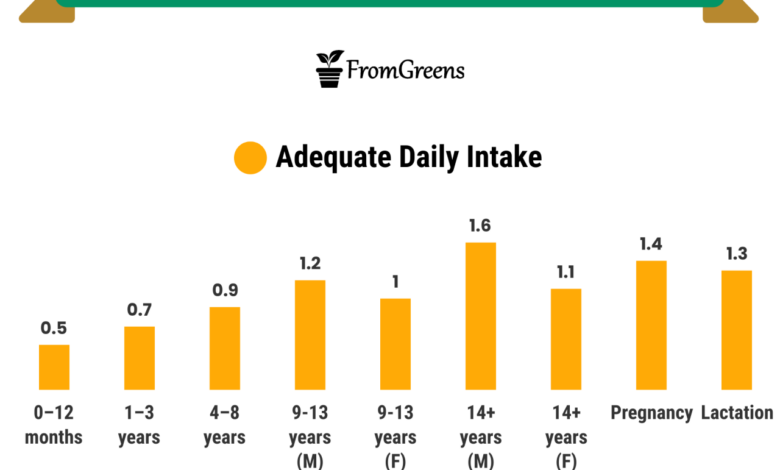
Fish Oil Recommendations as Per Age
Fish oil recommendations as per age are crucial for maximizing the health benefits of these essential fatty acids. From infancy to old age, the right dosage of omega-3s like EPA and DHA can significantly impact development, brain function, heart health, and more. This guide explores the specific needs of different age groups, addressing potential benefits, risks, and considerations for safe and effective supplementation.
We’ll delve into the science behind omega-3s and provide practical advice for incorporating them into your diet or supplement routine.
Understanding the nuances of fish oil supplementation across the lifespan is key to harnessing its potential. We’ll examine the optimal dosages for various life stages, discuss different formulations, and address common concerns about safety and potential interactions with other medications. Whether you’re a parent looking to support your child’s development or an adult seeking to improve your own well-being, this comprehensive guide will provide the information you need to make informed decisions.
Fish Oil Dosage for Infants and Toddlers (0-3 years)
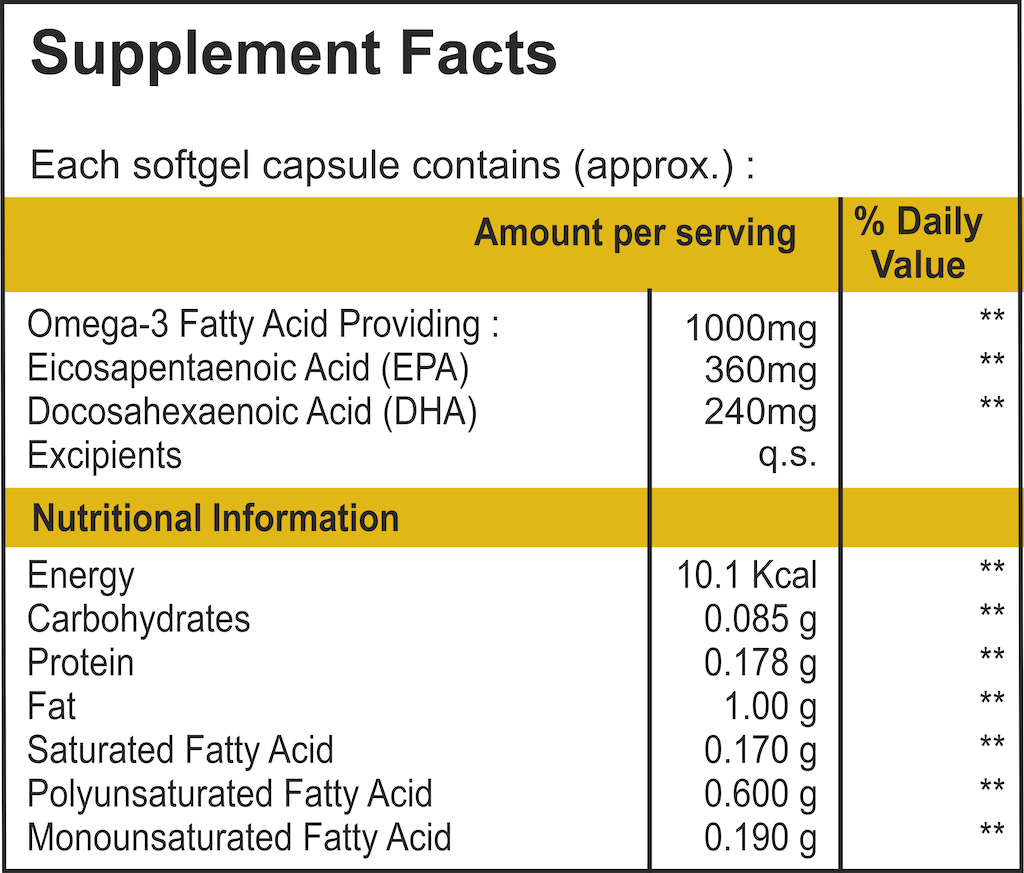
Source: zedonnutrition.com
Introducing fish oil to a baby or toddler’s diet is a decision that requires careful consideration. While omega-3 fatty acids, particularly DHA and EPA, are crucial for brain development and overall health, it’s vital to understand the potential benefits and risks before supplementation. This section will guide you through the complexities of fish oil supplementation for this age group, focusing on appropriate dosages and potential interactions with other medications.
Benefits and Risks of Fish Oil Supplementation for Infants and Toddlers
Omega-3 fatty acids, specifically DHA and EPA, are essential for brain development, eye health, and immune function in infants and toddlers. DHA is a major structural component of the brain and retina, and adequate intake during early childhood is linked to improved cognitive development and visual acuity. EPA contributes to reducing inflammation and supporting immune system function. However, there are potential risks associated with fish oil supplementation.
These include the possibility of allergic reactions (particularly to fish), vitamin A toxicity (if the fish oil is not purified properly), and the potential for interactions with other medications. Therefore, consultation with a pediatrician before introducing fish oil supplements is strongly recommended. The benefits must be carefully weighed against the potential risks, and the decision should be made on a case-by-case basis.
Fish Oil Formulations for Infants and Toddlers
Choosing the right fish oil formulation for infants and toddlers is critical. The following table compares different formulations, highlighting their Omega-3 fatty acid content and other ingredients. Remember, always check with your pediatrician before selecting a product.
| Product Name (Example) | DHA (mg/ml) | EPA (mg/ml) | Other Ingredients |
|---|---|---|---|
| Brand A Infant Fish Oil Drops | 50 | 10 | Vitamin E (as natural tocopherols), Triglycerides |
| Brand B Toddler Fish Oil Capsules | 100 | 20 | Olive Oil, Natural Flavors |
| Brand C Baby DHA Supplement | 80 | 5 | Sunflower Oil, Lecithin |
| Brand D Algae-Based DHA Supplement | 70 | 0 | Vegetable Glycerin, Natural Flavors |
*Note: These are example values and may vary significantly depending on the brand and specific product. Always refer to the product label for accurate information.*
Potential Drug Interactions with Fish Oil in Infants and Toddlers
While generally safe, fish oil can interact with certain medications. For example, fish oil may increase the risk of bleeding when taken with blood thinners (though this is less of a concern with the lower doses typically used in infant supplements). It’s also crucial to note that some medications may affect the absorption or metabolism of omega-3 fatty acids.
Therefore, it is absolutely essential to inform your pediatrician about all medications and supplements your child is taking before introducing fish oil. This will help prevent potential adverse reactions and ensure your child’s safety. A pediatrician can provide personalized advice based on your child’s specific health condition and medication regimen.
Fish Oil Recommendations for Preschoolers and School-Aged Children (3-12 years)
Choosing the right fish oil supplement for your preschooler or school-aged child can feel overwhelming. This age group presents unique considerations, balancing the need for essential fatty acids with the challenges of administering supplements to young, often picky eaters. This guide provides information to help you make informed decisions about incorporating fish oil into your child’s diet.Determining appropriate fish oil dosages requires considering both your child’s weight and their existing dietary intake of omega-3 fatty acids.
While there isn’t a universally agreed-upon dosage, many experts recommend a daily intake of EPA and DHA combined, expressed in milligrams (mg). A good starting point is to consult your pediatrician or a registered dietitian who can assess your child’s individual needs and provide personalized recommendations. They can also help determine if your child is already getting enough omega-3s from their diet, reducing the need for supplementation.
For example, a child who regularly consumes fatty fish like salmon might require a lower dose than a child whose diet lacks these sources.
Fish Oil Forms for Children: Advantages and Disadvantages
The form of fish oil you choose significantly impacts its palatability and ease of administration. Several options are available, each with its own set of benefits and drawbacks.
- Liquid Fish Oil: Liquid fish oil is often considered the easiest to administer, especially for younger children. It can be easily mixed into food like yogurt or applesauce. However, it can have a strong fishy taste that some children may find unpleasant, and it may require refrigeration to maintain freshness.
- Capsules: Capsules offer a more concentrated dose of fish oil. However, they are unsuitable for very young children who may have difficulty swallowing them. Furthermore, the fishy aftertaste can still be an issue for some children, even after swallowing.
- Gummies: Gummies are a popular choice due to their appealing taste and texture. Many children readily accept them. However, gummies often contain added sugars and may not provide as high a concentration of omega-3s as liquid or capsule forms. Always check the sugar content before choosing gummies.
Introducing Fish Oil to Your Child’s Diet
Successfully introducing fish oil to your child’s diet hinges on overcoming potential taste and texture challenges. Here are some helpful strategies:
- Start with a small dose: Begin with a lower dosage than recommended and gradually increase it over several days or weeks to allow your child’s palate to adjust.
- Mask the taste: Mix liquid fish oil into foods your child enjoys, such as smoothies, yogurt, or applesauce. The stronger flavors of these foods can help to mask the fishy taste.
- Offer a reward: For older children, consider offering a small reward after they take their fish oil. This can help to create positive associations with the supplement.
- Be patient and persistent: It may take time for your child to accept fish oil. Don’t get discouraged if they initially refuse it. Continue to offer it in different ways, and eventually, they may come around.
Fish Oil Intake for Teenagers (13-19 years)
Source: bestinnature.com
The teenage years are a period of significant growth and development, both physically and mentally. During this crucial stage, ensuring adequate nutrition is paramount for supporting healthy brain function, hormonal balance, and overall well-being. Fish oil, rich in omega-3 fatty acids EPA and DHA, plays a vital role in these processes, offering potential benefits that extend beyond general health.Teenage years are characterized by rapid physical growth, hormonal shifts, and increased cognitive demands.
The brain undergoes significant development during adolescence, making it particularly susceptible to nutritional deficiencies. Omega-3 fatty acids are essential building blocks for brain cells, contributing to optimal cognitive function and emotional regulation. Furthermore, they play a role in managing inflammation, a process linked to various adolescent health concerns. Supplementing with fish oil can help bridge any nutritional gaps and support the body’s natural developmental processes.
Health Benefits of Fish Oil Supplementation for Teenagers
Fish oil’s impact on adolescent health is multifaceted. Its benefits stem primarily from the omega-3 fatty acids EPA and DHA, which are crucial for various bodily functions.
- Improved Cognitive Function: DHA is a major structural component of the brain, vital for memory, learning, and concentration. Studies suggest that adequate DHA intake can improve academic performance and reduce symptoms of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) in some adolescents.
- Reduced Inflammation: Chronic inflammation is linked to various health problems, including acne, mood disorders, and autoimmune diseases. Omega-3s possess anti-inflammatory properties, potentially mitigating these issues.
- Improved Mood and Mental Well-being: Omega-3 fatty acids are increasingly recognized for their role in supporting mental health. They may help alleviate symptoms of depression and anxiety, common challenges faced by teenagers.
- Support for Healthy Heart Function: Omega-3s contribute to cardiovascular health by reducing triglyceride levels and blood pressure, factors that are important for long-term well-being.
- Enhanced Athletic Performance: Some research indicates that omega-3 supplementation may improve athletic performance by reducing muscle soreness and inflammation after strenuous activity.
Potential Side Effects of Excessive Fish Oil Consumption in Teenagers
While fish oil generally offers numerous benefits, excessive consumption can lead to potential side effects. It’s crucial to adhere to recommended dosages.
- Gastrointestinal Issues: High doses of fish oil can cause nausea, diarrhea, stomach upset, and heartburn. Starting with a lower dose and gradually increasing it can help minimize these effects.
- Increased Bleeding Risk: Omega-3s have blood-thinning properties. Teenagers with bleeding disorders or those taking blood-thinning medications should consult their doctor before taking fish oil supplements.
- Fishy Burps or Body Odor: Some individuals experience fishy burps or body odor after consuming high doses of fish oil. This can be mitigated by choosing high-quality, purified fish oil supplements.
- Drug Interactions: Fish oil can interact with certain medications, including blood thinners and some diabetes medications. It’s essential to discuss fish oil supplementation with a doctor or pharmacist, especially if the teenager is taking other medications.
Safe Usage Recommendations for Teenagers, Fish oil recommendations as per age
It’s crucial to consult a healthcare professional before starting any fish oil supplement regimen for a teenager. They can assess individual needs and recommend an appropriate dosage based on age, weight, health status, and any existing medical conditions. The recommended dosage varies depending on several factors, and self-medication should be avoided. Always choose high-quality, purified fish oil supplements from reputable brands to minimize the risk of contaminants.
Fish Oil Supplementation for Adults (20-64 years)
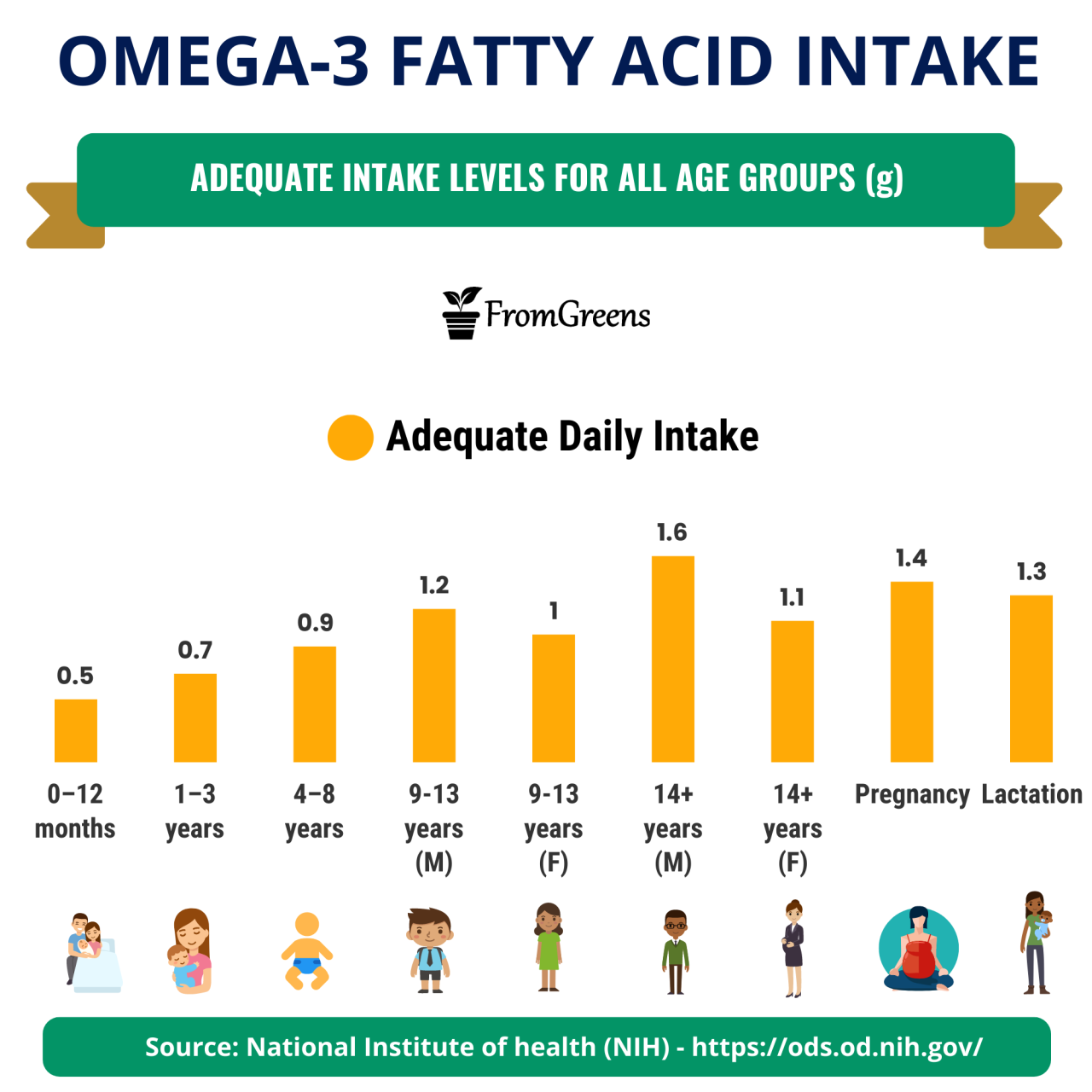
Source: fromgreens.com
Maintaining optimal health throughout adulthood requires a balanced diet and lifestyle, and incorporating essential fatty acids like EPA and DHA from fish oil can play a significant role. This section will explore the recommended intake, beneficial food sources, and the positive impacts of fish oil on various aspects of adult well-being.
The recommended daily intake of EPA and DHA for healthy adults varies depending on several factors, including overall health, diet, and activity levels. While there’s no universally agreed-upon single number, many health organizations suggest a combined intake of at least 250-500mg of EPA and DHA daily for general health benefits. Individuals with specific health conditions, such as cardiovascular disease or high triglycerides, may benefit from higher doses under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
It’s important to note that gender differences in recommended intake are not significantly established in current research; however, those with higher activity levels might consider a slightly higher intake to support increased energy expenditure and recovery.
Omega-3 Fatty Acid Sources and Nutritional Profiles
While fish oil supplements are a convenient way to increase EPA and DHA intake, incorporating omega-3 rich foods into your diet is equally important. The following table compares the nutritional profiles and potential benefits of various food sources.
| Food Source | EPA (mg/100g) | DHA (mg/100g) | Other Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|
| Salmon (wild-caught) | 1000-2000 | 500-1000 | Rich in protein, Vitamin D, and Potassium. Supports heart health and brain function. |
| Mackerel | 800-1500 | 400-800 | Good source of Vitamin B12 and Selenium. Supports immune function and bone health. |
| Sardines | 500-1000 | 300-600 | Excellent source of Calcium and Vitamin D. Supports bone health and cardiovascular health. |
| Flaxseeds | Low | Low | Rich in ALA (alpha-linolenic acid), an omega-3 fatty acid that the body can convert to EPA and DHA, although conversion rates are variable. Good source of fiber. |
Fish Oil and Cardiovascular Health
Extensive research supports the beneficial role of EPA and DHA in maintaining cardiovascular health. These omega-3 fatty acids help reduce triglycerides, lower blood pressure, and improve the overall function of the cardiovascular system. Studies have shown that regular consumption of fish oil can reduce the risk of heart attacks, strokes, and other cardiovascular events. For example, the PREDIMED study demonstrated that a Mediterranean diet supplemented with extra virgin olive oil or nuts significantly reduced the incidence of major cardiovascular events, partly attributed to the increased omega-3 intake from the diet.
Fish Oil and Joint Health
The anti-inflammatory properties of EPA and DHA make them beneficial for joint health. These fatty acids can help reduce pain and inflammation associated with conditions like osteoarthritis. While not a cure, studies suggest that fish oil supplementation can improve joint mobility and reduce the need for pain medication in some individuals. One notable study demonstrated a significant reduction in joint pain and stiffness among participants with osteoarthritis who consumed fish oil supplements daily for several months.
Fish Oil and Mental Well-being
Emerging research indicates a link between omega-3 fatty acid intake and mental well-being. EPA and DHA are crucial components of brain cell membranes and play a role in neurotransmitter function. Studies suggest that adequate omega-3 intake may help improve mood, reduce symptoms of depression and anxiety, and enhance cognitive function. While more research is needed to fully understand the mechanisms, many observational studies have linked higher fish consumption (and thus higher omega-3 intake) to a reduced risk of cognitive decline and depression.
Fish Oil and Older Adults (65+ years): Fish Oil Recommendations As Per Age
As we age, our bodies undergo various changes, and maintaining optimal health becomes increasingly important. Fish oil, rich in omega-3 fatty acids EPA and DHA, offers potential benefits for older adults facing specific health challenges often associated with aging. This section will explore how fish oil might support the health of seniors, while emphasizing the crucial need for careful consideration of individual health profiles and potential interactions with existing medications.Maintaining good health in later life is a complex endeavor, and many seniors face challenges like age-related cognitive decline and joint pain.
Omega-3 fatty acids, particularly EPA and DHA found abundantly in fish oil, have shown promise in mitigating some of these issues. However, it’s vital to remember that fish oil is a supplement, not a cure, and should be approached with careful consideration of an individual’s unique health circumstances.
Age-Related Cognitive Decline and Fish Oil
Studies suggest a potential link between omega-3 fatty acid intake and improved cognitive function in older adults. While more research is needed to definitively establish causality, some studies indicate that regular consumption of EPA and DHA may help to slow the progression of age-related cognitive decline and potentially reduce the risk of developing conditions like Alzheimer’s disease. The mechanisms behind these potential benefits are believed to involve reducing inflammation in the brain and protecting against oxidative stress, both of which are implicated in cognitive decline.
It is important to note that these benefits are not guaranteed and should not replace medical advice or treatment for cognitive impairment.
Joint Pain and Fish Oil
Many older adults experience joint pain and stiffness, often associated with osteoarthritis. The anti-inflammatory properties of omega-3 fatty acids may offer some relief. EPA and DHA can help reduce inflammation and pain associated with joint conditions, potentially improving mobility and quality of life. However, fish oil is not a replacement for prescribed medications or physical therapy for joint pain; it may be considered as a complementary approach under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
Choosing High-Quality Fish Oil Supplements for Older Adults
Selecting a suitable fish oil supplement for seniors requires careful consideration of several factors. It’s crucial to prioritize purity, potency, and potential interactions with other medications.Choosing a high-quality fish oil supplement is paramount for older adults. Here’s a guide:
- Purity: Look for supplements that are third-party tested for purity and free from heavy metals (like mercury) and PCBs (polychlorinated biphenyls). Certifications like those from NSF International or USP (United States Pharmacopeia) are strong indicators of quality and purity.
- Potency: Check the label for the amount of EPA and DHA per serving. Higher concentrations generally mean a more potent supplement, but it’s crucial to follow dosage recommendations from your doctor or pharmacist.
- Potential Drug Interactions: Fish oil can interact with certain medications, including blood thinners (like warfarin) and some anti-inflammatory drugs. Always consult your doctor or pharmacist before starting any new supplement, especially if you are on other medications. They can assess potential interactions and help determine a safe and appropriate dosage.
- Form: Fish oil is available in various forms, including capsules, softgels, and liquids. Consider factors like ease of swallowing and personal preferences when choosing a form. Consult your doctor for personalized recommendations.
Special Considerations for Pregnant and Breastfeeding Women
Pregnancy and breastfeeding are periods of significant physiological change, making nutritional needs paramount. Fish oil, rich in omega-3 fatty acids EPA and DHA, plays a crucial role in fetal development and infant health, but careful consideration of benefits and risks is essential. This section explores the complexities of fish oil supplementation during these crucial life stages.
Omega-3 fatty acids, particularly DHA, are vital for fetal brain and eye development. During pregnancy, adequate DHA intake is linked to improved cognitive function and visual acuity in the infant. Breastfeeding mothers also pass on these beneficial fats through their milk, continuing to support the infant’s development. However, concerns exist regarding potential mercury contamination in fish oil supplements and the overall safety profile for both mother and child.
Therefore, a balanced approach, considering individual circumstances and medical advice, is crucial.
Benefits of Fish Oil Supplementation During Pregnancy and Breastfeeding
The benefits of fish oil supplementation during pregnancy and breastfeeding primarily stem from the crucial role of DHA in fetal and infant development. DHA is a major structural component of the brain and retina, contributing significantly to cognitive function, visual acuity, and overall neurological development. Studies suggest that adequate DHA intake during pregnancy is associated with improved pregnancy outcomes, reduced risk of preterm birth, and enhanced infant neurodevelopment.
Furthermore, DHA in breast milk supports the continued development of the infant’s brain and eyes post-delivery.
Risks of Fish Oil Supplementation During Pregnancy and Breastfeeding
While the benefits are significant, potential risks associated with fish oil supplementation must be acknowledged. The primary concern is mercury contamination. Fish oil supplements can contain varying levels of mercury, a neurotoxin that can harm fetal and infant development. Excessive intake of vitamin A, also found in some fish oils, can be harmful during pregnancy. Furthermore, some individuals may experience side effects such as nausea, heartburn, or diarrhea.
It’s crucial to choose high-quality, purified fish oil supplements that have been tested for mercury and other contaminants.
Decision-Making Flowchart for Fish Oil Supplementation
The decision to supplement with fish oil during pregnancy and breastfeeding should be a collaborative process involving the pregnant woman, her healthcare provider, and a registered dietitian. The following flowchart provides a structured approach to this decision:
[Start]
→ Consult your doctor or midwife: Discuss your overall health, dietary habits, and potential risks and benefits of fish oil supplementation.
→ Assess your current omega-3 intake: Determine if you’re already consuming sufficient omega-3 fatty acids through diet.
→ Choose a high-quality, purified fish oil supplement: Look for supplements that are tested for purity and low in mercury. Consider EPA/DHA ratio.
→ Start with a low dose: Gradually increase the dosage as tolerated, following your doctor’s recommendations.
→ Monitor for side effects: Report any adverse reactions to your healthcare provider immediately.
→ Regular check-ups: Maintain regular prenatal or postpartum check-ups to monitor your health and your baby’s development.
[End]
Recommendations for Safe and Effective Fish Oil Consumption
To minimize the risk of mercury contamination, choose fish oil supplements from reputable brands that have undergone third-party testing for purity and heavy metal content. Look for supplements that specify the EPA and DHA content and are low in mercury. Follow the recommended dosage provided by your healthcare provider or as directed on the product label. Do not exceed the recommended dosage.
It is always best to obtain your omega-3 fatty acids from a varied diet rich in fatty fish, such as salmon, mackerel, and sardines, but supplementation may be necessary if dietary intake is insufficient. However, it’s crucial to be aware of the potential mercury content in these fish and to consume them in moderation.
Conclusive Thoughts
Navigating the world of fish oil supplementation can feel overwhelming, but understanding the specific needs of each age group empowers you to make informed choices. Remember, always consult with your doctor or a registered dietitian before starting any new supplement, especially if you have pre-existing health conditions or are taking other medications. By prioritizing quality supplements and tailoring your intake to your individual needs, you can unlock the remarkable health benefits of fish oil throughout your life.
Let’s embrace a proactive approach to wellness, one healthy omega-3 at a time!
Question & Answer Hub
What are the signs of fish oil deficiency?
Signs can be subtle and vary, but may include dry skin, poor cognitive function, increased inflammation, and mood changes. A blood test can confirm deficiency.
Can I take too much fish oil?
Yes, excessive intake can lead to side effects like nausea, diarrhea, and bleeding. Always follow recommended dosages.
Are there any interactions between fish oil and blood thinners?
Yes, fish oil can increase bleeding risk when combined with blood thinners. Consult your doctor before using fish oil if you take blood thinners.
Is it safe to give fish oil to babies with allergies?
If your baby has allergies, consult a pediatrician before introducing fish oil. A small test amount is advisable to monitor for reactions.
How can I tell if my fish oil supplement is high quality?
Look for third-party certifications (like IFOS) verifying purity and potency. Check for low levels of heavy metals and oxidation.
