Fertility Treatment Options for Women with PCOS
Fertility treatment options for women with PCOS can feel overwhelming, but understanding your choices is empowering. Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) affects millions, impacting ovulation and making conception challenging. This post explores various avenues, from lifestyle changes and medication to advanced reproductive technologies, helping you navigate your journey to parenthood.
We’ll delve into the science behind PCOS and its effect on fertility, examining hormonal imbalances and their impact on egg quality and ovulation. Then, we’ll explore practical strategies like diet, exercise, and stress management, showcasing how lifestyle modifications can significantly improve your chances of conceiving. We’ll also discuss various fertility medications, comparing their effectiveness and side effects, and explain the ins and outs of procedures like IVF and IUI.
Finally, we’ll address the emotional side of fertility struggles and offer resources for support.
Understanding PCOS and its Impact on Fertility
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is a hormonal disorder affecting many women of reproductive age, significantly impacting their fertility. Understanding the intricate interplay of hormones and its effect on ovulation and egg quality is crucial for effective treatment and improved chances of conception.
Hormonal Imbalances in PCOS and Their Effect on Fertility
PCOS is characterized by an imbalance of reproductive hormones. Specifically, women with PCOS often have elevated levels of androgens (male sex hormones) like testosterone. This increased androgen production interferes with the normal functioning of the ovaries. High levels of luteinizing hormone (LH) relative to follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) further disrupt the delicate balance needed for regular ovulation. Insulin resistance, another common feature of PCOS, can exacerbate these hormonal imbalances and contribute to irregular periods and ovulation dysfunction.
The combined effect of these hormonal disruptions makes it difficult for the ovaries to release mature eggs regularly, a prerequisite for successful conception.
PCOS’s Disruption of Ovulation and Egg Quality
The elevated androgens in PCOS can lead to a condition called anovulation, where the ovaries fail to release an egg each month. Even when ovulation does occur, the quality of the eggs produced may be compromised. The ovarian follicles, which contain the developing eggs, may not mature properly, resulting in eggs that are less likely to be fertilized.
Furthermore, the presence of numerous small, fluid-filled cysts on the ovaries, a hallmark of PCOS, can further impede the development and release of healthy eggs. This combination of irregular or absent ovulation and compromised egg quality significantly reduces the chances of natural conception.
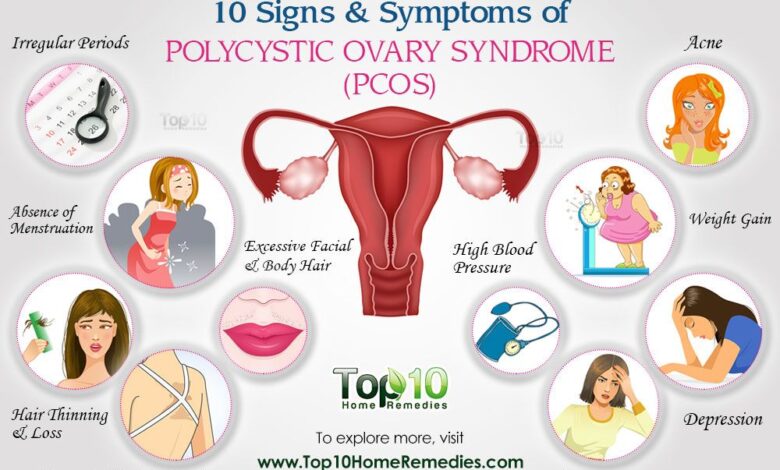
Common PCOS Symptoms and Their Link to Infertility
Many women with PCOS experience a range of symptoms that can be directly linked to infertility. Irregular or absent menstrual periods (oligomenorrhea or amenorrhea) are common, reflecting the disruption in ovulation. Excessive hair growth (hirsutism), acne, and weight gain are also frequently observed, stemming from the elevated androgen levels. These symptoms are not only aesthetically challenging but also indicative of the underlying hormonal imbalances that affect fertility.
While not all women with PCOS experience every symptom, the presence of several of these signs should prompt a consultation with a healthcare professional to assess fertility potential.
So, you’re researching fertility treatment options for women with PCOS? It’s a complex journey, and finding the right path can feel overwhelming. Interestingly, research into completely different areas, like how an eye test might detect dementia risk in older adults, as discussed in this fascinating article can eye test detect dementia risk in older adults , highlights how early detection and intervention are key in various health areas.
This reminds me how crucial early intervention is also in managing PCOS and maximizing chances of successful fertility treatment.
Diagnosing PCOS: A Comprehensive Overview
Diagnosing PCOS typically involves a combination of methods. A thorough medical history, including details about menstrual cycles, symptoms, and family history, is the first step. A physical examination may reveal signs of hirsutism or other physical manifestations of the condition. Blood tests are essential to measure hormone levels, including testosterone, LH, FSH, and insulin. Ultrasound imaging of the ovaries allows visualization of the characteristic polycystic appearance, characterized by numerous small follicles.
The diagnosis of PCOS relies on the presence of at least two of these three criteria: irregular periods, elevated androgen levels, and polycystic ovaries on ultrasound. It’s important to note that the diagnostic process may require multiple visits and tests to obtain a comprehensive understanding of the individual’s condition.
Lifestyle Modifications for Improving Fertility in PCOS

Source: pinimg.com
Living with PCOS can present challenges to fertility, but thankfully, lifestyle changes can significantly improve your chances of conceiving. By focusing on diet, exercise, stress management, and weight management, you can take proactive steps to support your reproductive health. These changes aren’t just about getting pregnant; they contribute to overall well-being and can alleviate many PCOS symptoms.
Dietary Changes for PCOS and Fertility
A balanced diet plays a crucial role in managing PCOS symptoms and improving fertility. The goal is to reduce insulin resistance, inflammation, and androgen levels. This involves focusing on whole, unprocessed foods and limiting refined carbohydrates, processed foods, and unhealthy fats.A sample meal plan might include:
- Breakfast: Oatmeal with berries and nuts, or Greek yogurt with fruit and a sprinkle of chia seeds.
- Lunch: Large salad with grilled chicken or fish, plenty of vegetables, and a light vinaigrette dressing.
- Dinner: Baked salmon with roasted vegetables (broccoli, sweet potatoes, asparagus), or lentil soup with whole-grain bread.
- Snacks: Handful of almonds, apple slices with peanut butter, or a small portion of dark chocolate.
It’s important to consult a registered dietitian or nutritionist to create a personalized meal plan that caters to your individual needs and preferences. They can help you navigate food choices and ensure you’re meeting your nutritional requirements.
The Benefits of Regular Exercise for Women with PCOS
Regular physical activity is essential for managing PCOS. Exercise helps improve insulin sensitivity, reduce weight, and regulate hormone levels. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise per week, such as brisk walking, swimming, or cycling. Incorporate strength training exercises at least twice a week to build muscle mass, which further improves insulin sensitivity. Examples include squats, lunges, push-ups, and weight lifting.
Remember to listen to your body and gradually increase the intensity and duration of your workouts.
Stress Management and its Impact on Fertility
Chronic stress can disrupt hormonal balance and negatively impact fertility. High levels of cortisol, the stress hormone, can interfere with ovulation and make it harder to conceive. Practicing stress-reduction techniques is vital. These can include:
- Mindfulness and meditation: Regular practice can help calm the mind and reduce anxiety.
- Yoga and deep breathing exercises: These promote relaxation and reduce stress hormones.
- Spending time in nature: Connecting with nature has been shown to have calming effects.
- Getting enough sleep: Aim for 7-8 hours of quality sleep per night.
Finding healthy coping mechanisms for stress is crucial for overall well-being and fertility.
Weight Management and Fertility in PCOS
Weight loss, even a modest amount, can significantly improve fertility in women with PCOS. Losing weight helps improve insulin sensitivity and regulate hormone levels, making ovulation more regular. A weight management plan should combine a healthy diet, as described above, with regular exercise. It’s important to adopt a sustainable approach to weight loss, focusing on gradual and consistent changes rather than quick fixes.
Consult your doctor or a registered dietitian for guidance on a safe and effective weight loss plan tailored to your specific needs. A gradual weight loss of 5-10% of your body weight can often make a substantial difference. For example, a woman weighing 200 pounds might aim to lose 10-20 pounds. This should be done under medical supervision to ensure it is done safely and effectively.
Fertility Medications for PCOS
PCOS can significantly impact fertility by disrupting ovulation. Fortunately, several medications can help women with PCOS conceive. These medications work through different mechanisms to stimulate ovulation and improve the chances of pregnancy. Choosing the right medication depends on individual factors like the severity of PCOS, response to previous treatments, and overall health. It’s crucial to work closely with a fertility specialist to determine the best course of action.
Ovulation-Inducing Medications: A Comparison
The following table compares several common ovulation-inducing medications used in the treatment of PCOS-related infertility. Success rates can vary greatly depending on individual factors and the specific medication regimen. It’s essential to remember that these are averages and individual results may differ.
| Medication Name | Mechanism of Action | Side Effects | Success Rates (Approximate) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Clomiphene Citrate (Clomid) | Blocks estrogen receptors in the hypothalamus, leading to increased GnRH release and subsequent FSH and LH surge, stimulating follicle growth and ovulation. | Hot flashes, mood swings, headaches, ovarian cysts, multiple pregnancies (twins or higher), visual disturbances. | 25-40% per cycle |
| Letrozole | Inhibits aromatase, an enzyme that converts androgens to estrogen. This leads to increased FSH and LH levels, stimulating follicle growth and ovulation. | Hot flashes, headaches, nausea, joint pain, increased risk of multiple pregnancies. | 20-30% per cycle (often considered comparable to or slightly better than clomiphene in some studies) |
| Gonadotropins (FSH & LH) | Directly stimulate follicle growth and maturation by mimicking the natural hormones FSH and LH. | Ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS), multiple pregnancies, headaches, mood swings, injection site reactions. | Higher success rates than Clomiphene Citrate and Letrozole, but higher risk of complications. Success rates vary significantly depending on dosage and individual response. |
Clomiphene Citrate: Mechanism and Side Effects
Clomiphene citrate (Clomid) is a commonly used first-line treatment for PCOS-related infertility. It works by blocking estrogen receptors in the hypothalamus. This action tricks the body into thinking estrogen levels are low, leading to increased production of gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH). GnRH then stimulates the pituitary gland to release more follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH). The increased FSH and LH levels promote follicle growth and maturation in the ovaries, ultimately triggering ovulation.
However, Clomid can cause side effects such as hot flashes, mood swings, headaches, and a slightly increased risk of multiple pregnancies. In rare cases, it can also cause visual disturbances.
Letrozole: Ovulation Induction and Efficacy, Fertility treatment options for women with pcos
Letrozole is an aromatase inhibitor, meaning it blocks the enzyme aromatase, which is responsible for converting androgens into estrogen. By reducing estrogen production, letrozole indirectly increases FSH and LH levels, thereby stimulating follicular growth and ovulation. Studies suggest letrozole may be comparable to or slightly more effective than clomiphene citrate in inducing ovulation in women with PCOS, with potentially fewer side effects in some cases.
However, it also carries risks such as hot flashes, headaches, and a slightly increased risk of multiple pregnancies.
Gonadotropins (FSH and LH) in Severe PCOS Infertility
In cases where clomiphene citrate and letrozole have failed to induce ovulation, or when a woman has more severe forms of PCOS, gonadotropins (FSH and LH) may be used. These medications directly stimulate the ovaries, promoting follicle growth and maturation. Gonadotropins are injected daily, and their dosage is carefully monitored through ultrasound and blood tests to minimize the risk of ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS), a potentially serious complication.
While gonadotropins have higher success rates than clomiphene citrate and letrozole, they also carry a greater risk of side effects, including OHSS and multiple pregnancies.
Assisted Reproductive Technologies (ART) for PCOS
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) can significantly impact fertility, making conception challenging for many women. When lifestyle modifications and fertility medications prove insufficient, assisted reproductive technologies (ART) offer a powerful pathway to pregnancy. Two of the most common ART procedures are in vitro fertilization (IVF) and intrauterine insemination (IUI). Understanding the differences and choosing the right approach is crucial for maximizing success.
IVF and IUI: A Comparison
The decision between IVF and IUI hinges on several factors related to a woman’s individual circumstances and the severity of her PCOS. A careful assessment by a fertility specialist is essential to determine the most appropriate path.
- IVF (In Vitro Fertilization): IVF involves retrieving eggs from the ovaries, fertilizing them with sperm in a laboratory setting, and then transferring the resulting embryos into the uterus. This is a more complex and invasive procedure, but it offers a higher chance of success for women with severe PCOS or other significant fertility challenges.
- IUI (Intrauterine Insemination): IUI is a less invasive procedure where specially prepared sperm is directly placed into the uterus around the time of ovulation. This procedure is simpler and less expensive than IVF, but it has a lower success rate, especially for women with severe PCOS or other significant fertility issues. It is often attempted first if there are fewer significant obstacles to conception.
The IVF Process: A Step-by-Step Overview
IVF is a multi-step process requiring careful monitoring and management. The goal is to stimulate the ovaries to produce multiple mature eggs, retrieve those eggs, fertilize them, and then transfer healthy embryos back into the uterus.
- Ovarian Stimulation: Fertility medications are administered to stimulate the ovaries to produce multiple mature eggs. This process is carefully monitored through blood tests and ultrasounds to ensure optimal egg development and avoid overstimulation.
- Egg Retrieval: Once the eggs are mature, a minor surgical procedure is performed to retrieve them using a needle guided by ultrasound. This is typically done under sedation or light anesthesia.
- Fertilization: The retrieved eggs are then combined with the partner’s or donor sperm in a laboratory dish to allow fertilization. The embryologist monitors the eggs for fertilization and early embryo development.
- Embryo Transfer: After a few days of development in the lab, one or more healthy embryos are transferred into the uterus using a thin catheter. This is a painless procedure.
The IUI Procedure and Success Rates in Women with PCOS
IUI involves a simpler process compared to IVF. The procedure typically begins with monitoring ovulation using blood tests and ultrasounds. Once ovulation is imminent, a prepared sperm sample is inserted into the uterus using a thin catheter. The procedure is generally well-tolerated and requires minimal recovery time.Success rates for IUI in women with PCOS vary widely, depending on factors such as age, the severity of PCOS, and the cause of infertility.
While IUI can be successful for some women with PCOS, it is generally less effective than IVF for those with more significant fertility challenges. Studies suggest that IUI success rates in women with PCOS are lower than those without PCOS. For example, a study might show a success rate of 10-15% per cycle for women with PCOS undergoing IUI, compared to a higher rate in women without PCOS.
Selection Criteria for IVF vs. IUI in PCOS
The choice between IVF and IUI depends on various factors, including the woman’s age, the severity of her PCOS, the duration of infertility, and the results of previous fertility treatments. Women with severe PCOS, significant tubal damage, or other significant fertility issues are more likely to benefit from IVF. Women with milder forms of PCOS and fewer complicating factors might have a reasonable chance of success with IUI, often as a first-line approach.
A detailed assessment by a reproductive endocrinologist is crucial to guide the decision-making process, weighing the potential benefits and risks of each procedure. Factors such as cost and time commitment should also be considered.
Surgical Interventions for PCOS-Related Infertility

Source: prepladder.com
For some women with PCOS, lifestyle changes and medication aren’t enough to overcome infertility. In these cases, surgical intervention may be considered as a potential pathway to pregnancy. These procedures aim to improve ovarian function and increase the chances of ovulation. It’s crucial to understand that surgery isn’t a guaranteed solution, and the decision to proceed should be made in close consultation with a fertility specialist.
Laparoscopic Ovarian Drilling (LOD)
Laparoscopic ovarian drilling (LOD) is a minimally invasive surgical procedure used to treat PCOS-related infertility. It involves using a laparoscope, a thin, lighted tube with a camera, to make small incisions in the abdomen. Through these incisions, specialized instruments are inserted to destroy or cauterize some of the ovarian tissue containing the increased number of small cysts characteristic of PCOS.
The mechanism of action is believed to be related to reducing the production of androgens (male hormones) by the ovaries, thereby restoring a more regular menstrual cycle and improving ovulation. The procedure aims to restore a balance in hormone production, leading to a greater chance of conception.
Benefits and Risks of LOD
LOD can offer several potential benefits, including improved ovulation rates, more regular menstrual cycles, and increased chances of pregnancy. However, like any surgical procedure, there are potential risks. These can include bleeding, infection, damage to surrounding organs, and the possibility that the procedure may not improve fertility. Furthermore, the benefits of LOD may not be long-lasting, and some women may require repeat procedures or further fertility treatments.
The success rate of LOD varies depending on factors such as the woman’s age, the severity of her PCOS, and the experience of the surgeon.
Other Surgical Options for Treating PCOS-Related Infertility
While LOD is the most common surgical intervention for PCOS-related infertility, other surgical options exist. These might include procedures to remove ovarian cysts or address other anatomical issues that may be contributing to infertility. For instance, if a woman has significant uterine fibroids (benign tumors in the uterus) that are impeding implantation, a myomectomy (surgical removal of fibroids) might be considered.
In cases of severe endometriosis (a condition where uterine tissue grows outside the uterus), laparoscopic surgery may be used to remove the endometrial tissue. The choice of surgical intervention depends entirely on the individual’s specific circumstances and the findings of a thorough fertility evaluation.
Recovery Process Following Surgical Interventions for PCOS
The recovery process following surgical interventions for PCOS varies depending on the specific procedure performed. For LOD, patients typically experience minimal discomfort and can return to their normal activities within a few days. However, more extensive procedures may require a longer recovery period. Patients should follow their doctor’s instructions carefully regarding pain management, activity restrictions, and follow-up appointments.
The recovery period also involves monitoring for any potential complications and ensuring the body is healing appropriately. Most women are able to attempt conception once their recovery is complete and their doctor approves.
Managing PCOS-Related Infertility
Successfully navigating PCOS-related infertility requires a comprehensive and personalized approach that goes beyond addressing symptoms alone. It necessitates a collaborative effort between the patient and a team of healthcare professionals, working together to optimize her chances of conception. This holistic strategy acknowledges the complex interplay of hormonal imbalances, lifestyle factors, and emotional well-being in influencing fertility outcomes.
The Importance of a Multidisciplinary Approach
Effective management of PCOS infertility hinges on a multidisciplinary team. An endocrinologist specializes in hormonal disorders, diagnosing and treating PCOS’s underlying hormonal imbalances. A reproductive endocrinologist or fertility specialist possesses expertise in assisted reproductive technologies (ART) and other advanced fertility treatments. Other professionals, such as registered dietitians, psychologists, and acupuncturists, may also play crucial roles in providing tailored support and addressing individual needs.
This collaborative approach ensures a well-rounded assessment and treatment plan that considers all aspects of the patient’s health and well-being. For example, a dietitian can help create a personalized nutrition plan to manage weight and insulin resistance, while a psychologist can provide emotional support and coping strategies.
Creating a Personalized Treatment Plan
Developing a personalized treatment plan involves a thorough assessment of the individual’s specific circumstances. This begins with a comprehensive evaluation by the endocrinologist and fertility specialist, which may include blood tests, ultrasounds, and other diagnostic procedures to assess ovarian function and hormone levels. Based on these findings, the plan may incorporate lifestyle modifications such as weight management, dietary changes, and regular exercise.
If lifestyle changes alone are insufficient, medication, such as metformin or clomiphene citrate, may be prescribed to stimulate ovulation. If these interventions fail to achieve pregnancy, the team may recommend ART, such as intrauterine insemination (IUI) or in-vitro fertilization (IVF). The choice of treatment depends on the individual’s age, overall health, and specific fertility challenges. For instance, a woman with severe PCOS and significant insulin resistance might benefit from a combination of metformin, lifestyle modifications, and ultimately, IVF.
Challenges Faced During Fertility Treatment and Coping Strategies
Undergoing fertility treatment can be emotionally and physically demanding. Women with PCOS may face unique challenges, including irregular cycles, weight fluctuations, and the emotional toll of repeated treatments. The unpredictability of the process, coupled with potential side effects of medications, can add to the stress. Effective coping strategies include maintaining open communication with the healthcare team, seeking emotional support from family, friends, or support groups, and practicing stress-reduction techniques such as yoga, meditation, or mindfulness.
Establishing realistic expectations and focusing on self-care are also crucial. For example, joining a PCOS support group can provide a sense of community and shared experience, offering valuable emotional support and practical advice.
The Emotional and Psychological Impact of Infertility and Support Resources
Infertility can significantly impact a woman’s emotional and psychological well-being. The emotional burden can be intensified for women with PCOS due to the added layer of managing a chronic condition. Feelings of anxiety, depression, guilt, and isolation are common. Seeking professional support from therapists or counselors specializing in infertility is vital. Support groups, online forums, and resources from organizations dedicated to reproductive health can provide valuable emotional support, practical information, and a sense of community.
Open communication with partners and loved ones is also essential in navigating the emotional challenges of infertility. Many infertility clinics offer counseling services or can refer patients to appropriate mental health professionals. Utilizing these resources can significantly improve emotional well-being throughout the fertility journey.
Final Summary
The path to parenthood for women with PCOS may require patience and persistence, but it’s definitely achievable. Remember, you’re not alone. By understanding your options, actively managing your PCOS, and seeking support from healthcare professionals and your community, you can significantly increase your chances of success. This journey is unique to you, and finding the right approach requires open communication with your doctor and a focus on self-care.
Stay strong, stay informed, and know that there is hope.
Questions Often Asked: Fertility Treatment Options For Women With Pcos
What are the chances of getting pregnant naturally with PCOS?
It varies greatly depending on the severity of PCOS and other factors. Some women conceive naturally, while others need assistance.
How long should I try to conceive naturally before seeking treatment?
Generally, it’s recommended to try for 6-12 months before seeking medical help. However, if you’re over 35, you may want to consult a doctor sooner.
Is IVF always necessary for PCOS-related infertility?
No, many women with PCOS successfully conceive with lifestyle changes, medication like Clomiphene Citrate or Letrozole, or IUI. IVF is usually considered when other methods have failed.
How much does fertility treatment cost?
Costs vary significantly depending on the treatment, location, and insurance coverage. It’s best to discuss costs with your fertility clinic directly.
