Donald Trump Halts USAID India Healthcares Fate
Donald trump halts usaid what it means for india healthcare sector – Donald Trump Halts USAID: What it Means for India Healthcare Sector – that’s a headline that sent shockwaves through the global health community. The potential ramifications of a US aid cutoff to India’s healthcare system are immense, impacting everything from HIV/AIDS prevention to maternal health initiatives. This isn’t just about numbers on a spreadsheet; it’s about the lives of millions of vulnerable people who rely on this critical funding.
Let’s delve into the potential consequences and explore the ripple effects across India’s healthcare landscape.
Imagine the impact on polio eradication efforts, already a delicate balancing act, or the potential disruption to tuberculosis control programs. The implications extend beyond specific diseases, touching upon the entire healthcare infrastructure, including the training and support of healthcare workers. We’ll explore alternative funding avenues, the geopolitical implications, and the urgent need for a robust response to mitigate the potential crisis.
Impact on USAID Funding for India

Source: futurecdn.net
A potential halt to USAID funding would significantly impact India’s healthcare sector, given the substantial role the agency has played in bolstering various health initiatives over the years. Understanding the historical funding levels and the specific programs affected is crucial to assessing the potential ramifications of such a decision.
USAID’s Historical Funding for India’s Healthcare
USAID has been a major contributor to India’s healthcare infrastructure and programs for decades. While precise figures fluctuate yearly depending on priorities and global events, a consistent and substantial amount of funding has been channeled into various healthcare areas. This support has often focused on strengthening existing systems, improving access to healthcare services, and tackling specific health challenges like HIV/AIDS, tuberculosis, and maternal mortality.
The scale of this support makes a potential disruption a matter of serious concern.
Specific Programs and Initiatives Affected by a Potential Halt
A complete halt to USAID funding would immediately affect numerous ongoing programs. These range from large-scale initiatives aimed at improving primary healthcare access in underserved rural areas to targeted interventions focused on specific diseases. For instance, programs supporting the training of healthcare workers, the procurement and distribution of essential medicines, and the implementation of disease surveillance systems would be jeopardized.
The impact would be felt across all levels of the healthcare system, from community health centers to national-level disease control programs.
Breakdown of Funding Allocation Across Different Healthcare Areas
USAID’s funding in India’s healthcare sector is typically spread across several key areas. A significant portion has traditionally been allocated to combating HIV/AIDS, with funding supporting prevention, treatment, and care programs. Maternal and child health has also received substantial investment, focusing on improving maternal mortality rates and ensuring access to quality healthcare for pregnant women and children.
Tuberculosis control programs have also benefited from significant USAID funding, supporting efforts to diagnose, treat, and prevent the spread of the disease. Other areas, such as strengthening health systems and improving sanitation, have also received considerable support. The exact percentage allocation varies from year to year based on evolving needs and global health priorities.
Comparison of USAID Funding Before and After a Hypothetical Halt
The following table illustrates a hypothetical scenario, showing the potential impact of a complete halt in USAID funding across different healthcare areas. These figures are illustrative and based on estimations, reflecting a potential drastic reduction in support. The actual impact would depend on the specific programs affected and the ability of the Indian government and other organizations to fill the gap.
| Program Area | Pre-Halt Funding (USD Million) | Post-Halt Funding (USD Million) | Percentage Change |
|---|---|---|---|
| HIV/AIDS | 100 | 0 | -100% |
| Maternal Health | 75 | 0 | -100% |
| Tuberculosis | 50 | 0 | -100% |
| Health Systems Strengthening | 25 | 0 | -100% |
Alternative Funding Sources for India’s Healthcare
With USAID’s potential reduced involvement in Indian healthcare, exploring alternative funding mechanisms becomes crucial to maintain the momentum of existing projects and support future initiatives. Several avenues exist, each with its own set of advantages and drawbacks that need careful consideration. The success of these alternatives hinges on effective strategic partnerships and a clear understanding of the political landscape.
Bilateral Agreements
Bilateral agreements offer a direct route to securing funding. Countries like the UK, Japan, Germany, and Canada have strong existing healthcare collaborations with India and could expand these partnerships to fill the potential USAID gap. These agreements can be tailored to specific healthcare needs and priorities, offering flexibility and potentially stronger political ties. However, the success of such agreements depends heavily on the political will and priorities of both participating nations.
A change in government or shifting geopolitical priorities could impact funding continuity. For example, a bilateral agreement might focus on strengthening primary healthcare infrastructure in a specific state, mirroring a previously USAID-funded project. The success of such an agreement depends on clear targets, efficient implementation mechanisms, and sustained commitment from both sides.
Private Sector Investment
The private sector, including pharmaceutical companies, medical technology firms, and private equity investors, represents a significant potential source of funding. Private investment can bring in much-needed capital and technological expertise. However, profit motives may prioritize certain areas over others, potentially leading to unequal access to healthcare services. Concerns around pricing and affordability of treatments funded by private entities also need careful consideration.
For instance, a private pharmaceutical company might invest in developing and distributing a new drug for a specific disease, but its accessibility may be limited due to high costs, leaving the less fortunate population without access to critical healthcare.
Multilateral Organizations
Organizations like the World Bank, Asian Development Bank (ADB), and the Global Fund to Fight AIDS, Tuberculosis and Malaria offer another avenue for funding. These organizations often have established processes for funding healthcare projects, and their expertise in managing large-scale initiatives can be invaluable. However, accessing funding from these organizations can be a competitive and bureaucratic process, often requiring extensive proposal preparation and adherence to strict guidelines.
Furthermore, their funding priorities might not always perfectly align with India’s specific healthcare needs. The World Bank, for example, might prioritize projects focused on improving sanitation and water access, indirectly contributing to improved health outcomes, but perhaps not directly addressing the specific needs of a previously USAID-funded program focused on maternal health.
Political and Diplomatic Implications
Shifting funding sources away from USAID inevitably carries political and diplomatic implications. The nature of these implications depends on the chosen alternative sources. Bilateral agreements could strengthen ties with specific countries, while reliance on private sector investment might reduce governmental control over healthcare policy. Diversifying funding sources can enhance India’s strategic autonomy, reducing dependence on a single donor.
However, navigating the complexities of multiple funding partners requires skillful diplomacy and careful coordination to avoid conflicting priorities and ensure effective program implementation. A shift towards increased engagement with multilateral organizations might strengthen India’s position within the global health governance architecture, but it might also involve accepting certain conditions attached to the funding.
Consequences for Specific Healthcare Initiatives
The potential halting of USAID funding to India’s healthcare sector would have far-reaching and devastating consequences, impacting numerous ongoing initiatives crucial for public health. The extent of the damage will depend on the duration of the funding freeze and the ability of the Indian government and other international partners to step in and fill the gap. However, the immediate and long-term effects on several key programs are undeniable.
Impact on Tuberculosis Control Programs
Tuberculosis (TB) remains a significant public health challenge in India. USAID has been a major contributor to India’s National Tuberculosis Elimination Program (NTEP), providing funding for capacity building, diagnostic tools, and treatment regimens. A halt in USAID funding would directly impact NTEP’s ability to reach its targets.
Program Disruption: Funding cuts could lead to disruptions in the supply chain of essential TB medicines and diagnostic equipment, hindering early detection and treatment. This would also impact training programs for healthcare workers, leading to a decline in the quality of care.
Service Delivery Gaps: Reduced funding would likely mean fewer diagnostic centers operational, longer waiting times for testing and treatment, and decreased access to care for marginalized populations. This could result in a rise in TB cases and increased mortality rates.
Human Resource Impacts: USAID funding often supports the salaries and training of healthcare workers involved in TB control. A funding halt could lead to job losses or a reduction in the workforce, further weakening the program’s capacity.
Research Setbacks: USAID funding also supports research into new TB diagnostics and treatments. A funding freeze could significantly hamper progress in this area, delaying the development of more effective interventions.
Consequences for Maternal and Child Health Initiatives
USAID has significantly contributed to improving maternal and child health outcomes in India through various programs focused on improving access to antenatal care, skilled birth attendance, and immunization. The consequences of a funding halt in this sector would be particularly severe.
Program Disruption: Programs providing training for community health workers, supporting mobile health clinics, and distributing essential medicines and supplies for mothers and children would be immediately affected.
Donald Trump’s halting of USAID funding had a ripple effect globally, impacting even seemingly unrelated areas. The reduced support for healthcare initiatives abroad means less funding for crucial programs, highlighting the interconnectedness of global health. Thinking about this made me remember a completely different, yet equally important, health challenge: effectively managing conditions like Tourette Syndrome in children, something I learned more about from this great resource on strategies to manage Tourette syndrome in children.
Ultimately, the consequences of reduced funding from the Trump administration’s decisions on international healthcare are far-reaching and impact even the most localized health challenges.
Service Delivery Gaps: Reduced access to antenatal care could lead to increased maternal mortality rates and complications during childbirth. Decreased immunization coverage would leave children vulnerable to preventable diseases.
Human Resource Impacts: The training and deployment of skilled birth attendants and community health workers rely heavily on USAID support. A funding halt would severely impact the availability of these crucial human resources.
Scenario: Potential Impact on Polio Eradication
India successfully eradicated polio in 2014, a feat largely attributed to extensive vaccination campaigns supported by organizations like USAID. However, the virus remains a threat in neighboring countries, and maintaining high vaccination coverage remains crucial to prevent re-emergence. A complete withdrawal of USAID funding could have devastating consequences:
Program Disruption: The logistical support provided by USAID for the polio eradication program, including vaccine procurement, cold chain maintenance, and surveillance activities, would cease. This would severely hamper the ability to quickly respond to outbreaks.
Service Delivery Gaps: Reduced vaccination coverage, particularly in remote and underserved areas, would leave children vulnerable to polio infection. The lack of surveillance would also hinder early detection of outbreaks.
Human Resource Impacts: The training and support of health workers involved in polio surveillance and vaccination campaigns would be compromised, leading to a reduction in the skilled workforce and weakening the program’s capacity.
Geopolitical Implications and International Relations
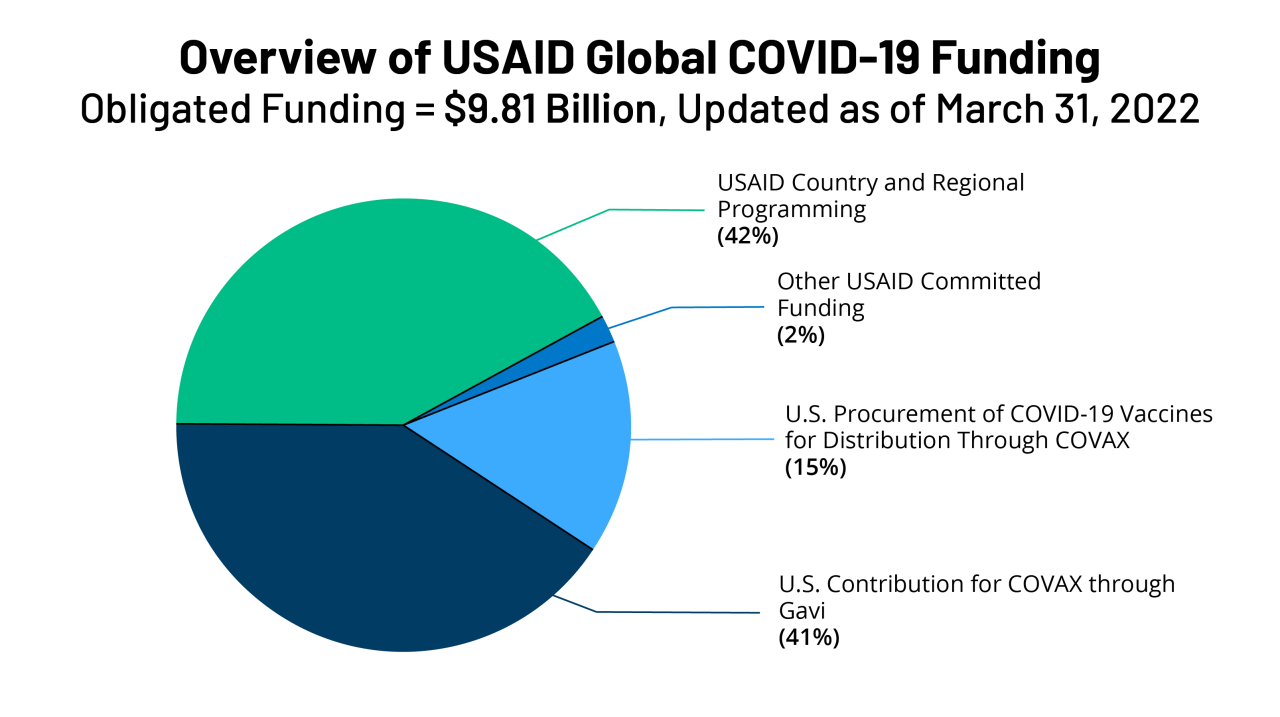
Source: kff.org
A potential halt in USAID funding for India’s healthcare sector carries significant geopolitical weight, extending far beyond bilateral relations. It would ripple through global health initiatives and reshape the dynamics of international cooperation, prompting reactions from various international actors. The implications are complex and far-reaching, impacting not only India but also the broader global health landscape and the strategic positioning of the United States.The decision to curtail or halt USAID funding to India’s healthcare sector would undoubtedly be interpreted within a broader geopolitical context.
The current global landscape is characterized by increasing great power competition, with the United States and China vying for influence across various sectors, including healthcare. A reduction in US aid could be seen as a strategic shift, potentially creating a vacuum that other nations, including China, might seek to fill. This could significantly alter the balance of power and influence in the region, impacting India’s healthcare policy choices and its overall relationship with the United States.
Impact on US-India Relations in the Healthcare Sector
A reduction in US aid would strain the already complex relationship between the US and India in the healthcare sector. Years of collaboration on initiatives like vaccine development and disease surveillance could be jeopardized. Trust and cooperation, essential for effective healthcare partnerships, might erode, leading to a less coordinated approach to tackling shared health challenges. India might seek alternative partnerships to compensate for the loss of US funding, potentially shifting its alliances and priorities.
This could affect joint research efforts, technology transfer, and the overall effectiveness of health interventions. The ramifications could be felt across multiple levels, from research and development to the delivery of healthcare services to vulnerable populations.
Implications for Global Health Initiatives and International Cooperation, Donald trump halts usaid what it means for india healthcare sector
The potential halt in USAID funding to India’s healthcare sector would send shockwaves through global health initiatives. India plays a crucial role in numerous global health programs, often acting as a regional hub for disease surveillance and vaccine distribution. Reduced funding would weaken India’s capacity to participate effectively in these initiatives, potentially leading to decreased global health security and increased vulnerability to outbreaks.
International cooperation on health matters, already challenged by geopolitical tensions and resource constraints, would be further strained. This could undermine efforts to achieve global health goals such as the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), particularly those related to health. The potential for decreased global health security resulting from a weakened Indian healthcare system is a significant concern.
Responses of Other International Actors
Other international actors would likely respond differently to a change in US aid to India’s healthcare sector. Some nations, particularly those with competing geopolitical interests, might see this as an opportunity to expand their influence. China, for example, might increase its healthcare aid and investment in India, potentially seeking to establish closer ties and gain strategic advantage. Other countries, committed to multilateralism and global health security, might step in to fill the funding gap, but the scale of their response would likely be limited.
The European Union, for instance, might increase its development assistance, but it is unlikely to completely offset the loss of US funding. The overall response will depend on the individual geopolitical agendas and priorities of each actor, resulting in a complex and potentially unstable landscape for India’s healthcare sector. This underscores the interconnectedness of global health and international politics.
Impact on Vulnerable Populations: Donald Trump Halts Usaid What It Means For India Healthcare Sector
A reduction or halt in USAID healthcare funding for India would disproportionately impact already vulnerable populations, exacerbating existing health disparities and potentially leading to a significant deterioration in health outcomes for millions. The consequences extend beyond simple numbers, affecting the very fabric of social well-being and economic stability within these communities.The potential increase in health disparities is a serious concern.
India’s healthcare system, while improving, still struggles to reach remote and marginalized areas. USAID funding often plays a crucial role in bridging this gap, providing essential support for programs that target the most vulnerable. Without this support, existing inequalities are likely to widen significantly.
Donald Trump’s halting of USAID funding had a ripple effect, impacting various healthcare initiatives in India. This reduction in aid could exacerbate existing organ shortage issues, making breakthroughs like the recent fda approves clinical trials for pig kidney transplants in humans even more crucial for exploring alternative solutions. Ultimately, the long-term consequences for Indian healthcare remain uncertain, highlighting the global interconnectedness of health systems.
Vulnerable Groups Most Affected
The most vulnerable populations in India who rely heavily on USAID-funded healthcare programs include those living in poverty, women, children, people with disabilities, tribal communities (Adivasis), and those residing in remote or conflict-affected areas. These groups often lack access to basic healthcare services, sanitation, and nutritious food, making them exceptionally susceptible to the consequences of reduced funding. For instance, women in rural areas might face increased maternal mortality rates due to limited access to antenatal care and skilled birth attendance.
Children in impoverished communities may suffer from higher rates of malnutrition and preventable diseases.
So, Trump halting USAID funding – a massive blow to India’s healthcare, right? It impacts everything from disease prevention to elderly care. Thinking about the elderly, I stumbled upon this fascinating article about how an eye test might predict dementia risk – check it out: can eye test detect dementia risk in older adults. That kind of early detection could be huge, especially given the strain on resources after the USAID cuts.
It really highlights the complex web of global health challenges.
Increased Health Disparities
Halting USAID funding would likely lead to a widening of the already significant health disparities across India. Access to essential medicines, vaccinations, and preventative healthcare services would decrease, particularly in underserved areas. This would result in a surge in preventable diseases, increased morbidity and mortality rates, and a significant setback in achieving India’s health goals. We might see a resurgence of diseases previously under control, like polio or measles, particularly among children in marginalized communities.
Furthermore, the lack of funding for health education and awareness campaigns could further hinder progress in improving health outcomes.
Specific Health Outcomes Worsening
Decreased funding could lead to a worsening of several key health indicators. Maternal mortality rates are likely to increase due to reduced access to prenatal care, skilled birth attendants, and emergency obstetric care. Infant and child mortality rates would also likely rise due to decreased access to vaccinations, nutrition programs, and treatment for common childhood illnesses. The prevalence of infectious diseases, particularly in areas with poor sanitation and hygiene, would likely increase.
Finally, access to treatment for chronic diseases like tuberculosis and HIV/AIDS could be severely compromised, leading to increased morbidity and mortality among affected individuals.
Compromised Healthcare Services
The following healthcare services, crucial for marginalized communities, may be significantly compromised:
- Maternal and Child Health Services: Reduced access to antenatal care, skilled birth attendance, postnatal care, and immunization programs, impacting maternal and child mortality rates.
- Preventive Healthcare: Decreased access to vaccinations, disease surveillance, and health education programs, leading to increased prevalence of preventable diseases.
- Treatment for Infectious Diseases: Reduced access to diagnosis and treatment for tuberculosis, HIV/AIDS, malaria, and other infectious diseases.
- Nutrition Programs: Reduced support for supplementary feeding programs for pregnant women, children, and those suffering from malnutrition.
- Healthcare Infrastructure: Delayed or cancelled improvements to healthcare facilities in remote and underserved areas.
Outcome Summary
The potential halt of USAID funding to India’s healthcare sector is a serious issue with far-reaching consequences. While alternative funding sources exist, they may not fully compensate for the loss of US support, leaving vulnerable populations at risk. The situation highlights the critical role of international cooperation in global health and the need for proactive strategies to ensure continued access to vital healthcare services in India.
The future of healthcare in India, and indeed global health initiatives, hangs in the balance, demanding immediate attention and collaborative solutions.
Helpful Answers
What specific programs within India’s healthcare system are most reliant on USAID funding?
Many programs are heavily reliant, including those focusing on HIV/AIDS, maternal and child health, tuberculosis control, and family planning. The specific programs and their dependence vary, necessitating a detailed analysis of individual initiatives.
Could private sector investment fully replace USAID funding?
While private sector investment could play a role, it’s unlikely to fully replace USAID funding. Private investment often prioritizes profitability, potentially leaving underserved and marginalized communities without access to essential healthcare.
What role do multilateral organizations like the WHO play in this situation?
Multilateral organizations like the WHO can step in to provide some support, but their resources are often limited and may not fully offset the loss of USAID funding. They would likely play a coordinating and advocacy role, working with other international actors to address the funding gap.
