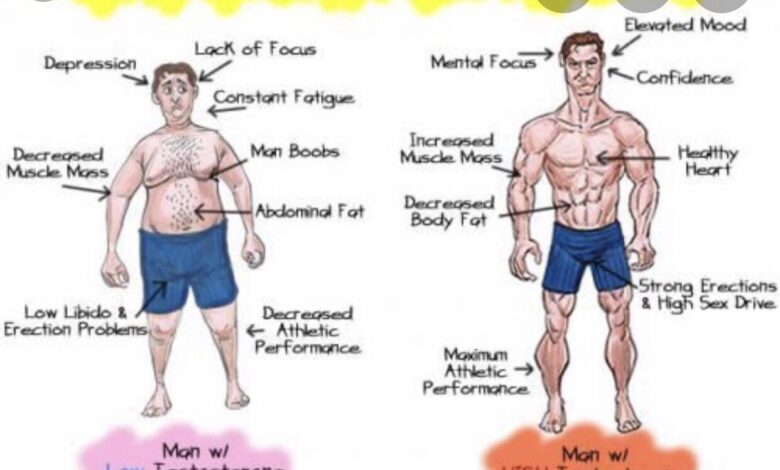
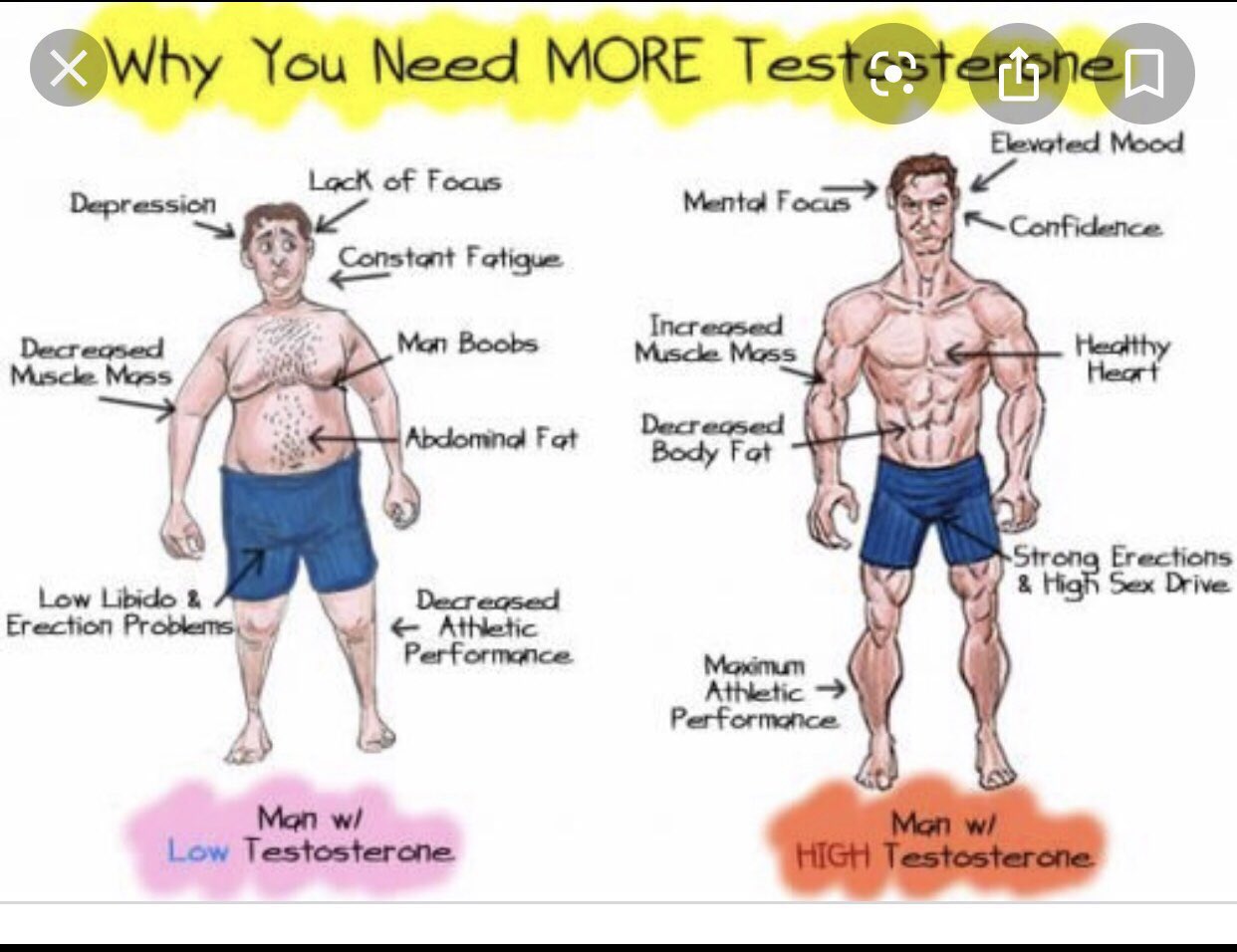
Can Testosterone Affect Your Cholesterol Levels?
Can testosterone affect your cholesterol levels? That’s a question many men, and increasingly women, are asking. Testosterone, the primary male sex hormone, plays a multifaceted role in our bodies, and its influence on cholesterol—the good, the bad, and the triglycerides—is a complex story. We’ll delve into the science behind the connection, exploring how testosterone might impact your lipid profile and what factors can influence this relationship.
Get ready for a fascinating look at this often-overlooked interplay!
Understanding the different types of cholesterol (HDL, LDL, and triglycerides) is crucial. We’ll examine how testosterone might affect their synthesis and breakdown, reviewing the latest research to paint a clearer picture. We’ll also compare its effects in men and women, highlighting the nuances that make each situation unique. Think of it as a personalized cholesterol detective story, where testosterone is the prime suspect!
Testosterone’s Impact on Cholesterol Metabolism: Can Testosterone Affect Your Cholesterol Levels
Testosterone, a crucial hormone for male development and function, also plays a role in lipid metabolism, influencing cholesterol levels. Understanding this interaction is vital because cholesterol, while essential for bodily functions, can contribute to cardiovascular disease if imbalanced. This section will explore the complex relationship between testosterone and cholesterol, examining its effects on different cholesterol fractions and considering variations based on sex.
Cholesterol Fractions and Cardiovascular Health
Cholesterol exists in various forms, each with distinct roles in cardiovascular health. Low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, often called “bad” cholesterol, contributes to plaque buildup in arteries, leading to atherosclerosis and potentially heart attacks or strokes. High-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol, or “good” cholesterol, helps remove LDL cholesterol from the arteries, protecting against cardiovascular disease. Triglycerides are another type of fat in the blood, and high levels are associated with increased risk of heart disease.
Maintaining a healthy balance between these cholesterol fractions is crucial for cardiovascular health.
Mechanisms of Testosterone’s Influence on Cholesterol
Testosterone’s impact on cholesterol metabolism is multifaceted and not fully understood. It’s believed to influence cholesterol synthesis and breakdown through several pathways. For instance, testosterone can affect the activity of enzymes involved in cholesterol production in the liver. Additionally, testosterone might influence the expression of genes regulating cholesterol transport and metabolism. The exact mechanisms are complex and involve interactions with other hormones and metabolic pathways.
Further research is needed to fully elucidate these interactions.
So, I’ve been researching how testosterone impacts cholesterol, and it’s a complex relationship. It seems higher testosterone can sometimes raise LDL (“bad”) cholesterol, which is a concern. But then I stumbled upon this fascinating article about how an eye test might predict dementia risk in older adults, can eye test detect dementia risk in older adults , which made me wonder about the interconnectedness of these seemingly unrelated health markers.
Getting older brings a whole host of hormonal and physiological changes, so understanding these links is crucial for preventative health strategies related to testosterone and cholesterol.
Research on Testosterone’s Effect on Lipid Profiles
Existing research presents a mixed picture of testosterone’s effect on lipid profiles. Some studies suggest that testosterone can increase HDL cholesterol levels and potentially decrease LDL cholesterol in men, potentially improving their lipid profile. However, other studies have found no significant impact or even an adverse effect on cholesterol levels, particularly in certain populations or with higher doses of testosterone.
The inconsistencies might be due to differences in study design, participant characteristics, testosterone administration methods, and the presence of other health conditions. The impact is likely complex and dependent on various factors.
Testosterone’s Effects on Cholesterol in Men and Women
The effects of testosterone on cholesterol levels differ between men and women due to inherent hormonal differences. In men, testosterone replacement therapy (TRT) is sometimes used to address low testosterone levels (hypogonadism). Studies on TRT have shown varying effects on cholesterol, with some showing improvements and others reporting no significant change or even a slight increase in LDL cholesterol.
In women, the impact of testosterone is less extensively studied and generally less pronounced due to lower baseline testosterone levels. Furthermore, the presence of estrogen and other female hormones significantly influences lipid metabolism, complicating the interpretation of testosterone’s effects.
Summary of Testosterone’s Potential Effects on Cholesterol Fractions
| Cholesterol Fraction | Potential Positive Effects of Testosterone | Potential Negative Effects of Testosterone | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| HDL Cholesterol | Increased levels, potentially improving cardiovascular health | Minimal to no reported negative effects consistently across studies | Effect varies based on individual factors and dosage. |
| LDL Cholesterol | May decrease levels in some individuals, improving cardiovascular risk | May increase levels in some individuals, increasing cardiovascular risk | Inconsistencies across studies highlight the complexity of this relationship. |
| Triglycerides | Some studies show slight decreases; further research is needed. | May increase levels in some individuals, potentially worsening cardiovascular risk. | The impact is less consistently studied than the effects on HDL and LDL. |
Factors Influencing the Relationship Between Testosterone and Cholesterol
The relationship between testosterone and cholesterol isn’t straightforward; it’s a complex interplay influenced by several factors beyond just testosterone levels. Understanding these contributing elements is crucial for accurately assessing individual risk and tailoring appropriate interventions. While testosterone can sometimes negatively affect cholesterol profiles, the overall picture is nuanced and depends heavily on individual circumstances.
Age and Testosterone’s Effect on Cholesterol, Can testosterone affect your cholesterol levels
Age significantly impacts both testosterone production and cholesterol metabolism. As men age, their testosterone levels naturally decline, often leading to changes in lipid profiles. This age-related decline can be accompanied by increased LDL (“bad”) cholesterol and decreased HDL (“good”) cholesterol, even independently of testosterone replacement therapy (TRT). Conversely, in younger men, the impact of testosterone on cholesterol may be different, potentially showing less of a negative effect or even a positive influence in some cases.
Therefore, considering a man’s age is paramount when evaluating the interplay between testosterone and cholesterol.
Dietary Habits and Cholesterol Management
Diet plays a pivotal role in cholesterol levels, regardless of testosterone status. A diet high in saturated and trans fats directly elevates LDL cholesterol, while a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and fiber promotes healthier cholesterol profiles. This is especially important for men undergoing TRT, as a poor diet can exacerbate any negative impact of testosterone on lipids. Conversely, a healthy diet can potentially mitigate or even counteract some of the adverse effects.
For instance, a diet focused on omega-3 fatty acids, found in fatty fish, can help raise HDL cholesterol levels and improve overall cardiovascular health.
Exercise and its Influence on Lipid Profiles
Regular physical activity is a cornerstone of cardiovascular health and positively impacts cholesterol levels. Exercise helps lower LDL cholesterol, raise HDL cholesterol, and improve overall lipid profiles. This benefit applies whether or not an individual is receiving TRT. In fact, incorporating regular exercise into a lifestyle alongside TRT can significantly lessen the potential negative effects of testosterone on cholesterol, acting as a powerful counterbalance.
Studies have shown that even moderate exercise can produce significant improvements in cholesterol levels.
Genetic Predisposition and Cholesterol Levels
Genetic factors play a substantial role in determining both baseline cholesterol levels and individual responses to testosterone. Some individuals are genetically predisposed to higher cholesterol levels, regardless of their testosterone levels or lifestyle choices. Family history of high cholesterol or cardiovascular disease is a significant risk factor that should be considered alongside testosterone’s impact. Genetic testing can provide valuable insight into individual susceptibility and inform personalized management strategies.
Pre-existing Conditions and Cholesterol
Pre-existing conditions such as diabetes, obesity, and metabolic syndrome can significantly influence cholesterol levels and interact with testosterone. These conditions often involve dyslipidemia (abnormal lipid levels) independently of testosterone. Therefore, managing these underlying health issues is crucial before considering TRT or when assessing the impact of naturally occurring testosterone levels on cholesterol. Treating these conditions effectively can help improve cholesterol profiles, regardless of testosterone levels.
Interactions Between Testosterone Therapy and Cholesterol-Lowering Medications
Testosterone therapy can interact with cholesterol-lowering medications, such as statins. In some cases, these interactions may require adjustments in medication dosages or careful monitoring of cholesterol levels. It’s essential to have open communication with your physician if you are considering TRT and are already taking cholesterol-lowering medications. Close monitoring of lipid profiles is crucial to ensure safe and effective management.
Dietary Choices: Mitigating or Exacerbating Effects
The following dietary choices can either mitigate or exacerbate the effects of testosterone on cholesterol:
- Mitigating Effects: Increasing consumption of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins (fish, poultry), and healthy fats (avocado, nuts, olive oil).
- Exacerbating Effects: Consuming excessive amounts of saturated and trans fats found in red meat, processed foods, fried foods, and baked goods.
Testosterone Replacement Therapy and Cholesterol

Source: healthyhormones.us
So, testosterone and cholesterol – it’s a complex relationship, right? Men’s higher testosterone levels can sometimes impact cholesterol profiles, but it’s not a simple cause-and-effect. Understanding how diet plays a role is crucial, which brings me to a fascinating article I recently read: are women and men receptive of different types of food and game changing superfoods for women , highlighting how dietary choices can significantly influence both hormone levels and cholesterol.
Ultimately, managing cholesterol effectively often requires a personalized approach, considering individual factors and dietary needs.
Testosterone replacement therapy (TRT) is a common treatment for men with low testosterone levels (hypogonadism). However, the impact of TRT on cholesterol levels is a complex issue, with both potential benefits and risks that need careful consideration. Understanding this relationship is crucial for both doctors and patients making informed decisions about TRT.TRT can influence cholesterol levels in several ways, leading to both positive and negative effects.
The overall impact varies significantly depending on individual factors, baseline cholesterol levels, and the specific type and dosage of testosterone used.
Potential Risks and Benefits of TRT on Cholesterol Levels
While TRT can sometimes improve certain aspects of the lipid profile, it also carries the potential to negatively affect others. For instance, some studies suggest that TRT may increase LDL (“bad”) cholesterol levels, particularly in individuals already at risk for cardiovascular disease. Conversely, it might increase HDL (“good”) cholesterol and reduce triglycerides in some men. The net effect on cardiovascular risk is not consistently clear and depends on the individual’s overall health profile and response to the therapy.
It’s important to note that these effects are not universally experienced, and the magnitude of change varies considerably. A careful assessment of the individual’s risk factors is crucial before initiating TRT.
Monitoring Strategies for Cholesterol During TRT
Regular monitoring of cholesterol levels is essential during TRT. This typically involves periodic blood tests to measure total cholesterol, LDL cholesterol, HDL cholesterol, and triglycerides. The frequency of these tests depends on the individual’s baseline lipid profile, risk factors for cardiovascular disease, and response to therapy. Generally, baseline cholesterol levels are assessed before initiating TRT, and then monitored at regular intervals (e.g., every 3-6 months) during treatment.
Any significant changes in cholesterol levels should be carefully evaluated, and adjustments to the TRT regimen or other medical interventions may be necessary. For example, if LDL cholesterol increases significantly, lifestyle modifications (diet and exercise) or lipid-lowering medications might be recommended in conjunction with TRT.
So, I’ve been researching how testosterone impacts cholesterol, and it’s a complex relationship. It’s fascinating to consider the hormonal shifts women experience, like those discussed in this article about Karishma Mehta freezing her eggs – karishma mehta gets her eggs frozen know risks associated with egg freezing – and how those might interact with cholesterol levels.
Ultimately, managing cholesterol, whether you’re considering hormone changes or not, is crucial for long-term health.
Decision-Making Flowchart for Prescribing TRT Considering Cholesterol Levels
The decision to prescribe TRT should be a careful and individualized process. A flowchart can help visualize this decision-making process:[Diagram Description: The flowchart would begin with a box labeled “Patient presents with symptoms of hypogonadism and low testosterone levels.” This would lead to two branches: “Patient has normal or near-normal cholesterol levels” and “Patient has abnormal cholesterol levels (high LDL, low HDL, high triglycerides).” The first branch would lead to a box labeled “Consider TRT, initiate therapy, and monitor cholesterol levels regularly.” The second branch would lead to a box labeled “Assess cardiovascular risk factors and overall health.” This box would branch to two more boxes: “High cardiovascular risk” and “Low cardiovascular risk.” The “High cardiovascular risk” branch would lead to a box labeled “Weigh risks and benefits carefully; consider lifestyle modifications and/or lipid-lowering medication before initiating TRT.” The “Low cardiovascular risk” branch would lead to a box labeled “Consider TRT, initiate therapy, and monitor cholesterol levels very closely.” All branches ultimately lead to a final box: “Regular monitoring of cholesterol and testosterone levels.” This flowchart visually represents the careful consideration needed when balancing the benefits of TRT with the potential risks related to cholesterol.]
Clinical Implications and Individual Variability
The relationship between testosterone and cholesterol isn’t a simple one-size-fits-all scenario. While some men experience beneficial effects on their lipid profiles with testosterone therapy, others may see negative changes, highlighting the crucial need for individualized assessment and management. Understanding the nuances of this interaction is paramount for clinicians and patients alike to ensure safe and effective testosterone replacement therapy (TRT).The impact of testosterone on cholesterol levels varies significantly depending on several factors, including baseline lipid profiles, age, the presence of other health conditions, and the dosage and type of testosterone administered.
Ignoring this variability can lead to potentially harmful consequences, emphasizing the importance of careful monitoring and personalized treatment strategies.
Patient Populations Susceptible to Adverse Effects
Several patient populations are more likely to experience adverse effects on cholesterol levels from testosterone. These include individuals with pre-existing hyperlipidemia (high cholesterol), metabolic syndrome, a history of cardiovascular disease, or those with a family history of these conditions. Men with insulin resistance or type 2 diabetes are also at increased risk, as testosterone can sometimes negatively impact insulin sensitivity, potentially exacerbating existing metabolic issues.
Older men, due to age-related changes in lipid metabolism, may also be more susceptible to adverse cholesterol changes with testosterone therapy. Careful monitoring of lipid profiles is particularly critical in these high-risk groups.
Personalized Management Strategies for Healthy Cholesterol
Effective management of cholesterol levels in men using testosterone requires a personalized approach. This begins with a thorough baseline assessment, including a complete lipid profile (total cholesterol, LDL cholesterol, HDL cholesterol, and triglycerides), assessment of cardiovascular risk factors, and a comprehensive medical history. Regular monitoring of lipid profiles during TRT is essential, typically every 3-6 months, to detect any significant changes.
If adverse changes are observed, adjustments to the testosterone dosage, formulation, or the addition of cholesterol-lowering medications (statins or other lipid-lowering agents) may be necessary. Lifestyle modifications, such as diet and exercise, play a crucial role in supporting healthy cholesterol levels and should be strongly encouraged.
Hypothetical Case Study: Mr. Jones and TRT
Mr. Jones, a 58-year-old male, presented with symptoms of hypogonadism, including decreased libido, fatigue, and erectile dysfunction. His baseline lipid profile revealed slightly elevated LDL cholesterol (145 mg/dL) and low HDL cholesterol (35 mg/dL), placing him at moderate cardiovascular risk. He commenced TRT with a low dose of testosterone gel. After three months, his LDL cholesterol increased to 160 mg/dL, while his HDL cholesterol remained low.
His physician adjusted his testosterone dosage downward and introduced a statin medication. Regular monitoring over the next six months showed a gradual reduction in LDL cholesterol to 130 mg/dL and a slight improvement in HDL cholesterol to 40 mg/dL. This case illustrates the importance of close monitoring and the need for individualized adjustments to TRT based on individual responses and risk factors.
Mr. Jones’ initial response highlighted the potential for adverse effects in men with pre-existing dyslipidemia, emphasizing the necessity for proactive management and the potential need for adjunctive therapies.
Future Research Directions

Source: 222ta.co
While significant progress has been made in understanding the interplay between testosterone and cholesterol, several key areas require further investigation to paint a complete picture of this complex relationship. A more nuanced understanding will not only enhance our diagnostic capabilities but also pave the way for the development of more personalized and effective therapeutic strategies.The current literature reveals inconsistencies in the observed effects of testosterone on cholesterol levels, highlighting the need for more robust and comprehensive research designs.
This includes larger, more diverse patient populations and longer-term follow-up studies to accurately capture the long-term effects of testosterone fluctuations and interventions. Furthermore, the influence of genetic factors, lifestyle choices, and comorbidities on this relationship remains largely under-explored.
Investigating Genetic Predisposition and Lifestyle Factors
A deeper understanding of individual genetic variations influencing the response to testosterone and its impact on lipid profiles is crucial. Genome-wide association studies (GWAS) could identify specific genes that modulate the interaction between testosterone and cholesterol metabolism. Concurrently, the impact of lifestyle factors, such as diet, exercise, and smoking, on this relationship needs further scrutiny. For instance, research could explore whether a Mediterranean diet, known for its cardioprotective effects, modifies the effect of testosterone on LDL cholesterol in men with hypogonadism.
Similarly, the effects of regular exercise on HDL cholesterol levels in the context of testosterone replacement therapy require further investigation. This multifaceted approach would help personalize treatment strategies based on an individual’s genetic profile and lifestyle.
Developing Novel Therapeutic Approaches
Current treatments for dyslipidemia often focus on individual lipid parameters, neglecting the potential interplay with hormonal levels. Future research should focus on developing novel therapeutic approaches that target both testosterone and cholesterol metabolism simultaneously. This might involve the development of new drugs that modulate both testosterone production and lipid profiles, or the optimization of existing therapies to minimize adverse effects on lipid levels.
For example, researchers could investigate the potential of selective androgen receptor modulators (SARMs) that preferentially target tissues benefiting from androgenic effects while minimizing systemic effects on lipid profiles. Alternatively, combining existing cholesterol-lowering drugs with testosterone replacement therapy, while carefully monitoring lipid profiles, could be explored. The development of personalized treatment plans based on individual lipid profiles and testosterone levels will improve the efficacy and safety of therapeutic interventions.
Concluding Remarks
Source: twimg.com
So, can testosterone affect your cholesterol levels? The answer, as we’ve seen, is a nuanced “yes,” depending on individual factors and the specific type of cholesterol. While testosterone replacement therapy (TRT) might offer benefits, careful monitoring of cholesterol levels is crucial. Lifestyle choices, like diet and exercise, play a significant role in mitigating potential negative effects. Ultimately, a personalized approach, guided by your doctor, is key to maintaining healthy cholesterol levels, regardless of your testosterone levels.
It’s all about finding the right balance for your body’s unique needs!
Expert Answers
What are the early warning signs of high cholesterol?
High cholesterol often has no noticeable symptoms. Regular blood tests are the best way to detect it.
Can diet alone lower high cholesterol?
Dietary changes can significantly improve cholesterol levels for some, but medication might be necessary for others.
Is it safe to take testosterone supplements without a doctor’s supervision?
No, absolutely not. Testosterone supplements can have serious side effects and should only be used under medical supervision.
How often should I get my cholesterol checked?
Frequency depends on your risk factors and your doctor’s recommendations. Adults should generally have their cholesterol checked at least every 5 years.
