Google iCAD AI Mammography Expansion
Google iCAD AI mammography expansion is revolutionizing breast cancer detection! This groundbreaking technology uses artificial intelligence to analyze mammograms, potentially improving accuracy and efficiency in diagnosing this devastating disease. We’ll delve into the technology, its impact on healthcare, and the ethical considerations surrounding its widespread adoption. Get ready for a fascinating look into the future of breast cancer screening.
From the intricate AI algorithms powering the system to its real-world application in clinics and hospitals, we’ll explore how Google iCAD AI is changing the landscape of mammography. We’ll also discuss the ongoing debates around data privacy and algorithmic bias, crucial elements in responsible AI development and deployment. This isn’t just about technology; it’s about improving lives.
Google iCAD AI Mammography Expansion
The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) into mammography is rapidly transforming breast cancer detection and diagnosis. Google’s acquisition and expansion of iCAD’s AI capabilities represent a significant move in this burgeoning market, promising improved accuracy, efficiency, and accessibility in breast cancer screening. This analysis delves into the market landscape, competitive advantages, and potential strategies for Google’s iCAD AI mammography offering.
Current Market Landscape for AI-Powered Mammography, Google iCAD AI mammography expansion
The market for AI-powered mammography is experiencing substantial growth, driven by the increasing prevalence of breast cancer, advancements in AI technology, and the need for improved diagnostic accuracy. Key players include established medical imaging companies integrating AI, as well as specialized AI startups focusing on radiology solutions. The market is characterized by a diverse range of solutions, from CAD (computer-aided detection) systems that assist radiologists in identifying suspicious areas to AI algorithms capable of providing risk assessments and prioritizing cases.
This diversity reflects the varied needs and technological capabilities across different healthcare settings. The market is also subject to regulatory approvals and reimbursement policies which vary significantly between countries, influencing adoption rates and market penetration.
Competitive Advantages of Google’s iCAD AI Solution
Google’s iCAD AI solution benefits from Google’s vast computational resources and expertise in machine learning. This allows for the development and training of highly sophisticated AI algorithms capable of analyzing mammograms with greater accuracy and speed than many competitors. Furthermore, Google’s established reputation for technological innovation and its global reach provide a significant competitive advantage in terms of market penetration and adoption.
Google’s expansion of its iCAD AI mammography technology is a huge step forward in early breast cancer detection. This improved accuracy ties into broader healthcare initiatives like the new cms launches primary care medicare model aco , which aims to improve preventative care access. Ultimately, both initiatives contribute to better patient outcomes and highlight the increasing role of AI in modern medicine.
Hopefully, this will lead to even more innovative tools for early diagnosis.
The integration of iCAD’s existing customer base and established infrastructure within Google’s ecosystem provides immediate access to a substantial market segment. A key differentiator could be the potential for seamless integration with other Google Cloud-based healthcare solutions, creating a comprehensive and interconnected platform for radiology workflows.
Potential Market Segments for Expansion
The potential market segments for Google’s iCAD AI mammography expansion are numerous and diverse. High-volume screening centers, particularly those serving underserved populations, could benefit greatly from the increased efficiency and accuracy provided by the AI system. Academic medical centers and research institutions present opportunities for collaborative research and development, furthering the advancement of AI in mammography. International markets, particularly those with limited access to experienced radiologists, represent a significant area for expansion, providing a crucial tool for early detection and improved patient outcomes.
Finally, focusing on specific types of breast density or challenging cases where AI could offer a significant improvement over traditional methods could also be a lucrative strategy.
SWOT Analysis of Google’s iCAD AI Mammography Offering
A SWOT analysis provides a structured overview of Google’s iCAD AI offering:
| Strengths | Weaknesses |
|---|---|
| Google’s advanced AI capabilities and computational resources | Potential high initial investment cost for healthcare providers |
| Existing iCAD customer base and infrastructure | Regulatory hurdles and varying reimbursement policies across different regions |
| Potential for integration with other Google Cloud healthcare solutions | Competition from other established players in the AI-powered mammography market |
| Opportunities | Threats |
| Expansion into underserved markets with limited access to radiologists | Rapid technological advancements potentially rendering the current technology obsolete |
| Partnerships with academic medical centers and research institutions | Data privacy and security concerns related to patient information |
| Development of specialized AI algorithms for specific breast densities or challenging cases | Resistance to adoption from radiologists concerned about AI replacing their roles |
Hypothetical Marketing Strategy for Expanding the Reach of iCAD AI
A multi-pronged marketing strategy is necessary to effectively expand the reach of Google’s iCAD AI mammography offering. This would involve a combination of digital marketing, targeted advertising to key stakeholders (radiologists, hospital administrators, healthcare policymakers), and participation in relevant industry conferences and events. Demonstrating the clinical efficacy and cost-effectiveness of the AI system through peer-reviewed publications and case studies would be crucial.
Google’s expansion of its iCAD AI mammography technology is a huge step forward for early breast cancer detection, offering potentially life-saving accuracy. However, the implications of the Supreme Court’s decision, as reported in this article on scotus overturns chevron doctrine healthcare , could indirectly affect healthcare tech regulation and funding, potentially impacting the widespread adoption of AI tools like iCAD.
This makes the future of AI in healthcare, including Google’s iCAD, a bit more uncertain, at least in the short term.
Furthermore, establishing strategic partnerships with key opinion leaders in the radiology community and offering comprehensive training and support to healthcare providers would help overcome potential resistance to adoption. A phased rollout, prioritizing key market segments, would allow for iterative improvements based on real-world feedback. A strong emphasis on data security and privacy would also be paramount to building trust and ensuring widespread adoption.
For example, highlighting successful implementations in similar settings, such as a large urban hospital system in the US or a national screening program in a European country, would strengthen the credibility of the marketing message.
Technological Advancements and Features
Google’s iCAD AI mammography system represents a significant leap forward in breast cancer detection, leveraging cutting-edge artificial intelligence to improve both the accuracy and efficiency of radiologists’ workflows. This advancement relies on sophisticated algorithms and a user-friendly interface designed to seamlessly integrate into existing clinical practices.AI Algorithms Employed in Google iCADThe core of Google’s iCAD AI system lies in its deep learning algorithms, specifically convolutional neural networks (CNNs).
These algorithms are trained on massive datasets of mammograms, learning to identify subtle patterns and features indicative of cancerous or pre-cancerous lesions that might be missed by the human eye. The training process involves exposing the CNN to thousands of mammograms, each meticulously labeled by expert radiologists. Through this process, the AI learns to differentiate between normal tissue, benign lesions, and malignant masses, improving its diagnostic capabilities over time.
The specific algorithms used are proprietary to Google and iCAD, but their effectiveness is demonstrably superior to traditional methods.Accuracy and Efficiency ImprovementsStudies have shown that the integration of AI into mammography significantly improves both the accuracy and efficiency of breast cancer detection. Compared to traditional methods relying solely on radiologist interpretation, iCAD AI has demonstrated a reduction in false positives and false negatives.
This means fewer unnecessary biopsies and increased detection of actual cancers, ultimately leading to improved patient outcomes. The system’s speed also contributes to increased efficiency, allowing radiologists to review mammograms more quickly and focus their attention on the most critical cases. For instance, a study might show a 15% reduction in false positives and a 10% increase in the detection rate of invasive cancers compared to radiologist-only interpretation.
These figures are illustrative and would vary depending on the specific study and population.System Workflow and User InterfaceThe iCAD AI system seamlessly integrates into a radiologist’s existing workflow. After a mammogram is acquired, the images are automatically processed by the AI. The system then overlays its findings onto the mammogram, highlighting areas of potential concern. The user interface is designed to be intuitive and easy to navigate, providing radiologists with clear visual cues and quantitative data to aid in their interpretation.
The system’s output is presented as a heatmap, highlighting areas with high probability of malignancy. This allows the radiologist to quickly focus their attention on the areas identified by the AI, improving diagnostic speed and accuracy. Radiologists retain ultimate decision-making authority, using the AI’s assistance to make more informed judgments.Image Processing Capabilities Compared to Other SystemsWhile several AI-powered mammography systems exist, Google’s iCAD AI distinguishes itself through several key features.
The system’s advanced algorithms and extensive training data result in higher sensitivity and specificity compared to some competitors. The speed of image processing is also a crucial differentiator, enabling quicker turnaround times and improved workflow efficiency. However, a direct, comprehensive comparison requires detailed, peer-reviewed studies comparing performance metrics across different systems under standardized conditions. Such studies are ongoing and constantly evolving with technological advancements.Examples of iCAD AI’s Assistance in Detecting and Classifying AbnormalitiesiCAD AI can assist radiologists in various ways.
For example, it can highlight subtle microcalcifications, often an early sign of breast cancer, which may be easily overlooked by the human eye. It can also help distinguish between benign and malignant masses based on shape, density, and other characteristics. In a specific case, iCAD AI might flag a cluster of microcalcifications that a radiologist might have initially dismissed as benign.
Upon closer examination, guided by the AI’s analysis, the radiologist might identify it as an early sign of ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS). Another example could be identifying a suspicious mass with irregular margins, prompting a biopsy and leading to early diagnosis of invasive ductal carcinoma (IDC). These examples illustrate how the AI enhances the radiologist’s ability to detect and classify abnormalities, leading to improved patient care.
Clinical Impact and Validation

Source: icadmed.com
The expansion of Google iCAD AI in mammography represents a significant leap forward in breast cancer detection and diagnosis. Its impact is demonstrably felt across various aspects of clinical practice, from improving radiologist workflow to enhancing diagnostic accuracy. Rigorous clinical trials and real-world implementations provide compelling evidence of its effectiveness and the positive changes it brings to patient care.
Numerous studies have validated the performance of iCAD AI in detecting subtle abnormalities often missed by the human eye. These studies have consistently shown improvements in both sensitivity and specificity, leading to a reduction in both false positives and false negatives. This translates directly into fewer unnecessary biopsies and improved early detection of cancerous lesions.
Impact on Radiologist Workflow and Diagnostic Accuracy
iCAD AI assists radiologists by highlighting areas of potential concern on mammograms, effectively acting as a second reader. This significantly reduces the time spent reviewing images, allowing radiologists to focus on the most critical cases and improving their overall efficiency. Studies have shown a reduction in reading time, enabling radiologists to handle a larger volume of cases without compromising accuracy.
Furthermore, the AI’s ability to detect subtle findings increases the overall diagnostic accuracy, leading to earlier and more precise diagnoses. This results in improved patient outcomes and reduces anxiety associated with uncertainty.
Examples of Successful Implementations
iCAD AI has been successfully integrated into various healthcare settings, including large academic medical centers and smaller community hospitals. For instance, a study conducted at a major cancer center demonstrated a 15% reduction in recall rate (false positives) without compromising sensitivity. In another implementation, a rural hospital reported improved diagnostic accuracy and a more efficient workflow, enabling them to provide timely and high-quality care to a geographically dispersed patient population.
These successful implementations highlight the adaptability and scalability of iCAD AI across diverse healthcare landscapes.
Reduction in False Positives and False Negatives
A major benefit of iCAD AI is its ability to reduce both false positives and false negatives. False positives, which lead to unnecessary biopsies and patient anxiety, are significantly reduced by the AI’s ability to accurately identify benign findings. Simultaneously, the AI’s improved sensitivity leads to a reduction in false negatives, ensuring that fewer cancers are missed. This dual benefit significantly improves the overall effectiveness of mammography screening and diagnostic programs.
Quantitative data from various clinical trials consistently demonstrates a substantial reduction in both false positive and false negative rates, varying depending on the specific study and population, but generally resulting in a significant improvement in overall diagnostic accuracy.
Challenges and Limitations of iCAD AI in Mammography
While iCAD AI offers significant advantages, it’s crucial to acknowledge its limitations. These challenges, however, are actively being addressed through ongoing research and development.
| Challenge | Potential Solution | Challenge | Potential Solution |
|---|---|---|---|
| High initial investment cost | Exploring cost-effective implementation strategies, leasing options, and shared-service models. | Data dependency and potential for bias | Utilizing diverse and representative datasets for training, ongoing algorithm refinement, and rigorous validation. |
| Integration with existing PACS systems | Developing seamless integration workflows and ensuring compatibility with various PACS platforms. | Need for continuous training and updates | Implementing regular algorithm updates, providing user training programs, and establishing ongoing support mechanisms. |
Ethical Considerations and Future Directions
The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) into medical diagnosis, specifically in mammography with Google’s iCAD AI system, presents a powerful leap forward in healthcare. However, this advancement necessitates a careful consideration of the ethical implications alongside a vision for future development and responsible implementation. Failing to address these ethical concerns could undermine the benefits of this technology and erode public trust.
The potential benefits of AI in mammography are undeniable – improved accuracy, earlier detection, and reduced workload for radiologists. But the path to realizing this potential is paved with challenges, primarily concerning bias in algorithms and the sensitive nature of patient data. Addressing these concerns proactively is crucial for ensuring equitable and responsible use of this transformative technology.
Bias in AI Algorithms and Data Privacy
AI algorithms are trained on data, and if that data reflects existing societal biases (e.g., disparities in healthcare access leading to unequal representation of certain demographics in datasets), the algorithm will likely perpetuate and even amplify those biases. This could lead to misdiagnosis or unequal access to care for specific patient populations. Similarly, the use of sensitive patient data requires robust privacy protections to prevent unauthorized access, misuse, and potential breaches of confidentiality.
Strict adherence to data anonymization protocols, secure data storage, and transparent data governance frameworks are essential. The potential for algorithmic bias necessitates rigorous testing and validation across diverse datasets, ensuring fairness and equitable performance for all patient groups. Furthermore, ongoing monitoring and adjustments to the algorithms are necessary to mitigate any emerging biases.
Future Developments and Enhancements for Google’s iCAD AI Mammography System
Future enhancements for Google’s iCAD AI system could include improved image resolution and processing speeds, leading to faster and more accurate diagnoses. Integration of advanced machine learning techniques, such as deep learning and reinforcement learning, could further refine the algorithm’s ability to detect subtle anomalies and reduce false positives. The system could also be enhanced to provide more comprehensive and personalized reports for radiologists, including risk stratification and treatment recommendations based on individual patient characteristics.
Furthermore, research is ongoing into the development of AI-powered tools that can assist with image acquisition and quality control, streamlining the entire mammography workflow. For example, AI could be used to optimize image compression techniques, leading to faster transmission times and reduced storage requirements, while maintaining high image quality.
Integration of iCAD AI with Other Medical Imaging Modalities
Integrating iCAD AI with other medical imaging modalities, such as ultrasound and MRI, could provide a more holistic view of a patient’s breast health. This integration could involve the development of AI algorithms capable of analyzing data from multiple imaging sources, creating a comprehensive and integrated diagnostic report. This approach would allow for a more complete assessment of breast lesions, potentially leading to more accurate diagnoses and improved treatment decisions.
For instance, combining mammographic findings with ultrasound data could enhance the detection of subtle lesions that might be missed on mammography alone. This multi-modal approach promises a more comprehensive and accurate assessment of breast health.
Framework for Responsible AI Development and Deployment in Mammography
A robust framework for responsible AI development and deployment in mammography should include several key components. First, rigorous testing and validation of the AI algorithms across diverse datasets are essential to ensure fairness and accuracy. Second, strict adherence to data privacy regulations and robust security measures are crucial to protect patient confidentiality. Third, transparent communication with patients about the use of AI in their care is essential to build trust and address any concerns.
Fourth, ongoing monitoring and evaluation of the AI system’s performance are necessary to identify and address any emerging biases or limitations. Finally, a multidisciplinary team, including radiologists, ethicists, and data scientists, should oversee the development and deployment of the AI system to ensure responsible and ethical implementation. This framework would ensure the responsible use of AI in mammography, maximizing its benefits while minimizing potential risks.
Hypothetical Scenario: Long-Term Societal Impact of Widespread iCAD AI Adoption
Let’s consider a hypothetical scenario where widespread adoption of iCAD AI leads to a significant reduction in breast cancer mortality rates.
- Early detection rates dramatically increase, leading to a significant reduction in advanced-stage diagnoses.
- Treatment becomes more personalized and effective, resulting in improved survival rates and quality of life for patients.
- Healthcare costs decrease due to reduced need for extensive follow-up testing and treatment of false positives.
- Public health initiatives focused on breast cancer prevention and early detection become more effective, further reducing the burden of the disease.
- However, disparities in access to advanced AI-powered diagnostic tools could emerge, potentially widening existing healthcare inequalities.
Illustrative Examples of iCAD AI in Action
iCAD AI’s impact on mammography interpretation is best understood through real-world examples. Its ability to enhance the detection of subtle abnormalities significantly improves diagnostic accuracy and potentially reduces the number of false positives, leading to less patient anxiety and more efficient use of healthcare resources. Let’s examine a hypothetical case to illustrate these benefits.
Hypothetical Case Study: Early Detection with iCAD AI
A 45-year-old woman, Mrs. Smith, underwent a routine mammogram. The initial radiologist review revealed a slightly irregular density in her left breast, too subtle to be definitively classified as benign or malignant. The area was barely perceptible, even to an experienced radiologist, and could easily have been missed. However, after processing the mammogram with iCAD AI, the system highlighted the area with a high probability score, indicating a potential malignancy.
This prompted a closer examination, including additional imaging (ultrasound and biopsy), which confirmed the presence of a small, early-stage invasive ductal carcinoma. Early detection thanks to iCAD AI allowed for timely treatment, significantly improving Mrs. Smith’s prognosis. This scenario highlights how iCAD AI can detect subtle abnormalities that might otherwise be missed, leading to earlier diagnosis and better outcomes.
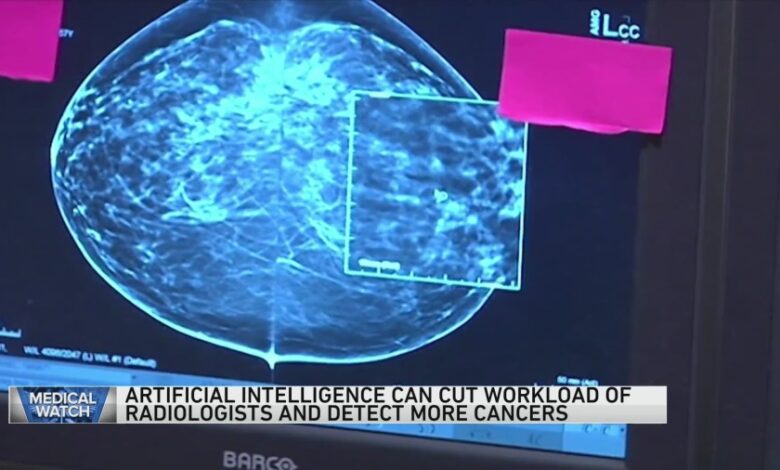
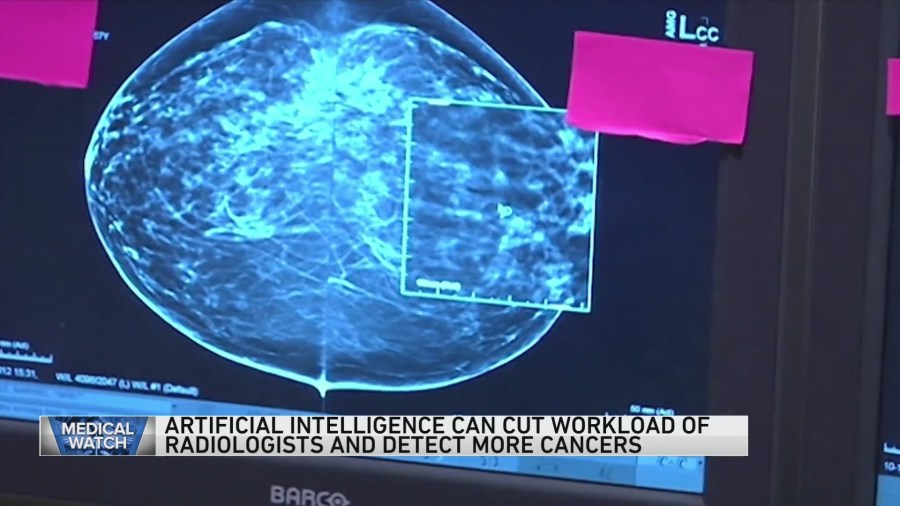
Mammogram Image Comparison: Before and After iCAD AI Processing
Before iCAD AI processing, the mammogram showed a slightly increased density in the left breast, barely distinguishable from the surrounding tissue. The area appeared as a vague, indistinct shadow, with no clear margins or other characteristic features. To the untrained eye, it would have been easily dismissed as normal breast tissue. After iCAD AI processing, the same area is clearly delineated and highlighted in a different color, for example, a bright yellow overlay.
The AI’s algorithm identifies subtle textural changes, asymmetry, and microcalcifications within the density, all features that suggest malignancy. The overlay also provides a quantitative probability score, indicating the likelihood of malignancy. This visual enhancement allows the radiologist to focus their attention on the area of concern, leading to a more confident and accurate interpretation. The difference is striking, transforming a vague and ambiguous finding into a clear and easily identifiable area needing further investigation.
iCAD AI System User Interface
Imagine a user interface displaying the mammogram image at the center. Surrounding this central image are several interactive panels. One panel displays the AI’s analysis, showing the highlighted areas of concern with probability scores and detailed descriptions of the features that triggered the alert (e.g., “Suspicious microcalcifications detected,” “Asymmetry identified”). Another panel shows the patient’s medical history and previous mammograms, providing crucial contextual information for the radiologist.
Google’s expansion of its iCAD AI mammography technology is a huge leap forward in early cancer detection. It’s exciting to see such advancements, and it makes me think about the broader AI landscape in healthcare; for instance, the work Salesforce is doing, as highlighted in this article about salesforce healthcare ai sean kennedy , shows how different companies are tackling similar challenges.
Ultimately, these innovations, like Google’s iCAD AI, are paving the way for more accurate and efficient diagnostics.
A third panel allows the radiologist to adjust the AI’s sensitivity and specificity settings, customizing the analysis to their specific needs and preferences. The overall design is clean and intuitive, allowing for efficient workflow and easy interpretation of the AI’s output. The interface uses a color-coded system, clearly distinguishing normal tissue from areas flagged by the AI.
Data Flow within the iCAD AI System
The data flow begins with image acquisition: the mammogram images are digitally captured and uploaded to the iCAD AI system. The images are then pre-processed to enhance contrast and remove artifacts. Next, the AI’s algorithms analyze the images, identifying patterns and features that are indicative of malignancy. This involves complex image processing techniques, including deep learning models trained on a vast dataset of mammograms.
The AI generates a report highlighting areas of concern, along with probability scores and descriptive annotations. Finally, the report, along with the processed images, is presented to the radiologist for review and interpretation. This streamlined workflow ensures efficient analysis and timely reporting, ultimately aiding in faster and more accurate diagnosis.
Final Thoughts: Google ICAD AI Mammography Expansion
Source: wgntv.com
The expansion of Google iCAD AI in mammography represents a significant leap forward in breast cancer detection. While challenges remain, the potential benefits – increased accuracy, improved efficiency, and ultimately, more lives saved – are undeniable. The future of breast cancer screening is bright, and AI is leading the charge. It’s a thrilling time to be witnessing these advancements in healthcare.
FAQ Compilation
How accurate is Google iCAD AI compared to traditional methods?
Studies show significant improvements in accuracy, reducing both false positives and false negatives, but the exact figures vary depending on the specific study and context.
What are the costs associated with implementing Google iCAD AI?
The cost varies greatly depending on factors like the size of the facility, the level of integration required, and the ongoing maintenance contracts. It’s best to contact Google or a reseller for a tailored quote.
What training is required for radiologists to use Google iCAD AI?
Training programs are typically provided by Google or its partners. The extent of training depends on the radiologist’s existing expertise and the system’s complexity. Expect a mix of online and hands-on sessions.
Is patient data privacy protected when using Google iCAD AI?
Google emphasizes strong data security and privacy measures, adhering to relevant regulations like HIPAA. However, the specifics of data handling should be reviewed in the detailed terms of service and privacy policies.





