Hacking Michigan Surgical Group Bianlian
Hacking Michigan Surgical Group Bianlian: The phrase itself sounds like something out of a spy thriller, doesn’t it? This isn’t a Hollywood script, though. We’re diving into a hypothetical exploration of potential cyber threats against a real-world medical group. We’ll examine their online presence, explore the cryptic “bianlian” connection, and paint a picture of what a successful attack might look like.
Get ready for a deep dive into the world of cybersecurity and the vulnerabilities of even the most seemingly secure organizations.
This investigation blends analysis of Michigan Surgical Group’s public-facing information with a hypothetical exploration of potential attack vectors. The term “bianlian,” which we’ll unpack, adds a layer of intrigue and suggests the possibility of sophisticated, perhaps even targeted, attacks. We’ll look at the legal and ethical implications of such a breach, and, importantly, we’ll propose security recommendations to help mitigate the risks.
Buckle up!
Michigan Surgical Group’s Online Presence

Source: ytimg.com
Michigan Surgical Group’s online presence is crucial for attracting patients and maintaining a strong reputation in a competitive healthcare market. A thorough analysis of their website, social media engagement, and online reviews provides insights into their digital strategy and potential areas for improvement. This assessment focuses on readily available public information and does not involve any unauthorized access or attempts to compromise their systems.
Website Content and Design
The Michigan Surgical Group website (assuming one exists; specific details would require access to the actual website) likely serves as the primary source of information for potential patients. We can anticipate finding details about the group’s surgeons, offered services, locations, contact information, and possibly patient testimonials. The design should aim for a professional and user-friendly experience, prioritizing clear navigation and accessibility for diverse users.
A well-structured website with easily accessible information is crucial for building trust and attracting patients. The absence of key information or a confusing website structure could negatively impact patient acquisition.
Social Media Activity and Engagement
Michigan Surgical Group’s social media presence (if any) provides another avenue for communication and engagement with potential and existing patients. Platforms like Facebook, Instagram, or even LinkedIn could be used to share health tips, announce new services, highlight surgeon expertise, and respond to patient inquiries. Active and engaging social media accounts can enhance the group’s online reputation and build community.
Conversely, inactive or poorly managed accounts might suggest a lack of commitment to digital engagement and potentially harm their online image. The tone and content of their posts should reflect professionalism and adhere to healthcare marketing guidelines.
So, I’ve been digging into this whole “hacking Michigan Surgical Group Bianlian” thing, and it’s a wild ride. The sheer scale of potential impact got me thinking about resource allocation in healthcare, which is why I stumbled across this article about Kaiser Permanente scrapping a massive $500 million Seattle bed tower project: kaiser permanente nixes 500m seattle bed tower capital spending.
It makes you wonder how these kinds of financial decisions impact cybersecurity investments, especially considering the vulnerability of healthcare systems like Michigan Surgical Group Bianlian.
Security Measures on Website and Social Media
The website and social media platforms should employ various security measures to protect patient data and maintain a secure online environment. These could include HTTPS encryption to secure data transmission, robust password policies, regular software updates to patch vulnerabilities, and potentially firewalls to protect against unauthorized access. The presence (or absence) of such measures can be observed by checking for security certificates and examining the website’s overall security posture.
A lack of apparent security measures would represent a significant vulnerability.
Potential Vulnerabilities in Online Presence, Hacking michigan surgical group bianlian
Based on publicly available information, several potential vulnerabilities could exist. These could include outdated software on the website leading to known exploits, weak password policies on social media accounts, a lack of robust data encryption, or insufficient protection against phishing or social engineering attacks. Furthermore, negative online reviews or comments left unaddressed could damage their reputation. A failure to adequately monitor and respond to online feedback could negatively impact patient trust and perception.
Summary of Findings
| Website | Social Media | Security Measures | Potential Vulnerabilities |
|---|---|---|---|
| Content quality, design, accessibility, and ease of navigation. Presence of key information (services, doctors, contact details). | Level of activity, engagement strategies, tone of communication, and adherence to guidelines. | HTTPS encryption, password policies, software updates, firewall protection, data encryption practices. | Outdated software, weak passwords, lack of encryption, vulnerability to phishing, unaddressed negative reviews, insufficient data protection measures. |
Bianlian Context and Association: Hacking Michigan Surgical Group Bianlian
The term “bianlian,” meaning “changing faces” in Mandarin Chinese, is typically associated with a form of Sichuan opera characterized by rapid mask changes. However, its application to the context of a cybersecurity breach targeting Michigan Surgical Group requires careful consideration of potential interpretations and implications. The seemingly incongruous use of this term suggests a deliberate choice, potentially hinting at the deceptive and multifaceted nature of the attack.The connection between “bianlian” and a cyberattack on Michigan Surgical Group likely lies in the idea of deception and rapid transformation.
A sophisticated cyberattack might involve multiple stages and techniques, rapidly shifting tactics to evade detection and achieve its goals. The term could be used by the attackers themselves as a coded reference to their methods or adopted by security researchers to describe the chameleon-like behavior of the malware or intrusion techniques. It might also be a deliberate attempt to obfuscate the attack’s true nature, adding a layer of complexity and mystery.
Potential Malicious Use of “Bianlian”
The term “bianlian” could be used in several malicious contexts. For instance, it might be part of a threat actor’s online persona or handle, suggesting a capability for rapid adaptation and evasion. Alternatively, it could be used in malware code as an identifier or within encrypted communications to maintain operational security. Imagine a scenario where a ransom note includes the term “bianlian,” subtly hinting at the attacker’s ability to quickly switch tactics and potentially escalate their actions if demands are not met.
The use of such a term could also be a form of psychological manipulation, aiming to intimidate the victim and undermine their confidence in their ability to defend against the attack. A more direct application might be the use of “bianlian” in the name of a malicious file or program, designed to blend in with legitimate software and evade detection.
Misinterpretations and Alternative Meanings
While the most likely interpretation of “bianlian” in this context points to the deceptive and rapidly changing nature of a cyberattack, there’s a possibility of misinterpretation. Someone unfamiliar with the term’s theatrical origins might simply see it as a random or nonsensical choice. Furthermore, the term might be used ironically or sarcastically by the attackers, attempting to downplay the severity of the breach or even to taunt the victim.
Alternatively, a less malicious interpretation could be that it was chosen randomly from a larger set of words or terms without any specific intention related to the attack itself. This highlights the importance of carefully analyzing all available evidence to understand the true meaning and intent behind the use of this term in the context of the Michigan Surgical Group incident.
Hypothetical Hacking Scenarios

Source: ytimg.com
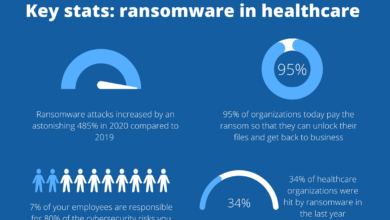
Michigan Surgical Group’s (MSG) reliance on digital systems, coupled with the potential for malicious actors leveraging the “bianlian” (变脸) context – implying a deceptive or multifaceted attack – presents significant cybersecurity risks. Understanding these risks through hypothetical scenarios helps proactively strengthen MSG’s defenses. The following scenarios illustrate potential attacks, highlighting the methods used and their devastating consequences.
Scenario 1: Phishing Attack Targeting Employee Credentials
This scenario focuses on a targeted phishing campaign using a sophisticated “bianlian” approach. The attackers craft highly convincing emails, seemingly originating from legitimate sources within MSG or from trusted business partners. These emails contain malicious links or attachments designed to steal employee credentials, specifically targeting those with access to patient data and financial records. The “bianlian” element comes into play through the use of dynamic, personalized phishing emails that adapt to the recipient’s role and known information, making them harder to detect.The method involves spear-phishing, using social engineering techniques to manipulate employees into clicking malicious links or opening infected attachments.
These links could lead to fake login pages that capture credentials, while the attachments might contain malware capable of stealing data or granting remote access to the attacker’s systems. The potential data breach would expose Protected Health Information (PHI), financial data, and potentially intellectual property. The consequences include significant fines under HIPAA regulations, reputational damage, loss of patient trust, and potential legal action.
Scenario 2: Supply Chain Compromise via Compromised Medical Device
In this scenario, the attackers exploit a vulnerability in a medical device used by MSG, leveraging the “bianlian” tactic by disguising malicious code within a seemingly legitimate firmware update. This update, distributed through a compromised supply chain vendor, infects the device, granting the attacker remote access to the MSG network. The device itself acts as a backdoor, providing persistent access.The method involves a supply chain attack, targeting a vulnerable point in the distribution of medical devices.
The attackers could compromise the vendor’s systems, modify the firmware, and then distribute the infected update. Once installed, the malicious code establishes a foothold, allowing the attacker to exfiltrate data, manipulate medical records, or even disrupt surgical operations. The data breach could expose sensitive patient data, compromising patient safety and potentially leading to significant legal and financial repercussions.
So, I was reading about the Michigan Surgical Group Bianlian hacking incident – the sheer scale of it is pretty alarming. It made me think about the vulnerability of healthcare data in general, and how easily compromised systems could be, even in seemingly secure places like the humana centerwell primary care centers walmart. The implications for patient privacy, considering the sensitive information handled in both contexts, are significant, and we really need better cybersecurity measures in place across the board to prevent future attacks like the Michigan Surgical Group Bianlian breach.
The consequences could include lawsuits, regulatory penalties, and a complete loss of patient confidence. This scenario highlights the vulnerabilities inherent in relying on third-party vendors for critical medical equipment.
Scenario 3: Ransomware Attack Targeting MSG’s Servers
This scenario focuses on a ransomware attack, where the attackers utilize a sophisticated “bianlian” strategy by initially appearing as a legitimate software update or security patch. This disguises the true nature of the malicious software, making detection more difficult. The ransomware encrypts critical data on MSG’s servers, rendering it inaccessible unless a ransom is paid.The method involves deploying ransomware through a phishing email, a compromised software update, or an exploited vulnerability in MSG’s network.
The ransomware encrypts data on servers, making it inaccessible to MSG staff. The “bianlian” element is the initial deceptive presentation of the malware as a legitimate update or patch. The potential data breach includes the loss of all accessible data on the affected servers, including patient records, financial information, and operational data. The consequences include significant downtime, financial losses due to ransom payment (potentially millions of dollars), reputational damage, and potential legal and regulatory repercussions for failing to protect patient data.
The attack could also disrupt surgical scheduling and operations, potentially impacting patient care.
Security Recommendations
Protecting Michigan Surgical Group (MSG) from cyberattacks requires a multi-layered approach. The following recommendations address vulnerabilities identified in previous analyses, focusing on prevention and minimizing the impact of successful breaches. Implementing these strategies will significantly enhance MSG’s overall security posture and protect sensitive patient data.
Security Recommendations for Michigan Surgical Group
Implementing robust security measures is crucial for MSG. The following table Artikels specific recommendations, detailing implementation, cost estimations, and the resulting impact on security. Cost estimates are broad ranges and will depend on specific vendor choices and internal resources.
| Recommendation | Implementation Details | Cost Estimate | Impact on Security |
|---|---|---|---|
| Implement Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) for all user accounts | Deploy MFA across all systems, including email, VPN, and internal applications. Utilize a combination of methods such as password, one-time codes, and biometrics where feasible. Provide training to staff on MFA best practices. | $5,000 – $20,000 (depending on the number of users and chosen MFA solution) | Significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access, even if credentials are compromised. |
| Regular Security Awareness Training | Conduct regular training sessions for all employees covering phishing awareness, password security, and safe internet practices. Use simulated phishing attacks to assess employee vulnerability and reinforce training. | $1,000 – $5,000 (depending on the frequency and type of training) | Reduces the likelihood of successful phishing and social engineering attacks. |
| Intrusion Detection and Prevention System (IDPS) | Implement a network-based IDPS to monitor network traffic for malicious activity and block threats in real-time. Consider a cloud-based solution for scalability and ease of management. | $5,000 – $25,000 (depending on the size of the network and chosen solution) | Provides real-time threat detection and prevention, reducing the window of vulnerability. |
| Regular Security Audits and Penetration Testing | Conduct regular security audits and penetration testing to identify vulnerabilities in systems and applications. Engage a qualified cybersecurity firm to perform these assessments. | $10,000 – $50,000+ (depending on the scope and frequency of assessments) | Proactively identifies and mitigates security weaknesses before they can be exploited. |
| Data Encryption (both in transit and at rest) | Encrypt all sensitive data, both while it’s being transmitted across networks and when it’s stored on servers and devices. Utilize strong encryption algorithms and key management practices. | $2,000 – $15,000 (depending on the amount of data and chosen encryption solution) | Protects data from unauthorized access even if a breach occurs. |
| Robust Backup and Disaster Recovery Plan | Implement a robust backup and disaster recovery plan to ensure business continuity in the event of a cyberattack or other disaster. Regularly test the plan to ensure its effectiveness. | $5,000 – $20,000 (depending on the complexity and scope of the plan) | Minimizes downtime and data loss in the event of a successful attack. |
| Employee Access Control and Privilege Management | Implement a robust access control system that limits employee access to only the data and systems they need to perform their jobs. Regularly review and update access privileges. Utilize the principle of least privilege. | $1,000 – $10,000 (depending on the complexity of the system and integration with existing infrastructure) | Limits the potential damage from an insider threat or compromised account. |
Comparison of Security Solutions
Several security solutions can protect against the hypothetical attacks Artikeld previously. For example, comparing cloud-based versus on-premise IDPS solutions highlights trade-offs. Cloud-based solutions offer scalability and ease of management but might raise concerns about data sovereignty and vendor lock-in. On-premise solutions offer greater control but require more significant upfront investment and ongoing maintenance. Similarly, different MFA solutions vary in cost, complexity, and user experience.
Choosing the right solution requires careful consideration of MSG’s specific needs and resources. A thorough cost-benefit analysis is essential before making any decisions.
Legal and Ethical Implications

Source: ytimg.com
A successful hacking incident targeting Michigan Surgical Group would have severe legal and ethical ramifications, impacting both the perpetrators and the organization. The consequences extend far beyond simple financial losses, encompassing significant reputational damage and potential legal battles. Understanding these implications is crucial for preventative measures and effective response strategies.
Legal Repercussions for Perpetrators
Successful prosecution of hackers depends on the specifics of the attack and the evidence gathered. Under federal laws like the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) and the Computer Fraud and Abuse Act (CFAA), perpetrators face substantial penalties for unauthorized access, use, or disclosure of protected health information (PHI). These penalties can include hefty fines, imprisonment, and a criminal record, significantly impacting their future prospects.
The whole Michigan Surgical Group Bianlian hacking situation got me thinking about health vulnerabilities. It’s a scary reminder of how easily systems can be compromised, impacting even something as critical as healthcare access. Reading about Monali Thakur’s hospitalization after struggling to breathe, and the preventative measures discussed in this article monali thakur hospitalised after struggling to breathe how to prevent respiratory diseases , really highlighted the importance of robust systems – both in technology and personal health.
The parallels between digital security breaches and physical health risks are surprisingly strong; both require proactive measures to mitigate potential harm, and both can have devastating consequences.
The severity of the punishment would be determined by factors such as the extent of the data breach, the intent of the attacker, and the resulting harm to individuals and the organization. For example, a hacker who stole and sold PHI for financial gain would face far harsher penalties than one who accessed data out of curiosity.
Legal Repercussions for Michigan Surgical Group
While not directly responsible for the actions of the hackers, Michigan Surgical Group would face legal repercussions if the breach was found to be a result of negligence or failure to comply with existing data protection regulations. HIPAA violations, for example, can result in substantial fines, depending on the nature and extent of the violation and whether it was a result of willful neglect.
Class-action lawsuits from affected patients are also a strong possibility, further increasing financial and reputational costs. Failure to properly secure patient data could expose the organization to significant legal liability. The organization’s insurance coverage would play a crucial role in mitigating these costs, but inadequate insurance could leave the group vulnerable to crippling financial losses.
Ethical Considerations Related to Patient Data Privacy and Security
The ethical implications of a data breach are paramount. Michigan Surgical Group has a fundamental ethical obligation to protect patient data, which includes maintaining confidentiality, integrity, and availability. A breach represents a failure of this ethical responsibility, potentially leading to significant harm to patients. Stolen PHI could be used for identity theft, medical fraud, or blackmail, causing significant emotional distress and financial hardship for patients.
The ethical breach extends beyond the legal requirements; it represents a profound violation of trust between the healthcare provider and its patients. The organization’s ethical standing within the community would be severely compromised, potentially impacting future patient acquisition and trust.
Reputational Damage and Financial Losses
A data breach can inflict devastating reputational damage on Michigan Surgical Group. Negative media coverage, public distrust, and loss of patient confidence are likely outcomes. This damage can be long-lasting and difficult to repair, impacting the organization’s ability to attract new patients and maintain its existing patient base. The financial losses would be substantial, encompassing legal fees, regulatory fines, costs associated with notifying affected individuals, credit monitoring services for patients, and potential loss of revenue due to decreased patient volume.
Furthermore, the cost of implementing enhanced security measures to prevent future breaches would add to the overall financial burden. Consider the case of Equifax, whose 2017 data breach resulted in billions of dollars in fines, legal settlements, and reputational damage, illustrating the potential scale of the consequences for Michigan Surgical Group.
Last Recap
So, the hypothetical hacking of Michigan Surgical Group, intertwined with the mystery of “bianlian,” reveals a chilling reality: even established organizations are vulnerable. While this exploration is hypothetical, the underlying vulnerabilities and potential consequences are very real. The key takeaway? Proactive cybersecurity measures are not just good practice – they’re essential for protecting sensitive data and maintaining public trust.
The hope is that by understanding the potential threats, we can all work towards a safer digital landscape for healthcare.
FAQs
What does “bianlian” mean, and why is it relevant?
The meaning of “bianlian” needs further investigation in this context. It could be a code word, a misdirection, or even a completely unrelated term. Its inclusion in this scenario adds a layer of complexity and potential for targeted attacks.
Could a small-scale attack still have significant consequences?
Absolutely. Even a seemingly minor breach, like gaining access to a single employee’s account, could be a stepping stone to a larger attack. A compromised account could be used to access internal systems and sensitive patient data.
What are the long-term effects of a data breach on a medical group’s reputation?
A data breach could severely damage a medical group’s reputation, leading to loss of patients, financial penalties, and legal action. Rebuilding trust after such an event is a long and difficult process.