
Ear Pimples Causes & How to Get Rid of Them
Ear pimples: causes of pimple formation in ear and how to get rid of it – that’s the burning question we’re tackling today! Ever felt that annoying itch or throbbing pain inside your ear? It might be a pimple, and while seemingly insignificant, these little bumps can be surprisingly bothersome. We’ll delve into the anatomy of your ear canal, the culprits behind those pesky pimples (bacteria, inflammation, even your own earwax!), and explore effective home remedies and when you should seek professional help.
Get ready to banish those ear pimples for good!
From understanding the different types of bacteria that thrive in your ear canal to exploring the role of sebaceous glands and excessive earwax buildup, we’ll cover it all. We’ll also look at how underlying skin conditions like acne and eczema can contribute to ear pimples. We’ll equip you with practical, step-by-step guides on safe ear cleaning techniques, the benefits of warm compresses, and the responsible use of over-the-counter treatments.
We’ll even touch on natural remedies, but remember, safety first! Finally, we’ll Artikel when to seek medical attention, because sometimes, those ear pimples need a professional’s touch.
Understanding Ear Pimple Formation: Causes Of Pimple Formation In Ear And How To Get Rid Of It
Ear pimples, also known as furuncles or boils, are a common annoyance that can cause significant discomfort. They occur within the ear canal, a complex structure susceptible to infection due to its unique anatomy and environment. Understanding the causes and characteristics of these pimples is crucial for effective treatment and prevention.
Ear Canal Anatomy and Susceptibility to Infection
The ear canal is a narrow, S-shaped tube lined with skin containing hair follicles, sweat glands, and ceruminous glands that produce earwax. This skin is continuous with the skin of the outer ear and is prone to irritation and infection. The presence of hair follicles makes the ear canal susceptible to folliculitis, an inflammation of the hair follicles, which can lead to pimple formation.
Furthermore, the ear canal’s relatively moist and warm environment provides an ideal breeding ground for bacteria. The natural accumulation of earwax, while protective, can also trap bacteria and debris, increasing the risk of infection if not properly managed.
Bacteria Involved in Ear Pimple Formation
Several types of bacteria are commonly implicated in ear pimple development. Staphylococcus aureus is a frequent culprit, known for its ability to cause skin infections. Other bacteria, such as Pseudomonas aeruginosa and various streptococcal species, can also contribute to ear infections leading to pimple formation. These bacteria often colonize the skin of the ear canal, and under certain conditions, can proliferate and cause infection.
The presence of these bacteria doesn’t automatically mean a pimple will form; however, they are crucial factors in the development of infection.
Factors Triggering Ear Pimple Formation
Several factors can trigger ear pimple formation. Poor hygiene practices, such as infrequent cleaning of the ear canal or the use of contaminated cotton swabs, can introduce bacteria and irritate the skin. Ear piercings, particularly if not properly cared for, can create entry points for infection. Underlying medical conditions, such as diabetes, which can compromise the immune system, can increase susceptibility to infections, including ear pimples.
Finally, trauma to the ear canal, such as from scratching or inserting foreign objects, can also create an environment conducive to infection.
Symptoms of Ear Pimples
Ear pimples typically present with localized pain, swelling, and redness in the affected area of the ear canal. There may also be pus-filled discharge from the pimple. The severity of symptoms can vary depending on the size and extent of the infection. In some cases, the swelling can be significant enough to partially or completely obstruct the ear canal, leading to hearing difficulties.
Fever and enlarged lymph nodes in the neck may also occur in more severe cases.
Symptom Summary Table, Causes of pimple formation in ear and how to get rid of it
| Symptom | Severity | Possible Cause | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pain | Mild to severe | Inflammation, infection | Over-the-counter pain relievers, warm compress |
| Swelling | Mild to severe | Inflammatory response, infection | Warm compress, avoid touching or squeezing |
| Redness | Mild to moderate | Inflammation | Avoid irritating the area |
| Pus-filled discharge | Variable | Bacterial infection | Consult a doctor for appropriate treatment |
Common Causes of Ear Pimples
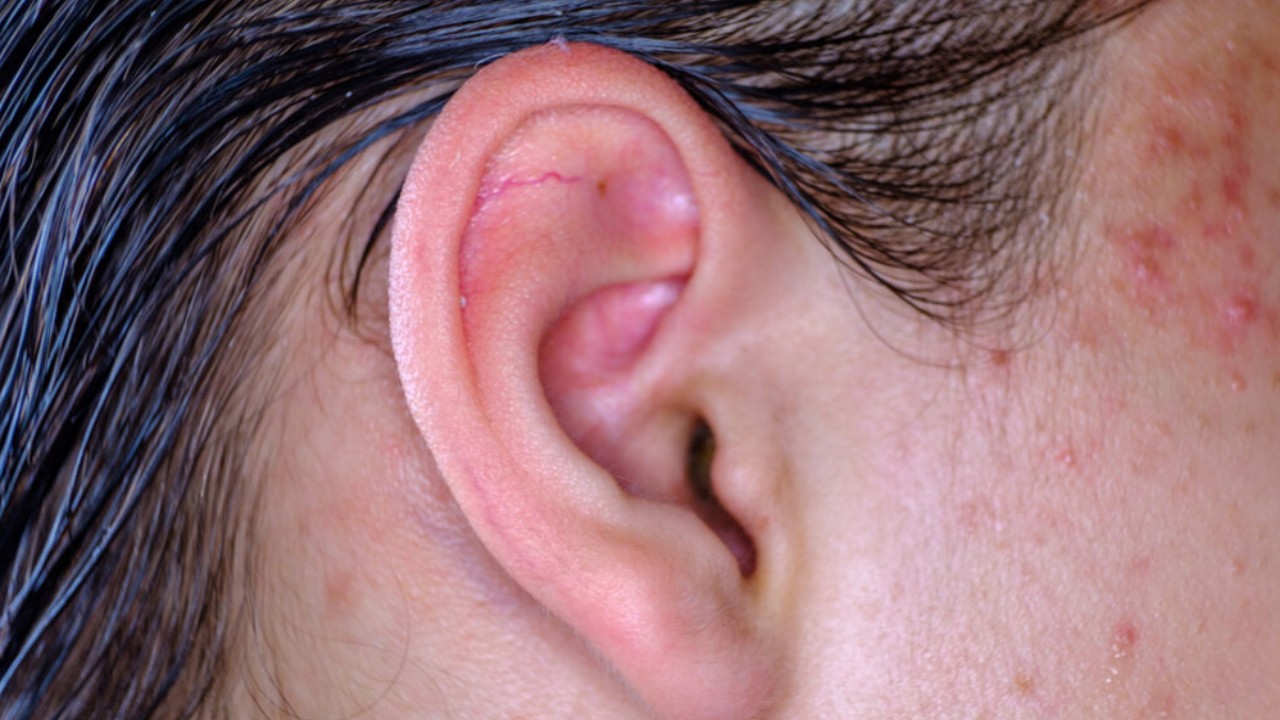
Source: pinkvilla.com
Ear pimples, while less common than facial acne, can be surprisingly bothersome. Understanding their causes is the first step towards effective treatment. Several factors contribute to their formation, often involving a combination of internal and external influences. Let’s delve into the specifics.
The Role of Sebaceous Glands in Ear Pimple Formation
Sebaceous glands are tiny oil-producing glands found throughout the body, including the ear canal. These glands secrete sebum, an oily substance that lubricates the skin and hair. In the ear, an overproduction of sebum, perhaps due to hormonal fluctuations or genetic predisposition, can clog pores. This blockage traps bacteria and dead skin cells, creating a breeding ground for inflammation and ultimately, a pimple.
The trapped sebum can also oxidize, leading to the formation of blackheads or comedones, which can then become inflamed and infected.
The Impact of Excessive Earwax Buildup
Earwax, or cerumen, is a naturally occurring substance that protects the ear canal. However, excessive buildup of earwax can create a similar problem to sebum overproduction. The waxy substance can clog pores, trapping dirt, debris, and bacteria. This trapped material can irritate the skin, leading to inflammation and the formation of pimples. Furthermore, the moist environment created by excessive earwax provides an ideal breeding ground for bacteria and fungi, potentially leading to infection and more severe inflammation.
Inflammation and Infection as Contributors to Ear Pimple Formation
Inflammation is a key player in the development of ear pimples. Any irritation or blockage of the pores in the ear canal, as discussed above, triggers an inflammatory response. This response involves the body sending immune cells to the affected area, causing redness, swelling, and pain. If bacteria invade the clogged pore, an infection can develop, further exacerbating the inflammation and resulting in a larger, more painful pimple.
Common bacteria involved include Staphylococcus aureus.
The Connection Between Skin Conditions and Ear Pimples
Certain skin conditions can predispose individuals to developing ear pimples. Acne, a common skin condition characterized by clogged pores and inflammation, can manifest in the ear canal. Similarly, eczema, a chronic inflammatory skin condition, can cause irritation and inflammation in the ear, making it more susceptible to pimple formation. Individuals with these conditions may find that their ear pimples are more frequent or severe.
Categorization of Ear Pimple Causes by Underlying Mechanism
The causes of ear pimples can be broadly categorized by their underlying mechanisms:
- Obstructive: Excessive sebum production, excessive earwax buildup, and foreign bodies blocking pores.
- Inflammatory: Irritation from earwax, foreign bodies, or allergic reactions, leading to inflammation.
- Infectious: Bacterial or fungal infections, often secondary to obstruction or inflammation.
- Dermatological: Manifestations of underlying skin conditions such as acne or eczema.
Home Remedies and Treatments for Ear Pimples

Source: resurchify.com
Dealing with an ear pimple can be uncomfortable, but thankfully, several home remedies and treatments can provide relief and promote healing. Remember, however, that these methods are for outer ear pimples only. If you experience pain, significant swelling, or pus discharge, consult a doctor immediately.
Safe Outer Ear Cleaning to Prevent Pimple Formation
Regular, gentle cleaning of the outer ear is crucial in preventing pimple formation. Avoid using cotton swabs, which can push dirt and bacteria further into the ear canal and potentially damage the eardrum. Instead, use a soft, damp washcloth to gently wipe the outer ear and visible parts of the ear canal. This should be done daily as part of your regular hygiene routine.
Excessive cleaning, however, can irritate the skin, so moderation is key.
Application of Warm Compresses to Reduce Swelling and Pain
Warm compresses can help reduce swelling and pain associated with ear pimples. The heat increases blood flow to the area, promoting healing and reducing inflammation.
Over-the-Counter Topical Treatments for Ear Pimples
Several over-the-counter topical treatments can help manage ear pimples. Antiseptic creams containing ingredients like benzoyl peroxide can kill bacteria and reduce inflammation. However, benzoyl peroxide can sometimes cause skin dryness and irritation. Antibiotic ointments, containing bacitracin or neomycin, can help fight bacterial infections. However, prolonged use can lead to antibiotic resistance, and some individuals may experience allergic reactions.
Always follow the product instructions carefully and discontinue use if irritation occurs.
Homemade Remedy Using Natural Ingredients
A diluted tea tree oil solution can be applied topically to the pimple. Tea tree oil possesses antimicrobial properties, but it can be irritating to the skin if used undiluted. Always dilute it with a carrier oil like coconut oil (a ratio of 1:10 tea tree oil to carrier oil is a good starting point). Aloe vera gel, known for its soothing and anti-inflammatory properties, can also be applied directly to the pimple.
However, ensure the aloe vera product is pure and free of additives that might irritate sensitive skin. Always perform a patch test on a small area of skin before applying any homemade remedy to the entire affected area.
Visual Representation of Applying a Warm Compress
The image depicts a person gently holding a clean, soft washcloth, saturated with warm (not hot) water, against the affected area of their outer ear. The washcloth is folded to a comfortable size and thickness, covering the pimple without pressing too hard. The person’s expression is relaxed and comfortable, suggesting a gentle and soothing application. The background is simple and uncluttered, focusing attention on the process of applying the compress.
The overall tone of the image is calm and reassuring.
When to Seek Medical Attention
Ear pimples, while often minor annoyances, can sometimes signal a more serious underlying issue. Ignoring persistent or worsening symptoms can lead to complications, so understanding when professional help is needed is crucial. This section will Artikel the warning signs, potential complications, treatment options, and a decision-making process to guide you.
Signs and Symptoms Requiring Medical Evaluation
Several signs indicate that your ear pimple requires a doctor’s attention. These include significant pain, swelling extending beyond the immediate pimple area, fever, redness spreading across the ear or face, pus discharge with a foul odor, hearing loss or muffled sounds, and symptoms persisting for more than a week despite home treatment. The presence of any of these symptoms suggests a possible infection requiring medical intervention.
For example, a pimple accompanied by a high fever could indicate a systemic infection, demanding immediate medical attention.
Potential Complications of Untreated Ear Pimples
Untreated ear pimples can lead to several complications. Infection can spread from the pimple to surrounding tissues, potentially causing cellulitis (a bacterial skin infection) or even more serious infections. In some cases, the infection might reach the middle ear, leading to otitis media (middle ear infection), which can cause significant pain and hearing loss. Severe infections can also result in permanent hearing damage or, in rare instances, spread to the brain, causing life-threatening conditions like meningitis.
Ignoring a seemingly minor ear pimple could have severe repercussions.
Medical Treatments for Severe Ear Pimples
For severe ear pimples, medical treatments are often necessary. Antibiotics, either oral or topical, are commonly prescribed to combat bacterial infections. If the pimple is large and filled with pus, a doctor might perform a minor surgical procedure to drain the infection. This involves making a small incision to release the pus and promote healing. In cases of severe infection or complications like cellulitis, hospitalization and intravenous antibiotics may be required.
The choice of treatment depends on the severity of the infection and the individual’s overall health.
Situations Where Home Remedies Are Insufficient
Home remedies are effective for minor ear pimples that show signs of improvement. However, they are insufficient when dealing with severe pain, significant swelling, signs of spreading infection (redness, warmth, swelling beyond the initial area), fever, pus with foul odor, or hearing impairment. If a pimple is accompanied by any of these symptoms, delaying professional medical care can lead to worsening of the condition and potentially serious complications.
For instance, attempting to treat a pimple that is already accompanied by a fever with home remedies is inappropriate and could delay necessary medical intervention.
Decision-Making Flowchart for Ear Pimple Treatment
The following flowchart Artikels the decision-making process for determining whether to treat an ear pimple at home or seek medical advice:[Imagine a flowchart here. It would start with a box: “Ear Pimple Present?” Yes leads to: “Pain, Swelling, Redness, Pus, Fever, Hearing Loss?” Yes leads to “Seek Medical Attention”. No leads to “Try Home Remedies”. A box under “Try Home Remedies” would say “Improvement within 1 week?”.
Yes leads to “Continue Home Remedies”. No leads to “Seek Medical Attention”.]
Prevention Strategies for Ear Pimples

Source: optiderma.com
Preventing ear pimples involves a multifaceted approach focusing on maintaining good ear hygiene and addressing underlying skin conditions. Regular cleaning and careful handling of your ears and any assistive devices can significantly reduce your risk of developing these bothersome blemishes.
Maintaining Good Ear Hygiene
Cleanliness is paramount in preventing ear pimples. The outer ear, particularly the area around the ear canal opening, is susceptible to the buildup of dirt, oil, and bacteria, all of which can contribute to pimple formation. Regular cleaning helps to remove these irritants and create a less hospitable environment for bacteria to thrive. Ignoring this can lead to inflammation and subsequent pimples.
Best Practices for Cleaning the Outer Ear
Proper cleaning techniques are crucial. Avoid harsh scrubbing, which can irritate the delicate skin around your ears.
- Use a soft, damp washcloth to gently cleanse the outer ear and surrounding skin during your daily shower or bath.
- For stubborn dirt or oil, consider using a mild, fragrance-free cleanser specifically designed for sensitive skin. Apply a small amount to the washcloth and gently wipe the area.
- Rinse thoroughly with warm water to remove any residue.
- Pat the area dry with a clean towel; avoid rubbing.
Appropriate tools are just as important as the techniques. Avoid anything abrasive or potentially damaging to the delicate ear skin.
Risks Associated with Cleaning the Inner Ear
It is critically important to avoid inserting cotton swabs or other objects into the ear canal. This practice can push earwax deeper into the canal, potentially leading to impaction, infection, and even damage to the eardrum. Earwax naturally migrates out of the ear canal, and attempting to remove it manually often does more harm than good. If you suspect a wax buildup, consult a doctor or audiologist.
Managing Underlying Skin Conditions
Certain skin conditions, such as acne or seborrheic dermatitis, can predispose individuals to ear pimples. Managing these conditions effectively can significantly reduce the risk of pimple formation in the ears. This may involve topical treatments prescribed by a dermatologist or other appropriate medical professional. These treatments often focus on controlling inflammation and reducing bacterial growth. Regular consultation with a dermatologist is recommended for ongoing management of these conditions.
Cleaning Hearing Aids to Prevent Ear Infections and Pimples
Hearing aids, if not cleaned properly, can become breeding grounds for bacteria and contribute to ear infections and pimples.
- Follow the manufacturer’s instructions carefully for cleaning your specific hearing aid model. This often involves using a soft, dry cloth or a specialized cleaning brush to remove debris.
- For more thorough cleaning, use a mild soap and water solution, ensuring the aid is completely dry before reinsertion.
- Regularly inspect the hearing aid for any signs of damage or buildup, and replace any worn components as recommended by the audiologist.
- Store hearing aids in a clean, dry case when not in use to prevent dust and moisture accumulation.
Proper hearing aid hygiene is essential for maintaining ear health and preventing complications.
Ending Remarks
So, there you have it – a comprehensive guide to conquering those ear pimples! Remember, maintaining good ear hygiene is key to prevention. Regular, gentle cleaning of the outer ear, avoiding cotton swabs, and addressing any underlying skin conditions can significantly reduce your risk. While home remedies can be effective for mild cases, don’t hesitate to seek medical advice if your pimple is particularly painful, persistent, or accompanied by other concerning symptoms.
Your ears deserve the best care, so take charge of your ear health and keep those pimples at bay!
Common Queries
Can ear pimples cause hearing loss?
Usually not, unless the infection is severe and spreads to the middle ear. If you experience hearing changes alongside an ear pimple, seek medical attention immediately.
Are ear pimples contagious?
Generally, no. However, if the pimple is caused by a bacterial infection, it’s crucial to practice good hygiene to prevent spreading it to other areas of your body.
How long does it take for an ear pimple to heal?
This varies depending on the cause and severity. Minor pimples may clear up within a few days, while more significant ones may take a week or more. Persistent pimples require medical attention.
Can I pop an ear pimple?
Absolutely not! Popping it can worsen the infection, lead to scarring, and potentially damage your eardrum. Resist the urge!
