
Elevance Private Equity Primary Care Partnership
Elevance Private Equity Primary Care Partnership: It sounds like a mouthful, right? But this model is reshaping how we access and experience primary care. Imagine a system where private equity investment fuels innovation and efficiency in your local doctor’s office. That’s the core idea behind these partnerships, a blend of financial expertise and medical practice that’s both promising and potentially problematic.
This post dives into the details, exploring the upsides, downsides, and everything in between.
We’ll examine the structure of these partnerships, looking at the roles of private equity firms, physician groups, and management companies. We’ll also analyze the investment strategies, operational improvements, and the crucial regulatory considerations. Most importantly, we’ll assess the impact – both positive and negative – on patient care and access. Get ready for a deep dive into the world of private equity and primary care!
Defining the Partnership

Source: slideplayer.com
Elevance Private Equity’s focus on primary care partnerships is fascinating, especially considering the scale of similar ventures. A prime example of this model’s success is seen in the rapid expansion of Humana Centerwell primary care centers in Walmart stores, as detailed in this article: humana centerwell primary care centers walmart. This demonstrates the potential for significant growth and reach within the primary care market, influencing the strategic decisions of firms like Elevance.
Private equity (PE) investment in primary care is transforming the healthcare landscape. These partnerships represent a significant shift from traditional solo or small group practices, offering potential for increased efficiency, improved patient care, and enhanced profitability. Understanding the structure and mechanics of these partnerships is crucial for anyone involved in or observing this evolving sector.The structure of a typical private equity-backed primary care partnership involves three key players: the private equity firm, the physician group, and a management services organization (MSO).
The PE firm provides the capital for expansion and operational improvements. The physicians contribute their medical expertise and patient base. The MSO, often a separate entity, handles the day-to-day management of the practice, including billing, staffing, and marketing. This three-legged stool model distributes responsibilities and leverages the unique strengths of each partner.
Roles and Responsibilities of Partners
The private equity firm’s role is primarily financial. They invest capital, provide strategic guidance, and often bring expertise in operational efficiency and scaling businesses. The physicians are responsible for delivering patient care, maintaining high clinical standards, and building relationships with patients. The MSO manages the business aspects of the practice, freeing up physicians to focus on patient care.
Each partner has clearly defined responsibilities and accountability measures within a comprehensive operating agreement. For example, the PE firm might set targets for revenue growth and profitability, while the MSO is accountable for operational efficiency and cost control. The physicians are held responsible for patient satisfaction scores and adherence to quality metrics.
Financial Model of the Partnership
Revenue streams typically include patient visits, insurance reimbursements, and potentially ancillary services such as lab testing or diagnostic imaging. Expenses include physician compensation, staff salaries, rent, supplies, and administrative costs. Profitability is determined by managing revenue streams effectively and controlling costs. A common financial model involves a combination of management fees and performance-based incentives. The PE firm receives a return on its investment through a combination of dividends and eventual sale of its stake in the partnership.
Profit sharing mechanisms are often included, distributing profits amongst the PE firm, physicians, and MSO based on pre-agreed percentages. For instance, a common arrangement might be a 70/30 split between the PE firm and the physician group, with the MSO receiving a fixed management fee and a smaller share of the profits.
Comparison with Other Primary Care Delivery Models
This PE-backed model differs significantly from traditional solo or small group practices, which often lack the capital and expertise for significant growth and operational improvements. Compared to hospital-employed physicians, the PE model offers greater autonomy and potential for higher earnings, although it also carries greater financial risk and management responsibilities. Independent physician associations (IPAs) offer a similar collaborative model, but often lack the significant capital infusion provided by PE firms.
The PE model can offer advantages in terms of scale, negotiating power with payers, and access to advanced technology and management expertise, leading to improved efficiency and potentially better patient outcomes. However, concerns about potential conflicts of interest and prioritization of profit over patient care remain a valid point of discussion. The success of this model heavily depends on effective governance and alignment of incentives among all partners.
Investment Strategy and Rationale
Elevance Private Equity’s investment strategy in the primary care sector is driven by a belief in the long-term growth potential of this essential healthcare segment. We see significant opportunities to improve operational efficiency, enhance patient experience, and ultimately deliver superior returns for our investors by partnering with high-quality primary care practices. Our approach focuses on identifying and supporting practices poised for significant expansion and improved profitability.The typical investment thesis for private equity firms in primary care centers on several key factors.
We look for practices with strong leadership teams, a proven track record of success, and a commitment to delivering high-quality patient care. Furthermore, we seek practices that are well-positioned to benefit from industry trends such as the increasing demand for primary care services, the shift towards value-based care, and the adoption of new technologies.
Key Drivers of Value Creation
Value creation in the primary care sector stems from several interconnected factors. Improving operational efficiency through streamlined processes, enhanced technology adoption, and optimized staffing models are critical. Expanding service offerings, such as adding telehealth capabilities or specialized services like chronic disease management, also drives value. Finally, negotiating favorable contracts with payers and leveraging economies of scale to reduce costs significantly contribute to profitability.
For example, a successful investment might involve consolidating several smaller practices into a larger network, allowing for centralized billing, purchasing, and administrative functions. This consolidation can lead to substantial cost savings and improved negotiating power with insurance providers.
Potential Risks and Challenges
Investing in primary care is not without its challenges. Regulatory changes, reimbursement rate fluctuations, and competition from other healthcare providers are significant risks. Physician recruitment and retention can also be a major hurdle, particularly in underserved areas. Furthermore, the integration of new technologies and the adoption of value-based care models require significant investment and expertise. For instance, the transition to value-based care necessitates significant changes in practice workflows and data analytics capabilities, which can be expensive and time-consuming to implement.
A thorough understanding of these risks and the development of mitigation strategies are crucial for success.
Due Diligence Process
Our due diligence process is rigorous and comprehensive. It involves a thorough review of the target practice’s financial performance, operational efficiency, clinical quality metrics, and compliance history. We conduct extensive interviews with physicians, staff, and patients to assess the practice’s culture and reputation. Furthermore, we analyze the market dynamics in the target practice’s geographic area, including competition, demographics, and payer mix.
This multi-faceted approach allows us to assess the practice’s long-term viability and potential for growth. The process also includes a detailed legal and regulatory review to ensure compliance with all applicable laws and regulations. Finally, we assess the management team’s capabilities and their ability to execute the proposed growth strategy.
Operational Improvements and Strategies
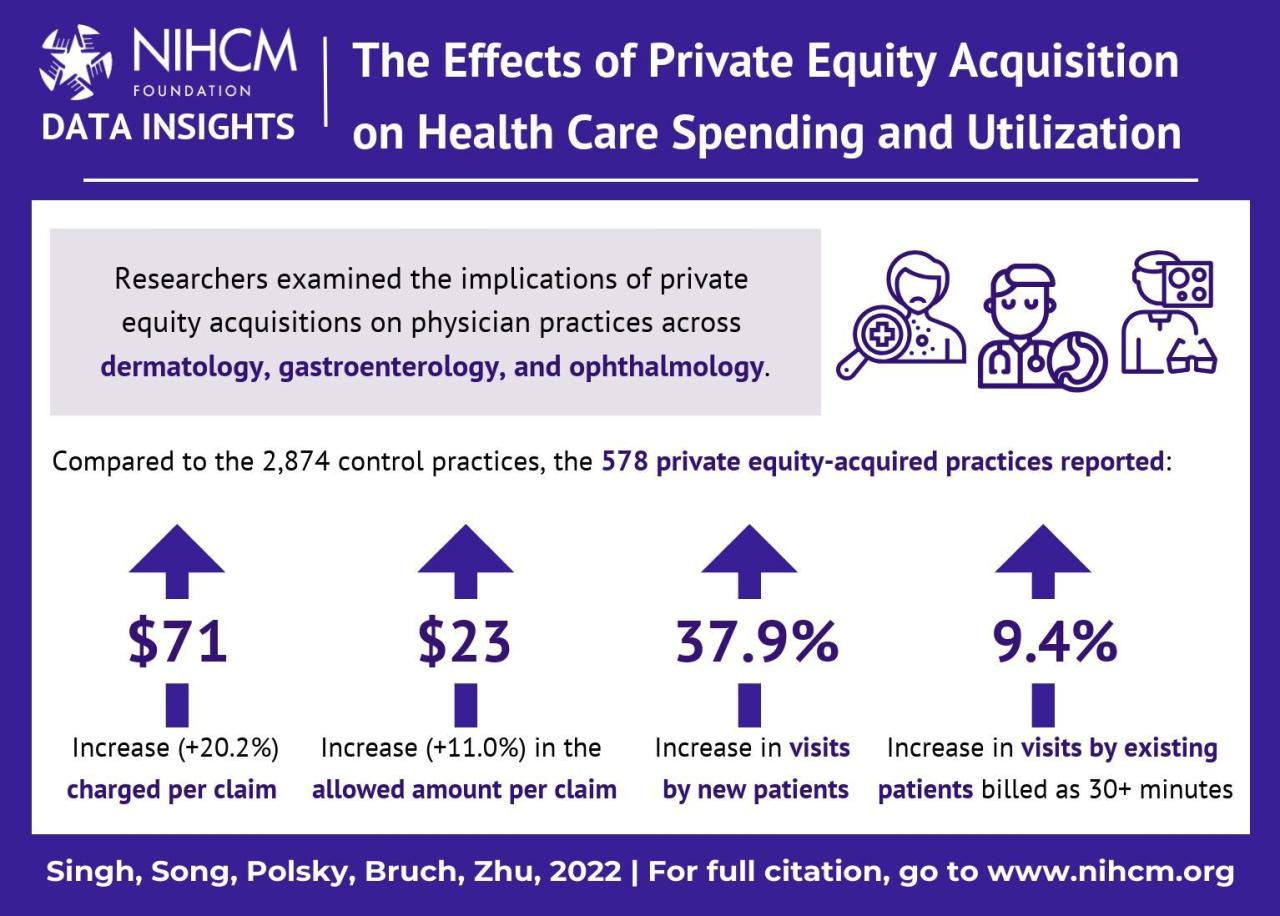
Source: nihcm.org
Private equity investment in primary care often focuses on improving operational efficiency and profitability while enhancing patient care. This involves a multi-pronged approach targeting operational improvements, technology integration, and workforce optimization. Successful strategies leverage data analytics to identify areas for improvement and implement scalable solutions across multiple clinics.
Operational Improvements Implemented by Private Equity Firms
Private equity firms typically implement several key operational improvements in their primary care partnerships. These improvements often lead to significant increases in efficiency and profitability. The following table illustrates potential pre- and post-investment metrics, highlighting the impact of these strategies. Note that these are illustrative examples and actual results will vary depending on the specific circumstances of each partnership.
| Metric | Pre-Investment | Post-Investment | Change |
|---|---|---|---|
| Patient Satisfaction (NPS Score) | 65 | 78 | +13 |
| Operational Efficiency (Patients per Physician per Day) | 15 | 20 | +5 |
| Revenue per Physician | $500,000 | $650,000 | +$150,000 |
| Physician Turnover Rate | 15% | 8% | -7% |
Improving Patient Access and Reducing Wait Times
A key focus for improving patient experience is enhancing access and reducing wait times. Strategies include implementing online scheduling systems, expanding appointment slots during peak hours, utilizing telehealth for routine follow-ups, and optimizing appointment durations through improved workflow processes. For example, one PE-backed primary care group successfully reduced average wait times by 40% by implementing a sophisticated appointment scheduling system that incorporated real-time patient flow data and predictive analytics.
This allowed them to allocate appointment slots more efficiently and minimize patient wait times.
Enhancing Physician Recruitment and Retention
Attracting and retaining high-quality physicians is crucial for the long-term success of any primary care partnership. Strategies include offering competitive compensation and benefits packages, providing opportunities for professional development and leadership roles, fostering a positive and supportive work environment, and investing in advanced technology to reduce administrative burden on physicians. One successful approach involves offering physicians equity stakes in the practice, aligning their financial incentives with the overall success of the partnership.
This creates a sense of ownership and encourages greater commitment.
Implementing Technology Solutions to Improve Efficiency and Patient Care
Technology plays a vital role in enhancing efficiency and patient care. Implementing electronic health records (EHRs), patient portals, telehealth platforms, and practice management software can streamline administrative tasks, improve communication, and enhance the overall patient experience. For example, the integration of a robust EHR system can automate appointment reminders, facilitate secure messaging between patients and physicians, and improve the accuracy of billing and coding.
Furthermore, telehealth capabilities can expand access to care for patients in remote areas or with mobility limitations, increasing patient satisfaction and improving health outcomes.
Regulatory and Legal Considerations
Navigating the regulatory landscape for private equity investment in primary care requires a keen understanding of complex and evolving rules. Failure to comply can lead to significant financial penalties, reputational damage, and even legal action. This section Artikels key regulatory and legal considerations for our partnership.The regulatory environment surrounding private equity investment in healthcare, specifically primary care, is multifaceted and varies by jurisdiction.
Federal and state laws govern aspects such as antitrust compliance, healthcare fraud and abuse, patient privacy (HIPAA), and licensing requirements for healthcare providers. These regulations aim to protect patients, ensure fair competition, and prevent conflicts of interest. Understanding and adhering to these regulations is paramount for the success and longevity of our partnership.
Antitrust Laws and Regulations
Antitrust laws are designed to prevent monopolies and promote competition. In the context of private equity investment in primary care, this means scrutinizing potential acquisitions or mergers to ensure they don’t unduly reduce competition within a specific geographic market. The Federal Trade Commission (FTC) and the Department of Justice (DOJ) actively review such transactions, often requiring extensive documentation and analysis to demonstrate that the proposed investment will not harm consumers through higher prices or reduced access to care.
For example, a private equity firm attempting to acquire a significant number of primary care practices in a small town might face intense scrutiny from regulators concerned about the potential for monopolistic practices. Our partnership will proactively engage with regulatory bodies to ensure compliance and avoid potential legal challenges.
Healthcare Fraud and Abuse
The healthcare industry is unfortunately susceptible to fraud and abuse. Private equity investors in primary care must implement robust compliance programs to prevent and detect such activities. The False Claims Act, for instance, imposes significant penalties for knowingly submitting false or fraudulent claims to government payers like Medicare and Medicaid. Our partnership will establish clear policies and procedures to ensure billing accuracy, appropriate coding, and adherence to all relevant regulations to minimize risk.
This will involve regular audits, training for staff, and a strong compliance culture.
Patient Privacy (HIPAA) Compliance
The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) sets strict standards for protecting the privacy and security of patient health information (PHI). Private equity firms investing in primary care must ensure that their portfolio companies comply fully with HIPAA regulations. This includes implementing appropriate security measures, training staff on HIPAA compliance, and establishing procedures for handling PHI appropriately.
Failure to comply with HIPAA can result in substantial fines and legal repercussions. Our partnership will prioritize HIPAA compliance through regular audits, employee training, and the implementation of advanced security systems.
Key Legal Considerations for Contract Negotiation
Effective contract negotiation is crucial for the success of this partnership. Several key legal considerations must be addressed:
- Exclusivity and Non-Compete Clauses: These clauses define the scope of the partnership and protect against conflicts of interest. Carefully defining the geographic area and the types of services covered is essential.
- Intellectual Property Rights: Clear ownership and usage rights for intellectual property, such as medical software or proprietary treatment protocols, need to be established.
- Data Privacy and Security: Contracts should address data ownership, access, and security measures, particularly concerning patient health information.
- Termination and Dispute Resolution: Clear procedures for termination of the partnership and mechanisms for resolving disputes should be included.
- Indemnification and Liability: Contracts should allocate responsibility for potential liabilities and provide indemnification provisions to protect the partners.
- Regulatory Compliance: The contracts should explicitly Artikel the parties’ responsibilities regarding regulatory compliance, including HIPAA and antitrust laws.
Impact on Patient Care and Access
Private equity (PE) investment in primary care is a rapidly evolving landscape, presenting both opportunities and challenges for patient care and access. While the influx of capital can potentially improve infrastructure, technology, and staffing, concerns remain regarding the potential for profit maximization to outweigh patient needs. A careful examination of the potential impacts, both positive and negative, is crucial for stakeholders involved.The integration of PE into primary care can lead to significant improvements in patient care.
Increased funding can translate into better facilities, upgraded technology (like electronic health records and telehealth platforms), and recruitment of additional qualified healthcare professionals, ultimately enhancing the quality of care provided. This could also lead to expanded access to care, particularly in underserved communities where resources are limited. However, a key concern revolves around the potential for PE firms to prioritize profitability over patient well-being, leading to reduced service quality, increased wait times, and a focus on high-margin procedures rather than comprehensive primary care.
Positive Impacts of Private Equity Investment on Patient Care
PE investment can facilitate the expansion of primary care services, particularly in underserved areas. For example, a PE-backed primary care provider might invest in building new clinics in rural or low-income communities, increasing access to care for patients who previously lacked it. Furthermore, the infusion of capital can support the adoption of innovative technologies, improving efficiency and patient experience.
Elevance Private Equity’s partnership with primary care providers is all about improving patient outcomes. A key area of focus should be preventative care, as understanding and managing risk factors is crucial. For instance, check out this article on risk factors that make stroke more dangerous to see how proactive healthcare can make a huge difference.
Ultimately, Elevance’s investment aims to build a healthier future through better access to comprehensive primary care.
This could include implementing telehealth platforms for remote consultations, streamlining appointment scheduling, and enhancing data analysis for better patient management. Improved infrastructure, such as updated medical equipment and comfortable waiting areas, can also contribute to a more positive patient experience. Finally, increased financial resources can allow practices to recruit and retain highly skilled physicians and other healthcare professionals, leading to improved quality of care.
Negative Impacts of Private Equity Investment on Patient Care
Conversely, the pursuit of profit maximization by PE firms can negatively impact patient care. There’s a potential for cost-cutting measures that compromise the quality of care, such as reducing staffing levels, limiting access to specialists, or increasing patient volume per provider. The emphasis on profitability may lead to a shift away from comprehensive primary care towards procedures with higher profit margins, potentially neglecting preventative care and chronic disease management.
Furthermore, the increased administrative burden associated with PE involvement can divert resources and attention away from direct patient care. A focus on rapid expansion and consolidation can also lead to a decline in the patient-physician relationship, as providers may face pressure to see more patients in shorter timeframes.
Comparison of Patient Experiences Across Different Primary Care Models
Comparing patient experiences in PE-backed practices to those in other models (e.g., independent practices, non-profit clinics) requires careful consideration of various factors. While PE-backed practices might offer improved facilities and technology, independent practices may foster stronger physician-patient relationships due to a more personalized approach. Non-profit clinics often prioritize community needs and affordability, providing care to vulnerable populations. Direct comparisons are difficult due to a lack of standardized data collection across different primary care models.
However, research focusing on patient satisfaction scores, wait times, and access to care in different practice settings could offer valuable insights.
Examples of Successful and Unsuccessful Implementations of Private Equity Partnerships, Elevance private equity primary care partnership
While specific data on PE-backed primary care’s impact on patient outcomes is limited due to a lack of publicly available, standardized metrics, anecdotal evidence suggests a mixed bag. Some PE partnerships have successfully modernized practices, improved access, and enhanced patient experience through technology and staffing improvements. However, other instances have resulted in increased patient volumes, reduced provider time per patient, and potential compromises in the quality of care due to cost-cutting measures.
A lack of transparency regarding the financial performance and patient outcomes of PE-backed primary care practices hinders comprehensive analysis.
Strategies for Mitigating Negative Impacts on Patient Care
Several strategies can help mitigate the potential negative impacts of PE investment on patient care. These include establishing clear performance metrics focused on patient outcomes, rather than solely on financial returns. Independent oversight bodies could monitor PE-backed practices to ensure adherence to quality standards and ethical guidelines. Transparency and public reporting of key performance indicators, including patient satisfaction, access to care, and quality metrics, would help hold PE firms accountable.
Furthermore, regulations and policies could be implemented to protect against practices that prioritize profit over patient well-being, ensuring a balance between financial viability and high-quality care.
Future Trends and Projections

Source: mekdesmezgebu.com
The intersection of private equity and primary care is poised for significant growth, driven by factors such as an aging population, increasing healthcare costs, and the ongoing evolution of healthcare delivery models. Analyzing current trends and projecting future developments is crucial for understanding the long-term viability and impact of this partnership. This section will explore projected growth, emerging trends, disruptive technologies, and the long-term sustainability of the Elevanse Private Equity Primary Care Partnership model.
Projections for private equity investment in primary care point towards a robust expansion in the coming years. Several market research firms predict a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) exceeding 15% for the next decade. This growth is fueled by the increasing attractiveness of primary care as an asset class, offering relatively stable cash flows and opportunities for operational improvement and scale.
Elevance Private Equity’s focus on primary care partnerships makes me think about the bigger picture of healthcare consolidation. The recent news that the Federal Trade Commission is suing to block Novant Health and Community Health Systems’ hospital acquisition, as reported here: federal trade commission sues block novant health community health systems hospital acquisition , highlights the ongoing debate around market competition and access to care.
This legal battle underscores the complexities Elevance faces in navigating the evolving landscape of healthcare investments.
For example, the significant investment by large PE firms like Welsh, Carson, Anderson & Stowe (WCAS) in physician groups demonstrates the confidence in this sector’s potential. These investments are not solely focused on acquisition; they also involve significant capital expenditures for technological upgrades, staff training, and expansion into underserved areas.
Private Equity Investment Growth Projections
While precise figures vary depending on the source and methodology, a consensus is emerging around significant growth. Conservative estimates suggest a doubling of private equity investment in primary care within the next five years, with more aggressive projections pointing to a tripling or even quadrupling. This growth is expected to be driven by several factors, including the increasing consolidation of physician practices, the need for capital investment to support technological advancements, and the potential for improved operational efficiency through private equity’s expertise.
Emerging Trends Shaping the Future of Primary Care
Several key trends are reshaping the primary care landscape, significantly impacting the Elevanse partnership. These trends are not independent; rather, they interact and reinforce each other, creating a dynamic and evolving environment.
- Value-Based Care: The shift from fee-for-service to value-based care models is accelerating. This means providers are increasingly compensated based on the quality and outcomes of care, rather than the volume of services provided. This incentivizes investments in preventative care and population health management, which align well with the long-term goals of the partnership.
- Technological Advancements: Telehealth, remote patient monitoring, and artificial intelligence (AI) are transforming how primary care is delivered. These technologies offer opportunities for increased access, improved efficiency, and better patient outcomes. The partnership’s ability to leverage these technologies will be crucial for its success.
- Consolidation and Integration: The increasing consolidation of physician practices and the integration of primary care with other healthcare services are major trends. This allows for economies of scale, improved coordination of care, and a more comprehensive approach to patient management.
Disruptive Technologies and Their Impact
The rapid advancement of technology presents both opportunities and challenges for the partnership. The successful integration of these technologies will be crucial for maintaining a competitive edge and achieving long-term sustainability.
- AI-powered diagnostics: AI algorithms can analyze patient data to improve diagnostic accuracy and efficiency, reducing the burden on physicians and improving patient outcomes. For example, AI can assist in early detection of diseases like diabetes or heart disease through analysis of patient records and wearable sensor data.
- Telehealth platforms: These platforms expand access to care, particularly for patients in rural or underserved areas. Features like remote monitoring and virtual consultations can improve patient engagement and reduce healthcare costs.
- Electronic health records (EHR) integration: Seamless EHR integration is crucial for efficient data sharing and improved care coordination. This requires significant investment in technology and training but can lead to significant improvements in operational efficiency and patient outcomes. For instance, improved data analysis can lead to better population health management and more proactive interventions.
Long-Term Sustainability of the Partnership Model
The long-term sustainability of the Elevanse partnership hinges on several factors. Its ability to adapt to evolving market dynamics, effectively leverage technological advancements, and maintain a focus on patient-centered care will be critical. The partnership’s commitment to value-based care, its strategic investments in technology, and its focus on operational efficiency position it favorably for long-term success. The strong track record of Elevanse in operational improvements, coupled with the growing demand for high-quality primary care, creates a positive outlook for the partnership’s continued growth and sustainability.
Last Recap: Elevance Private Equity Primary Care Partnership
The Elevance Private Equity Primary Care Partnership model presents a complex picture. While the promise of improved efficiency and access to care is enticing, potential downsides related to patient care quality and the inherent conflicts of interest need careful consideration. Ultimately, the success of this model hinges on a delicate balance between financial goals and the ethical obligation to provide high-quality, patient-centered care.
The future of primary care may well depend on navigating this intricate landscape successfully.
FAQ Explained
What is the typical return on investment for private equity firms in primary care?
ROI varies significantly depending on factors like market conditions, the specific partnership’s performance, and the length of the investment period. While some investments yield substantial returns, others may fall short of expectations.
How do these partnerships affect physician autonomy?
This is a key concern. The level of physician autonomy can vary greatly depending on the specific partnership agreement. Some partnerships maintain a high degree of physician autonomy, while others may involve more centralized control and decision-making.
What are the potential long-term consequences of increased private equity involvement in primary care?
The long-term effects are still unfolding and subject to debate. Potential positive outcomes include improved efficiency and access, while potential negative consequences include increased costs, reduced patient choice, and compromised quality of care if not managed properly.





