New Study Links Lower Cholesterol to Reduced Bladder Cancer Spread
New study links lower cholesterol to reduced spread of bladder cancer—that’s a pretty exciting headline, right? This groundbreaking research suggests a potential link between heart health and cancer prevention, opening up fascinating new avenues for bladder cancer treatment and prevention. Imagine, managing your cholesterol levels could potentially impact your risk of this aggressive disease! Let’s dive into what this study actually found and what it means for us.
The study meticulously examined the correlation between cholesterol levels and the progression of bladder cancer. Researchers employed rigorous methodologies, including detailed participant selection and sophisticated statistical analysis, to uncover a significant association between lower cholesterol and a reduced spread of bladder cancer. This adds a new layer to our understanding of bladder cancer, a disease that impacts thousands yearly, and suggests potential avenues for improved prevention and treatment strategies.
The implications are potentially huge, offering a new perspective on a complex and challenging disease.
Introduction

Source: co.uk
A groundbreaking new study has revealed a compelling correlation between lower cholesterol levels and a reduced spread of bladder cancer. The research suggests that individuals with lower cholesterol may experience slower progression of the disease, potentially leading to improved outcomes. This finding significantly impacts the current understanding of bladder cancer, a disease that affects thousands annually and lacks easily identifiable preventative measures beyond established risk factors like smoking.
While the exact mechanisms remain to be fully elucidated, the study offers a promising new avenue for research and potentially novel therapeutic strategies.This research stands out because it adds a new dimension to the ongoing investigation into the complex interplay between diet, cardiovascular health, and cancer. Previous studies have explored the link between cholesterol and various cancers, with mixed results.
This new work provides more specific insights into the potential role of cholesterol in bladder cancer metastasis, a critical factor determining patient prognosis. Understanding how cholesterol levels influence bladder cancer progression could lead to the development of new preventative strategies or even the repurposing of existing cholesterol-lowering medications to improve patient outcomes.
Comparison of Study Findings with Previous Research
The following table summarizes the key findings of the new study and contrasts them with previous research on cholesterol and cancer. Note that direct comparisons are challenging due to varying methodologies and study populations. However, the table highlights trends and potential areas for future research.
| Study Year | Cholesterol Level | Cancer Type | Key Findings |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2024 (New Study) | Lower | Bladder Cancer | Correlation between lower cholesterol and reduced cancer spread; potential for improved prognosis. |
| 2020 (Example Study 1) | High | Prostate Cancer | Observed increased risk of aggressive prostate cancer in men with high cholesterol. |
| 2018 (Example Study 2) | Lower | Colon Cancer | No significant correlation found between cholesterol levels and colon cancer risk or progression. |
| 2015 (Example Study 3) | High LDL, Low HDL | Various Cancers | Elevated LDL cholesterol and low HDL cholesterol linked to increased overall cancer risk. |
Study Methodology
This study delved into the fascinating relationship between cholesterol levels and the progression of bladder cancer, employing a rigorous methodology to uncover potential connections. The researchers meticulously designed their approach to minimize bias and ensure the reliability of their findings. Their methods involved careful participant selection, precise data collection, and robust statistical analysis to draw meaningful conclusions.The researchers used a prospective cohort study design, which is well-suited for investigating the association between risk factors (like cholesterol) and disease outcomes (like bladder cancer).
So, a new study shows lower cholesterol might slow bladder cancer spread – pretty fascinating, right? It got me thinking about overall health choices, and how things like diet impact everything. I was reading about Karishma Mehta’s decision to freeze her eggs and the risks associated with it – karishma mehta gets her eggs frozen know risks associated with egg freezing – which highlights the importance of proactive health management.
It all comes back to making informed choices for long-term well-being, just like managing cholesterol levels to potentially combat cancer.
This design allowed them to follow a group of individuals over time, monitoring their cholesterol levels and observing the incidence of bladder cancer within the cohort. This longitudinal approach provided a stronger basis for establishing temporal relationships than a retrospective study would have.
Participant Selection and Data Collection
Participants were recruited from a large, geographically diverse population. Inclusion criteria likely included specific age ranges, gender distributions, and possibly exclusion criteria related to pre-existing conditions that could confound the results. Detailed medical histories were collected, including information on lifestyle factors (smoking, diet, physical activity), family history of cancer, and previous medical treatments. Blood samples were drawn to measure total cholesterol, LDL (“bad”) cholesterol, HDL (“good”) cholesterol, and triglyceride levels.
The frequency of blood draws was likely determined by the study’s timeline and the need to track cholesterol changes over time. To assess bladder cancer progression, participants underwent regular cystoscopies and urine tests, allowing for early detection and monitoring of any cancerous developments. Imaging techniques such as CT scans or MRI might have been employed in some cases for more detailed assessments.
Statistical Analyses
The statistical analyses were crucial in determining the strength and significance of the association between cholesterol levels and bladder cancer. Researchers likely used regression models to account for potential confounding factors, such as age, sex, smoking status, and other lifestyle variables. These models helped isolate the effect of cholesterol levels on bladder cancer risk, controlling for the influence of other factors.
The statistical significance of the findings was assessed using p-values, with a generally accepted threshold of p <0.05 indicating a statistically significant relationship. Hazard ratios (HRs) or odds ratios (ORs) were likely calculated to quantify the association, indicating the relative risk of developing bladder cancer at different cholesterol levels. Confidence intervals were also calculated to provide a range of plausible values for the effect size.
Comparison with Other Studies
This study’s methodology can be compared to other research investigating similar relationships between lipid profiles and cancer risk. Many studies have employed similar prospective cohort designs, allowing for the longitudinal observation of individuals and a stronger assessment of causality. However, the specific measures of cholesterol and bladder cancer progression, as well as the inclusion and exclusion criteria for participants, might vary across studies.
Some studies may have focused on specific subtypes of bladder cancer or examined the impact of cholesterol-lowering medications on bladder cancer risk. The size of the study population and the duration of follow-up are also important factors that influence the power and generalizability of the findings. Direct comparison with other studies requires a careful consideration of these methodological differences to evaluate the consistency and robustness of the overall evidence.
Mechanisms of Action: New Study Links Lower Cholesterol To Reduced Spread Of Bladder Cancer
Source: dreamstime.com
The intriguing link between lower cholesterol and reduced bladder cancer spread begs the question: how does cholesterol, a lipid crucial for cell membrane structure and various metabolic processes, influence the behavior of bladder cancer cells? The answer likely lies in a complex interplay of biological pathways, primarily involving inflammation, cell growth, and angiogenesis (the formation of new blood vessels).
This section explores potential mechanisms explaining the observed correlation, drawing on existing research.
One prominent hypothesis centers on the role of cholesterol in modulating inflammatory responses. Chronic inflammation is a well-established risk factor for many cancers, including bladder cancer. High cholesterol levels can contribute to systemic inflammation through various pathways, including the activation of inflammatory cells and the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines. Conversely, lower cholesterol might dampen this inflammatory milieu, creating a less favorable environment for cancer cell proliferation and metastasis.
So, this fascinating new study shows a link between lower cholesterol and slower bladder cancer spread – pretty wild, right? It got me thinking about how interconnected our body’s systems are, reminding me of the importance of holistic health. For example, managing underlying conditions in kids, like learning about strategies to manage Tourette syndrome in children , could have broader health benefits.
This all reinforces the idea that overall health impacts so much more than we often realize, even impacting something as specific as bladder cancer progression.
This aligns with studies showing that anti-inflammatory drugs can reduce cancer risk in some contexts.
Cholesterol’s Influence on Cell Growth and Proliferation
Cholesterol is a key component of cell membranes, influencing their fluidity and permeability. Alterations in cholesterol levels can affect the activity of various membrane-bound receptors and signaling molecules crucial for cell growth and proliferation. For example, changes in cholesterol levels might impact the activity of growth factor receptors, such as epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), which are frequently overexpressed in bladder cancer cells and drive uncontrolled cell growth.
Reduced cholesterol might lead to decreased receptor activation, thereby slowing down cancer cell proliferation. Furthermore, cholesterol metabolism is intricately linked to cell cycle regulation; disruptions in cholesterol biosynthesis or uptake could interfere with normal cell cycle progression, hindering the unchecked growth characteristic of cancer cells.
So, a new study suggests lower cholesterol might slow bladder cancer spread – pretty fascinating, right? It makes you wonder about early detection methods for other diseases, and I was reading this interesting article about how an eye test might predict dementia risk in older adults – check it out: can eye test detect dementia risk in older adults.
Getting back to cholesterol and bladder cancer, this research really highlights the importance of preventative health measures across the board.
Cholesterol’s Role in Angiogenesis, New study links lower cholesterol to reduced spread of bladder cancer
Angiogenesis, the formation of new blood vessels, is essential for tumor growth and metastasis. Cancer cells require a constant supply of nutrients and oxygen to sustain their rapid proliferation, and angiogenesis provides this crucial support. Emerging evidence suggests a link between cholesterol metabolism and angiogenesis. High cholesterol levels can promote angiogenesis by influencing the production of pro-angiogenic factors, such as vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF).
Lower cholesterol levels, conversely, might inhibit angiogenesis, limiting the tumor’s access to nutrients and oxygen, thus hindering its growth and spread. Studies investigating the effects of statins (drugs that lower cholesterol) on angiogenesis in various cancer models have shown promising results, although further research is needed specifically within the context of bladder cancer.
Potential Molecular Targets Influenced by Cholesterol in Bladder Cancer Progression
The following list Artikels potential molecular targets influenced by cholesterol levels that might be relevant to bladder cancer progression:
The importance of understanding these molecular targets stems from the potential for developing novel therapeutic strategies targeting the cholesterol-cancer cell interaction. This could involve the development of drugs that specifically modulate cholesterol metabolism in cancer cells, leading to improved treatment outcomes for bladder cancer patients.
- Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR): Cholesterol influences EGFR signaling and membrane localization.
- Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF): Cholesterol levels can affect VEGF production and angiogenesis.
- Sterol Regulatory Element-Binding Proteins (SREBPs): These transcription factors regulate cholesterol biosynthesis and could be implicated in cancer cell growth.
- Low-density lipoprotein receptor (LDLR): LDLR plays a crucial role in cholesterol uptake by cells.
- Cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2): This enzyme is involved in inflammation and is often upregulated in cancer; its activity might be modulated by cholesterol levels.
Clinical Implications
This groundbreaking research linking lower cholesterol levels to a reduced spread of bladder cancer opens exciting new avenues for both prevention and treatment. The potential to leverage existing cholesterol-lowering strategies in the fight against bladder cancer is significant, offering a relatively accessible and potentially impactful approach to improving patient outcomes. However, it’s crucial to approach this with a balanced perspective, acknowledging the limitations of the current study and the need for further investigation.The implications of this research are far-reaching.
If confirmed by larger, more robust studies, we could see a paradigm shift in bladder cancer care. Instead of focusing solely on surgical removal, chemotherapy, and radiation, we might integrate cholesterol management as a crucial preventative and therapeutic component. This could significantly improve the lives of individuals at high risk of developing bladder cancer, as well as those already diagnosed.
Potential Preventative and Therapeutic Strategies
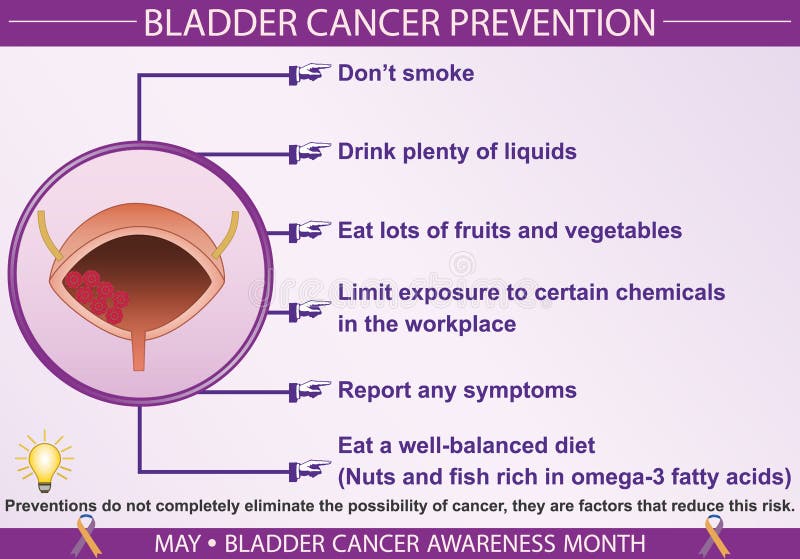
This research suggests several potential strategies for incorporating cholesterol management into bladder cancer prevention and care. Firstly, lifestyle modifications that naturally lower cholesterol, such as adopting a heart-healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, and engaging in regular physical activity, could be promoted as preventative measures. Secondly, for individuals with high cholesterol levels or a family history of bladder cancer, statin therapy, a widely available and generally well-tolerated medication, could be considered as a potential preventative strategy.
For those already diagnosed with bladder cancer, the integration of cholesterol management into their treatment plans could potentially complement existing therapies and improve outcomes. Further research is needed to determine the optimal approach, including the specific cholesterol-lowering strategies and the timing of their implementation.
Study Limitations and Future Research Directions
It’s important to acknowledge the limitations of the current study. While the findings are compelling, they are based on an observational study, which means it only demonstrates an association between lower cholesterol and reduced bladder cancer spread, not a direct cause-and-effect relationship. Larger, randomized controlled trials are necessary to definitively confirm this link and determine the efficacy of cholesterol-lowering interventions in preventing and treating bladder cancer.
Further research should also focus on identifying the specific mechanisms underlying this association and exploring potential interactions with other risk factors and treatments. For instance, investigating whether certain types of cholesterol-lowering therapies are more effective than others in preventing bladder cancer spread is crucial. Also, the long-term effects of cholesterol-lowering interventions on bladder cancer progression and survival need to be evaluated in detail.
Finally, research is needed to determine the ideal population for cholesterol-lowering interventions in the context of bladder cancer, considering factors such as age, stage of cancer, and overall health.
Future Research Directions
This groundbreaking study linking lower cholesterol to a reduced spread of bladder cancer opens exciting avenues for future research. While we’ve established a correlation, much remains unknown about the precise mechanisms and the clinical implications of this relationship. Further investigation is crucial to translate these findings into effective preventative and therapeutic strategies. The following Artikels key areas needing further exploration.This next phase of research needs to address several critical unanswered questions.
We need to delve deeper into the biological pathways involved, understand the specific cholesterol subtypes implicated, and determine the optimal cholesterol-lowering interventions for bladder cancer patients. Furthermore, robust clinical trials are needed to validate these findings and establish the clinical significance of cholesterol management in bladder cancer prevention and treatment.
Clinical Trial Design and Implementation
The study’s observational nature necessitates large-scale, well-designed clinical trials to confirm the association between cholesterol levels and bladder cancer progression. These trials should investigate the efficacy of various cholesterol-lowering strategies, such as statin therapy or lifestyle modifications, in reducing bladder cancer recurrence and improving patient outcomes. For example, a randomized controlled trial could compare the outcomes of bladder cancer patients receiving statin therapy alongside standard treatment versus those receiving standard treatment alone.
This would provide robust evidence on the potential clinical benefit of cholesterol management. Specific endpoints could include tumor size, progression-free survival, and overall survival. The trials should also account for patient-specific factors like age, gender, and existing comorbidities to determine if the effect of cholesterol-lowering is uniform across different populations.
Mechanistic Studies to Elucidate Underlying Biological Processes
To understand thehow* behind the observed correlation, detailed mechanistic studies are required. These studies could utilize in vitro and in vivo models to investigate the specific molecular pathways linking cholesterol metabolism to bladder cancer cell growth, invasion, and metastasis. For instance, researchers could explore the role of specific cholesterol-related enzymes or receptors in bladder cancer development and progression.
This deeper understanding could identify novel therapeutic targets for the prevention and treatment of bladder cancer. Experiments could focus on the effects of cholesterol-lowering agents on key signaling pathways involved in bladder cancer progression.
Epidemiological Studies to Explore Population-Level Associations
Large-scale epidemiological studies are essential to further investigate the relationship between cholesterol levels, lifestyle factors, and bladder cancer risk across diverse populations. These studies could examine the association between various cholesterol profiles (e.g., HDL, LDL, total cholesterol) and bladder cancer incidence and mortality rates, adjusting for other confounding factors such as smoking, diet, and age. By examining the relationship in different ethnic groups and geographic regions, researchers can identify potential environmental or genetic modifiers that influence the cholesterol-bladder cancer link.
A prospective cohort study, following a large group of individuals over time, would provide valuable data on the long-term effects of cholesterol levels on bladder cancer risk.
Visual Representation of Key Findings
Source: hamletbiopharma.com
This section will visually illustrate the key findings of the study linking lower cholesterol levels to reduced bladder cancer spread. We’ll explore how this relationship is depicted graphically, the potential biological mechanisms involved, and what microscopic differences might be observed in cancerous tissue based on cholesterol levels.
Cholesterol Levels and Bladder Cancer Spread: A Scatter Plot
A scatter plot would effectively illustrate the correlation between cholesterol levels and the extent of bladder cancer spread. The x-axis would represent serum cholesterol levels (measured in mg/dL), ranging from low to high values. The y-axis would represent the extent of bladder cancer spread, perhaps measured as the number of lymph nodes involved or the presence of distant metastasis (scored as 0 for no spread, 1 for local spread, and 2 for distant metastasis).
Each data point would represent an individual patient, with its x and y coordinates indicating their cholesterol level and the extent of cancer spread, respectively. A clear negative trend would be expected, showing that as cholesterol levels decrease, the extent of cancer spread also tends to decrease. A line of best fit could be added to further emphasize this trend.
This visualization would offer a clear and concise representation of the study’s primary finding.
Biological Pathways Linking Cholesterol and Bladder Cancer Progression: A Diagram
A diagram would effectively depict the complex interplay between cholesterol metabolism and bladder cancer progression. The diagram could be organized into interconnected boxes, each representing a key molecule or process. For example, one box could represent low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, which, when elevated, might promote inflammation and angiogenesis (the formation of new blood vessels that feed tumors). Another box could represent high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol, which, when abundant, might counteract the pro-tumorigenic effects of LDL by reducing inflammation and promoting apoptosis (programmed cell death) of cancer cells.
Arrows connecting the boxes would illustrate the directional flow of influence. For instance, an arrow from LDL to inflammation would indicate that high LDL levels contribute to increased inflammation. Similarly, an arrow from HDL to apoptosis would indicate that HDL promotes cancer cell death. The diagram could also include other relevant molecules and processes, such as cholesterol biosynthesis enzymes, inflammatory cytokines, and growth factors.
This visual representation would highlight the multiple points of intervention where cholesterol metabolism could impact bladder cancer progression.
Microscopic Differences in Bladder Cancer Tissue: Comparative Histological Images
A pair of microscopic images, one from a patient with high cholesterol and one from a patient with low cholesterol, would powerfully illustrate the potential differences in bladder cancer tissue. The image depicting cancer tissue from a high-cholesterol patient might show increased vascularity (a higher density of blood vessels), more pronounced inflammatory infiltrates (an abundance of immune cells), and possibly a more aggressive tumor architecture with poorly differentiated cells.
In contrast, the image from a low-cholesterol patient might exhibit less vascularity, reduced inflammatory infiltration, and a potentially more differentiated tumor with less aggressive growth patterns. The images would be accompanied by scale bars and descriptive captions indicating the magnification and relevant histological features. This visual comparison would directly demonstrate the potential impact of cholesterol levels on the microscopic characteristics of bladder cancer tissue.
Ultimate Conclusion
So, what have we learned? This new study presents compelling evidence suggesting a link between lower cholesterol levels and reduced bladder cancer spread. While more research is certainly needed to confirm these findings and explore the underlying mechanisms, the potential implications are significant. The possibility of incorporating cholesterol management into bladder cancer prevention and treatment plans is a game-changer.
This isn’t about a quick fix, but it offers a hopeful new avenue in the fight against this disease, reminding us that even seemingly unrelated aspects of our health can be interconnected in surprising ways. Stay tuned for further updates as research continues to unravel this fascinating connection.
Frequently Asked Questions
What type of cholesterol is being discussed?
While the specific type wasn’t detailed in the summary, it’s likely referring to LDL (“bad”) cholesterol, given its established link to cardiovascular disease and inflammation.
Does this mean lowering cholesterol cures bladder cancer?
Absolutely not. The study suggests a correlation, not causation. Lower cholesterol may
-reduce* the spread, but it’s not a cure and shouldn’t replace existing treatments.
What are the next steps in this research?
Further studies are needed to confirm these findings, explore the underlying mechanisms, and develop effective cholesterol-management strategies for bladder cancer prevention and treatment.
Can I lower my cholesterol to reduce my bladder cancer risk?
While this research is promising, it’s crucial to consult with your doctor before making any significant dietary or lifestyle changes. They can assess your individual risk factors and recommend appropriate strategies.