Better Crisis Communications 5 Steps for Better Patient & Staff Engagement
Better crisis communications 5 steps for better patient staff engagement – Better Crisis Communications: 5 Steps for Better Patient & Staff Engagement – navigating a healthcare crisis effectively isn’t just about medical expertise; it’s about clear, consistent communication. This post dives into a five-step plan designed to build trust and collaboration among patients and staff during stressful situations. We’ll explore proactive strategies, communication channels, and methods for measuring the success of your crisis communication efforts.
Get ready to transform how your healthcare organization handles challenging times.
From crafting a comprehensive crisis communication plan to utilizing various communication channels effectively, we’ll cover everything you need to know. We’ll also look at how to measure the effectiveness of your strategies and use feedback to improve future responses. This isn’t just about surviving a crisis; it’s about thriving through it and strengthening your relationships with both patients and staff.
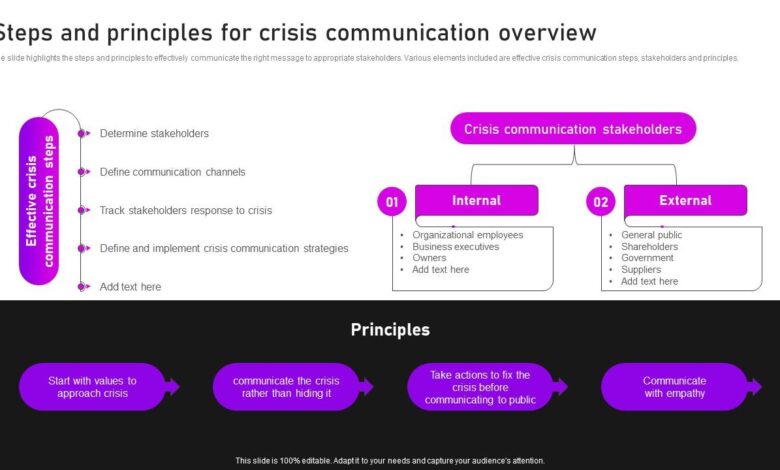
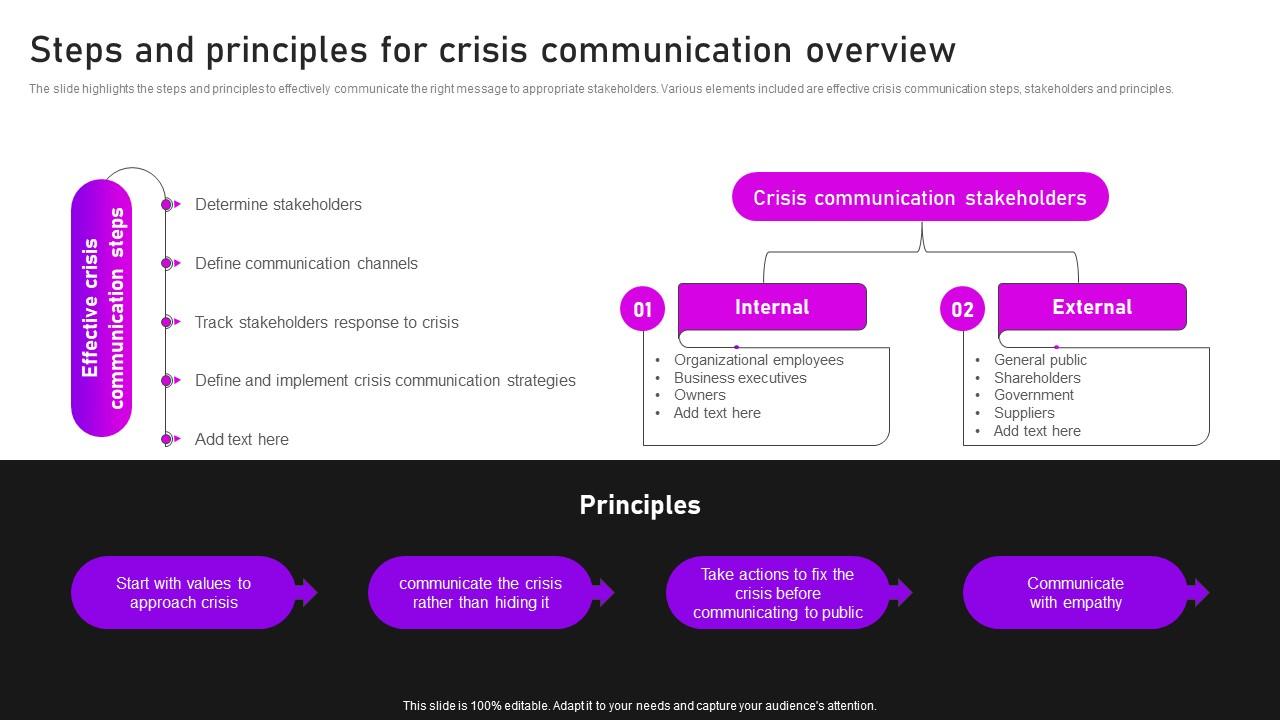
Defining Effective Crisis Communication in Healthcare
Source: slideteam.net
Effective crisis communication in healthcare is paramount for maintaining patient and staff trust, minimizing negative impacts, and ensuring the safety and well-being of everyone involved. It’s not merely about disseminating information; it’s about building and maintaining relationships during times of extreme pressure. A successful strategy requires proactive planning, clear and consistent messaging, and a deep understanding of the needs of all stakeholders.Successful crisis communication strategies in healthcare settings share several key characteristics.
These include speed and accuracy in disseminating information, consistent messaging across all platforms, empathy and transparency in addressing concerns, and proactive engagement with the media and the public. Crucially, effective strategies are developedbefore* a crisis hits, allowing for a swift and coordinated response when needed. This proactive approach reduces confusion and fosters confidence in the organization’s ability to handle difficult situations.
The Impact of Timely and Transparent Communication
Timely and transparent communication significantly influences patient and staff trust during crises. When information is shared promptly and honestly, it reduces anxiety and speculation. Patients and staff are more likely to cooperate and follow instructions when they feel informed and valued. Conversely, delays or a lack of transparency can breed mistrust, leading to panic, rumors, and potential legal ramifications.
For example, during a hospital-wide outbreak of a contagious disease, immediate and open communication about the situation, including the steps being taken to contain it, would significantly reduce fear and enhance cooperation from patients and staff. Conversely, withholding information or downplaying the severity could erode trust and lead to a more chaotic situation.
Examples of Communication Failures and Their Consequences
Several high-profile healthcare crises have demonstrated the devastating consequences of communication failures. For instance, the delayed and inconsistent communication surrounding the initial outbreak of COVID-19 in various locations led to widespread confusion and panic. The lack of clear, consistent messaging from public health officials contributed to the rapid spread of misinformation and mistrust in authorities. Similarly, failures to promptly disclose medical errors or adverse events can lead to loss of public confidence, legal action, and reputational damage for healthcare institutions.
A hospital failing to disclose a significant medication error that resulted in patient harm, for example, would likely face severe consequences, including loss of accreditation and potential lawsuits.
The Importance of a Multi-faceted Communication Plan
A comprehensive crisis communication plan must address the diverse needs of various stakeholders. This includes patients, families, staff, the media, government agencies, and the wider community. Each group requires tailored communication strategies, taking into account their specific information needs, communication preferences, and emotional responses during a crisis. For example, communication with patients might focus on their immediate care and treatment, while communication with staff might prioritize safety protocols and emotional support.
Engaging the media proactively and providing accurate information can help prevent the spread of misinformation, while communication with government agencies ensures compliance with regulations and facilitates a coordinated response. A well-structured plan, therefore, anticipates these different needs and ensures that consistent messaging is delivered across all platforms.
Building Strong Patient Engagement During Crises: Better Crisis Communications 5 Steps For Better Patient Staff Engagement
Source: slideteam.net
Effective communication is paramount during healthcare crises. A well-designed strategy can significantly reduce patient anxiety, improve compliance with instructions, and foster trust in the healthcare system. This involves proactive communication, utilizing multiple channels, and tailoring information to diverse audiences. Failing to engage patients effectively during a crisis can lead to misinformation, confusion, and ultimately, poorer health outcomes.
A Proactive Communication Strategy for Addressing Patient Anxieties
A proactive approach to communication is crucial for managing patient anxieties during a crisis. Instead of reacting to concerns as they arise, a well-defined strategy anticipates potential worries and addresses them preemptively. This involves identifying key concerns based on the nature of the crisis (e.g., infectious disease outbreak, natural disaster impacting hospital services). Then, create messages that directly address these concerns with accurate, empathetic, and reassuring language.
For example, during a widespread flu outbreak, messages might address concerns about contagion, treatment options, and the availability of resources. Regular, scheduled updates, even if there’s no significant change, help maintain a sense of control and prevent rumors from spreading.
Best Practices for Utilizing Various Communication Channels
Reaching patients effectively requires a multi-channel approach. Email remains a reliable method for delivering detailed information, particularly for patients with established electronic health records. Text messaging is ideal for brief, urgent updates or appointment reminders. Social media platforms, like Facebook or Twitter, can be used to disseminate information widely, but require careful monitoring and management to avoid the spread of misinformation.
Effective crisis communication, especially the 5 steps for better patient-staff engagement, hinges on clear, timely information flow. This is where technology steps in; for example, check out how nuance integrates generative AI scribe with Epic EHRs , potentially streamlining record-keeping and freeing up staff to focus on direct patient interaction during a crisis. Ultimately, improved communication systems are key to navigating any emergency successfully.
Consider using a combination of these methods to ensure maximum reach and accessibility. For example, a hospital might use email for detailed updates on service disruptions, text messages for appointment confirmations and cancellations, and social media to share general updates and reassure the community. It is important to remember that different patient demographics utilize different channels differently.
A thorough understanding of your patient base will inform channel selection.
Providing Accurate, Consistent, and Understandable Information, Better crisis communications 5 steps for better patient staff engagement
Clarity and consistency are essential when communicating with patients during a crisis. Information should be presented in plain language, avoiding medical jargon. Visual aids, such as infographics or short videos, can significantly improve comprehension, especially for patients with low health literacy. Multiple formats (e.g., translated materials, audio recordings) should be considered to cater to diverse needs. Maintaining consistent messaging across all communication channels is crucial to avoid confusion and build trust.
For example, instead of complex medical terms, use simple explanations like “This medicine helps your body fight off the infection.” Consistency across all platforms (website, email, social media) ensures that patients receive the same information regardless of where they look.
Sample Communication Template for Crisis Updates
Subject: Important Update Regarding [Crisis Name] at [Hospital Name]
Dear [Patient Name],
We are writing to update you on the current situation regarding [Crisis Name]. [Briefly describe the situation and its impact]. [Clearly state what actions patients should take]. [Provide links to additional resources or contact information]. We are committed to ensuring your safety and well-being. We will continue to provide updates as the situation evolves. [State the date and time of the next update]. Thank you for your understanding.
Sincerely,
[Hospital Name]
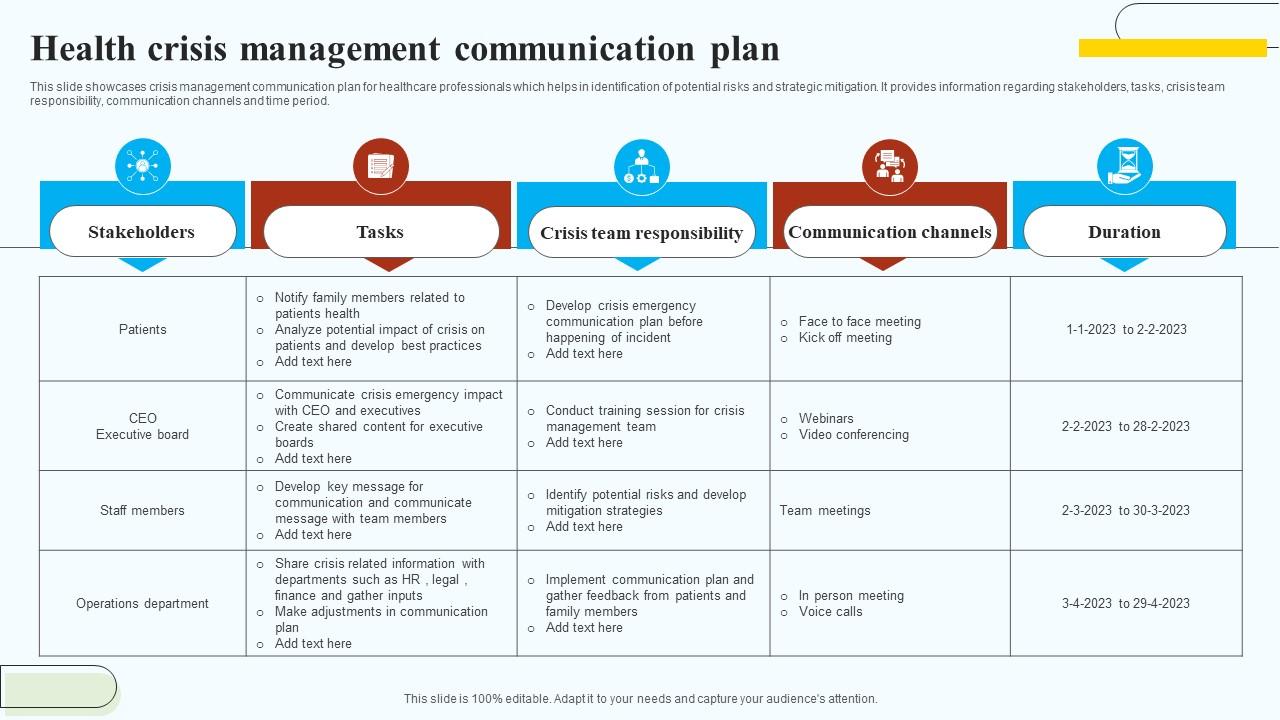
Fostering Staff Engagement and Collaboration During Crises
Effective crisis communication isn’t just about informing patients and the public; it’s equally crucial to engage and support the healthcare staff who are on the front lines. A well-engaged team is a resilient team, better equipped to handle the pressures of a crisis and provide optimal patient care. Failing to prioritize staff well-being during a crisis can lead to burnout, decreased morale, and ultimately, compromised patient safety.Maintaining open communication and fostering a sense of collaboration among staff is paramount during challenging times.
This involves proactive information sharing, transparent leadership, and creating avenues for feedback and support. When staff feel heard and valued, they are more likely to remain engaged and committed to their roles, even under immense pressure.
Strategies for Keeping Healthcare Staff Informed and Engaged
Keeping staff informed requires a multi-pronged approach. Regular updates, delivered through multiple channels, ensure information reaches everyone, regardless of their role or location. This includes using a variety of communication methods to cater to different preferences and ensure information accessibility. For example, a combination of email blasts for official announcements, intranet updates for detailed information, and short, frequent text messages for urgent updates can be highly effective.
Regularly scheduled briefings, both live and recorded, offer opportunities for two-way communication, allowing staff to ask questions and receive direct answers from leadership. Furthermore, creating dedicated online forums or chat groups allows for informal communication and peer support, fostering a sense of community during stressful periods. Finally, acknowledging and appreciating staff contributions publicly can significantly boost morale and engagement.
Facilitating Open Communication and Feedback Channels
Establishing multiple channels for feedback is vital. This could involve anonymous suggestion boxes, online feedback forms, regular staff surveys, or even informal “open door” policies where staff can readily approach managers with concerns. Actively soliciting feedback demonstrates a commitment to listening and valuing staff input. Leadership should actively respond to feedback, explaining decisions and demonstrating transparency in the decision-making process.
This fosters trust and reduces anxieties. Regular feedback sessions, either in person or virtual, provide a structured forum for addressing concerns and building rapport between staff and management. Crucially, leadership needs to be responsive and demonstrate a willingness to act on valid concerns raised by the staff.
Effective Internal Communication Tools and Techniques
Several tools can enhance internal communication during a crisis. A well-designed intranet portal serves as a central hub for critical information, updates, and resources. Instant messaging platforms, such as Slack or Microsoft Teams, facilitate quick communication and collaboration among teams. Dedicated crisis communication software can help manage information flow efficiently and track responses. Using visual aids like infographics or short videos can help convey complex information clearly and concisely, particularly when dealing with a large volume of data or technical details.
For example, an infographic detailing infection control protocols during a pandemic would be far more accessible than a lengthy email.
Conducting Regular Staff Briefings and Q&A Sessions
A structured approach to staff briefings is essential. These briefings should be held regularly, ideally daily during a crisis, and at a time convenient for most staff. A clear agenda should be distributed beforehand, outlining the topics to be covered. Briefings should begin with a summary of the current situation, followed by updates on key developments, planned actions, and any necessary changes in protocols.
The Q&A session should be allocated sufficient time, allowing staff to voice concerns and seek clarification. Leadership should be prepared to answer questions honestly and transparently, even if they don’t have all the answers. Following the briefing, a summary of key points and answers to frequently asked questions should be distributed to ensure everyone is informed, even those who couldn’t attend.
Post-briefing feedback mechanisms can also help to continuously improve the effectiveness of the briefings.
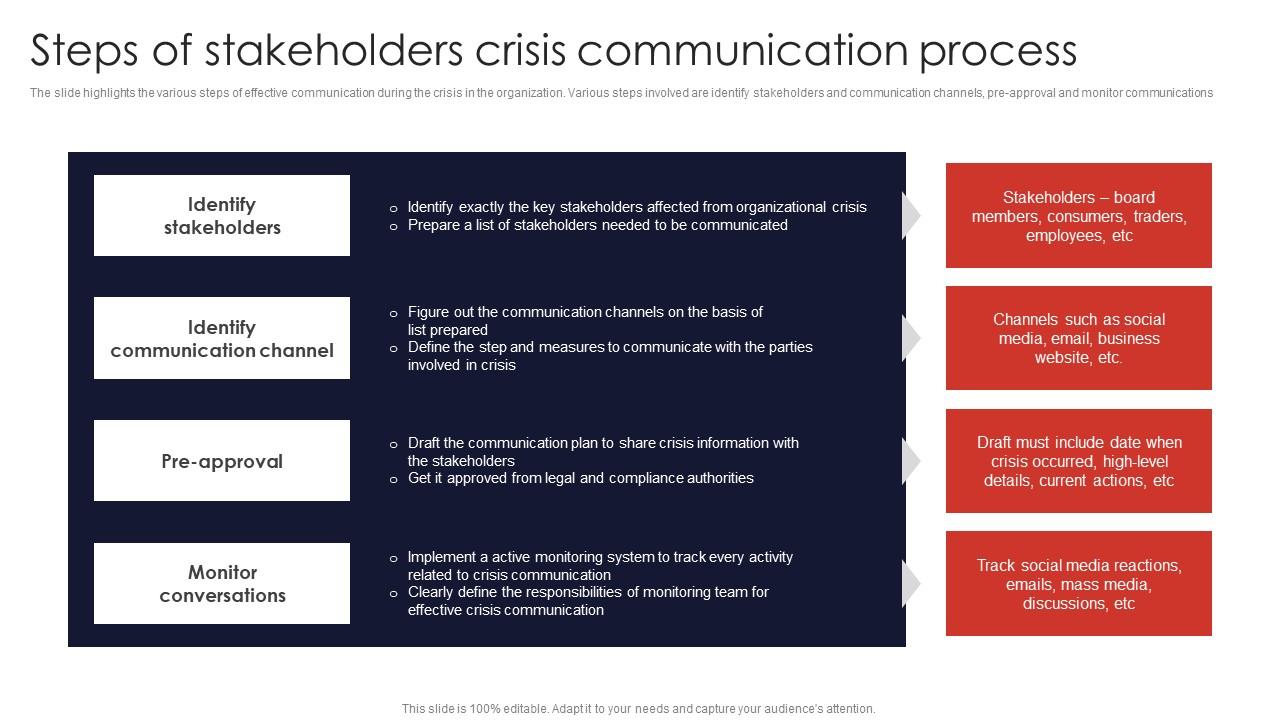
Developing a Proactive Crisis Communication Plan
A robust crisis communication plan is not a luxury but a necessity for any healthcare organization. It’s the bedrock upon which effective responses are built, ensuring clear, consistent messaging during tumultuous times. A well-defined plan minimizes confusion, protects reputation, and ultimately, safeguards patient and staff well-being. Without one, even minor incidents can escalate into major crises.A proactive approach to crisis communication involves anticipating potential issues, developing clear protocols, and assigning roles and responsibilities before a crisis hits.
This preparation significantly reduces reaction time and allows for a more coordinated and effective response. The key is to have a detailed plan ready to deploy, rather than scrambling to create one amidst the chaos of a real crisis.
Defining Roles and Responsibilities
Establishing clear roles and responsibilities is crucial for efficient crisis communication. Each team member should understand their specific tasks and reporting lines. Ambiguity can lead to delays and conflicting messages. The following table Artikels key roles and their associated responsibilities within a sample crisis communication team. This should be tailored to the specific needs and structure of your organization.
| Role | Responsibilities | Contact Information | Backup |
|---|---|---|---|
| Crisis Communication Director | Overall leadership, strategic direction, media liaison | [Contact Details] | [Backup Contact Details] |
| Public Relations Officer | Media relations, press releases, social media management | [Contact Details] | [Backup Contact Details] |
| Internal Communications Manager | Staff communication, intranet updates, employee support | [Contact Details] | [Backup Contact Details] |
| IT Support | Website maintenance, system stability, communication technology | [Contact Details] | [Backup Contact Details] |
Identifying and Prioritizing Key Messages
During a crisis, information overload is a real threat. A system for identifying and prioritizing key messages ensures consistent and accurate information reaches all stakeholders. This involves crafting concise, easily understandable messages that address the most pressing concerns. For example, during a disease outbreak, key messages might focus on prevention measures, treatment options, and available resources. These messages should be pre-approved and readily available for immediate dissemination.
Managing Media Inquiries and Maintaining a Consistent Narrative
Media inquiries can be intense during a crisis. A designated spokesperson, trained in media relations, is essential for managing these interactions. This spokesperson should deliver consistent messaging across all platforms, avoiding contradictory statements or speculation. The organization should also develop a media response protocol, outlining procedures for handling interviews, press releases, and social media interactions. This protocol should emphasize accuracy, transparency, and empathy.
For example, a pre-prepared Q&A document addressing anticipated questions can streamline responses and ensure consistency.
Regular Review and Update of the Crisis Communication Plan
The healthcare environment is constantly evolving. New technologies, regulations, and potential threats emerge regularly. Therefore, the crisis communication plan should be a living document, reviewed and updated at least annually, or more frequently if significant changes occur within the organization or the external environment. This review should include feedback from team members involved in previous crises, enabling continuous improvement and adaptation.
Regular drills and simulations can also help identify weaknesses and refine procedures. For instance, following a significant weather event that impacted operations, the plan could be revised to incorporate better procedures for managing communication during power outages.
Measuring the Effectiveness of Crisis Communication Efforts
Effective crisis communication isn’t just about reacting swiftly; it’s about understanding whether your strategies truly resonated with patients and staff. Measuring the effectiveness allows you to refine your approach, ensuring future crises are handled with greater efficiency and empathy. This involves a multi-faceted approach encompassing feedback collection, data analysis, and the strategic use of key performance indicators.Evaluating the effectiveness of crisis communication requires a systematic approach focusing on both patient and staff experiences.
This goes beyond simply assessing whether information was disseminated; it delves into how that information was received, understood, and acted upon. By carefully analyzing feedback and key performance indicators, healthcare organizations can identify areas for improvement and build more resilient communication strategies.
Methods for Evaluating Patient and Staff Satisfaction
Gathering feedback from patients and staff is crucial for understanding the impact of your crisis communication. This can be achieved through various methods, including surveys (both online and paper-based), focus groups, and individual interviews. Surveys allow for broad data collection, while focus groups and interviews provide deeper insights into individual experiences and perspectives. For example, a post-crisis survey could ask patients about their understanding of the situation, their level of trust in the healthcare provider, and their overall satisfaction with the communication received.
Similarly, staff surveys could assess their understanding of protocols, their access to information, and their perceived level of support during the crisis.
Collecting and Analyzing Feedback to Identify Areas for Improvement
Once feedback is collected, it needs to be systematically analyzed to identify trends and areas for improvement. This often involves using statistical software to analyze quantitative data from surveys, and thematic analysis to interpret qualitative data from focus groups and interviews. For instance, if a recurring theme in patient feedback highlights difficulty understanding medical terminology used in communications, this suggests a need for simpler, more accessible language in future crisis communication plans.
Similarly, if staff feedback reveals inadequate access to critical information during the crisis, this points to a need for improved internal communication channels.
Effective crisis communication, especially the 5 steps for better patient and staff engagement, is crucial for any healthcare organization. This is even more critical given the current climate, as highlighted by this article on healthcare executives say talent acquisition labor shortages business risk , where staffing shortages directly impact a facility’s ability to respond effectively during a crisis.
Strong internal communication becomes a lifeline, ensuring everyone is informed and prepared, ultimately protecting both patients and staff.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) for Assessing Crisis Communication Success
Several KPIs can be used to assess the success of crisis communication initiatives. These metrics offer quantifiable measures of communication effectiveness. Examples include:
- Patient satisfaction scores: Measured through surveys assessing understanding, trust, and overall satisfaction.
- Staff satisfaction scores: Similar to patient scores, but focusing on staff understanding of protocols, access to information, and perceived support.
- Timeliness of information dissemination: Measuring how quickly critical information reached patients and staff.
- Accuracy of information: Assessing the correctness and consistency of messages across all communication channels.
- Number of complaints or inquiries received: A high number might indicate communication failures requiring attention.
These KPIs, when tracked consistently, can provide a clear picture of communication effectiveness across different crises.
Using Post-Crisis Evaluations to Inform Future Crisis Communication Plans
Post-crisis evaluations are invaluable for refining future crisis communication plans. By analyzing feedback and KPI data, organizations can identify strengths and weaknesses in their existing strategies. For example, if the analysis reveals that social media was ineffective during a particular crisis, the future plan might allocate resources to other communication channels, such as text messaging or email. Furthermore, regular reviews of the crisis communication plan itself, including drills and simulations, should be conducted to ensure it remains up-to-date and relevant.
This iterative process of evaluation and improvement is crucial for building a robust and effective crisis communication system.
Effective crisis communication, especially the 5 steps for better patient and staff engagement, is crucial in healthcare. Tools like generative AI are transforming how we handle these situations; for instance, check out this fascinating interview with Amy Waldron on google cloud healthcare amy waldron generative AI and its potential applications. This technology could revolutionize how quickly and accurately we disseminate vital information during a crisis, ultimately improving patient and staff outcomes.
Last Word
Source: slideteam.net
Mastering crisis communication in healthcare isn’t a one-time fix; it’s an ongoing process of improvement. By implementing these five steps – defining effective communication, building patient engagement, fostering staff collaboration, developing a proactive plan, and measuring effectiveness – you can significantly enhance your organization’s resilience and build stronger relationships based on trust and transparency. Remember, effective communication during a crisis isn’t just about delivering information; it’s about providing reassurance and fostering a sense of shared purpose.
So, invest the time and effort – your patients and staff will thank you for it.
User Queries
What if we don’t have the resources for sophisticated communication technology?
Even simple methods like regular email updates, phone calls, and well-placed posters can be highly effective. Prioritize clear, consistent messaging over technological bells and whistles.
How do we deal with conflicting information from different sources during a crisis?
Designate a single spokesperson to manage all external communications and ensure all internal communications are aligned with the official message. Transparency about uncertainties is better than spreading misinformation.
How do we handle negative social media comments during a crisis?
Respond promptly, empathetically, and professionally. Acknowledge concerns, offer support, and redirect negative comments to appropriate channels. Don’t engage in arguments.
What if a crisis happens outside of normal working hours?
Your crisis communication plan should include an on-call system and pre-designated communication channels for after-hours emergencies. Ensure key personnel have access to necessary information and communication tools.
