
Healthcare execs should plan ahead Generative AI McKinsey
Healthcare execs should plan ahead generative AI McKinsey – that’s the urgent message echoing through the healthcare industry. The rapid advancement of generative AI presents both incredible opportunities and significant challenges for healthcare leaders. From streamlining administrative tasks to revolutionizing patient care, the potential impact is undeniable. But navigating this new landscape requires careful consideration of ethical implications, data security, and the potential disruption to existing workflows.
This post delves into McKinsey’s insights and offers a roadmap for healthcare executives to harness the power of generative AI responsibly and effectively.
We’ll explore how generative AI can reshape strategic planning, optimize resource allocation, and enhance risk management. We’ll also examine its potential to revolutionize operational efficiency, improve patient care coordination, and transform workforce management. Finally, we’ll address the crucial concerns surrounding data privacy, ethical considerations, and the responsible implementation of this transformative technology.
Generative AI’s Impact on Healthcare Executive Decision-Making
The rapid advancement of generative AI presents both unprecedented opportunities and significant challenges for healthcare executives. Its ability to process and analyze vast amounts of data, generate insightful reports, and predict future trends is poised to revolutionize strategic planning, resource allocation, and risk management within the healthcare sector. Understanding its potential impact is crucial for navigating the complexities of the modern healthcare landscape.
Generative AI’s Alteration of Strategic Planning Processes, Healthcare execs should plan ahead generative AI McKinsey
Generative AI can significantly transform strategic planning in three key ways. First, it can accelerate the process of market analysis by rapidly synthesizing information from diverse sources, including patient data, competitor activities, and regulatory changes. This allows executives to identify emerging trends and opportunities more quickly. Second, it can facilitate scenario planning by generating multiple plausible future scenarios based on different assumptions and variables, enabling more robust and adaptable strategic plans.
For example, a generative AI model could simulate the impact of different pricing strategies on patient volume and revenue under various economic conditions. Finally, it can enhance communication and collaboration within the planning team by automatically generating summaries of key findings, reports, and presentations, saving valuable time and resources.
Generative AI’s Impact on Healthcare Resource Allocation
Generative AI can optimize resource allocation by providing data-driven insights into areas such as staffing, equipment, and budget distribution. By analyzing historical data and predicting future demand, AI can help healthcare organizations allocate resources more efficiently and effectively. For instance, an AI model could predict the optimal number of nurses needed for each shift based on patient volume, acuity levels, and staff availability, minimizing overtime costs and ensuring adequate patient care.
Similarly, AI can optimize the allocation of expensive medical equipment, ensuring its utilization is maximized and minimizing idle time. This allows for more efficient use of capital and resources, ultimately improving the overall financial performance of the organization.
Generative AI’s Enhancement of Healthcare Risk Management Strategies
Generative AI can significantly improve risk management by identifying and assessing potential risks more effectively. It can analyze large datasets to detect patterns and anomalies that might indicate potential problems, such as increased infection rates or medication errors. Early identification of these risks allows for proactive intervention, minimizing potential harm and financial losses. Furthermore, generative AI can assist in developing and implementing risk mitigation strategies by simulating the impact of various interventions and identifying the most effective approaches.
Healthcare execs need to seriously consider how generative AI, as McKinsey suggests, can improve patient care. This includes proactive measures to address preventable illnesses; for example, learning from situations like Monali Thakur’s hospitalization, as detailed in this article monali thakur hospitalised after struggling to breathe how to prevent respiratory diseases , highlights the urgent need for better preventative care strategies.
Ultimately, leveraging AI for early detection and intervention could significantly reduce such crises, aligning perfectly with forward-thinking healthcare strategies.
For example, by analyzing patient data, AI can predict which patients are at high risk of readmission and recommend preventative measures, such as personalized discharge plans and follow-up appointments. This proactive approach can substantially reduce readmission rates and improve patient outcomes.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Generative AI in Healthcare Executive Decision-Making
| Benefits | Drawbacks |
|---|---|
| Improved decision-making speed and accuracy through data-driven insights. | Potential for bias in algorithms and data, leading to unfair or inaccurate outcomes. |
| Enhanced strategic planning and resource allocation efficiency. | High implementation costs and the need for specialized expertise. |
| Proactive risk management and identification of potential problems. | Concerns about data privacy and security. |
| Increased operational efficiency and cost savings. | Lack of transparency and explainability in some AI models. |
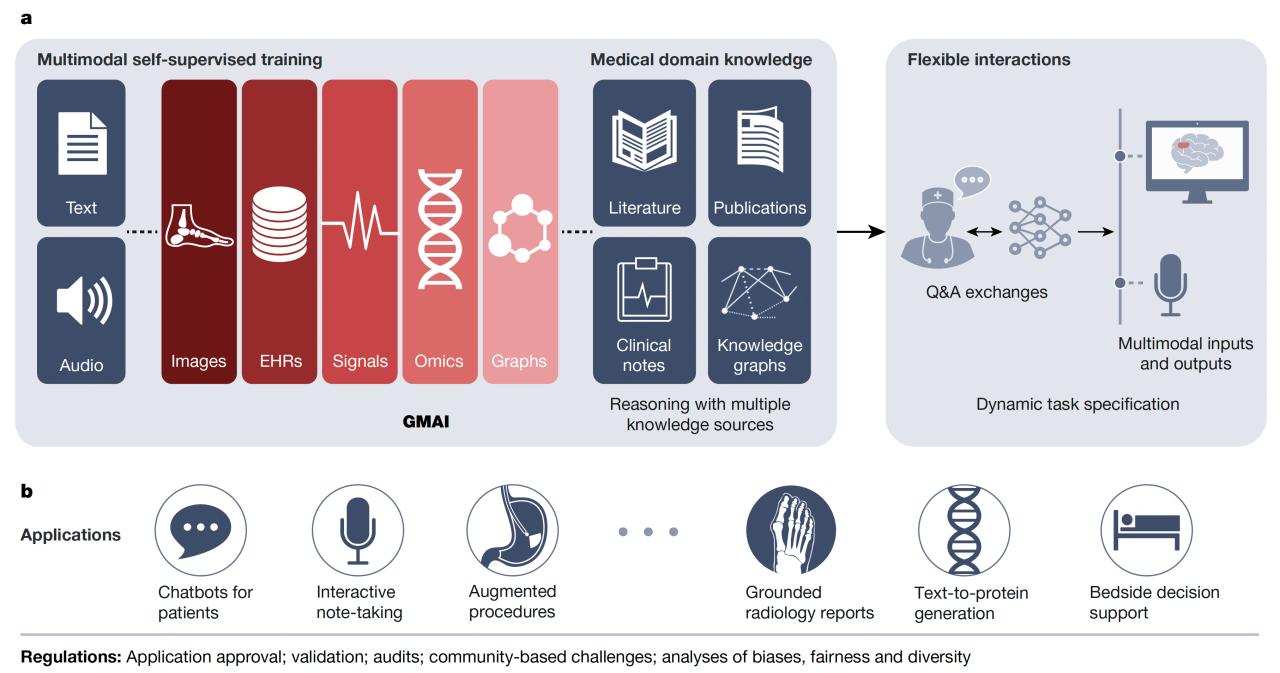
Utilizing Generative AI for Enhanced Operational Efficiency
Source: substackcdn.com
Generative AI is poised to revolutionize healthcare operations, offering significant improvements in efficiency and effectiveness across various departments. By automating tasks, improving communication, and optimizing resource allocation, generative AI can free up valuable time and resources, allowing healthcare professionals to focus on what matters most: patient care. This section explores several key areas where generative AI can make a substantial impact.
Streamlining Administrative Tasks
Generative AI can significantly reduce the burden of administrative tasks in healthcare. For instance, it can automate the generation of patient intake forms, pre-populate electronic health records (EHRs) with relevant information from various sources, and even draft initial correspondence with patients or insurance companies. This automation not only saves administrative staff time but also reduces the risk of human error, ensuring accuracy and consistency in documentation.
Imagine the time saved by automatically generating appointment reminders, follow-up letters, or even personalized patient education materials. The potential for cost savings and increased productivity is substantial.
Improving Patient Care Coordination and Communication
Generative AI can enhance patient care coordination by facilitating seamless communication between healthcare providers and patients. For example, AI-powered chatbots can answer frequently asked questions, schedule appointments, and provide patients with personalized health information. Furthermore, generative AI can summarize complex medical information in a clear and concise manner, improving communication between specialists and primary care physicians. This improved communication ensures that patients receive timely and accurate information, leading to better health outcomes.
Consider the impact of an AI system that automatically flags potential medication interactions or alerts clinicians to concerning changes in a patient’s condition based on their EHR data.
Optimizing Supply Chain Management
Healthcare supply chains are complex and often prone to disruptions. Generative AI can help optimize this process by predicting demand for medical supplies, identifying potential bottlenecks, and streamlining logistics. For example, AI can analyze historical data and current trends to forecast the need for specific medications or equipment, minimizing stockouts and reducing waste. It can also optimize delivery routes and inventory management, ensuring that supplies are available when and where they are needed.
A hospital facing a potential shortage of a critical medication could utilize generative AI to predict the impact and proactively manage its supply chain to prevent a crisis.
Workflow Diagram: Appointment Scheduling with Generative AI
The following workflow illustrates how generative AI can streamline the appointment scheduling process:
- Patient Request: Patient initiates an appointment request through a patient portal or chatbot.
- AI Assessment: Generative AI assesses the request, considering patient history, physician availability, and appointment type.
- Scheduling Options: AI presents the patient with several suitable appointment times and locations.
- Patient Selection: Patient selects a preferred appointment time and location.
- Calendar Integration: AI automatically adds the appointment to the physician’s calendar and sends confirmation to the patient.
- Reminder System: AI generates and sends automated appointment reminders to the patient via SMS or email.
This automated process reduces manual effort for both patients and staff, leading to increased efficiency and improved patient satisfaction.
Generative AI and the Future of Healthcare Workforce Management: Healthcare Execs Should Plan Ahead Generative AI McKinsey
The healthcare industry is facing a looming crisis: a severe shortage of qualified professionals across all disciplines. Generative AI offers a potential lifeline, promising to revolutionize workforce management and alleviate some of the immense pressure on healthcare systems. This technology’s ability to automate tasks, enhance training, and improve recruitment processes could significantly impact the future of healthcare staffing.
However, ethical considerations and potential challenges must be carefully addressed to ensure responsible and effective implementation.Generative AI’s Potential in Healthcare Workforce Recruitment and TrainingGenerative AI can significantly streamline the recruitment process. Imagine AI-powered chatbots pre-screening applicants, identifying those most likely to be a good fit based on specific criteria and skills. These systems could also create personalized job descriptions, attracting a wider pool of candidates.
Furthermore, generative AI can revolutionize training. AI-powered tools can create realistic simulations for practicing procedures, personalized learning paths based on individual needs and strengths, and interactive tutorials, leading to faster and more effective training programs. For example, a surgical resident could practice complex procedures in a virtual environment, receiving immediate feedback from the AI on technique and precision.
McKinsey’s advice for healthcare execs to proactively plan for generative AI is crucial, especially considering the recent complexities in the sector. The impact of events like the elevance health earnings q1 change, cyberattack, and shifts in Medicaid and Medicare Advantage highlights the need for adaptable strategies. Successfully navigating these challenges requires forward-thinking leadership, making AI planning even more vital for long-term stability.
This allows for repeated practice without risk to patients and provides a more efficient learning process than traditional methods.
McKinsey’s advice for healthcare execs to plan for generative AI is spot on; the field is evolving rapidly, demanding proactive strategies. Consider the recent FDA approval of clinical trials for pig kidney transplants in humans, as reported here: fda approves clinical trials for pig kidney transplants in humans. This breakthrough highlights the need for AI in analyzing vast datasets to optimize transplant success rates and personalize treatments, further emphasizing the urgency of McKinsey’s recommendations.
Automating Routine Tasks Versus Tasks Requiring Human Judgment
Generative AI excels at automating repetitive, data-driven tasks. Scheduling appointments, managing patient records, processing insurance claims – these are all areas where AI can significantly increase efficiency and reduce the workload on human staff. However, tasks requiring complex decision-making, critical thinking, empathy, and nuanced understanding of human behavior are still best left to humans. For instance, diagnosing a patient’s illness, providing emotional support, and making ethical judgments regarding patient care remain firmly within the realm of human expertise.
The effective use of generative AI involves strategically identifying tasks suitable for automation, leaving those requiring human judgment and interaction intact. A hospital might use AI to schedule appointments and manage patient records, but the diagnosis and treatment plan would still require a physician’s expertise.
Challenges and Ethical Considerations
The implementation of generative AI in healthcare workforce management presents several challenges. Data privacy and security are paramount. Ensuring the confidentiality of sensitive patient and employee information is critical. Bias in algorithms is another significant concern. If the training data used to develop AI systems reflects existing biases in healthcare, the AI may perpetuate or even amplify those biases in recruitment, training, and other processes.
Finally, the displacement of human workers is a legitimate concern. Careful planning and retraining initiatives are essential to mitigate the potential negative impacts on the workforce. Transparency and accountability are crucial. Healthcare organizations must be transparent about how they are using AI in workforce management and be accountable for the outcomes.
Addressing a Staffing Shortage in a Hypothetical Scenario
Let’s consider a hypothetical scenario: a large hospital is facing a critical shortage of nurses in its emergency department. Generative AI could be used to address this in several ways. First, an AI-powered recruitment tool could be deployed to proactively identify and attract qualified nurses from a wider geographical area, customizing job postings to appeal to specific skill sets and preferences.
Second, the AI could generate personalized training modules focusing on high-demand emergency procedures, enhancing the skills of existing nurses and enabling them to handle a greater workload. Third, the AI could optimize nurse scheduling based on predicted patient flow, ensuring adequate staffing levels during peak hours and minimizing overtime costs. This multi-pronged approach leverages generative AI’s capabilities to efficiently and effectively tackle a pressing staffing challenge.
McKinsey’s Perspective on Generative AI in Healthcare
McKinsey & Company, a global management consulting firm, has extensively researched and published numerous reports on the transformative potential of generative AI across various industries, including healthcare. Their perspective emphasizes both the immense opportunities and the significant challenges associated with integrating this technology into healthcare systems. This analysis focuses on their key findings and recommendations, exploring the potential ROI, regulatory and ethical considerations, and illustrating a potential consulting project proposal.
McKinsey’s Key Findings and Recommendations
McKinsey’s research consistently highlights the potential of generative AI to significantly improve healthcare outcomes and operational efficiency. Their findings suggest that generative AI can revolutionize areas such as drug discovery, personalized medicine, diagnostics, and administrative tasks. Key recommendations often include a phased approach to implementation, prioritizing use cases with high potential impact and manageable risk. They stress the importance of data quality, robust security measures, and a strong focus on ethical considerations throughout the implementation process.
A strategic approach, focusing on identifying clear value propositions and integrating AI seamlessly into existing workflows, is crucial for successful adoption.
McKinsey’s Insights on Return on Investment (ROI)
McKinsey’s analysis suggests that the ROI of generative AI in healthcare can be substantial, but it’s highly dependent on the specific application and the organization’s ability to effectively implement and integrate the technology. For instance, automating administrative tasks like claims processing can lead to significant cost savings. In drug discovery, generative AI can accelerate the identification of promising drug candidates, reducing the time and cost associated with bringing new treatments to market.
However, McKinsey cautions that realizing this ROI requires careful planning, including investments in infrastructure, talent acquisition, and change management. A successful implementation hinges on aligning AI initiatives with strategic organizational goals and measuring progress against clear, defined metrics. For example, a hospital system might see a 15-20% reduction in administrative costs within three years of implementing an AI-powered claims processing system, offsetting the initial investment in software and training.
McKinsey’s Analysis of Regulatory and Ethical Implications
McKinsey acknowledges the significant regulatory and ethical implications associated with the use of generative AI in healthcare. Issues such as data privacy, algorithmic bias, and the potential for misdiagnosis need careful consideration. Compliance with regulations like HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) is paramount. McKinsey recommends proactive engagement with regulatory bodies and the development of robust ethical frameworks to guide the responsible use of generative AI.
Transparency in algorithms, data provenance, and decision-making processes is crucial to build trust and ensure accountability. Furthermore, addressing potential biases in training data and ensuring fairness in the application of AI are critical ethical considerations. For example, a lack of diversity in training datasets could lead to inaccurate diagnoses for certain patient populations, highlighting the need for rigorous testing and validation.
Potential McKinsey Consulting Project Proposal: Implementing Generative AI in a Large Hospital System
This proposal Artikels a project to implement generative AI in a large hospital system, focusing on improving patient care and operational efficiency. The project will be phased, starting with a pilot program focusing on automating the generation of patient summaries from clinical notes. This pilot will involve: (1) Data assessment and preparation: evaluating the quality and suitability of existing clinical data; (2) Model development and training: using a subset of the data to train a generative AI model capable of generating concise and accurate patient summaries; (3) Pilot implementation: deploying the model in a limited clinical setting and monitoring its performance; (4) Evaluation and refinement: analyzing the results of the pilot program and refining the model based on feedback from clinicians and patients; (5) Scaling and integration: expanding the implementation of the model to other departments within the hospital system, integrating it with existing electronic health record (EHR) systems.
The project will include ongoing monitoring and evaluation of the model’s performance, as well as training for clinicians on the use of the new technology. The anticipated benefits include improved efficiency in documentation, reduced physician burnout, and potentially improved patient care through more readily available and concise patient information. The project timeline will be 12-18 months, with a detailed budget outlining costs associated with data preparation, model development, implementation, and ongoing support.
Key performance indicators (KPIs) will include the accuracy of the generated summaries, the time saved by clinicians, and the overall impact on patient care.
Addressing Potential Risks and Challenges of Generative AI in Healthcare
Source: ebsedu.org
The transformative potential of generative AI in healthcare is undeniable, but its implementation isn’t without significant risks. Successfully integrating this technology requires a proactive approach to managing these challenges, ensuring patient safety and ethical considerations remain paramount. Ignoring these risks could lead to significant setbacks and erode public trust.
Bias and Fairness in AI Algorithms
Generative AI models are trained on vast datasets, and if these datasets reflect existing societal biases (e.g., racial, socioeconomic), the AI system will likely perpetuate and even amplify these biases in its outputs. This could lead to inaccurate diagnoses, inappropriate treatment recommendations, and unequal access to care. Mitigation strategies involve carefully curating training datasets to ensure representation across diverse populations and employing rigorous testing and validation processes to identify and correct biases.
Regular audits of AI systems for fairness and equity are also crucial. For example, an AI system trained primarily on data from a specific demographic might misdiagnose conditions in patients from other demographics.
Data Privacy and Security Concerns
Healthcare data is highly sensitive and protected by stringent regulations like HIPAA. Generative AI models require access to large amounts of patient data for training and operation, increasing the risk of data breaches and unauthorized access. Robust security measures, including data encryption, access control, and regular security audits, are essential. Furthermore, anonymization and de-identification techniques should be employed to minimize the risk of re-identification.
Consider the potential consequences of a breach – not only the legal repercussions but also the erosion of patient trust.
Lack of Transparency and Explainability
Many generative AI models, particularly deep learning models, function as “black boxes,” making it difficult to understand how they arrive at their decisions. This lack of transparency can hinder trust and accountability, especially in high-stakes medical contexts. Efforts should be made to develop more explainable AI (XAI) techniques that provide insights into the reasoning behind AI-generated recommendations. This allows clinicians to assess the validity of the AI’s suggestions and intervene if necessary.
For instance, a system recommending a specific treatment should ideally explain the factors influencing that recommendation.
Best Practices for Responsible Implementation of Generative AI in Healthcare
The responsible implementation of generative AI in healthcare demands a commitment to ethical principles and robust safeguards. A multi-faceted approach is required.
- Establish clear ethical guidelines and governance frameworks for the development and deployment of AI systems in healthcare.
- Prioritize data privacy and security by implementing robust security measures and adhering to relevant regulations (e.g., HIPAA).
- Invest in research and development of explainable AI (XAI) techniques to enhance transparency and accountability.
- Ensure diverse representation in training datasets to mitigate bias and promote fairness.
- Conduct rigorous testing and validation of AI systems to ensure accuracy and reliability.
- Establish mechanisms for continuous monitoring and evaluation of AI systems to identify and address potential issues.
- Promote collaboration between clinicians, AI developers, and ethicists to ensure responsible AI development and deployment.
- Educate healthcare professionals and patients about the capabilities and limitations of generative AI in healthcare.
Closing Notes
Source: geniusai.io
The integration of generative AI into healthcare is inevitable, and forward-thinking executives are already charting a course for its successful implementation. By understanding the potential benefits and proactively addressing the risks, healthcare organizations can leverage generative AI to improve patient outcomes, enhance operational efficiency, and secure a competitive advantage in the evolving healthcare landscape. McKinsey’s guidance underscores the importance of strategic planning, responsible implementation, and a focus on ethical considerations.
The future of healthcare is being written now, and those who embrace generative AI thoughtfully will be best positioned to shape it.
Detailed FAQs
What are the biggest risks of implementing generative AI in healthcare?
Major risks include data breaches compromising patient privacy, algorithmic bias leading to unfair or inaccurate diagnoses, and the potential for job displacement due to automation.
How can healthcare organizations ensure the ethical use of generative AI?
Ethical use requires establishing clear guidelines, prioritizing transparency and explainability in AI decision-making, and implementing robust oversight mechanisms to prevent bias and ensure fairness.
What is the return on investment (ROI) for generative AI in healthcare?
The ROI varies depending on the specific application, but potential benefits include reduced operational costs, improved efficiency, enhanced patient care, and new revenue streams.
How can healthcare systems prepare their workforce for the age of generative AI?
Preparation involves investing in reskilling and upskilling programs to equip staff with the necessary skills to work alongside AI systems, focusing on roles that require human judgment and empathy.





