How to Know If You Need Medicine for Blood Pressure
How to know if you need medicine for blood pressure? It’s a question many of us ponder, especially as we age or if we have a family history of heart issues. High blood pressure, or hypertension, often has no noticeable symptoms, making it a silent threat. Understanding your blood pressure readings, recognizing risk factors, and knowing when to seek professional help are crucial steps in managing your heart health.
This post will guide you through the process of determining if medication is necessary for you, while also highlighting the importance of lifestyle changes that can significantly impact your blood pressure.
We’ll explore the different stages of hypertension, the various ways to monitor your blood pressure effectively, and discuss the potential long-term health consequences of untreated high blood pressure. We’ll also delve into the different types of blood pressure medications available, their potential side effects, and the vital role your doctor plays in creating a personalized treatment plan. Ultimately, the goal is to empower you with the knowledge to make informed decisions about your health and to work collaboratively with your healthcare provider to achieve optimal blood pressure management.
Understanding Blood Pressure Readings
Source: universityhealthnews.com
Knowing your blood pressure numbers is crucial for managing your heart health. Understanding what those numbers mean and what influences them is the first step in taking control. This section will break down the components of a blood pressure reading and discuss factors that can affect the results.
Blood Pressure Components: Systolic and Diastolic Pressure
Blood pressure is measured in millimeters of mercury (mmHg) and consists of two numbers: systolic and diastolic pressure. Systolic pressure is the higher number, representing the pressure in your arteries when your heart beats and pushes blood out. Diastolic pressure is the lower number, indicating the pressure in your arteries when your heart rests between beats. A healthy blood pressure reading reflects a balance between these two phases of the cardiac cycle.
For example, a reading of 120/80 mmHg means a systolic pressure of 120 mmHg and a diastolic pressure of 80 mmHg.
Blood Pressure Categories
It’s essential to understand how your blood pressure reading fits into established categories. These categories help determine the level of risk and guide treatment decisions. The following table Artikels the different blood pressure categories according to the American Heart Association and American College of Cardiology guidelines:
| Category | Systolic (mmHg) | Diastolic (mmHg) | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Normal | Less than 120 | Less than 80 | Blood pressure is within a healthy range. |
| Elevated | 120-129 | Less than 80 | Blood pressure is higher than normal, increasing the risk of hypertension. |
| Stage 1 Hypertension | 130-139 | 80-89 | Indicates hypertension, requiring lifestyle modifications and possibly medication. |
| Stage 2 Hypertension | 140 or higher | 90 or higher | Indicates high blood pressure, necessitating medical intervention and lifestyle changes. |
Factors Influencing Blood Pressure Readings
Several factors can influence your blood pressure reading, making it crucial to have multiple readings taken under different circumstances for an accurate assessment. These factors include:
Time of day: Blood pressure tends to be lower in the morning and higher in the evening. This natural variation highlights the importance of consistent monitoring throughout the day if necessary.
Stress: Experiencing stress can cause a temporary spike in blood pressure. Chronic stress can contribute to persistently elevated blood pressure.
Activity level: Physical activity can temporarily increase blood pressure, but regular exercise generally contributes to lower blood pressure in the long term. Immediately after strenuous activity, blood pressure may be higher than usual.
Medications: Certain medications can affect blood pressure, either raising or lowering it. It’s essential to discuss any medications you’re taking with your doctor.
Caffeine and alcohol: Both caffeine and alcohol can cause temporary increases in blood pressure. Excessive consumption can contribute to long-term high blood pressure.
Hydration: Dehydration can lead to increased blood pressure. Maintaining adequate fluid intake is important for blood pressure regulation.
Recognizing Symptoms of High Blood Pressure
High blood pressure, or hypertension, is often called a “silent killer” because it frequently shows no noticeable symptoms. This makes regular check-ups crucial for early detection and management. Many people live with high blood pressure for years without realizing it, leading to serious health problems down the line. Understanding potential symptoms, even if subtle, can prompt you to seek medical attention.Many people with high blood pressure experience no symptoms at all, even when their blood pressure is dangerously high.
This is why regular checkups are so important. However, some people may experience certain symptoms, though these are often non-specific and could be indicative of other health issues.
Common Symptoms Associated with High Blood Pressure
It’s important to understand that the symptoms listed below are not always directly caused by high blood pressure and can be associated with a variety of other health conditions. If you experience any of these, it is vital to consult your doctor for proper diagnosis and management. They may order a blood pressure test and other examinations to determine the underlying cause of your symptoms.
- Severe headaches: These are often described as throbbing headaches, particularly in the back of the head. They can be persistent and intense.
- Dizziness or lightheadedness: A feeling of faintness or unsteadiness can sometimes be a sign of high blood pressure.
- Shortness of breath: Difficulty breathing, especially with exertion, could be a symptom.
- Nosebleeds: Frequent or unusually severe nosebleeds may be a warning sign.
- Fatigue: Persistent tiredness and lack of energy can be indicative of various health problems, including hypertension.
Long-Term Health Consequences of Untreated Hypertension
Untreated high blood pressure significantly increases your risk of developing serious and life-threatening health conditions. The sustained high pressure on your blood vessels damages them over time, leading to a cascade of problems.
- Heart disease: High blood pressure is a major risk factor for coronary artery disease, heart attacks, and heart failure. The constant strain on the heart weakens it and makes it less efficient.
- Stroke: Hypertension dramatically increases the risk of stroke, which occurs when blood flow to the brain is interrupted. This can cause permanent brain damage or death.
- Kidney disease: High blood pressure damages the blood vessels in the kidneys, reducing their ability to filter waste products from the blood. This can lead to kidney failure.
- Vision problems: Damage to the blood vessels in the eyes can cause vision loss or blindness. Hypertensive retinopathy is a specific eye condition related to high blood pressure.
- Peripheral artery disease (PAD): High blood pressure can narrow and harden arteries in the legs and feet, reducing blood flow and leading to pain, numbness, and potentially amputation.
Importance of Regular Blood Pressure Monitoring
Regular blood pressure monitoring is essential for early detection and management of hypertension. Even if you feel perfectly healthy, consistent monitoring allows for early intervention, preventing long-term damage and reducing the risk of serious complications.
Regular blood pressure checks, even if you feel well, are crucial for preventing serious health issues associated with hypertension.
Risk Factors for High Blood Pressure
High blood pressure, or hypertension, doesn’t develop overnight. It’s often the result of a combination of factors, some within your control and some not. Understanding these risk factors is crucial for effective prevention and management. Knowing what increases your risk allows you to make informed choices to protect your heart health.
Risk factors for hypertension are broadly categorized as modifiable and non-modifiable. Modifiable factors are those you can change through lifestyle adjustments, while non-modifiable factors are those you cannot change, such as your genetics or age. Let’s explore both categories in detail.
Modifiable Risk Factors for Hypertension
Lifestyle plays a significant role in determining your blood pressure. Making healthy choices can significantly reduce your risk of developing hypertension, or help manage it if you already have it. These choices impact your cardiovascular health in profound ways.
For instance, a diet high in sodium and saturated fats contributes directly to elevated blood pressure. Conversely, regular physical activity strengthens the heart, improves circulation, and helps regulate blood pressure. Smoking, a major risk factor for numerous health problems, constricts blood vessels, leading to increased blood pressure. Let’s examine the impact of these lifestyle choices more closely.
Impact of Lifestyle Choices on Blood Pressure
The impact of lifestyle choices on blood pressure is undeniable. A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, low in sodium, saturated and trans fats, significantly lowers blood pressure. Regular physical activity, ideally at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week, helps lower blood pressure and improve cardiovascular health. Conversely, smoking dramatically increases blood pressure and the risk of heart disease and stroke.
Excessive alcohol consumption also contributes to hypertension. The cumulative effect of these choices can be substantial, either protecting against or contributing to high blood pressure. For example, a study published in the “Journal of the American Medical Association” showed that individuals who adopted a DASH (Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension) diet experienced a significant reduction in their systolic and diastolic blood pressure readings.
Non-Modifiable Risk Factors for Hypertension
Certain factors increase your risk of high blood pressure regardless of lifestyle choices. These are inherent characteristics that cannot be changed. Understanding these factors allows for proactive management and monitoring of blood pressure.
Risk Factors and Associated Health Implications
| Risk Factor | Type | Health Implications | Management Strategies |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (over 65) | Non-Modifiable | Increased risk of hypertension and cardiovascular disease. | Regular blood pressure monitoring and adherence to treatment plans. |
| Family History of Hypertension | Non-Modifiable | Higher likelihood of developing hypertension. | Early screening and lifestyle modifications to mitigate risk. |
| Obesity | Modifiable | Increased strain on the heart and blood vessels, leading to higher blood pressure. | Weight management through diet and exercise. |
| Smoking | Modifiable | Damages blood vessels, leading to increased blood pressure and risk of heart disease and stroke. | Smoking cessation programs and support. |
| High Sodium Diet | Modifiable | Increased fluid retention, raising blood pressure. | Reducing sodium intake through dietary changes. |
| Lack of Physical Activity | Modifiable | Contributes to weight gain, weakens cardiovascular system, and increases blood pressure. | Regular exercise and physical activity. |
| Stress | Modifiable | Can temporarily raise blood pressure; chronic stress contributes to hypertension. | Stress management techniques such as yoga, meditation, and relaxation exercises. |
| Chronic Kidney Disease | Non-Modifiable (often) | Kidney dysfunction affects blood pressure regulation. | Medical management of kidney disease. |
When to Seek Medical Attention
High blood pressure, or hypertension, is often a silent killer, meaning it may not present obvious symptoms. However, some situations demand immediate medical attention, regardless of whether you’re experiencing noticeable symptoms. Understanding when to seek help can be crucial in preventing serious health complications. Ignoring warning signs can have severe consequences, so prompt action is key.High blood pressure can lead to serious complications like stroke, heart attack, kidney failure, and blindness if left untreated.
Therefore, it’s vital to know when to seek immediate medical care. Even if your blood pressure readings are typically within a manageable range, certain circumstances require urgent medical attention.
Hypertensive Crises
A hypertensive crisis occurs when blood pressure rises suddenly to dangerously high levels. This is a medical emergency requiring immediate hospitalization. Symptoms can include severe headache, shortness of breath, nosebleeds, and chest pain. A hypertensive crisis can damage vital organs if not treated promptly. For example, a person experiencing a sudden, intense headache accompanied by blurred vision and nausea should seek immediate emergency care.
The rapid rise in blood pressure can cause brain swelling or bleeding, leading to a stroke.
Symptoms Indicating Severe Complications
Several symptoms indicate a potentially life-threatening complication related to high blood pressure and necessitate immediate medical intervention. These symptoms often point to damage to vital organs.
- Severe, persistent headache: A sudden, intense headache that doesn’t respond to over-the-counter pain relievers is a serious warning sign.
- Shortness of breath: Difficulty breathing, especially when at rest, could signify heart failure or other serious complications.
- Chest pain or pressure: Chest pain or pressure, especially if radiating to the arm or jaw, might indicate a heart attack.
- Vision changes: Blurred vision, double vision, or sudden vision loss can be signs of stroke or other neurological complications.
- Numbness or weakness: Numbness or weakness on one side of the body, especially if accompanied by facial drooping, is a classic sign of stroke.
- Confusion or disorientation: Sudden confusion or disorientation can also indicate a serious neurological event.
- Seizures: Uncontrolled seizures can be triggered by dangerously high blood pressure.
Situations Requiring a Healthcare Professional Consultation
Even without dramatic symptoms, certain situations warrant a consultation with a healthcare professional regarding blood pressure management.
- Consistent high blood pressure readings: If your home blood pressure readings consistently show elevated numbers, even if you don’t feel unwell, it’s crucial to seek medical advice. Regular monitoring is essential for effective management.
- Newly diagnosed hypertension: Following a diagnosis of hypertension, regular check-ups and consultations with a doctor are vital to develop a personalized treatment plan.
- Changes in medication: If you experience any side effects or notice a change in the effectiveness of your blood pressure medication, consult your doctor immediately. Dosage adjustments or alternative medications may be necessary.
- Significant lifestyle changes: Significant lifestyle changes, such as starting a strenuous exercise program or making major dietary alterations, should be discussed with your doctor to ensure they don’t negatively impact your blood pressure.
- Pregnancy: High blood pressure during pregnancy can be dangerous for both mother and baby, requiring close monitoring and management by a healthcare professional.
Non-Medication Approaches to Managing Blood Pressure
High blood pressure, or hypertension, is a serious condition, but thankfully, many cases can be managed effectively without relying solely on medication. Lifestyle modifications play a crucial role in lowering blood pressure and reducing the risk of heart disease and stroke. By adopting a holistic approach encompassing diet, exercise, and stress management, you can significantly improve your cardiovascular health.
Dietary Changes for Blood Pressure Control
Dietary changes are fundamental in managing blood pressure. A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein, while limiting sodium, saturated fat, and added sugars, is key. The DASH diet (Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension) is a prime example of an effective dietary plan for lowering blood pressure.The DASH diet emphasizes increased consumption of potassium-rich foods like bananas and spinach, magnesium-rich foods such as almonds and dark chocolate, and calcium-rich foods such as dairy products (low-fat or fat-free).
It also recommends limiting processed foods, red meat, and sugary drinks. Studies have shown that the DASH diet can significantly lower systolic and diastolic blood pressure, sometimes by as much as 11-14 mmHg. This reduction can be comparable to the effects of some blood pressure medications.
The Benefits of Regular Physical Activity
Regular physical activity is another powerful tool in managing hypertension. Exercise helps lower blood pressure by improving cardiovascular fitness, reducing stress, and promoting weight loss. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic activity per week, spread throughout the week.It’s important to choose activities you enjoy to ensure adherence. Here are some suitable exercises:
- Brisk walking
- Jogging
- Swimming
- Cycling
- Dancing
- Gardening
Even incorporating short bursts of activity throughout the day, such as taking the stairs instead of the elevator, can make a difference. Remember to consult your doctor before starting any new exercise program, especially if you have pre-existing health conditions.
Stress Management Techniques
Chronic stress can significantly elevate blood pressure. Effective stress management techniques are therefore essential for managing hypertension. Stress reduction methods include:
- Regular meditation or mindfulness practices
- Yoga
- Deep breathing exercises
- Spending time in nature
- Engaging in hobbies
- Sufficient sleep (7-8 hours per night)
These techniques help lower cortisol levels, a hormone associated with the “fight or flight” response, which can contribute to elevated blood pressure. Finding healthy coping mechanisms for stress is crucial for long-term blood pressure control. Learning to manage stress can be just as effective as medication in some cases.
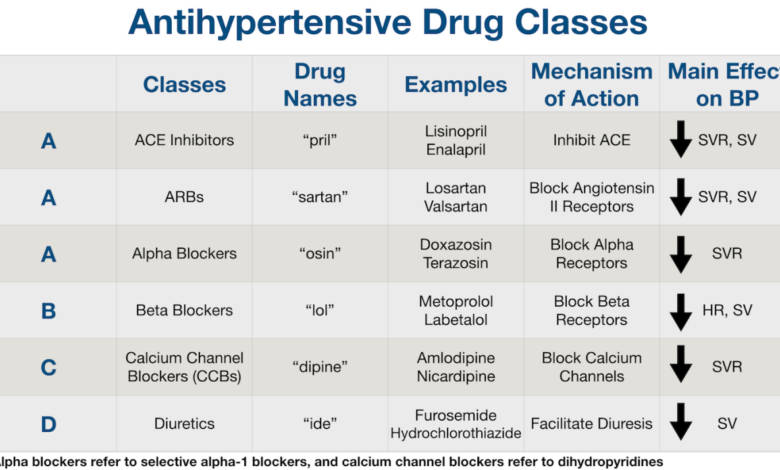
Types of Blood Pressure Medications
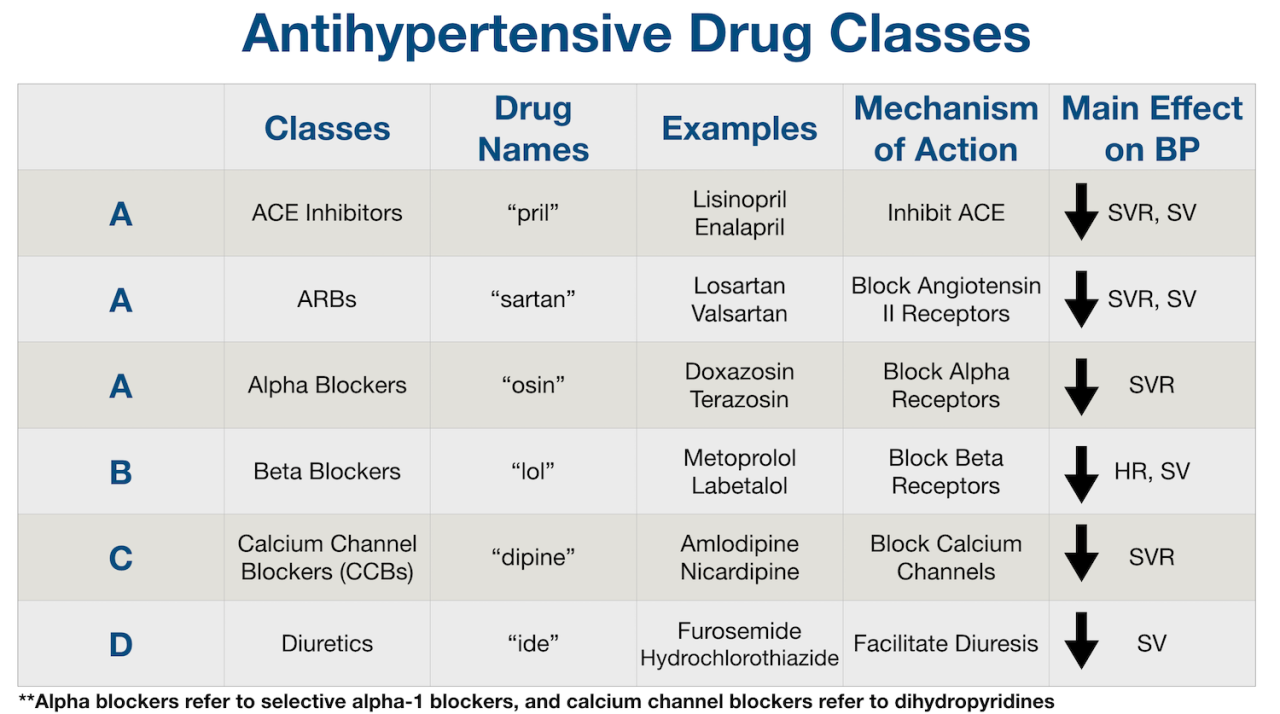
Source: squarespace-cdn.com
High blood pressure, or hypertension, often requires medication to manage effectively. There are several classes of blood pressure medications, each working through different mechanisms to lower blood pressure. Choosing the right medication depends on individual factors like other health conditions, age, and potential side effects. It’s crucial to work closely with your doctor to find the best treatment plan for you.
Understanding how these medications work can help you feel more informed and involved in your healthcare decisions. Remember, this information is for educational purposes and shouldn’t replace advice from your doctor or other qualified healthcare professional.
Diuretics
Diuretics, often called “water pills,” increase the excretion of sodium and water from the body through urine. This reduces the volume of blood circulating, thus lowering blood pressure. Common examples include thiazide diuretics (like hydrochlorothiazide) and loop diuretics (like furosemide). Thiazide diuretics are usually the first line of treatment for many individuals. They are generally well-tolerated, but can cause side effects such as increased urination, dehydration, and electrolyte imbalances (low potassium, for example).
Loop diuretics are more potent and are often used for individuals with more severe hypertension or kidney problems, but can cause more pronounced side effects.
ACE Inhibitors
Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors block the production of angiotensin II, a hormone that narrows blood vessels. By inhibiting this process, ACE inhibitors help relax and widen blood vessels, reducing blood pressure. Common examples include lisinopril and ramipril. Side effects can include a dry cough (a fairly common side effect that can lead to medication changes), dizziness, and kidney problems in some individuals.
Angiotensin Receptor Blockers (ARBs)
ARBs work similarly to ACE inhibitors by blocking the effects of angiotensin II, but they do so by blocking the angiotensin II receptors instead of the enzyme that produces it. This makes them a good alternative for people who experience the dry cough associated with ACE inhibitors. Examples include valsartan and losartan. Side effects are generally similar to ACE inhibitors, but the dry cough is less common.
Beta-Blockers, How to know if you need medicine for blood pressure
Beta-blockers reduce the heart’s workload by slowing the heart rate and reducing the force of contractions. This lowers the blood pressure. Common examples include metoprolol and atenolol. Side effects can include fatigue, dizziness, and slowed heart rate (bradycardia). They are often used to treat hypertension alongside other conditions such as angina and heart failure.
Calcium Channel Blockers
Calcium channel blockers relax blood vessels by reducing the flow of calcium into the cells of the blood vessel walls. This relaxation leads to wider blood vessels and lower blood pressure. Common examples include amlodipine and diltiazem. Side effects can include headache, dizziness, and swelling in the ankles. Different types of calcium channel blockers have varying effects on the heart rate; some may slow it down, while others may not.
Alpha-Blockers
Alpha-blockers relax blood vessels by blocking the action of alpha-adrenergic receptors in the blood vessels. This causes vasodilation and reduces blood pressure. Common examples include doxazosin and terazosin. Side effects can include dizziness, lightheadedness, and fainting, particularly when standing up suddenly (orthostatic hypotension). They are often used to treat hypertension in conjunction with other conditions like benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH).
Comparison of Blood Pressure Medications
| Medication Type | Mechanism of Action | Common Side Effects | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Diuretics (Thiazide & Loop) | Increases sodium and water excretion | Increased urination, dehydration, electrolyte imbalances | First-line treatment for many; loop diuretics are more potent |
| ACE Inhibitors | Blocks angiotensin II production | Dry cough, dizziness, kidney problems | Effective but can cause a troublesome cough |
| ARBs | Blocks angiotensin II receptors | Similar to ACE inhibitors, but less cough | Alternative for those intolerant to ACE inhibitors |
| Beta-Blockers | Slows heart rate and reduces contractility | Fatigue, dizziness, bradycardia | Often used for angina and heart failure as well |
| Calcium Channel Blockers | Relaxes blood vessels by reducing calcium influx | Headache, dizziness, ankle swelling | Different types affect heart rate differently |
| Alpha-Blockers | Relaxes blood vessels by blocking alpha-adrenergic receptors | Dizziness, lightheadedness, orthostatic hypotension | Often used for BPH as well |
The Role of a Doctor in Managing Blood Pressure
Managing high blood pressure effectively requires a collaborative partnership between you and your doctor. Regular check-ups are crucial not only for monitoring your blood pressure but also for addressing any underlying health issues that might contribute to it. Your doctor plays a vital role in diagnosing the condition, creating a personalized treatment plan, and ensuring its effectiveness over time.Regular check-ups are essential for ongoing blood pressure management.
Consistent monitoring allows your doctor to detect any significant changes or trends in your blood pressure readings, even subtle ones that might go unnoticed at home. This proactive approach helps prevent potential complications associated with hypertension, such as heart attack, stroke, and kidney disease. During these visits, your doctor will also assess your overall health, taking into account other risk factors and potential interactions with other medications you might be taking.
Diagnosing Hypertension and Determining Treatment
Diagnosing hypertension involves a thorough assessment. This includes taking multiple blood pressure readings at different times to confirm consistently elevated levels. Your doctor will also review your medical history, family history of hypertension, and lifestyle factors like diet, exercise, and smoking habits. Based on this comprehensive evaluation, they’ll determine the severity of your hypertension and recommend an appropriate treatment plan.
This plan might involve lifestyle modifications alone, medication, or a combination of both. For example, a patient with mildly elevated blood pressure and no other health concerns might initially focus on dietary changes and increased physical activity. However, a patient with severely elevated blood pressure and existing heart conditions would likely require immediate medication alongside lifestyle changes.
Monitoring Treatment Effectiveness and Adjusting Treatment Plans
Once a treatment plan is established, regular follow-up appointments are vital to monitor its effectiveness. Your doctor will track your blood pressure readings and assess your overall health. If your blood pressure remains elevated despite lifestyle changes and medication, your doctor might adjust the dosage, change the type of medication, or add additional medications to optimize your treatment. For instance, a patient initially prescribed a single medication might require the addition of a second medication if their blood pressure doesn’t respond adequately to the first.
This ongoing monitoring and adjustment ensure that your treatment plan remains effective and tailored to your specific needs and response. The goal is to achieve and maintain a healthy blood pressure level to minimize your risk of serious health complications.
Understanding Medication Side Effects
Taking medication for high blood pressure is a common practice, but it’s crucial to understand that these medications, like many others, can have side effects. These side effects vary greatly depending on the individual, the specific medication, and the dosage. While many side effects are mild and manageable, others can be more serious and require medical attention. Being informed about potential side effects is key to responsible medication management and adherence to treatment plans.Many different types of blood pressure medications exist, and each carries its own set of potential side effects.
It’s important to remember that not everyone experiences side effects, and the severity of any side effects can vary widely. Open communication with your doctor is essential to navigate these potential issues and ensure your treatment is as effective and safe as possible.
Common Side Effects of Blood Pressure Medications
Blood pressure medications can cause a range of side effects, some more common than others. These can impact various bodily systems. Understanding these possibilities allows for proactive management and helps patients feel more empowered in their healthcare journey.
- Diuretics (water pills): These medications increase urination, which can lead to dehydration, dizziness, and frequent urination, especially at night. Electrolyte imbalances, such as low potassium, are also a possibility.
- ACE inhibitors: These medications can cause a persistent dry cough, fatigue, dizziness, and in rare cases, angioedema (swelling of the face, lips, tongue, or throat).
- Angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs): Similar to ACE inhibitors, ARBs can cause dizziness, fatigue, and rarely, angioedema.
- Beta-blockers: These can cause fatigue, dizziness, slowed heart rate, and in some cases, depression or sexual dysfunction.
- Calcium channel blockers: Common side effects include headache, dizziness, flushing, and swelling in the ankles.
Managing and Reporting Side Effects
If you experience any side effects while taking blood pressure medication, it’s crucial to document them and report them to your healthcare provider. Keeping a journal of when and how frequently you experience each side effect, along with the severity, is helpful for your doctor to assess the situation. This detailed information can help determine if the side effects are manageable or if adjustments to the medication or dosage are necessary.
Don’t hesitate to contact your doctor even if you feel the side effects are minor; early intervention can often prevent more significant problems.
Patient Education and Medication Adherence
Understanding the potential side effects of your medication is vital for medication adherence. Many people stop taking their medication because of unpleasant side effects, leading to uncontrolled blood pressure and increased health risks. However, many side effects are manageable, and your doctor can work with you to find strategies to mitigate them. This might involve adjusting the dosage, changing medications, or implementing lifestyle changes to minimize discomfort.
Open communication with your doctor, along with a clear understanding of the medication’s purpose and potential side effects, is crucial for successful long-term blood pressure management.
Closing Summary: How To Know If You Need Medicine For Blood Pressure
Taking control of your blood pressure is a journey, not a race. While medication might be necessary for some, lifestyle changes are often the first line of defense and can make a significant difference. Remember, regular check-ups with your doctor are essential for monitoring your blood pressure and adjusting your treatment plan as needed. Don’t hesitate to ask questions and advocate for your health.
By understanding your body and working closely with your healthcare team, you can take proactive steps towards a healthier, longer life. This knowledge empowers you to make informed choices about your wellbeing, ensuring a healthier future.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is considered a normal blood pressure reading?
Generally, a blood pressure reading below 120/80 mmHg is considered normal.
Can stress cause a temporary spike in blood pressure?
Yes, stress can temporarily raise blood pressure. Chronic stress, however, can contribute to long-term hypertension.
Are there any natural ways to lower blood pressure besides medication?
Yes, lifestyle changes such as diet (DASH diet), regular exercise, stress management techniques, and quitting smoking can significantly lower blood pressure.
How often should I check my blood pressure?
This depends on your individual risk factors and your doctor’s recommendations. Regular monitoring, especially if you have high blood pressure, is crucial.
What should I do if I experience a sudden, severe headache along with dizziness?
Seek immediate medical attention as these could be symptoms of a hypertensive crisis.