
House Republicans Pass Budget Blueprint Medicaid Cuts
House Republicans pass budget blueprint medicaid cuts – that headline alone sent shockwaves through the healthcare community, didn’t it? This isn’t just about numbers on a spreadsheet; it’s about real people, families, and the very fabric of our healthcare system. We’re diving deep into the proposed cuts, exploring their potential impact on vulnerable populations, and examining the political maneuvering behind this controversial budget blueprint.
Get ready for a no-holds-barred look at what could be a seismic shift in American healthcare.
The House Republican budget blueprint proposes significant cuts to Medicaid, a program providing healthcare to millions of low-income Americans. This move has sparked intense debate, pitting concerns about fiscal responsibility against the potential for devastating consequences for vulnerable individuals and families. We’ll examine the specifics of the proposed cuts, analyzing their potential impact on access to care, the quality of services, and the overall health and well-being of Medicaid recipients.
We’ll also look at the political climate surrounding the proposal and explore potential alternatives.
The Budget Blueprint
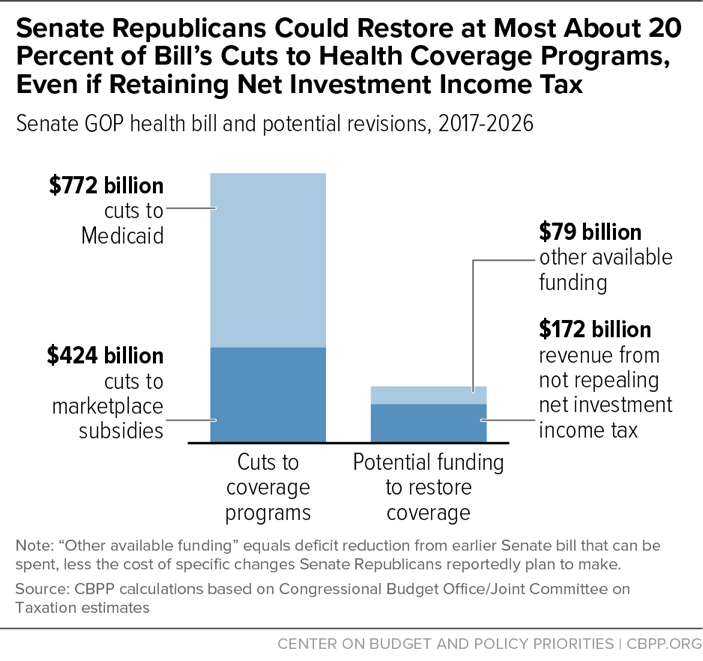
Source: cbpp.org
The House Republicans have released their budget blueprint, a proposal outlining their vision for federal spending. This plan has generated significant debate, particularly concerning its proposed cuts to Medicaid, a crucial healthcare program for millions of Americans. The following details the blueprint’s key components and the implications of its proposed changes.
Medicaid Funding Proposals
The blueprint proposes significant changes to Medicaid funding. Instead of the current open-ended federal matching system, the plan suggests shifting to a per-capita cap, limiting the amount of federal funding allocated per enrollee. This would place a hard limit on federal spending for Medicaid, regardless of the number of individuals needing care or the rising costs of healthcare. The argument from proponents is that this will incentivize states to manage their Medicaid programs more efficiently.
The House Republicans’ budget blueprint, proposing significant Medicaid cuts, got me thinking about healthcare access. It’s chilling to read about Monali Thakur’s hospitalization, detailed in this article monali thakur hospitalised after struggling to breathe how to prevent respiratory diseases , highlighting the vulnerability of individuals facing respiratory issues. These cuts could severely limit access to preventative care and treatment, potentially leading to more situations like Monali’s.
Critics, however, argue that this will lead to reduced access to care and poorer health outcomes for vulnerable populations. Further, the plan includes provisions to increase work requirements for able-bodied adults receiving Medicaid benefits.
Projected Spending Cuts
The budget blueprint projects substantial reductions in overall federal spending, with a significant portion of the cuts targeting Medicaid. While precise figures vary depending on the model used and assumptions made, estimates suggest billions of dollars in reduced Medicaid spending over the next decade. For example, some analyses predict annual reductions exceeding $100 billion by the end of the decade.
These cuts could translate to reduced benefits, fewer covered services, or stricter eligibility criteria, depending on how states choose to implement the changes. The impact on individual states will vary greatly, depending on their existing Medicaid populations and the structure of their state programs.
Budget Comparison
The following table compares the proposed budget to previous years’ budgets, highlighting the projected changes in Medicaid spending. Note that these figures are estimates and subject to revision based on future economic conditions and legislative actions. The data below represents a simplified illustration based on hypothetical scenarios, for purposes only and should not be considered precise predictions.
It is crucial to consult official government reports for precise budget figures.
| Year | Total Spending (Billions) | Medicaid Spending (Billions) | Percentage Change in Medicaid Spending |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2022 (Actual) | 6.5 | 1.0 | – |
| 2023 (Proposed) | 6.3 | 0.9 | -10% |
| 2024 (Projected) | 6.0 | 0.8 | -11.1% |
| 2025 (Projected) | 5.8 | 0.7 | -12.5% |
Impact on Medicaid Beneficiaries

Source: cbpp.org
The proposed cuts to Medicaid funding Artikeld in the House Republicans’ budget blueprint represent a significant threat to the healthcare access and well-being of millions of Americans. These cuts could lead to reduced access to essential medical services, leaving vulnerable populations facing dire consequences. The potential ripple effects extend far beyond simple budgetary adjustments, impacting individuals, families, and communities across the nation.The proposed reductions in Medicaid funding could drastically limit access to healthcare for millions of recipients.
This means longer wait times for appointments, reduced availability of specialists, and potentially, delayed or forgone necessary treatments. The consequences of this restricted access are potentially devastating, especially for those with chronic conditions requiring ongoing care. The impact is not merely a matter of inconvenience; it’s a matter of life and death for many.
Reduced Access to Essential Healthcare Services
The cuts could lead to a decrease in the availability of vital healthcare services. This includes preventative care, such as annual checkups and screenings for early detection of diseases like cancer and diabetes. Further, access to mental health services, substance abuse treatment, and prescription drugs could be severely curtailed. The lack of preventative care can lead to more expensive and complicated health problems later on, ultimately costing more in the long run.
Reduced access to specialists, such as cardiologists or oncologists, could also result in delayed diagnosis and treatment, leading to poorer health outcomes.
Consequences for Vulnerable Populations
The most vulnerable populations, including children, pregnant women, the elderly, and individuals with disabilities, will bear the brunt of these cuts. These groups often rely heavily on Medicaid for their healthcare needs, and reduced funding could lead to significant health disparities. For example, children might miss out on crucial vaccinations, leading to increased rates of preventable diseases. Pregnant women might face limited access to prenatal care, increasing the risk of complications during pregnancy and childbirth.
The elderly could experience delays in receiving necessary long-term care, leading to decreased quality of life and increased strain on family caregivers.
Examples of Affected Services
Specific services likely to be affected include: home healthcare for the elderly and disabled, mental health and substance abuse treatment programs, prescription drug coverage, transportation assistance to medical appointments, and preventative care services like well-baby visits and cancer screenings. These cuts will disproportionately impact low-income families and individuals who already struggle to access healthcare.
Hypothetical Scenario: The Miller Family
Consider the Miller family: John, a construction worker, recently lost his job and his family relies on Medicaid for their healthcare. His wife, Sarah, is pregnant with their third child. With the proposed cuts, Sarah may face difficulty accessing prenatal care, potentially resulting in complications during her pregnancy. Their two young children might miss crucial vaccinations, increasing their risk of contracting preventable illnesses.
The family’s already precarious financial situation will be further strained by the potential increase in out-of-pocket medical expenses, creating a domino effect that threatens their overall well-being. This scenario, unfortunately, reflects the potential reality for countless families across the nation.
Political and Economic Context
The House Republicans’ budget blueprint, proposing significant Medicaid cuts, is a complex issue with far-reaching political and economic implications. Understanding the motivations behind these cuts, their potential consequences, and how they compare to alternative approaches is crucial for a comprehensive assessment. This analysis will delve into the political landscape surrounding the proposal, contrasting it with the Biden administration’s vision, and exploring the potential short-term and long-term economic repercussions.The proposed Medicaid cuts are driven by a confluence of political factors.
Republicans, generally advocating for smaller government and fiscal conservatism, view Medicaid as a program ripe for reform due to its substantial cost. The desire to reduce the national debt and control government spending are central tenets of their platform. Furthermore, there’s a long-standing debate within the Republican party regarding the appropriate role of government in healthcare, with some factions pushing for a greater reliance on market-based solutions.
This budget blueprint reflects these competing priorities and ideologies.
Comparison of Republican and Biden Administration Approaches to Healthcare Funding
The Republican budget proposal sharply contrasts with the Biden administration’s approach to healthcare funding. President Biden has consistently emphasized expanding access to affordable healthcare, including strengthening and expanding the Affordable Care Act (ACA) and investing in programs like Medicaid. The Biden administration’s focus is on increasing access to care and improving health outcomes, often prioritizing affordability and equity over strict budgetary constraints.
This fundamental difference in philosophy leads to vastly different proposals regarding healthcare funding and the role of government intervention. For instance, the Biden administration has supported increased funding for community health centers, while the Republican budget likely seeks to reduce funding for such initiatives.
Potential Economic Consequences of Medicaid Cuts
The proposed Medicaid cuts could have significant economic consequences, both in the short-term and long-term. Short-term impacts could include increased hospital bankruptcies, especially in rural areas heavily reliant on Medicaid reimbursements. This could lead to reduced access to care and potentially higher healthcare costs for everyone as the remaining providers absorb the increased demand. In the long term, the cuts could exacerbate health disparities, leading to poorer health outcomes and reduced workforce productivity.
Studies have shown a direct correlation between access to healthcare and economic productivity; reduced access translates to lost economic output. For example, a significant reduction in Medicaid coverage could lead to an increase in preventable hospitalizations and chronic disease management costs, ultimately impacting the economy.
Arguments For and Against the Budget Blueprint
The debate surrounding the Republican budget blueprint is complex and involves numerous considerations. A balanced view requires examining both the arguments in favor and against the proposed cuts.
The following points summarize the arguments for and against the proposed budget blueprint:
- Arguments in favor:
- Reduced government spending and national debt.
- Increased fiscal responsibility and long-term budget sustainability.
- Potential for increased efficiency and cost savings within the Medicaid program through reforms.
- Arguments against:
- Reduced access to healthcare for millions of vulnerable Americans.
- Exacerbation of existing health disparities and poorer health outcomes.
- Negative economic consequences, including increased hospital closures and reduced workforce productivity.
- Potential for increased uncompensated care costs for hospitals and healthcare providers.
State-Level Implications
The House Republicans’ proposed Medicaid cuts, as Artikeld in their budget blueprint, will significantly impact state governments, forcing difficult choices and potentially exacerbating existing healthcare disparities. The extent of these impacts will vary considerably depending on a state’s existing Medicaid program structure, its population demographics, and its overall fiscal health. This uneven impact necessitates a careful examination of the potential challenges and responses at the state level.The proposed changes could drastically alter the financial landscape for state Medicaid programs.
Reduced federal funding will necessitate either state budget cuts in other areas, increased state-level contributions to maintain current service levels, or, most likely, a combination of both. This will force states to make difficult decisions about which services to cut or limit, potentially impacting access to care for millions of vulnerable individuals.
The House Republicans’ budget blueprint, proposing significant Medicaid cuts, worries me. It makes me think about the increasing healthcare costs for aging populations, and how early detection of conditions like dementia is crucial. I recently read an interesting article on whether an eye test could help predict dementia risk – check it out: can eye test detect dementia risk in older adults.
If such early detection becomes more accessible, it might help manage healthcare expenses in the long run, potentially mitigating some of the impact of these proposed Medicaid cuts.
Medicaid Program Adjustments and Implementation Challenges
States will face a multitude of challenges in implementing the new budget. One significant hurdle will be the need to rapidly restructure existing Medicaid programs to accommodate reduced funding. This might involve renegotiating contracts with healthcare providers, limiting eligibility criteria, reducing benefits, or implementing stricter cost-containment measures. For instance, states might reduce the number of covered prescription drugs, limit the duration of long-term care services, or increase patient cost-sharing.
The logistical complexity of such changes, combined with the potential for legal challenges, presents a significant implementation barrier. Furthermore, states will need to navigate the complexities of navigating new federal regulations and guidelines, adding to the administrative burden. The timeline for implementation will also be a key factor, with a rapid rollout likely to exacerbate the challenges.
State Governor and Legislator Responses
The response from state governors and legislators will likely be varied and politically charged. States with Republican-controlled legislatures may be more inclined to accept the changes, perhaps viewing them as an opportunity to streamline their Medicaid programs and reduce spending. However, even in these states, the political pressure to protect vulnerable populations could lead to significant internal conflict and potentially even legal challenges to the federal changes.
House Republicans just passed their budget blueprint, and the proposed Medicaid cuts are seriously concerning. This comes on the heels of the Supreme Court decision, as reported in this article scotus overturns chevron doctrine healthcare , which significantly alters the landscape of healthcare regulations. This shift in power could make challenging those Medicaid cuts even harder, potentially leaving vulnerable populations with fewer resources.
Conversely, states with Democratic-controlled legislatures are likely to strongly oppose the cuts, potentially leading to legal battles and public protests. Governors will likely play a crucial role in mediating these conflicts, balancing the need to comply with federal mandates with the responsibility of protecting their constituents’ access to healthcare. We might see a range of responses, from seeking legal challenges to implementing creative solutions to mitigate the impact on their populations.
Budgetary Impacts Across States
The budgetary impacts will differ dramatically across states with varying demographics and healthcare needs. States with larger elderly populations, for example, will face disproportionately higher costs due to increased demand for long-term care services. Similarly, states with high rates of chronic diseases will see increased pressure on their healthcare systems, potentially requiring additional resources even with reduced federal funding.
States with predominantly rural populations might struggle with maintaining access to healthcare due to limited provider networks and transportation challenges. Conversely, states with younger populations and healthier demographics might experience a less dramatic impact, though they too will likely face budgetary pressures. For example, a state like Florida, with a large elderly population, will likely face significantly greater challenges than a state like Utah, with a younger population.
The financial burden will not be equally distributed, exacerbating existing health disparities.
Potential Alternatives and Solutions
The proposed Medicaid cuts raise serious concerns about access to healthcare for millions. However, achieving fiscal responsibility doesn’t necessitate drastic benefit reductions. Alternative approaches exist that can balance budgetary needs with the preservation of essential healthcare services. These strategies focus on improving efficiency, targeting resources, and promoting preventative care.
Several strategies can help reduce Medicaid spending without compromising quality of care. These include enhancing care coordination to reduce hospital readmissions, investing in preventative health programs to minimize costly emergency room visits, and leveraging technology to streamline administrative processes and improve care delivery. Furthermore, exploring innovative payment models that reward value over volume can incentivize providers to focus on cost-effective care.
Successful Cost-Saving Measures in Other States
Many states have successfully implemented cost-saving measures in their Medicaid programs without significantly impacting access to care. For example, some states have implemented managed care organizations (MCOs) which focus on coordinating care and reducing unnecessary hospitalizations. These MCOs often utilize data analytics to identify high-risk individuals and provide them with proactive interventions, resulting in better health outcomes and reduced costs.
Other states have invested heavily in telehealth services, expanding access to care in rural and underserved areas while simultaneously reducing transportation costs for beneficiaries. These programs have demonstrated positive impacts on both cost containment and patient satisfaction.
Policy Recommendations to Mitigate Negative Impacts
To mitigate the negative impacts of the proposed cuts, several policy recommendations can be implemented. Strengthening primary care infrastructure through increased funding and provider recruitment can prevent costly hospitalizations down the line. Expanding access to preventative services, such as vaccinations and screenings, can further reduce healthcare costs in the long run. Additionally, negotiating lower drug prices through bulk purchasing or leveraging the government’s bargaining power could significantly impact the overall Medicaid budget.
Investing in community-based health programs can also provide support to individuals with chronic conditions, reducing their need for expensive hospital care.
Hypothetical Model: Impact of Policy Changes on Medicaid Access and Healthcare Outcomes
Let’s consider a hypothetical model to illustrate the potential impact of different policy changes. Assume a state with 1 million Medicaid beneficiaries and an annual budget of $10 billion. Scenario A involves a 10% across-the-board cut, resulting in reduced access to care and potentially higher rates of preventable hospitalizations. Scenario B involves a 5% budget reduction achieved through enhanced care coordination and preventative services.
This scenario might result in fewer hospital readmissions and improved health outcomes, offsetting some of the cost savings. Scenario C combines a 2% budget reduction through administrative efficiencies with a 3% reduction achieved through negotiating lower drug prices. This strategy could minimize the impact on access to care while still achieving significant cost savings. These scenarios highlight how different policy choices can significantly impact both the budget and the health of Medicaid beneficiaries.
The model demonstrates that strategic investments in preventative care and efficient care delivery can yield better outcomes than blanket cuts. Real-world examples, such as the success of managed care programs in various states, support the effectiveness of such strategies.
Public Opinion and Reactions
The proposed Medicaid cuts within the House Republican budget blueprint have ignited a firestorm of public debate, revealing deep divisions across the political spectrum and within various stakeholder groups. The intensity of the reaction underscores the vital role Medicaid plays in the lives of millions of Americans and the significant consequences these cuts could have on healthcare access and the broader economy.The public response has been largely negative, with polls showing widespread disapproval of the proposed reductions.
This opposition stems from concerns about increased healthcare costs for vulnerable populations, potential disruptions to healthcare access, and the overall impact on the nation’s healthcare system. The level of opposition is not uniform, however, with some segments of the population expressing more or less concern depending on their personal circumstances and political affiliations.
Reactions of Stakeholder Groups
The proposed cuts have drawn strong reactions from various stakeholder groups, each with their own unique perspectives and concerns. Healthcare providers, particularly those serving Medicaid patients, fear a substantial reduction in revenue, potentially leading to service cuts, closures, and staff layoffs. This would disproportionately affect rural and underserved communities already facing healthcare shortages. Patient advocacy groups have voiced strong opposition, emphasizing the potential for increased uninsured rates, delayed or forgone care, and worsening health outcomes among vulnerable populations, including children, seniors, and individuals with disabilities.
Conversely, some business groups have argued that the cuts are necessary to control government spending and improve the long-term fiscal health of the nation.
Arguments For and Against the Budget
Proponents of the budget argue that the proposed Medicaid cuts are necessary to address the nation’s growing national debt and to rein in unsustainable government spending. They often highlight the need for fiscal responsibility and point to the potential for waste, fraud, and abuse within the Medicaid system. They advocate for market-based reforms and increased efficiency to improve the system’s overall effectiveness.
Opponents, on the other hand, contend that the proposed cuts will have devastating consequences for millions of Americans who rely on Medicaid for essential healthcare services. They argue that the cuts will disproportionately impact low-income individuals, families, and communities of color, exacerbating existing health disparities. They also highlight the potential negative economic impacts of the cuts, including job losses in the healthcare sector and reduced economic activity.
They advocate for alternative approaches to fiscal responsibility that do not compromise access to essential healthcare.
Key Media Coverage and Public Statements, House republicans pass budget blueprint medicaid cuts
The debate surrounding the proposed Medicaid cuts has been widely covered in the media, generating a significant amount of public discussion and commentary. Here are some key examples:
- The New York Times published several articles detailing the potential impact of the cuts on vulnerable populations and the healthcare system as a whole. These articles included interviews with healthcare providers, patient advocates, and policymakers, offering a diverse range of perspectives.
- The Kaiser Family Foundation released reports analyzing the potential financial and health consequences of the proposed cuts, providing detailed data and projections.
- Numerous statements from patient advocacy groups, such as the AARP and the American Hospital Association, strongly condemned the proposed cuts, highlighting the potential negative consequences for their members and the broader population.
- Several prominent politicians, including members of Congress and governors, have publicly voiced their opinions on the proposed cuts, with some expressing support and others expressing strong opposition.
- Major television networks and news outlets have extensively covered the debate, providing viewers with various perspectives and updates on the legislative process.
Summary: House Republicans Pass Budget Blueprint Medicaid Cuts
The proposed Medicaid cuts within the House Republican budget blueprint represent a significant challenge to the American healthcare system. While fiscal responsibility is undeniably important, the potential consequences of these cuts for millions of vulnerable Americans cannot be ignored. The debate is far from over, and the coming months will likely be filled with intense political maneuvering and public outcry.
The ultimate outcome will significantly shape the future of healthcare access for millions, highlighting the urgent need for thoughtful consideration and viable alternatives that balance fiscal responsibility with the well-being of our most vulnerable citizens.
Expert Answers
What specific services are most at risk from these cuts?
Services like preventative care, mental health services, and substance abuse treatment are often the first to be affected by funding reductions.
How will states respond to these proposed cuts?
States will likely face difficult choices, potentially including reducing provider reimbursements, limiting eligibility, or cutting benefits. Some states may challenge the legality of the cuts.
What are the long-term economic consequences of these cuts?
Reduced access to care could lead to increased hospitalizations and emergency room visits, ultimately driving up healthcare costs in the long run. It could also negatively impact the economy through decreased workforce productivity.
Are there any successful examples of cost-saving measures in other states’ Medicaid programs?
Yes, some states have implemented successful programs focusing on preventative care, care coordination, and managed care organizations to reduce costs while maintaining quality of care. These models could provide valuable lessons.





