Hospital operating margins improve, expense pressures continue – Kaufman Hall
Hospital operating margins improve expense pressures continue Kaufman Hall – Hospital operating margins improve, expense pressures continue – Kaufman Hall: That’s the headline, and it tells a fascinating story about the rollercoaster ride that is hospital finance. We’re seeing improvements in operating margins, yes, but the pressure from rising costs is far from over. This post dives into the key findings from Kaufman Hall’s analysis, exploring the factors driving margin improvements, the persistent expense challenges, and what this means for the future of healthcare delivery.
Get ready for a deep dive into the numbers and the implications!
Kaufman Hall’s recent report reveals a complex picture. While some hospitals are experiencing improved operating margins thanks to strategic initiatives and increased patient volume, the underlying pressure of escalating expenses remains a significant hurdle. We’ll examine the specific cost increases impacting hospital budgets – everything from staffing shortages and supply chain disruptions to the ever-increasing demands of technology. We’ll also look at the strategies hospitals are employing to navigate this challenging financial landscape and what that might mean for patient care and access.
Hospital Operating Margin Improvement
The recent reports from Kaufman Hall highlight a positive trend: hospital operating margins are improving. However, this improvement doesn’t negate the persistent pressure on hospital expenses. Understanding the drivers behind this margin improvement and the strategies employed by hospitals is crucial for navigating the complex financial landscape of healthcare.
Factors Contributing to Improved Hospital Operating Margins
Several interconnected factors have contributed to the recent improvement in hospital operating margins. These factors vary in their impact across different hospital systems, depending on size, location, patient demographics, and specific operational strategies. Some hospitals have benefited more significantly from certain factors than others. For example, a large urban hospital might see greater gains from increased patient volume, while a smaller rural hospital might rely more heavily on cost-cutting measures.
Kaufman Hall’s report on improving hospital operating margins is interesting, especially considering the ongoing expense pressures. One area where technology might offer some relief is in radiology; the recent news about Google iCAD AI mammography expansion suggests increased efficiency and potentially reduced costs through earlier and more accurate diagnoses. Ultimately, though, sustained margin improvement will depend on addressing multiple factors beyond just technological advancements, as Kaufman Hall emphasizes.
| Factor | Impact | Strategy | Result |
| Increased Patient Volume | Significant positive impact, especially in high-demand specialties. | Targeted marketing campaigns, improved access to care, expansion of services. | Higher revenue generation, improved capacity utilization. |
| Price Increases | Positive impact, but potential for reduced patient access and negative public perception. | Negotiation of higher reimbursement rates with insurers, implementation of value-based pricing models. | Increased revenue per patient, but potential for reduced volume if not managed carefully. |
| Cost Reduction Initiatives | Positive impact, but requires careful planning to avoid compromising quality of care. | Supply chain optimization, improved operational efficiency, workforce management strategies. | Lower operating expenses, improved profitability. |
| Government Funding and Subsidies | Variable impact, depending on the specific programs and eligibility criteria. | Application for relevant grants and subsidies, participation in government-sponsored programs. | Increased revenue stream, but often comes with stipulations and reporting requirements. |
| Improved Revenue Cycle Management | Positive impact, improving cash flow and reducing administrative costs. | Implementation of advanced billing systems, improved patient communication, proactive claims management. | Faster payment collection, reduced accounts receivable days. |
Strategies for Enhancing Operating Margins
Hospitals are employing a range of strategies to enhance their operating margins. These strategies often involve a combination of revenue enhancement and cost reduction measures, tailored to the specific circumstances of each hospital system. For instance, some hospitals are focusing on expanding high-margin services, while others are concentrating on streamlining their operations and reducing waste. The effectiveness of these strategies varies depending on market conditions and internal capabilities.
Persistent Expense Pressures
Source: datawrapper.de
Hospitals are facing a perfect storm of escalating costs, squeezing already tight operating margins. These pressures aren’t isolated incidents; they represent a fundamental shift in the healthcare landscape, impacting everything from staffing to supplies. Understanding the nature and scope of these expenses is crucial for developing effective strategies to ensure the long-term financial health of hospitals.The ongoing expense pressures faced by hospitals are multifaceted and deeply intertwined with broader economic and societal trends.
These pressures are not simply about inflation; they represent a complex interplay of factors impacting the cost of delivering care. For example, increased demand for services, coupled with a shortage of healthcare professionals, drives up labor costs significantly. Simultaneously, the rising cost of pharmaceuticals, medical devices, and advanced technologies adds further strain on already limited budgets. This complex interplay requires a nuanced understanding to develop effective solutions.
Rising Labor Costs
The healthcare industry is facing a significant workforce shortage, leading to intense competition for qualified professionals. This scarcity drives up salaries and benefits, placing a considerable burden on hospital budgets. Registered nurses, physicians, and specialized technicians are all in high demand, leading to increased recruitment and retention costs. Hospitals are resorting to strategies like offering sign-on bonuses, increased salaries, and enhanced benefits packages to attract and retain staff.
The effectiveness of these strategies varies depending on the specific hospital’s location and market conditions, with some hospitals struggling to compete effectively. For instance, rural hospitals often find it particularly challenging to attract and retain staff due to limited access to amenities and lower salaries compared to urban centers.
Increased Costs of Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices
The cost of pharmaceuticals and medical devices continues to climb, significantly impacting hospital expenses. The development and introduction of new, innovative technologies often come with a high price tag. Hospitals are forced to balance the need to provide patients with access to the latest treatments with the financial constraints of their budgets. Negotiating favorable contracts with pharmaceutical companies and medical device manufacturers is crucial, but even with effective negotiations, these costs represent a substantial portion of hospital expenditures.
For example, the increasing use of advanced imaging technologies, while improving diagnostic accuracy, adds to the overall cost of patient care.
Supply Chain Disruptions and Inflation
Recent years have highlighted the vulnerability of the healthcare supply chain. Disruptions, exacerbated by global events and increased demand, have led to shortages and price increases for essential medical supplies. This unpredictability makes it difficult for hospitals to accurately budget and plan for expenses. Inflationary pressures further compound these challenges, impacting the cost of everything from food and cleaning supplies to utilities and maintenance.
Strategies to mitigate these risks include diversifying suppliers, building up inventory of critical supplies, and implementing robust inventory management systems. However, these strategies often require significant upfront investment and may not fully offset the impact of unforeseen disruptions.
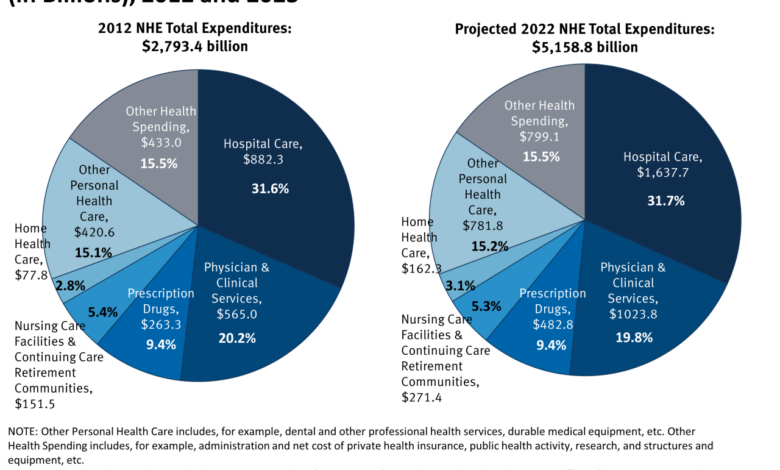
Major Expense Categories and Growth Rates
The following table illustrates the major expense categories within a typical hospital budget and their approximate growth rates over the past few years (these figures are illustrative and vary based on hospital size, location, and specific circumstances):
| Expense Category | Approximate Annual Growth Rate (%) |
|---|---|
| Salaries and Benefits | 4-6% |
| Pharmaceuticals | 5-7% |
| Medical Devices | 3-5% |
| Supplies and Services | 4-6% |
| Utilities | 2-4% |
Kaufman Hall’s Insights: Hospital Operating Margins Improve Expense Pressures Continue Kaufman Hall
Kaufman Hall, a leading healthcare consulting firm, regularly publishes analyses of hospital financial performance. Their reports offer valuable insights into the challenges and opportunities facing hospitals across the United States. This analysis will delve into their key findings regarding operating margins and expense pressures, examining their methodology and comparing their data with other industry sources.
So, Kaufman Hall’s report shows hospital operating margins are up, but cost pressures remain a huge challenge. This makes finding efficiencies crucial, and that got me thinking about improving care coordination. Check out this fascinating article on reimagining collaboration in senior care a technology driven approach , because streamlining processes through tech could be a key to easing those financial burdens for hospitals.
Ultimately, innovative solutions like this are essential to navigate the ongoing financial pressures facing healthcare.
Kaufman Hall’s analyses typically rely on a robust methodology incorporating data from a large sample of hospitals, representing diverse sizes, locations, and ownership structures. This extensive dataset allows for a comprehensive and nuanced understanding of industry trends. Their methodology often involves statistical modeling to identify key drivers of financial performance, controlling for factors such as patient mix, payer composition, and market conditions.
This rigorous approach enhances the reliability and validity of their findings. Specific techniques might include regression analysis to isolate the impact of various cost drivers on operating margins.
So, Kaufman Hall’s report shows hospital operating margins are up, but cost pressures remain a huge challenge. It got me thinking about how healthcare costs impact individuals – like the expenses related to conditions needing treatment, such as carpal tunnel syndrome. If surgery isn’t an option, exploring alternatives like those outlined in this helpful guide on ways to treat carpal tunnel syndrome without surgery is crucial for managing expenses and improving quality of life.
Ultimately, navigating both healthcare industry trends and personal health challenges requires careful planning and resourcefulness.
Key Findings on Hospital Financial Performance
Kaufman Hall’s recent reports consistently highlight the widening gap between revenue growth and escalating expenses as a major threat to hospital profitability. They often identify labor costs, supply chain disruptions, and inflationary pressures as significant contributors to rising expenses. While some hospitals have managed to improve operating margins through strategic initiatives like enhanced revenue cycle management and operational efficiencies, many others are struggling to keep pace with the rising cost of care.
The reports frequently emphasize the need for hospitals to adopt innovative strategies to address these challenges and ensure long-term financial viability.
Methodology Employed by Kaufman Hall
Kaufman Hall’s analysis usually begins with data collection from a broad range of hospitals. This data encompasses financial statements, operational metrics, and market characteristics. Data cleaning and validation are crucial steps to ensure accuracy and reliability. Once the data is prepared, advanced statistical techniques, such as regression analysis and benchmarking, are applied to identify trends and relationships between different variables.
For example, they might use regression analysis to determine the impact of staffing levels on labor costs, controlling for factors like patient volume and acuity. Benchmarking against peer institutions allows for a comparative assessment of financial performance and identification of best practices.
Visual Representation of Operating Margins and Expense Pressures
Imagine a scatter plot. The X-axis represents the percentage change in operating expenses over a given period (e.g., year-over-year). The Y-axis represents the change in operating margin (also year-over-year). Each data point represents a single hospital. Hospitals with high expense increases and low or negative margin changes would cluster in the upper-left quadrant, indicating financial distress.
Hospitals with low expense increases and positive margin changes would cluster in the lower-right quadrant, representing strong financial performance. The overall trend line would illustrate the correlation between expense growth and margin performance, likely showing a negative correlation – as expenses increase, margins tend to decrease.
Comparison with Other Industry Data Sources
Kaufman Hall’s findings generally align with data from other reputable sources, such as the American Hospital Association (AHA) and the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS). While specific numbers may vary due to differences in methodology and data samples, the overarching trends – increasing expense pressures and fluctuating operating margins – are consistently observed across these various sources.
For instance, both Kaufman Hall and the AHA have reported significant increases in labor costs and supply chain expenses impacting hospital profitability in recent years. The consistency across multiple independent data sources strengthens the validity of the overall conclusions.
Impact on Healthcare Delivery and Patient Care
Improved hospital operating margins and persistent expense pressures create a complex interplay with significant consequences for healthcare delivery and patient care. The ability of hospitals to invest in improvements, maintain staffing levels, and ensure patient access hinges on navigating this delicate balance. While increased margins offer opportunities for advancement, unrelenting cost increases pose substantial challenges.Improved margins, when effectively managed, can lead to substantial benefits for patients.
However, the extent to which these benefits materialize depends heavily on how hospitals prioritize their investments and manage their resources. Conversely, escalating expenses can severely restrict access to care, impacting patient outcomes and overall healthcare quality.
Technology and Infrastructure Investments
Improved operating margins provide hospitals with the financial resources to invest in advanced medical technologies, upgraded facilities, and improved infrastructure. This can translate to better diagnostic capabilities, more efficient treatment processes, and a more comfortable patient experience. For example, a hospital with increased margins might invest in new robotic surgery systems, leading to less invasive procedures and faster patient recovery times.
Conversely, constrained margins might delay or prevent necessary upgrades, potentially leading to outdated equipment and less efficient workflows, negatively affecting patient care. This could manifest in longer wait times for procedures or suboptimal treatment outcomes due to reliance on older technologies.
Access to Care and Patient Outcomes
Expense pressures can significantly impact patient access to care. Hospitals facing financial constraints may be forced to reduce services, limit the number of patients they can accept, or increase prices, thereby limiting access for vulnerable populations. For instance, a hospital struggling with high expenses might reduce its capacity for elective procedures, leading to longer wait times for patients requiring non-emergency care.
This delay in treatment can, in turn, negatively impact patient outcomes. Conversely, improved margins allow for expansion of services, potentially including the development of specialized clinics or outreach programs to underserved communities. This expansion directly contributes to improved access to care and potentially better patient outcomes.
Hospital Staffing Levels and Workforce Retention
The impact of financial pressures on hospital staffing is substantial. When hospitals face expense pressures, they may resort to measures like hiring freezes, reduced staff benefits, or even layoffs. This can lead to increased workloads for remaining staff, potentially compromising the quality of care and increasing burnout rates. High turnover rates, in turn, can further compromise the quality and consistency of patient care.
Conversely, improved margins can enable hospitals to offer competitive salaries and benefits, attracting and retaining skilled healthcare professionals. This can lead to improved staff morale, reduced turnover, and ultimately, enhanced patient care. A hospital with improved margins might invest in comprehensive training programs for its staff, leading to higher skill levels and improved patient outcomes.
Impact Summary Table
| Area of Impact | Positive Effects (Improved Margins) | Negative Effects (Expense Pressures) | Mitigation Strategies |
|---|---|---|---|
| Technology & Infrastructure | Investment in advanced technologies, improved facilities, enhanced patient experience. | Delayed upgrades, outdated equipment, inefficient workflows, compromised patient care. | Strategic budgeting, prioritizing essential upgrades, exploring innovative financing options. |
| Access to Care & Patient Outcomes | Expanded services, improved access for underserved communities, better patient outcomes. | Reduced services, increased prices, longer wait times, delayed or forgone treatment, compromised patient outcomes. | Prioritizing essential services, exploring partnerships, optimizing resource allocation, patient navigation programs. |
| Hospital Staffing | Competitive salaries & benefits, improved staff morale, reduced turnover, enhanced patient care, investment in training. | Hiring freezes, reduced benefits, layoffs, increased workloads, burnout, high turnover, compromised patient care. | Strategic workforce planning, competitive compensation packages, investment in staff well-being, succession planning. |
Future Outlook and Predictions for Hospital Finances
Source: kff.org
Predicting the future of hospital finances is a complex undertaking, requiring careful consideration of numerous interconnected factors. While the recent improvement in operating margins offers a glimmer of hope, significant challenges remain, and the path ahead is far from certain. This section will explore potential scenarios for hospital finances in the coming years, highlighting both opportunities and threats.
Projected Hospital Operating Margins, Hospital operating margins improve expense pressures continue Kaufman Hall
While recent data shows a positive trend, predicting future operating margins requires acknowledging the volatility inherent in the healthcare industry. Several factors, including inflation, staffing shortages, and changes in reimbursement models, will continue to exert pressure. A cautiously optimistic outlook might foresee modest margin improvements over the next few years, perhaps reaching pre-pandemic levels in some sectors. However, this improvement is contingent on successful cost-containment strategies and a more stable regulatory environment.
For example, hospitals focusing on efficiency improvements through technology adoption and streamlined processes might see stronger margin growth than those lagging in these areas. Conversely, hospitals in regions with persistently high labor costs and low patient volumes could struggle to maintain even current margins.
Future Challenges and Opportunities
The healthcare landscape is undergoing a rapid transformation, presenting both challenges and opportunities for hospital finances. The aging population, increasing prevalence of chronic diseases, and advances in medical technology all contribute to rising healthcare costs. Simultaneously, payment models are shifting towards value-based care, incentivizing hospitals to focus on quality and efficiency rather than simply volume. This shift necessitates investments in data analytics, care coordination, and population health management, which represent significant financial commitments but also potential for long-term cost savings and improved outcomes.
For example, hospitals successfully implementing telehealth programs have demonstrated improved access to care and reduced costs associated with in-person visits.
Strategies for Maintaining Financial Stability
Hospitals must adopt proactive strategies to navigate the complex financial challenges ahead. Diversification of revenue streams, including expanding into outpatient services, telehealth, and value-based care models, is crucial. Furthermore, strategic partnerships with other healthcare providers and technology companies can enhance efficiency and improve access to capital. Cost containment strategies, such as improving supply chain management, optimizing staffing models, and implementing advanced analytics to identify areas for improvement, are also essential.
For instance, hospitals employing data-driven decision-making for inventory management have demonstrated significant reductions in supply costs. Finally, strong financial planning and risk management are paramount, enabling hospitals to anticipate and mitigate potential financial shocks.
Key Factors Shaping Future Hospital Financial Performance
The financial health of hospitals will be significantly shaped by a confluence of factors. It’s important to consider these interconnected elements:
- Government Regulations and Reimbursement Policies: Changes in Medicare and Medicaid reimbursement rates, as well as new regulations related to price transparency and value-based care, will significantly impact hospital revenues.
- Technological Advancements: Adoption of new technologies, such as AI and telehealth, presents both opportunities for improved efficiency and cost savings, as well as significant upfront investment costs.
- Labor Market Dynamics: The ongoing shortage of healthcare professionals, particularly nurses and physicians, continues to drive up labor costs and presents a major challenge to hospital budgets.
- Consumer Preferences and Demand: Increasing consumer demand for convenience, transparency, and high-quality care will influence hospital investment decisions and service offerings.
- Economic Conditions: Macroeconomic factors, such as inflation and recessionary pressures, will impact patient volumes, insurance coverage, and hospital profitability.
Epilogue
The financial health of hospitals is a delicate balancing act. While the recent improvements in operating margins offer a glimmer of hope, the persistent pressure of rising expenses underscores the ongoing need for innovative cost-containment strategies and a proactive approach to financial management. The future of hospital finance depends on a multifaceted approach that addresses both revenue generation and expense control, ensuring that hospitals can continue to provide high-quality care while navigating the complexities of the healthcare industry.
It’s a story that deserves our continued attention.
FAQ Explained
What specific strategies are hospitals using to improve operating margins?
Strategies vary, but common approaches include improving efficiency through technology, negotiating better contracts with suppliers, focusing on high-margin services, and implementing robust revenue cycle management systems.
How does the increasing use of technology impact hospital expenses?
Technology can both increase and decrease expenses. While it offers potential for efficiency gains, the initial investment and ongoing maintenance costs can be substantial. The long-term cost-benefit analysis is crucial.
What is the impact of staffing shortages on hospital finances?
Staffing shortages lead to increased reliance on expensive temporary staff and overtime pay, significantly impacting hospital budgets and potentially compromising patient care.





