acquisition performance and long-term profitability of the combined entity.
Common Integration Strategies
Private equity firms typically employ a range of strategies to integrate acquired home care businesses. These strategies often involve a combination of approaches tailored to the specific circumstances of each acquisition. A standardized, phased approach, however, usually underpins the process.
- Rapid Integration: This strategy prioritizes swift consolidation of operations, systems, and branding. It’s often used when there are significant synergies to be realized quickly, or when the acquired company has operational inefficiencies that need immediate attention. For example, merging IT systems and billing processes early can lead to cost savings.
- Phased Integration: A more gradual approach, this allows for a more measured transition, minimizing disruption and allowing time for cultural adjustments. This might involve integrating different departments sequentially, starting with areas with the least client impact, such as back-office functions.
- Decentralized Integration: This approach maintains a degree of autonomy for the acquired company, allowing it to retain its brand and operational style to a larger extent. This can be beneficial when the acquired company has a strong brand reputation and loyal client base. For example, a highly-rated local home care provider might benefit from retaining its local identity and brand recognition.
Challenges in Integrating Acquired Home Care Businesses
Integrating home care businesses presents unique challenges compared to other sectors. The human element, the sensitivity of client care, and regulatory compliance all play significant roles.
- Client Retention: Maintaining client trust and continuity of care is paramount. Any disruption caused by integration can lead to client churn. Strategies to mitigate this include transparent communication with clients, minimizing changes to caregivers, and ensuring a smooth transition of services.
- Employee Retention: Caregivers are a valuable asset. Integration can cause uncertainty and anxiety among employees. Retention strategies include open communication, demonstrating a commitment to employee wellbeing, and offering competitive compensation and benefits packages.
- Regulatory Compliance: Home care is heavily regulated. Ensuring compliance with all relevant regulations across different states or regions post-acquisition is crucial, requiring careful due diligence and ongoing monitoring. Non-compliance can result in significant penalties.
- Technology Integration: Integrating disparate technology systems can be complex and time-consuming. A well-planned approach, possibly involving a phased migration to a unified system, is essential to avoid operational disruptions.
Strategies to Mitigate Integration Challenges
Effective mitigation requires proactive planning and execution.
- Comprehensive Due Diligence: Thorough pre-acquisition due diligence is essential to identify potential integration challenges early on. This includes evaluating the acquired company’s operational efficiency, technology infrastructure, regulatory compliance, and employee morale.
- Change Management Plan: A well-defined change management plan is crucial for guiding employees and clients through the integration process. This plan should Artikel the steps involved, the timeline, and the communication strategy.
- Strong Leadership and Communication: Strong leadership and transparent communication are essential to build trust and confidence among employees and clients during the integration process. Regular updates and open forums can address concerns and foster a sense of collaboration.
- Integration Team: Forming a dedicated integration team with representatives from both the acquiring and acquired companies can facilitate a smoother transition. This team should be responsible for developing and implementing the integration plan.
Optimizing Operations and Improving Profitability Post-Acquisition
Post-acquisition, optimizing operations and improving profitability involves leveraging synergies, streamlining processes, and improving efficiency.
- Cost Synergies: Identifying and realizing cost synergies through economies of scale is crucial. This might involve consolidating administrative functions, negotiating better rates with suppliers, or improving operational efficiencies.
- Revenue Enhancement: Strategies to enhance revenue include expanding service offerings, improving marketing and sales efforts, and optimizing pricing strategies. For example, offering additional services like telehealth or companion care can attract new clients and increase revenue streams.
- Technology Upgrades: Investing in technology upgrades can improve operational efficiency, reduce administrative costs, and enhance client care. This might include implementing a new scheduling system, electronic health record (EHR) system, or client management software.
- Data Analytics: Utilizing data analytics to monitor key performance indicators (KPIs) such as client satisfaction, caregiver retention, and operational efficiency can provide valuable insights for continuous improvement.
Regulatory Landscape and Compliance

Source: livestorm.co
Navigating the regulatory landscape is crucial for success in the home care industry, especially for companies undergoing private equity acquisitions. Failure to comply can lead to significant financial penalties, reputational damage, and operational disruptions. Understanding these regulations and proactively implementing a robust compliance program is paramount for both the acquiring firm and the target home care company.The home care sector is heavily regulated at both the federal and state levels, varying significantly by location.
Key regulations often involve licensing and certification requirements, employee background checks, patient privacy (HIPAA compliance), Medicare and Medicaid billing practices, and adherence to state-specific health and safety standards. These regulations are designed to protect vulnerable patients and ensure the quality of care provided.
Licensing and Certification Requirements
Each state has its own licensing and certification requirements for home care agencies. These requirements often include background checks for all staff, proof of insurance, detailed operational plans, and regular inspections to ensure compliance with state regulations. Failure to maintain valid licenses and certifications can result in immediate cessation of operations and significant penalties. For example, in California, a home care agency operating without the proper license could face fines exceeding $10,000 per violation.
Due diligence must thoroughly investigate the target company’s licensing and certification status in each state of operation.
HIPAA Compliance
The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) mandates strict rules for protecting patient health information (PHI). Home care agencies must implement robust security measures to safeguard electronic and paper PHI. This includes employee training on HIPAA regulations, secure data storage and transmission protocols, and procedures for handling breaches. Non-compliance with HIPAA can result in hefty fines and legal action.
A private equity firm acquiring a home care company must ensure that the company has a comprehensive HIPAA compliance program in place and that it is regularly audited.
Medicare and Medicaid Billing Compliance
Home care agencies that bill Medicare and Medicaid must adhere to strict billing and coding guidelines. Improper billing practices can lead to significant financial penalties, including repayment of funds and exclusion from participation in government programs. A thorough review of the target company’s billing practices is essential during the due diligence process. This involves verifying the accuracy of coding, documentation, and claims submission.
Examples of non-compliance include upcoding (billing for a more expensive service than provided) and unbundling (billing for multiple services when a single code should be used).
Creating a Compliance Plan for a Home Care Company Acquired by a Private Equity Firm
A comprehensive compliance plan should be developed and implemented immediately following the acquisition. This plan should include:
- A detailed risk assessment identifying potential compliance vulnerabilities.
- Implementation of robust policies and procedures to address identified risks.
- Regular training for all employees on relevant regulations and compliance requirements.
- Establishment of a compliance committee responsible for overseeing the compliance program.
- Regular internal audits to monitor compliance and identify areas for improvement.
- A process for reporting and investigating compliance violations.
The plan should also Artikel a clear escalation path for reporting and addressing compliance issues. Regular monitoring and review of the plan are essential to ensure its effectiveness. The plan should be tailored to the specific regulations applicable to the home care company’s operations in each state. This proactive approach minimizes risk and ensures the long-term success of the acquired company.
Potential Regulatory Risks Associated with Private Equity Ownership
Private equity firms often focus on improving efficiency and profitability. However, aggressive cost-cutting measures or rapid expansion can inadvertently increase the risk of regulatory non-compliance. For example, reducing staffing levels to cut costs could lead to inadequate patient care and violations of state regulations. Similarly, rapid expansion into new markets without proper due diligence regarding state-specific regulations could also result in non-compliance.
A balanced approach that prioritizes both profitability and compliance is essential for successful private equity ownership of home care companies. Thorough due diligence and a well-defined compliance program are critical to mitigate these risks.
Illustrative Case Study: A Successful Home Care Private Equity Sale
This case study details the successful acquisition of “Caring Hands Home Care,” a mid-sized home care agency operating in the southeastern United States, by “Apex Healthcare Partners,” a reputable private equity firm specializing in the healthcare sector. The sale exemplifies a well-executed transaction, showcasing the key factors contributing to a successful outcome for both the seller and the buyer.
Company Overview and Financial Performance
Caring Hands Home Care, established in 2005, provided a comprehensive range of in-home care services, including personal care, skilled nursing, and companionship. Prior to the sale, the company had consistently demonstrated strong financial performance, achieving an average annual revenue growth of 15% over the past five years. Their EBITDA (Earnings Before Interest, Taxes, Depreciation, and Amortization) margin consistently hovered around 18%, reflecting efficient operational management and a strong pricing strategy.
Their client base was diverse, encompassing both private pay and insurance-reimbursed clients, creating a stable revenue stream. Key performance indicators (KPIs) such as client satisfaction scores and employee retention rates were also significantly above industry averages. This robust financial performance, coupled with strong operational efficiency, made Caring Hands an attractive target for private equity investors.
Operational Efficiency and Scalability
Caring Hands had implemented a sophisticated technology platform for scheduling, client management, and payroll processing, improving operational efficiency and reducing administrative overhead. They also fostered a strong company culture focused on employee training and retention, leading to low turnover rates and high levels of client satisfaction. This operational excellence, coupled with a well-defined scalable business model, was a key selling point to Apex Healthcare Partners.
The company’s established processes and systems were readily adaptable to future expansion, making it an ideal platform for further growth.
“Their robust technology infrastructure and highly trained staff were key factors in our decision to acquire Caring Hands,” stated a spokesperson for Apex Healthcare Partners.
The Advocate Home Care private equity sale is huge news, impacting many dedicated caregivers. I’ve been thinking about the long hours and repetitive motions involved in home care, which can lead to issues like carpal tunnel syndrome. Fortunately, there are non-surgical options available, like those detailed on this helpful site: ways to treat carpal tunnel syndrome without surgery.
Understanding these treatments is crucial for ensuring the well-being of home care professionals, especially given the recent industry changes brought about by the Advocate sale.
Sale Process and Valuation
The sale process involved a competitive bidding process managed by a reputable investment banking firm. Multiple private equity firms expressed interest, ultimately leading to a highly competitive bidding war. The valuation was based on a combination of discounted cash flow (DCF) analysis and comparable company analysis, resulting in a purchase price representing a significant premium to Caring Hands’ EBITDA.
The transaction was finalized within six months of initiating the sale process, a testament to the efficient and well-managed process.
Post-Acquisition Strategies and Results
Following the acquisition, Apex Healthcare Partners implemented several post-acquisition strategies to enhance Caring Hands’ growth and profitability. These strategies included expanding service offerings into new geographic markets, investing in advanced technology solutions, and enhancing marketing and sales efforts. They also focused on recruiting and retaining high-quality caregivers. Within two years of the acquisition, Caring Hands experienced a significant increase in revenue and profitability, exceeding the projections Artikeld in the initial investment thesis.
The improved operational efficiency and expanded market reach resulted in a substantial return on investment for Apex Healthcare Partners.
“The integration process was seamless, and the post-acquisition strategies have yielded exceptional results, exceeding our initial expectations,” commented the CEO of Apex Healthcare Partners.
Exit Strategies for Private Equity Investors in Home Care
Private equity firms invest in home care businesses with the ultimate goal of realizing a return on their investment. This return is typically achieved through an exit strategy, which involves selling the business to another party. Several paths exist, each with its own set of advantages and disadvantages, and the optimal choice is heavily influenced by prevailing market conditions.
The most common exit strategies for private equity-backed home care companies involve either a sale to another company or an initial public offering (IPO). The decision-making process requires careful consideration of factors such as the company’s performance, the overall market climate, and the availability of potential buyers.
Sale to a Strategic Buyer
A strategic buyer is typically a larger company in the healthcare industry, such as another home care provider, a hospital system, or a large insurance company. These buyers often seek to acquire smaller companies to expand their market share, gain access to new technologies or services, or enhance their geographic reach. A strategic acquisition can be highly beneficial for both the seller and the buyer, as it allows for the seamless integration of resources and expertise.
Advantages of a sale to a strategic buyer include a relatively certain and potentially high sale price, quicker transaction timelines compared to an IPO, and the possibility of a smooth integration process due to the buyer’s existing industry knowledge. Disadvantages can include a lower sale price than might be achievable through an IPO, and potential integration challenges if the cultures of the two companies clash.
The buyer might also impose significant changes to the acquired company’s operations.
Initial Public Offering (IPO)
An IPO involves listing the home care company’s shares on a public stock exchange, allowing the private equity firm to sell its shares to the public and realize its investment. This can be a highly lucrative exit strategy, particularly if the company is performing well and the market is receptive to new listings. However, it’s a more complex and time-consuming process than a sale to a strategic buyer, requiring significant regulatory compliance and financial disclosures.
The advantages of an IPO include the potential for a very high valuation and significant returns for the private equity firm. It also provides liquidity for the investors. Disadvantages include the significant costs and effort involved in preparing for and executing an IPO, the ongoing regulatory scrutiny after the listing, and the potential for volatility in the company’s share price after the IPO.
The success of an IPO is highly dependent on market conditions, investor sentiment, and the company’s financial performance.
Sale to a Financial Buyer
Another potential exit strategy involves selling the home care business to another private equity firm or a similar financial buyer. This type of transaction often occurs when the current private equity firm has reached its investment horizon or sees limited further growth opportunities within the business. This option provides liquidity for the investors and allows another firm to continue developing the business.
Advantages include a relatively quick transaction, and a focus on financial metrics by the buyer, which can be appealing to sellers focused on a fast and efficient exit. Disadvantages might include less operational expertise from the buyer compared to a strategic buyer, and potential disruptions during the transition phase.
Market Conditions and Exit Strategy Selection
The choice of exit strategy is significantly influenced by prevailing market conditions. During periods of strong economic growth and high investor confidence, an IPO might be a more attractive option, as investors are more willing to invest in new companies and pay higher valuations. Conversely, during economic downturns or periods of market uncertainty, a sale to a strategic buyer might be a more prudent strategy, as it provides a more certain and predictable return.
For example, during the height of the COVID-19 pandemic, strategic acquisitions were more common due to increased demand for home healthcare services and the need for larger organizations to consolidate resources. Conversely, a robust economic environment might see several IPOs in the sector as investor appetite for growth stocks increases.
Ending Remarks
The Advocate Home Care private equity sale serves as a compelling case study for understanding the evolving dynamics of the home healthcare market and the significant role private equity plays in shaping its future. While financial gains are a driving force, the ultimate success of such acquisitions hinges on a delicate balance between profitability and the continued provision of high-quality care for vulnerable populations.
Understanding the complexities of due diligence, regulatory compliance, and post-acquisition integration is crucial for all stakeholders involved, from investors to caregivers to the patients themselves. The future of home healthcare is undoubtedly intertwined with the strategic investments made today.
FAQ Compilation
What are the potential risks of private equity ownership in home care?
Potential risks include focusing too heavily on cost-cutting measures that could compromise care quality, navigating complex regulatory landscapes, and managing the integration of multiple acquired companies.
How does the aging population impact the home care market?
The rapidly aging population globally is driving increased demand for home care services, creating a lucrative market for private equity investment.
What are some common exit strategies for private equity firms in home care?
Common exit strategies include an initial public offering (IPO), selling to a larger healthcare provider, or selling to another private equity firm.



