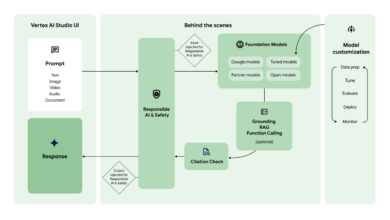
Generative AI Healthcare Workforce, Consumers, Deloitte Concerns
Generative AI healthcare workforce consumer concerns Deloitte: It’s a mouthful, isn’t it? But it speaks to a crucial conversation happening right now – the rapid advancement of AI in healthcare and the very real anxieties surrounding its impact. From doctors and nurses grappling with changing roles to patients questioning the reliability and privacy of AI-driven diagnoses, the implications are far-reaching and complex.
This post dives into the key concerns, exploring Deloitte’s insights and offering a glimpse into the future of healthcare in the age of generative AI.
We’ll examine how generative AI is poised to reshape the healthcare landscape, impacting everything from diagnostic accuracy to patient care. We’ll explore the potential for increased efficiency and reduced workloads for healthcare professionals, but also acknowledge the anxieties around job displacement and the ethical dilemmas surrounding algorithmic bias. Crucially, we’ll consider consumer perspectives – their trust (or lack thereof) in AI-powered healthcare, their privacy concerns, and their overall expectations for the future of medical care.
Generative AI’s Impact on Healthcare Workforce

Source: deloitte.com
Generative AI is poised to revolutionize the healthcare industry, significantly impacting the roles and responsibilities of healthcare professionals. Its potential to automate tasks, analyze data, and assist in diagnosis promises increased efficiency and improved patient care. However, the integration of this technology also raises concerns about job displacement and the need for workforce adaptation. Understanding these potential impacts is crucial for navigating the transition and harnessing the benefits of generative AI responsibly.
Generative AI’s Influence on Healthcare Professional Roles
The introduction of generative AI will undoubtedly reshape the tasks performed by healthcare workers. For instance, AI algorithms can analyze medical images, assisting radiologists and pathologists in identifying anomalies with greater speed and accuracy. This doesn’t necessarily mean replacing these specialists, but rather augmenting their capabilities, allowing them to focus on complex cases and patient interaction. Similarly, AI-powered chatbots can handle routine patient inquiries, freeing up nurses and administrative staff to concentrate on more critical tasks.
The focus will shift from repetitive, data-heavy tasks to higher-level decision-making, critical thinking, and personalized patient care.
Generative AI’s Task Augmentation and Replacement, Generative ai healthcare workforce consumer concerns deloitte
Generative AI can significantly augment or even replace specific tasks. In radiology, AI can pre-process images, detect potential abnormalities, and even generate preliminary reports, reducing the radiologist’s workload. In pathology, AI can assist in identifying cancerous cells, speeding up diagnosis and treatment. Administrative tasks, such as scheduling appointments and managing medical records, can be largely automated. However, the complete replacement of human professionals is unlikely in the near future, as the complexities of human interaction and ethical decision-making remain crucial.
For example, while AI can flag potential issues in a medical image, a radiologist’s expertise is still needed for accurate diagnosis and treatment planning.
Generative AI’s Impact Across Healthcare Specialties
The impact of generative AI will vary across different healthcare specialties. Radiology and pathology are likely to see the most immediate and significant changes due to the readily available digital data and the potential for automated image analysis. Nursing might experience a shift towards more patient-centered care, with AI handling administrative tasks and providing support for monitoring patients.
In surgery, AI could assist with planning procedures and providing real-time guidance during operations. However, the integration of AI will require significant training and adaptation for healthcare professionals in all specialties. For example, radiologists will need to learn how to interpret and utilize AI-generated reports effectively.
Increased Efficiency and Reduced Workload
The implementation of generative AI has the potential to significantly increase efficiency and reduce the workload for healthcare professionals. By automating repetitive tasks, AI frees up valuable time for more complex and demanding activities. This can lead to improved patient care, reduced burnout among healthcare workers, and increased overall productivity within healthcare systems. For example, a study by [Cite a relevant study here, replace bracketed information with actual citation] showed a significant reduction in diagnostic time for certain conditions using AI-assisted analysis.
This translates to faster treatment and better patient outcomes.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Generative AI Adoption
| Profession | Advantages | Disadvantages | Overall Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Radiologist | Increased diagnostic accuracy, reduced workload, faster turnaround time | Potential for job displacement concerns, need for retraining, reliance on AI accuracy | Significant augmentation, potential for increased efficiency and accuracy |
| Pathologist | Improved diagnostic accuracy, faster processing of samples, reduced workload | High initial investment costs, potential for misdiagnosis if AI is not properly validated | Significant augmentation, improved efficiency and accuracy |
| Nurse | Reduced administrative burden, improved patient monitoring, more time for patient interaction | Potential for de-skilling, reliance on technology, ethical considerations related to patient data privacy | Significant augmentation, improved efficiency and patient care |
| Physician (General Practice) | Improved diagnostic support, access to vast amounts of medical information, enhanced patient communication | Potential for over-reliance on AI, need for careful interpretation of AI-generated insights, ethical considerations | Significant augmentation, potential for improved diagnosis and patient care |
Consumer Perceptions and Trust in Generative AI Healthcare
The integration of generative AI into healthcare holds immense promise, but its successful adoption hinges critically on public acceptance and trust. Consumer attitudes towards AI in healthcare are complex and multifaceted, shaped by a combination of optimism about potential benefits and apprehension about potential risks. Understanding these perceptions is crucial for responsible development and deployment of these technologies.
Recent surveys reveal a mixed bag of consumer opinions. While many are intrigued by the possibilities of AI-powered diagnostics and personalized treatment plans, a significant portion express considerable reservations. This hesitancy stems from several key concerns, impacting the overall adoption rate and requiring careful consideration by developers and healthcare providers.
Consumer Concerns Regarding Accuracy, Reliability, and Security
Concerns about the accuracy and reliability of AI-driven healthcare solutions are widespread. Consumers worry about the potential for misdiagnosis or inaccurate treatment recommendations due to errors in the AI’s algorithms or limitations in the data it was trained on. This is especially pertinent in high-stakes medical decisions. Furthermore, security concerns related to data breaches and the potential misuse of sensitive patient information are paramount.
The fear of unauthorized access to medical records and the possibility of identity theft significantly impacts trust. These anxieties are heightened by the increasing reliance on interconnected digital systems, creating a larger attack surface.
Ethical Implications of Generative AI in Healthcare: Data Privacy and Algorithmic Bias
From a consumer perspective, the ethical implications of generative AI in healthcare are significant. Data privacy is a major concern. Consumers are rightly apprehensive about the collection, storage, and use of their personal health data by AI systems. The potential for data breaches and the lack of transparency regarding data usage practices fuel distrust. Additionally, algorithmic bias is a considerable ethical worry.
If the algorithms used in AI healthcare systems are trained on biased data, they may perpetuate and even amplify existing health disparities, leading to unequal access to quality care. For example, an AI system trained primarily on data from one demographic group might perform poorly when used on patients from a different group, resulting in unfair or inaccurate diagnoses and treatments.
Hypothetical Scenario Illustrating Consumer Anxieties
Imagine Sarah, a 45-year-old woman experiencing persistent chest pain. She decides to use a new AI-powered symptom checker app. After inputting her symptoms, the app suggests a relatively benign condition, dismissing the possibility of a heart attack. However, Sarah’s anxiety is heightened by the app’s inability to explain its reasoning, and the lack of a human doctor’s oversight.
The impersonal nature of the interaction and the potential for a serious misdiagnosis create significant distress, highlighting the importance of human-centered design and transparency in AI healthcare systems. This lack of transparency and the potential for error contribute to her reluctance to trust the AI’s assessment, leading her to seek a second opinion from a human doctor.
Strategies to Build Consumer Trust and Address Concerns
Building consumer trust in generative AI healthcare requires a multi-pronged approach.
The following strategies are crucial:
- Transparency and Explainability: AI systems should be designed to be transparent and explainable, allowing users to understand how decisions are made.
- Data Security and Privacy: Robust data security measures and clear data privacy policies are essential to build consumer confidence.
- Algorithmic Fairness and Bias Mitigation: Rigorous testing and mitigation strategies must be implemented to address algorithmic bias and ensure fairness.
- Human Oversight and Collaboration: AI should be used as a tool to augment, not replace, human expertise in healthcare.
- Education and Communication: Clear and accessible communication about the capabilities and limitations of AI in healthcare can help alleviate consumer anxieties.
- Regulatory Frameworks and Standards: Establishing clear regulatory frameworks and industry standards can help ensure responsible development and deployment of AI in healthcare.
Deloitte’s Perspective on Generative AI in Healthcare
Source: studyiq.com
Deloitte, a global leader in consulting, has extensively researched and published on the transformative potential of generative AI within the healthcare sector. Their analyses go beyond simple hype, delving into practical applications, potential pitfalls, and strategies for successful implementation. This perspective offers valuable insights for healthcare organizations navigating this rapidly evolving technological landscape.Deloitte’s published reports and analyses on generative AI in healthcare consistently highlight the technology’s potential to revolutionize various aspects of the industry, from drug discovery and personalized medicine to administrative tasks and patient engagement.
They often use case studies and real-world examples to illustrate their points, focusing on the tangible benefits and challenges. For example, a report might detail how generative AI is accelerating drug development by analyzing vast datasets to identify promising drug candidates, significantly reducing research time and costs. Another might focus on improving patient experiences through AI-powered chatbots providing 24/7 support and personalized health information.
Deloitte’s Predictions for Generative AI in Healthcare
Deloitte predicts a significant expansion of generative AI’s role in healthcare over the next decade. They foresee widespread adoption in areas such as clinical decision support, personalized treatment plans, and administrative efficiency improvements. For instance, they anticipate AI-powered diagnostic tools becoming increasingly sophisticated, assisting clinicians in making faster and more accurate diagnoses. Further, they envision generative AI playing a crucial role in streamlining administrative processes, reducing paperwork, and freeing up healthcare professionals to focus on patient care.
This includes predictions of significant cost savings and improved operational efficiency in hospitals and clinics. One example might be the automation of medical record transcription, leading to quicker turnaround times for patient information and reduced administrative burdens.
Deloitte’s Recommendations for Successful Generative AI Implementation
Deloitte emphasizes a phased and strategic approach to generative AI implementation. They advocate for a focus on addressing ethical considerations, data privacy, and regulatory compliance from the outset. Their recommendations often include prioritizing robust data governance, investing in employee training and upskilling, and establishing clear performance metrics. They also stress the importance of a collaborative approach, involving clinicians, IT specialists, and other stakeholders throughout the implementation process.
For successful adoption, Deloitte emphasizes the need for a well-defined strategy, clear goals, and a robust infrastructure capable of supporting AI applications.
Deloitte’s report on generative AI’s impact on the healthcare workforce highlights consumer concerns about job displacement and data privacy. However, the increasing reliance on digital tools also raises questions about repetitive strain injuries, like carpal tunnel syndrome, leading many to explore alternative treatments; check out this helpful guide on ways to treat carpal tunnel syndrome without surgery for some relief.
Ultimately, addressing both the technological advancements and the well-being of the workforce is crucial for successful AI integration in healthcare.
Comparison with Other Leading Firms
While specific predictions and recommendations may vary slightly between Deloitte and other leading consulting firms like McKinsey or Accenture, there’s a general consensus on the transformative potential of generative AI in healthcare. All these firms highlight the need for a cautious yet proactive approach, emphasizing the importance of addressing ethical and regulatory concerns alongside the technological opportunities. However, Deloitte’s focus on a phased implementation and robust data governance might be considered a more detailed and pragmatic approach compared to some other firms’ more general recommendations.
Deloitte’s Key Findings on Challenges and Opportunities
Deloitte’s research consistently identifies both significant opportunities and challenges associated with generative AI in healthcare. Opportunities include improved diagnostics, personalized medicine, enhanced efficiency, and reduced costs. Challenges include data privacy concerns, algorithmic bias, the need for robust validation and regulatory approval, and the ethical implications of using AI in healthcare decision-making. They also emphasize the need for ongoing monitoring and evaluation to ensure the responsible and ethical use of generative AI.
Deloitte’s key recommendations consistently emphasize a phased approach, prioritizing data governance, addressing ethical concerns, and fostering collaboration among stakeholders to ensure the responsible and effective implementation of generative AI in healthcare. A robust infrastructure, clear goals, and ongoing monitoring are also crucial for success.
Consumer Concerns Regarding Data Privacy and Security
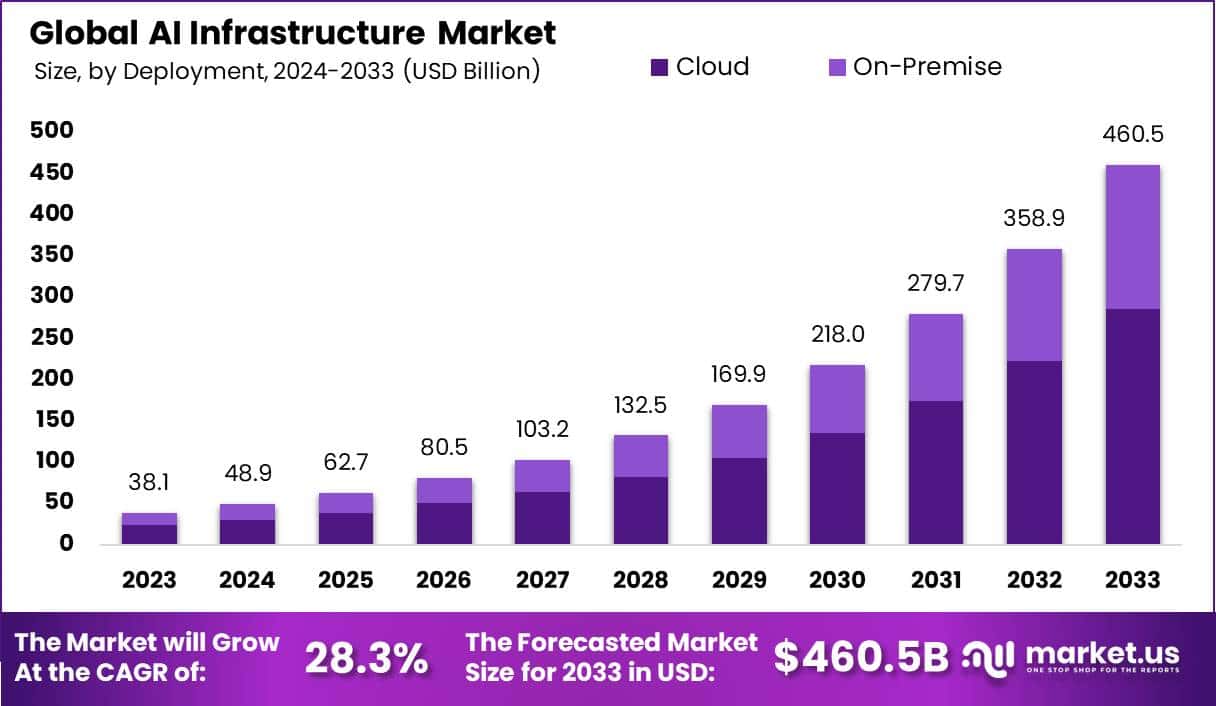
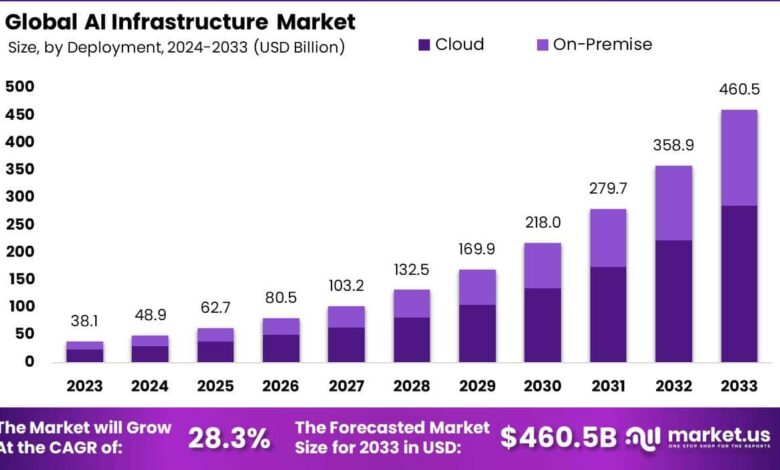
Source: market.us
The integration of generative AI into healthcare presents exciting possibilities, but it also raises significant concerns about the privacy and security of sensitive patient data. The very nature of these systems, which learn from vast datasets, necessitates a careful examination of the risks involved and the measures needed to mitigate them. Failure to address these concerns could severely undermine public trust and hinder the widespread adoption of this transformative technology.The potential for data breaches and misuse of sensitive patient information is a primary concern.
Deloitte’s report highlighted significant consumer concerns about the impact of generative AI on the healthcare workforce. These worries are valid, especially considering the potential for job displacement. However, innovative solutions are emerging, like those discussed in this insightful article on salesforce healthcare ai sean kennedy , which suggests that AI could also augment human capabilities. Ultimately, addressing these anxieties requires careful consideration of both the risks and opportunities presented by AI in healthcare.
Generative AI models, by their design, process and analyze large volumes of data, including protected health information (PHI). This creates a larger attack surface compared to traditional healthcare systems, increasing the risk of unauthorized access, theft, or manipulation of this data. Furthermore, the complexity of these AI systems can make identifying and addressing vulnerabilities challenging.
Data Privacy and Security Risks in Generative AI Healthcare
Generative AI in healthcare faces unique data privacy and security risks. The use of large language models (LLMs) trained on vast datasets, including potentially sensitive patient information, introduces vulnerabilities. For example, a model trained on data containing identifiable patient information might inadvertently generate outputs revealing such information, violating privacy regulations. Additionally, the potential for adversarial attacks, where malicious actors manipulate the input data to obtain unauthorized information, is a serious concern.
Another risk is the difficulty in ensuring the complete anonymization of data used for training and model validation, potentially leading to re-identification of patients.
Potential for Data Breaches and Misuse of Sensitive Patient Information
Data breaches in AI-driven healthcare systems can have severe consequences. Imagine a scenario where a generative AI system used for diagnosis inadvertently reveals a patient’s identity and medical condition in its output. This breach could lead to identity theft, discrimination, and reputational damage for both the patient and the healthcare provider. Furthermore, the misuse of sensitive patient data could be used for malicious purposes, such as insurance fraud or targeted advertising.
The scale of a breach involving a generative AI system could be significantly larger than in traditional systems due to the volume of data processed and the potential for unintended data leakage.
Regulatory Landscape and Compliance Requirements
The regulatory landscape for handling patient data in the context of generative AI is still evolving. Existing regulations like HIPAA in the United States and GDPR in Europe provide a framework, but their application to generative AI requires careful consideration. These regulations require robust data security measures, consent mechanisms, and data minimization principles. Compliance with these regulations requires organizations to implement rigorous data governance policies, including data access controls, audit trails, and incident response plans specifically designed for the unique challenges posed by generative AI.
Failure to comply can result in significant fines and reputational damage.
Adapting Current Data Protection Measures for Generative AI
Current data protection measures need to be adapted to address the unique challenges of generative AI. Traditional methods of data anonymization might be insufficient to protect against sophisticated re-identification techniques. Differential privacy, a technique that adds noise to data to protect individual privacy while preserving aggregate statistics, is one promising approach. Furthermore, techniques like federated learning, which trains models on decentralized data without directly sharing the data itself, can significantly enhance privacy.
Regular security audits and penetration testing are crucial to identify and address vulnerabilities specific to generative AI systems. Robust data governance frameworks and comprehensive employee training programs are essential to ensure compliance and responsible data handling.
Deloitte’s report on generative AI in healthcare highlights workforce anxieties and consumer concerns about data privacy. It’s fascinating to consider how these anxieties might intersect with individual health choices, such as diet. For example, understanding nutritional needs is crucial, and the article on are women and men receptive of different types of food and game changing superfoods for women raises questions about personalized medicine and how AI could help tailor health recommendations.
Ultimately, addressing consumer concerns about AI requires transparency and a focus on individual well-being, including informed dietary choices.
Best Practices for Ensuring Data Privacy and Security in Generative AI Healthcare Applications
To ensure data privacy and security, several best practices should be implemented:
- Implement robust access control measures to limit access to sensitive patient data only to authorized personnel.
- Employ advanced encryption techniques to protect data both at rest and in transit.
- Utilize differential privacy and federated learning to minimize the risk of data breaches and re-identification.
- Conduct regular security audits and penetration testing to identify and address vulnerabilities.
- Develop comprehensive incident response plans to effectively manage and mitigate data breaches.
- Implement robust data governance policies and procedures to ensure compliance with relevant regulations.
- Provide comprehensive training to employees on data privacy and security best practices.
- Regularly review and update security protocols to address emerging threats and vulnerabilities.
The Future of Generative AI and the Healthcare Consumer Experience
Generative AI is poised to revolutionize the healthcare landscape, profoundly impacting how consumers interact with and experience healthcare services. The potential benefits are vast, ranging from improved access and personalized care to more efficient and cost-effective systems. However, realizing this potential requires careful consideration of ethical implications and robust data privacy measures.
The integration of generative AI into healthcare will likely unfold in several key areas, creating a more proactive, personalized, and efficient healthcare ecosystem for consumers.
Potential Future Scenarios and Innovative Applications
Generative AI’s impact on the consumer healthcare experience will be transformative. Imagine a future where virtual assistants, powered by generative AI, provide 24/7 access to medical information, appointment scheduling, and medication reminders. These AI assistants could also analyze patient data to identify potential health risks and proactively suggest preventative measures. For example, an AI could analyze a patient’s wearable data and flag potential signs of a heart condition, prompting them to seek medical attention before a serious event occurs.
Beyond virtual assistants, generative AI can power sophisticated diagnostic tools, analyzing medical images with greater speed and accuracy than human clinicians, leading to earlier and more precise diagnoses. This could also extend to personalized treatment plans, where AI algorithms analyze a patient’s genetic makeup, lifestyle, and medical history to tailor treatment strategies to their specific needs. Finally, generative AI could streamline administrative tasks, freeing up healthcare professionals to focus on patient care.
Personalized Medicine and Proactive Healthcare Interventions
Generative AI excels at identifying patterns and correlations in large datasets. In healthcare, this translates to the potential for highly personalized medicine. By analyzing an individual’s genetic information, lifestyle factors, and medical history, generative AI can predict their risk for specific diseases and recommend tailored preventative measures. For instance, an AI might identify a predisposition to heart disease and suggest a personalized exercise and diet plan.
This proactive approach to healthcare could significantly reduce the incidence of chronic diseases and improve overall health outcomes. Furthermore, generative AI can analyze real-time patient data from wearable devices and telehealth platforms, enabling early detection of health deteriorations and prompt interventions. This is especially crucial for patients with chronic conditions who require continuous monitoring and adjustments to their treatment plans.
For example, an AI could monitor a diabetic patient’s blood sugar levels and automatically adjust their insulin dosage as needed.
Influence of Generative AI on Healthcare Costs and Accessibility
While the initial investment in generative AI technologies may be substantial, the long-term cost savings could be significant. By automating tasks, improving diagnostic accuracy, and enabling proactive interventions, generative AI can reduce the overall cost of healthcare. For example, early diagnosis of diseases through AI-powered imaging analysis could prevent costly hospitalizations and long-term treatments. Moreover, generative AI can improve healthcare accessibility, especially in underserved areas.
Telehealth platforms powered by AI can provide remote consultations and monitoring, bridging geographical barriers and making healthcare more readily available to individuals in remote or rural communities. AI-powered translation tools can also facilitate communication between patients and healthcare providers who speak different languages, eliminating language barriers to access.
Ideal Integration of Generative AI into the Future of Healthcare
The ideal integration of generative AI into healthcare prioritizes the consumer experience. This means creating systems that are user-friendly, intuitive, and transparent. Patients should have clear control over their data and understand how AI is being used to support their care. Trust and transparency are paramount. The future of healthcare with generative AI should be characterized by personalized, proactive, and accessible care, where technology empowers both patients and healthcare professionals to achieve better health outcomes.
This vision includes a seamless integration of AI tools into existing healthcare systems, ensuring interoperability and data security. Ultimately, the goal is to leverage the power of generative AI to create a healthcare system that is more efficient, effective, and patient-centered.
Wrap-Up: Generative Ai Healthcare Workforce Consumer Concerns Deloitte
The integration of generative AI into healthcare is undeniably transformative, promising incredible advancements in diagnosis, treatment, and patient care. However, the journey forward requires careful consideration of the workforce implications, consumer anxieties, and robust ethical frameworks. Deloitte’s insights, alongside ongoing research and public discourse, highlight the need for transparency, responsible development, and a patient-centric approach to ensure that AI benefits everyone.
The future of healthcare is being written now, and it’s a story we must all help shape.
Quick FAQs
What specific tasks in healthcare might generative AI replace?
AI could automate tasks like administrative work, preliminary diagnosis analysis (radiology, pathology), and appointment scheduling, freeing up human professionals for more complex cases.
How can consumer trust in AI-driven healthcare be improved?
Transparency about how AI systems work, clear communication about limitations, robust data security measures, and independent audits can significantly build consumer confidence.
What are the biggest data privacy risks with AI in healthcare?
Risks include unauthorized access to sensitive patient data, potential for bias in algorithms leading to unfair treatment, and difficulties in ensuring compliance with data protection regulations.
What is Deloitte’s overall stance on the future of generative AI in healthcare?
Deloitte generally views generative AI as having significant potential but emphasizes the need for responsible implementation, addressing ethical concerns, and ensuring patient safety and data privacy.