IT in Healthcare Enabling a More Efficient and Satisfied Workforce
It in healthcare enabling a more efficient and satisfied workforce – IT in Healthcare: Enabling a More Efficient and Satisfied Workforce – that’s the promise, and it’s a promise being delivered every day. From streamlining administrative tasks with electronic health records to fostering better team communication through mobile apps, technology is transforming healthcare in profound ways. This isn’t just about efficiency; it’s about creating a better work environment for healthcare professionals, leading to improved patient care and better overall outcomes.
This post delves into how technology is revolutionizing the healthcare industry, impacting both the workforce and the patients they serve.
We’ll explore the various ways technology is improving efficiency, boosting staff morale, enhancing data-driven decision-making, and even addressing critical security concerns. We’ll look at real-world examples, explore the potential of emerging technologies like AI and blockchain, and consider the future of IT’s role in shaping the healthcare landscape. Get ready to discover how technology is not just a tool, but a catalyst for positive change in the healthcare world.
Improved Efficiency Through IT in Healthcare: It In Healthcare Enabling A More Efficient And Satisfied Workforce

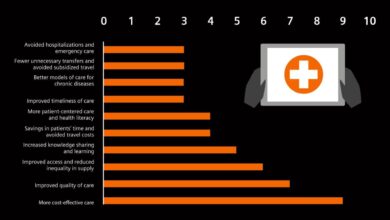
Source: culturemonkey.io
The integration of information technology (IT) is revolutionizing healthcare, driving significant improvements in efficiency and ultimately leading to better patient care and a more satisfied workforce. This transformation is largely fueled by advancements in electronic health records, telehealth platforms, and automated systems, all working together to streamline processes and reduce the administrative burden on healthcare professionals.
Electronic Health Records (EHRs) and Workflow Streamlining
Electronic Health Records (EHRs) have dramatically altered the way healthcare information is managed. The shift from paper-based charts to digital systems has resulted in significant improvements in workflow efficiency. EHRs provide instant access to a patient’s complete medical history, eliminating the time-consuming search for misplaced files or the need to manually transfer information between departments. This readily available information reduces the time spent on administrative tasks, allowing clinicians to focus more on direct patient care.
Furthermore, EHRs facilitate better communication between healthcare providers, improving coordination of care and reducing the risk of medical errors resulting from incomplete or conflicting information. Automated alerts and reminders within EHRs also assist in preventative care, such as scheduling follow-up appointments or flagging potential drug interactions.
Telehealth’s Impact on Appointment Scheduling and Patient Access
Telehealth has emerged as a powerful tool for enhancing access to care and streamlining appointment scheduling. Virtual consultations allow patients to connect with healthcare providers remotely, eliminating the need for travel and reducing wait times. This is particularly beneficial for patients in rural areas or those with mobility limitations. Online scheduling systems integrated with telehealth platforms further simplify the process, allowing patients to book appointments at their convenience, reducing the administrative burden on both the patient and the healthcare facility.
IT’s role in boosting healthcare efficiency and staff satisfaction is huge, streamlining workflows and reducing burnout. News of AdventHealth CEO Terry Shaw’s retirement, as reported in this article , highlights the importance of strong leadership in navigating these technological changes. Ultimately, effective IT implementation contributes to a happier, more productive healthcare workforce, ready to meet the future’s challenges.
The automated appointment reminders and confirmations sent via email or text message also minimize no-shows, optimizing clinic schedules and resource allocation.
Comparison of Manual and Automated Systems in Healthcare
The efficiency gains from automation are substantial. Consider the following comparison:
| Process | Manual Process | Automated Process | Efficiency Gain |
|---|---|---|---|
| Appointment Scheduling | Phone calls, manual calendar entries, potential for double-booking, high risk of missed appointments. | Online scheduling system, automated reminders, reduced double-booking, improved appointment adherence. | Significant reduction in administrative time, improved patient satisfaction, and higher appointment attendance. |
| Medication Dispensing | Manual verification of prescriptions, potential for errors in dosage or medication, time-consuming process. | Automated dispensing system, barcode scanning, reduced risk of errors, faster dispensing process. | Improved accuracy, reduced medication errors, faster dispensing, freeing up pharmacy staff for other tasks. |
| Billing and Claims Processing | Manual data entry, time-consuming reconciliation, high potential for errors, slow payment cycles. | Automated billing systems, electronic claims submission, reduced errors, faster payment processing. | Reduced administrative burden, faster payment cycles, improved revenue cycle management. |
| Patient Record Management | Paper-based charts, difficult to access, prone to loss or damage, inefficient retrieval. | Electronic Health Records (EHRs), instant access, improved data security, efficient data retrieval and sharing. | Improved accessibility, reduced risk of information loss, enhanced data security, improved care coordination. |
Workflow Optimization: Medication Dispensing with IT Solutions
The following diagram illustrates how IT solutions can optimize the medication dispensing process:[Imagine a flowchart here. The flowchart would begin with a physician prescribing medication via EHR. This would trigger an automated order to the pharmacy. The pharmacy system would verify the order against patient allergies and drug interactions within the EHR. The medication would then be dispensed by an automated system, with barcode scanning to ensure accuracy.
Finally, the system would update the patient’s EHR, reflecting the dispensed medication and generating a label for the patient. The entire process would be tracked and monitored by the system.] This automated system minimizes human error, speeds up the process, and ensures the correct medication is dispensed to the right patient at the right time.
Enhanced Workforce Satisfaction with IT Solutions
Healthcare professionals face immense pressure, leading to high burnout rates and impacting the quality of patient care. Implementing the right IT solutions can significantly alleviate this burden, fostering a more satisfied and engaged workforce. By streamlining workflows, improving communication, and providing access to valuable resources, technology empowers healthcare workers to focus on what truly matters: their patients.
Reduced Burnout Through IT Tool Implementation
The relentless demands of healthcare often lead to burnout. However, strategic use of IT can mitigate this. Electronic health records (EHRs), for instance, automate many administrative tasks, freeing up clinicians’ time for patient interaction. Automated appointment scheduling and reminder systems reduce no-shows and minimize administrative overhead. Furthermore, telehealth platforms allow for remote consultations, reducing travel time and extending reach to patients in remote areas, thus lessening the physical and mental burden on healthcare providers.
For example, a study by the American Medical Association showed a significant reduction in physician burnout in clinics that implemented comprehensive EHR systems with integrated patient communication tools.
Improved Team Collaboration via Mobile Devices and Communication Platforms
Effective communication is crucial in healthcare, and mobile devices and communication platforms play a vital role in improving team collaboration. Secure messaging apps allow for instant communication between colleagues, facilitating quick responses to critical situations and improving patient care coordination. Mobile access to patient records enables healthcare professionals to access crucial information anytime, anywhere, promoting seamless care transitions. For example, a hospital system implementing a unified communication platform reported a 20% reduction in medication errors due to improved communication between nurses and pharmacists.
The improved information flow and streamlined communication lead to reduced delays and improved efficiency, ultimately contributing to higher job satisfaction.
Tech in healthcare is revolutionizing things, leading to happier, more productive staff. For example, imagine the impact of improved organ allocation systems – the recent FDA approval of clinical trials for pig kidney transplants in humans, as reported on this site , is a huge step forward. This kind of advancement, facilitated by sophisticated IT systems, directly contributes to a more efficient and satisfied healthcare workforce by reducing wait times and improving patient outcomes.
IT-Driven Training and Development Programs for Enhanced Skills and Job Satisfaction, It in healthcare enabling a more efficient and satisfied workforce
Investing in IT-driven training and development programs is crucial for upskilling the healthcare workforce and boosting job satisfaction. Online learning platforms provide access to a wide range of courses and resources, allowing employees to learn at their own pace and convenience. Simulations and virtual reality training provide safe and effective environments to practice complex procedures, enhancing skills and confidence.
These programs not only improve employee competency but also demonstrate the organization’s commitment to their professional growth, leading to increased job satisfaction and reduced turnover. A recent survey showed that hospitals with robust online training programs reported significantly higher employee satisfaction and retention rates compared to those without.
IT Tools Enhancing Work-Life Balance for Healthcare Employees
The demanding nature of healthcare often blurs the lines between work and personal life. However, several IT tools can help healthcare professionals achieve a better work-life balance:
- Secure remote access to work systems: Allowing for flexible work arrangements and reducing the need for constant physical presence at the workplace.
- Automated scheduling and task management tools: Optimizing workflows and reducing the need for overtime.
- Time-tracking software: Ensuring accurate record-keeping and preventing burnout from excessive working hours.
- Mental health and wellness apps: Providing resources and support to manage stress and promote well-being.
These tools empower healthcare professionals to better manage their time and responsibilities, contributing significantly to a healthier work-life balance.
Data-Driven Decision Making and Improved Patient Outcomes
The integration of data analytics into healthcare is revolutionizing how we approach patient care, resource allocation, and overall system efficiency. By leveraging the vast amounts of data generated daily, healthcare providers can move beyond reactive medicine and embrace a proactive, data-driven approach that leads to better outcomes and a more satisfied workforce. This shift involves harnessing the power of analytics to identify trends, predict risks, and optimize processes for improved efficiency and patient well-being.Data analytics offers unprecedented opportunities to enhance healthcare resource allocation.
By analyzing patient demographics, historical data on treatment efficacy, and resource utilization patterns, healthcare systems can make more informed decisions about staffing levels, equipment purchases, and the allocation of specialized services. This ensures resources are deployed where they are most needed, minimizing waste and maximizing impact.
Improved Healthcare Resource Allocation Through Data Analytics
Analyzing historical data on patient admissions, length of stay, and resource consumption allows hospitals to predict future demand for beds, staff, and equipment. For instance, a hospital might observe a consistent surge in heart failure admissions during specific months. Using predictive modeling, they can proactively increase staffing levels in the cardiology department during these periods, ensuring adequate care without overspending during less busy times.
This approach optimizes resource allocation, minimizing wait times and improving patient experience. Similarly, analyzing data on medication usage can identify patterns of overprescription or underutilization, leading to cost savings and improved patient safety. This data-driven approach allows for more efficient inventory management and reduces waste associated with expired or unused medications.
Real-Time Data Visualization for Faster Decision-Making
Real-time data visualization tools provide healthcare professionals with an immediate and comprehensive overview of critical information. Imagine a hospital emergency room using a dashboard that displays real-time data on patient arrival rates, severity levels, and available beds. This visual representation allows staff to quickly assess the situation, prioritize patients, and efficiently allocate resources, reducing wait times and improving patient flow.
Furthermore, real-time monitoring of vital signs and lab results allows clinicians to detect potential complications early on, enabling timely interventions and potentially life-saving actions. The ability to visualize trends and patterns instantly empowers clinicians to make more informed and rapid decisions.
Case Study: Reducing Hospital Readmissions Through Data-Driven Insights
A large hospital system implemented a data-driven program to reduce hospital readmissions among heart failure patients. By analyzing patient data including demographics, medical history, medication adherence, and social determinants of health, they identified key risk factors associated with readmission. This analysis revealed that patients with poor medication adherence and limited access to post-discharge support were significantly more likely to be readmitted.
The hospital then implemented targeted interventions, including personalized medication management programs and increased access to home healthcare services for high-risk patients. The result was a substantial reduction in readmission rates, demonstrating the effectiveness of data-driven insights in improving patient outcomes and reducing healthcare costs.
Predictive Analytics for Enhanced Preventative Care
Predictive analytics allows healthcare providers to anticipate future health risks and proactively implement preventative measures. By analyzing patient data, including genetic information, lifestyle factors, and medical history, algorithms can identify individuals at high risk of developing specific conditions such as diabetes, heart disease, or certain types of cancer. This allows for targeted screening programs, lifestyle interventions, and early treatment strategies, significantly improving the chances of preventing or delaying the onset of these conditions.
For example, by identifying individuals at high risk of developing type 2 diabetes, preventative programs focusing on diet, exercise, and medication can be implemented to mitigate the risk. This proactive approach shifts the focus from treating disease to preventing it, leading to improved long-term health outcomes and reduced healthcare burdens.
Security and Privacy Considerations in Healthcare IT
The increasing reliance on IT in healthcare brings significant benefits, but also introduces substantial security and privacy risks. Protecting sensitive patient data is paramount, requiring robust security measures and strict adherence to regulations. Failure to do so can lead to hefty fines, reputational damage, and, most importantly, harm to patients.
Key Security Challenges Related to Storing and Transmitting Patient Data
Healthcare data is a prime target for cybercriminals due to its value and the potential for significant financial and reputational damage resulting from breaches. Challenges include data breaches from unauthorized access, malware infections, phishing attacks targeting employees, insider threats, and vulnerabilities in legacy systems. The sheer volume of data, often spread across multiple systems and locations, further complicates security management.
The transmission of data, particularly through unsecured networks or unencrypted channels, also presents a major vulnerability. For example, a ransomware attack could encrypt a hospital’s entire electronic health record (EHR) system, disrupting patient care and potentially costing millions in recovery efforts. Similarly, a phishing attack successfully tricking an employee into revealing login credentials could grant attackers access to sensitive patient information.
Best Practices for Ensuring Data Privacy and Compliance with Relevant Regulations (e.g., HIPAA)
Compliance with regulations like HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) in the US is crucial. This involves implementing robust access controls, limiting data access to only authorized personnel on a need-to-know basis, using strong encryption both at rest and in transit, regularly backing up data to secure offsite locations, and conducting thorough employee training on security awareness and privacy best practices.
IT in healthcare is revolutionizing workflows, leading to happier, more productive staff. A great example of this is the innovative work being done with AI, like what’s discussed in this insightful article on salesforce healthcare ai sean kennedy , showcasing how technology can streamline processes and reduce administrative burdens. Ultimately, leveraging technology like this means a better experience for both healthcare professionals and patients.
Regular security audits and vulnerability assessments are also essential for identifying and mitigating potential weaknesses. Data minimization, only collecting and storing the data absolutely necessary, is another key principle. Finally, a comprehensive incident response plan should be in place to effectively manage and mitigate the impact of any security breach. For instance, multi-factor authentication can significantly reduce the risk of unauthorized access, while regular employee training on phishing techniques can minimize the success rate of such attacks.
Cybersecurity Measures for Protecting Healthcare IT Infrastructure
A layered security approach is essential, combining multiple security measures to protect against various threats. This includes firewalls to control network traffic, intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDS/IPS) to monitor and block malicious activity, antivirus and anti-malware software to protect against infections, data loss prevention (DLP) tools to prevent sensitive data from leaving the network without authorization, and regular security patching and updates to address vulnerabilities.
Employing a robust security information and event management (SIEM) system for centralized security monitoring and logging is also critical. Furthermore, regular penetration testing and vulnerability scanning can proactively identify and address weaknesses in the IT infrastructure. For example, a robust firewall can prevent unauthorized external access, while an IDS/IPS can detect and block malicious network traffic attempting to exploit vulnerabilities.
Security Protocols for Healthcare IT Systems
| Protocol Category | Specific Protocol | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Access Control | Multi-factor authentication (MFA) | Requires multiple forms of authentication (e.g., password, security token, biometric scan) to access systems. |
| Data Encryption | AES-256 encryption | Uses strong encryption to protect data both at rest and in transit. |
| Network Security | Firewall implementation | Controls network traffic, blocking unauthorized access and malicious activity. |
| Data Backup and Recovery | Regular offsite backups | Ensures data can be recovered in case of a disaster or security breach. |
| Vulnerability Management | Regular security patching | Addresses known vulnerabilities in software and hardware to prevent exploitation. |
| Incident Response | Incident response plan | Provides a structured approach to managing and mitigating security incidents. |
| Employee Training | Security awareness training | Educates employees on security best practices and threats. |
| Data Loss Prevention (DLP) | DLP software implementation | Monitors and prevents sensitive data from leaving the network without authorization. |
The Future of IT in Healthcare

Source: isu.pub
The integration of technology into healthcare has revolutionized patient care and operational efficiency. However, the future promises even more transformative advancements, driven by innovations in artificial intelligence, blockchain, and the Internet of Medical Things (IoMT). These technologies are poised to reshape healthcare workflows, enhance data security, and ultimately lead to improved patient outcomes.
Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare
AI is rapidly transforming healthcare workflows and patient care. Machine learning algorithms can analyze vast amounts of patient data to identify patterns and predict potential health risks, enabling proactive interventions. For example, AI-powered diagnostic tools can analyze medical images with greater speed and accuracy than human radiologists, leading to faster diagnoses and more effective treatment plans. AI-driven chatbots can provide patients with 24/7 access to medical information and support, reducing the burden on healthcare professionals and improving patient satisfaction.
Furthermore, AI is being used to personalize treatment plans based on individual patient characteristics and genetic information, leading to more effective and targeted therapies. Consider the example of oncology, where AI assists in identifying optimal treatment strategies for cancer patients based on their specific tumor profiles and genetic makeup, resulting in improved survival rates and reduced side effects.
Blockchain Technology in Healthcare
Blockchain technology, known for its secure and transparent nature, offers significant potential for improving data security and interoperability in healthcare. Its decentralized structure ensures that patient data is not stored in a single, vulnerable location, reducing the risk of data breaches and unauthorized access. Furthermore, blockchain can facilitate secure and efficient sharing of patient data between healthcare providers, improving care coordination and reducing medical errors.
Imagine a scenario where a patient’s complete medical history, securely stored on a blockchain, is instantly accessible to any authorized healthcare provider involved in their care, eliminating the need for repeated tests and reducing the risk of conflicting treatments. This improved interoperability is crucial for managing chronic conditions and coordinating care across different healthcare settings.
The Internet of Medical Things (IoMT)
The Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) refers to the network of interconnected medical devices that collect and transmit patient data. These devices, ranging from wearable sensors to implantable devices, offer the potential for continuous monitoring of patients’ health status, enabling early detection of potential problems and proactive interventions. For example, wearable sensors can monitor a patient’s heart rate, blood pressure, and activity levels, providing real-time data to healthcare providers.
Implantable devices can monitor vital signs and deliver medication as needed, improving the management of chronic conditions. However, the implementation of IoMT devices also presents challenges, including data security concerns and the need for robust data management systems. The potential for data breaches and the need for interoperability between different devices are key considerations that need to be addressed to ensure the safe and effective use of IoMT.
Consider the example of a patient with congestive heart failure using a wearable heart rate monitor. This data, securely transmitted to their physician, allows for early detection of worsening symptoms and timely intervention, preventing hospitalizations.
A Futuristic Healthcare Scenario
Imagine a future where healthcare is personalized, proactive, and seamlessly integrated. A patient, fitted with a sophisticated wearable device that continuously monitors their vital signs and activity levels, experiences a slight increase in their heart rate during a stressful work meeting. The device, connected to a secure cloud-based platform using blockchain technology, immediately alerts their physician and a personalized AI-powered chatbot provides calming breathing exercises.
The physician reviews the patient’s data, including their complete medical history securely stored on the blockchain, and initiates a virtual consultation. Using AI-powered diagnostic tools, the physician assesses the situation and prescribes a personalized medication regimen, which is then delivered directly to the patient’s smart inhaler through a secure IoMT network. The entire process is seamless, efficient, and personalized, leading to early intervention and improved patient outcomes.
The visual is one of calm efficiency: a clean, minimalist interface displaying vital signs on a holographic projection, a friendly AI chatbot providing support, and a physician calmly reviewing data, all orchestrated by sophisticated, interconnected technology working in harmony. The overall aesthetic is one of futuristic sophistication, yet also comfort and accessibility, reflecting a healthcare system focused on both technological advancement and human-centered care.
Conclusion
The integration of IT in healthcare isn’t just a trend; it’s a necessity. As we’ve explored, technology offers a powerful pathway to a more efficient, satisfying, and ultimately, more effective healthcare system. By embracing innovative solutions and prioritizing data security, healthcare organizations can create a work environment where professionals thrive and patients receive the highest quality of care.
The future of healthcare is undeniably intertwined with technology, and the journey towards a more connected, efficient, and compassionate healthcare system is one worth embracing.
Answers to Common Questions
What are the biggest challenges in implementing IT solutions in healthcare?
Major challenges include high initial investment costs, integration with existing systems, staff training and resistance to change, and ensuring data security and privacy compliance.
How can IT improve patient outcomes beyond efficiency gains?
Improved data analysis leads to better preventative care, personalized treatment plans, and faster diagnosis through AI-powered tools. Telehealth expands access to care for remote patients.
What role does AI play in the future of healthcare IT?
AI promises to revolutionize diagnosis, treatment planning, drug discovery, and administrative tasks, freeing up human professionals to focus on patient interaction and complex cases.
Are there specific IT tools designed to reduce physician burnout?
Yes, tools like automated appointment scheduling, electronic prescription systems, and streamlined communication platforms can significantly reduce administrative burden and paperwork, thus alleviating burnout.