Healthcare Leaders Struggle with Inefficient Data Reporting on IMOs
Majority of healthcare leaders struggle with inefficient data report intelligent medical objects. It’s a frustrating reality: mountains of data, yet crucial insights remain hidden, hindering effective decision-making and impacting patient care. This isn’t just about clunky spreadsheets; it’s about the lost potential of intelligent medical objects (IMOs) – powerful tools hampered by poor data quality and accessibility. We’ll dive into the challenges, explore solutions, and uncover how better data management can revolutionize healthcare.
The consequences of this data bottleneck are far-reaching. Inefficient reporting leads to delayed diagnoses, suboptimal treatment plans, and increased operational costs. Imagine the possibilities if healthcare leaders could access real-time, accurate data – improving patient outcomes, streamlining workflows, and unlocking the true potential of IMOs. This post explores the current state of healthcare data reporting, identifies key challenges, and proposes solutions for a more data-driven future.
The Prevalence of Inefficient Data Reporting in Healthcare
Healthcare organizations sit on a goldmine of data – patient records, treatment outcomes, operational metrics, and financial information. However, the ability to effectively leverage this data is often hampered by inefficient reporting systems and processes. This leads to missed opportunities for improvement in patient care, operational efficiency, and financial performance. The challenge isn’t the lack of data, but rather the lack of readily accessible, actionable insights derived from it.
Challenges in Healthcare Data Reporting Efficiency
Many healthcare leaders grapple with the complexities of data reporting. Three significant hurdles consistently emerge: data silos, lack of standardized reporting processes, and insufficient analytical capabilities. Data silos, where information is scattered across different departments and systems, create fragmentation and hinder a holistic view. Inconsistent reporting methods across departments make comparisons and trend analysis difficult. Finally, a lack of robust analytical tools prevents the transformation of raw data into meaningful insights.
Consequences of Inefficient Data Reporting
The ramifications of inefficient data reporting are far-reaching. For patient care, it can lead to delayed diagnoses, suboptimal treatment plans, and increased medical errors due to a lack of readily available patient history or relevant research. Operationally, inefficient reporting impacts resource allocation, leading to potential overspending and understaffing. Financially, it can hinder accurate forecasting, budget planning, and the identification of cost-saving opportunities.
Ultimately, inefficient data reporting undermines the ability of healthcare organizations to deliver high-quality, cost-effective care.
Comparison of Data Reporting Methods in High-Performing and Low-Performing Organizations
The differences in data reporting strategies between high-performing and low-performing healthcare organizations are stark. High-performing organizations typically invest in integrated electronic health record (EHR) systems, employ standardized data collection and reporting protocols, and utilize advanced analytics tools to extract actionable insights. Conversely, low-performing organizations often rely on disparate systems, manual data entry, and limited analytical capabilities, resulting in fragmented and unreliable data.
| Characteristic | High-Performing Organizations | Low-Performing Organizations |
|---|---|---|
| Data Integration | Integrated EHR systems, data warehousing | Disparate systems, manual data entry |
| Reporting Processes | Standardized protocols, automated reporting | Inconsistent methods, manual reporting |
| Analytical Capabilities | Advanced analytics, data visualization tools | Limited analytical tools, basic reporting |
| Data Quality | High data quality, regular audits | Variable data quality, infrequent audits |
Impact of Inefficient Data on Intelligent Medical Objects (IMOs)
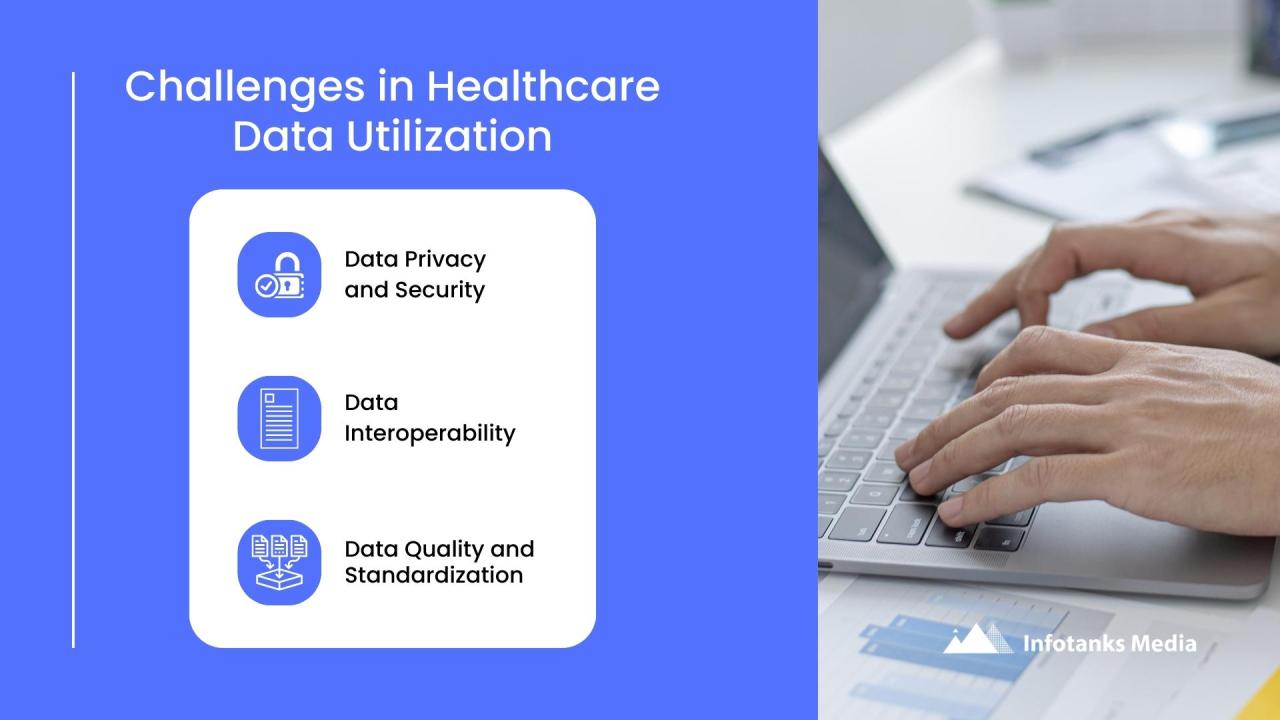
Source: iinfotanks.com
So many healthcare leaders are drowning in inefficient data, struggling to make sense of the deluge of information from intelligent medical objects. The solution might lie in advancements like those highlighted in this article about ai most exciting healthcare technology center connected medicine upmc , which explores how AI is streamlining data analysis. Ultimately, overcoming this data hurdle is crucial for better patient care, something we all need to work towards.
Inefficient data reporting is a significant bottleneck in realizing the full potential of Intelligent Medical Objects (IMOs). IMOs, designed to improve healthcare efficiency and patient outcomes through data-driven insights, are critically reliant on the quality and accessibility of the data they process. Poor data quality directly translates to flawed analyses, inaccurate predictions, and ultimately, suboptimal decision-making. This section will explore the detrimental effects of inefficient data reporting on IMOs and Artikel strategies for improvement.The effectiveness of IMOs hinges on receiving clean, consistent, and comprehensive data.
Inefficient data reporting, characterized by inconsistencies, missing values, and errors, directly undermines this foundation. For instance, an IMO designed to predict patient readmission risk might fail to accurately assess the risk if crucial data points, such as medication adherence or social determinants of health, are missing or unreliable. Similarly, an IMO used for diagnostic support might generate inaccurate diagnoses if the input data contains errors or inconsistencies in laboratory results or medical imaging interpretations.
The result is a loss of trust in the IMO’s output and a diminished ability to leverage its analytical capabilities.
Examples of Improved Data Reporting Enhancing IMO Functionality
Improved data reporting can dramatically enhance IMO functionality. Consider an IMO designed to optimize hospital bed allocation. With accurate and timely data on patient admissions, discharges, and anticipated lengths of stay, the IMO can more effectively predict bed demand, minimizing wait times and optimizing resource utilization. Another example involves an IMO used for personalized medicine. If the IMO receives comprehensive genomic data, patient medical history, and lifestyle information, it can tailor treatment plans with greater precision, potentially leading to improved patient outcomes.
The key is ensuring data integrity and completeness to maximize the IMO’s ability to process information effectively.
Crucial Data Elements for Optimizing IMO Performance
Several data elements are crucial for optimizing IMO performance. These include structured clinical data (e.g., diagnoses, procedures, medications), laboratory results, imaging data, patient demographics, and social determinants of health. The completeness and accuracy of these data elements directly impact the reliability and effectiveness of the IMO’s analyses. For example, missing information on allergies can lead to adverse drug events, while incomplete social determinants data might hinder accurate risk stratification.
Ensuring data standardization and interoperability across different healthcare systems is also vital for seamless data integration and improved IMO functionality. The consistent use of standardized terminologies and ontologies is key.
Strategies for Improving Data Quality to Support Better IMO Utilization
Three key strategies can significantly improve data quality to support better IMO utilization. First, implementing robust data governance frameworks ensures data quality throughout its lifecycle, from collection to analysis. This involves establishing clear data quality standards, implementing data validation rules, and regularly monitoring data quality metrics. Second, investing in advanced data cleaning and integration technologies allows for the automated identification and correction of data errors and inconsistencies.
This can include using machine learning algorithms to identify and flag potential data quality issues. Third, fostering a culture of data quality among healthcare professionals is crucial. This involves providing training on data entry best practices, emphasizing the importance of accurate data collection, and establishing clear accountability mechanisms for data quality. A collaborative approach, involving clinicians, data managers, and IT professionals, is essential for successful implementation.
Technological Solutions for Improving Data Reporting
The struggle with inefficient data reporting in healthcare is real, impacting everything from operational efficiency to patient care. Fortunately, technological advancements offer powerful solutions to streamline this process and unlock the true potential of data-driven decision-making. By leveraging modern data analytics platforms and implementing intelligent automation, healthcare leaders can transform their data reporting practices, leading to better outcomes and improved resource allocation.Data analytics platforms are crucial for streamlining data reporting.
These platforms offer a centralized location to collect, clean, and analyze data from disparate sources – electronic health records (EHRs), billing systems, wearable devices, and more. This consolidated view eliminates the time-consuming manual processes previously involved in gathering information from multiple systems, drastically reducing the time and effort required to generate reports. Furthermore, these platforms often incorporate advanced analytics capabilities, allowing for more sophisticated insights beyond simple descriptive statistics.
For example, predictive analytics can forecast patient readmission rates, allowing proactive interventions to improve patient outcomes and reduce healthcare costs.
Data Aggregation and Visualization System Design
A hypothetical system for efficient data aggregation and visualization for healthcare leaders could incorporate several key components. First, a secure, cloud-based data warehouse would serve as the central repository for all relevant healthcare data. This warehouse would integrate data from various sources using standardized APIs and data transformation techniques. Next, a robust data analytics engine would process this data, performing complex calculations and generating insightful metrics.
Finally, a user-friendly dashboard would provide interactive visualizations of key performance indicators (KPIs), allowing healthcare leaders to monitor performance, identify trends, and make data-driven decisions. This dashboard could be customized to display different metrics and visualizations based on the user’s role and responsibilities, providing a tailored view of the data. For example, a hospital administrator might prioritize metrics related to overall hospital performance, while a department head might focus on metrics specific to their department.
Data Visualization Techniques in Healthcare
Different data visualization techniques are suited to different types of healthcare data and analytical goals. Bar charts and pie charts are effective for displaying proportions and comparisons, such as the distribution of patients across different age groups or the prevalence of specific diseases. Line charts are useful for showing trends over time, such as the number of hospital admissions or the average length of stay.
So many healthcare leaders are drowning in inefficient data, struggling to make sense of the deluge to effectively use intelligent medical objects. This problem highlights the urgent need for innovative solutions, like those discussed in this article on the ais health equity revolution, featuring Rene Quashie and the Consumer Technology Association , which explores how AI can improve data analysis and accessibility.
Ultimately, overcoming these data hurdles is key to unlocking better patient care and, frankly, sanity for overwhelmed healthcare professionals.
Heatmaps can effectively visualize correlations between variables, such as the relationship between patient demographics and treatment outcomes. Finally, dashboards provide a holistic overview of multiple KPIs, providing a comprehensive view of organizational performance. The choice of visualization technique should always be guided by the specific question being asked and the nature of the data. For instance, a heatmap might be ideal for showing the correlation between patient characteristics and medication adherence, while a line graph might better illustrate the trend in infection rates over time.
It’s frustrating seeing how many healthcare leaders grapple with clunky data systems that hinder quick, informed decisions. Understanding patient risk profiles is crucial, and this is especially true when dealing with conditions like stroke; check out this article on risk factors that make stroke more dangerous to see what I mean. Efficient data reporting is key to identifying and managing these risks effectively, and sadly, many systems fall short, leaving valuable insights untapped.
Automation’s Role in Improving Report Accuracy and Timeliness
Automation significantly improves the accuracy and timeliness of data reports. Automated data extraction from various sources eliminates manual data entry errors, ensuring data accuracy. Scheduled report generation ensures timely delivery of critical information to decision-makers, allowing for proactive responses to emerging trends. Automated anomaly detection flags unusual patterns or outliers, prompting further investigation and potentially preventing adverse events.
For example, an automated system could detect a sudden increase in patient readmission rates for a specific surgical procedure, prompting a review of the post-operative care protocols. This proactive approach, enabled by automation, is crucial for maintaining high standards of patient care and operational efficiency.
Organizational and Cultural Factors Affecting Data Reporting
Let’s face it: even with the best technological solutions, inefficient data reporting in healthcare often boils down to people and processes. The way a healthcare organization is structured, the culture it fosters, and the skills of its workforce all significantly impact the quality and timeliness of data reporting. Ignoring these crucial human elements renders even the most advanced software useless.
Organizational barriers frequently hinder efficient data reporting. These obstacles often stem from a lack of alignment between departments, conflicting priorities, and insufficient resources dedicated to data management. A siloed approach, where different departments hoard data and operate in isolation, prevents a holistic view and undermines the value of the data collected. This not only limits the potential of intelligent medical objects (IMOs) but also impacts patient care, operational efficiency, and strategic decision-making.
Key Organizational Barriers to Efficient Data Reporting
Several key organizational barriers impede the efficient flow and utilization of healthcare data. Addressing these is paramount to fostering a data-driven culture.
- Lack of standardized processes and protocols: Inconsistent data collection methods across departments lead to fragmented and unreliable information.
- Insufficient data governance frameworks: Without clear roles, responsibilities, and policies regarding data ownership, access, and security, data management becomes chaotic.
- Limited resources (personnel, budget, technology): Data management is resource-intensive. Insufficient allocation of resources hinders the implementation and maintenance of efficient data reporting systems.
- Resistance to change and lack of buy-in from staff: New data reporting systems and processes require training and adaptation. Resistance from staff can significantly impede successful implementation.
- Poor data quality: Inaccurate, incomplete, or inconsistent data renders any analysis meaningless, highlighting the need for robust data validation processes.
Strategies to Foster a Data-Driven Culture
Cultivating a data-driven culture requires a multi-pronged approach that involves leadership commitment, employee engagement, and continuous improvement. It’s not a quick fix, but a journey that demands sustained effort and investment.
- Leadership commitment and sponsorship: Visible and vocal support from leadership is essential to demonstrate the importance of data and drive change.
- Clear communication and education: Regular communication about the importance of data and the benefits of data-driven decision-making is crucial.
- Incentivize data use and reporting: Recognizing and rewarding individuals and teams who effectively use and report data can encourage data-driven behavior.
- Invest in data infrastructure and technology: Providing staff with the necessary tools and technology to collect, analyze, and report data efficiently is vital.
- Establish a culture of continuous improvement: Regularly review and refine data reporting processes to ensure they remain efficient and effective.
Importance of Data Literacy Training for Healthcare Professionals
Data literacy is no longer a luxury; it’s a necessity for healthcare professionals. Without the ability to understand, interpret, and utilize data, healthcare organizations cannot leverage the full potential of their data assets. Training should equip professionals with the skills to effectively engage with data in their daily work.
- Basic data analysis skills: Training should cover fundamental statistical concepts and data visualization techniques.
- Understanding of data sources and types: Healthcare professionals need to understand the various sources of data and the different types of data used in healthcare.
- Interpretation of data and drawing conclusions: Training should focus on the ability to draw meaningful insights and conclusions from data.
- Ethical considerations related to data: Healthcare professionals must understand the ethical implications of data use and privacy.
Implementing a Comprehensive Data Governance Framework
A robust data governance framework provides the structure and guidelines necessary for effective data management. This framework should encompass policies, procedures, and responsibilities related to data quality, security, and access.
- Define data governance roles and responsibilities: Clearly assign roles and responsibilities for data management, including data owners, stewards, and custodians.
- Establish data quality standards: Define clear standards for data accuracy, completeness, consistency, and timeliness.
- Develop data security policies and procedures: Implement robust security measures to protect sensitive patient data.
- Create data access and usage policies: Define clear policies regarding who can access data and how it can be used.
- Implement data monitoring and auditing processes: Regularly monitor data quality and security and conduct audits to ensure compliance with policies and procedures.
Best Practices for Efficient Data Reporting and IMO Integration
We’ve established that many healthcare leaders grapple with inefficient data reporting, hindering the effective use of Intelligent Medical Objects (IMOs). This section focuses on practical steps to improve this situation, leading to better data-driven decision-making. By implementing these best practices, organizations can unlock the full potential of their data and seamlessly integrate it with IMO workflows.
Creating Effective Data Reports Using Readily Available Data
Effective data reporting starts with a clear understanding of your goals. What questions are you trying to answer? What decisions need to be informed? Once you have a defined objective, identify the relevant data sources within your existing systems – electronic health records (EHRs), billing systems, patient portals, etc. Begin by focusing on readily available data to build momentum and demonstrate value.
A step-by-step approach includes: 1) Defining the report’s purpose and target audience; 2) Identifying key data points; 3) Cleaning and validating the data; 4) Choosing appropriate visualizations (discussed below); 5) Creating the report; 6) Distributing the report to stakeholders; and 7) Regularly reviewing and updating the report based on feedback and changing needs. For instance, a report on patient readmission rates could use data from the EHR system, focusing on diagnoses, length of stay, and post-discharge follow-up.
Examples of Best Practices for Data Visualization
Data visualization is crucial for effective communication. Avoid overwhelming your audience with raw numbers. Instead, use charts and graphs to highlight key trends and insights. For example, a bar chart could effectively compare readmission rates across different patient demographics, while a line graph could track changes in a specific KPI over time. Consider using clear and concise labels, a consistent color scheme, and an appropriate scale to ensure readability.
A well-designed dashboard, incorporating multiple visualizations, can provide a comprehensive overview of key performance indicators. Imagine a dashboard showing readmission rates, average length of stay, and patient satisfaction scores, all presented visually in an easy-to-understand format. This allows healthcare leaders to quickly grasp the overall health of their operations.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) for Measuring the Effectiveness of Data Reporting Initiatives
Tracking the right KPIs is essential for evaluating the success of your data reporting efforts. The specific KPIs will vary depending on your organization’s goals, but some common examples include:
- Timeliness of report generation: How quickly are reports produced and distributed?
- Accuracy of data: How reliable is the information presented in the reports?
- Actionable insights: Are the reports leading to improvements in patient care or operational efficiency?
- User satisfaction: How satisfied are stakeholders with the reports’ usability and usefulness?
- Cost savings: Are the reports helping to reduce costs associated with inefficient processes?
- Reduction in medical errors: Are the reports contributing to a decrease in preventable medical errors?
- Improved patient outcomes: Are the reports leading to better health outcomes for patients?
These KPIs should be tracked consistently to monitor progress and identify areas for improvement.
Integrating Data Reporting Processes with IMO Workflows
Integrating data reporting with IMO workflows enhances decision-making by providing clinicians and administrators with timely, relevant information at the point of care. For example, an IMO might incorporate data on a patient’s allergies, medication history, and recent lab results to support clinical decision-making. Data reports can provide broader context, such as population-level trends in medication adherence or the effectiveness of specific treatment protocols.
This integration can be achieved through various technological solutions, such as data integration platforms, APIs, and customized dashboards that seamlessly integrate with existing IMO systems. This allows for a dynamic, data-driven approach to healthcare delivery, improving both the efficiency and quality of care. The key is to ensure the data is presented in a format that is easily accessible and understandable within the IMO workflow.
Future Trends in Healthcare Data Reporting and IMO Usage: Majority Of Healthcare Leaders Struggle With Inefficient Data Report Intelligent Medical Objects
The healthcare landscape is rapidly evolving, driven by technological advancements and a growing emphasis on data-driven decision-making. The future of healthcare data reporting and Intelligent Medical Object (IMO) utilization hinges on harnessing the power of emerging technologies to improve efficiency, security, and interoperability. This will lead to better patient care, reduced costs, and more effective research.
The Impact of Artificial Intelligence on Healthcare Data Reporting
AI is poised to revolutionize healthcare data reporting by automating many currently manual tasks. Machine learning algorithms can analyze vast datasets to identify patterns and anomalies that might be missed by human analysts, leading to earlier disease detection and more accurate diagnoses. For example, AI can be used to analyze patient records to predict hospital readmissions, allowing proactive interventions to prevent them.
Natural language processing (NLP) can extract key information from unstructured data, such as doctor’s notes and patient surveys, making it readily accessible for analysis and reporting. This automation frees up human resources to focus on more complex tasks and strategic decision-making. AI-powered predictive analytics can also help hospitals optimize resource allocation, improving efficiency and reducing costs.
The Role of Blockchain Technology in Enhancing Data Security and Interoperability
Blockchain technology offers a secure and transparent way to manage and share sensitive patient data. Its decentralized nature eliminates the need for a central authority, reducing the risk of data breaches. Each transaction is cryptographically secured and recorded on a distributed ledger, ensuring data integrity and traceability. Blockchain can facilitate seamless data exchange between different healthcare providers, improving interoperability and enabling more coordinated patient care.
Imagine a scenario where a patient’s medical history is securely stored on a blockchain, accessible only with their consent to authorized healthcare professionals involved in their care. This would drastically reduce the time and effort spent on data reconciliation and ensure consistent, up-to-date information is always available.
Emerging Technologies Improving IMO Integration within Healthcare Systems
The integration of IMOs within healthcare systems will be significantly enhanced by emerging technologies such as cloud computing, edge computing, and the Internet of Medical Things (IoMT). Cloud computing provides scalable and cost-effective storage and processing capabilities for large datasets, enabling efficient management and analysis of IMOs. Edge computing allows for faster processing of data closer to the source, reducing latency and improving real-time decision-making.
The IoMT connects medical devices and sensors, generating vast amounts of data that can be integrated with IMOs to provide a comprehensive view of a patient’s health status. For example, wearable sensors can continuously monitor vital signs, and this data can be seamlessly integrated into an IMO to provide real-time alerts and insights to healthcare providers.
Anticipated Evolution of Data Reporting and IMO Utilization in the Next Five Years, Majority of healthcare leaders struggle with inefficient data report intelligent medical objects
The following timeline illustrates the anticipated evolution of data reporting and IMO utilization:
| Year | Key Developments |
|---|---|
| 2024 | Increased adoption of AI-powered data analytics tools for improved efficiency and predictive modeling. Wider use of standardized data formats to improve interoperability. |
| 2025 | Significant growth in the use of blockchain technology for secure data sharing and management. More sophisticated IMOs incorporating real-time data from IoMT devices. |
| 2026 | Widespread implementation of cloud-based platforms for managing and analyzing healthcare data. Development of AI-driven decision support systems based on IMO data. |
| 2027 | Enhanced integration of IMOs with electronic health records (EHRs) and other healthcare systems. Emergence of new IMO applications focusing on personalized medicine and preventative care. |
| 2028 | Increased focus on data governance and compliance. Development of new regulatory frameworks to address the ethical and security implications of AI and IMO usage. |
Closure

Source: technoscore.com
The struggle with inefficient data reporting in healthcare is real, but it’s not insurmountable. By embracing technological solutions, fostering a data-driven culture, and implementing best practices, healthcare organizations can unlock the power of their data. Improved data reporting isn’t just about efficiency; it’s about enhancing patient care, improving operational effectiveness, and realizing the full potential of intelligent medical objects.
The journey towards a more data-informed healthcare system requires commitment, collaboration, and a willingness to adapt – the rewards, however, are immeasurable.
FAQ Overview
What are Intelligent Medical Objects (IMOs)?
IMOs are essentially smart medical devices or software applications that use data to improve healthcare processes. They can range from connected medical devices to sophisticated AI-powered diagnostic tools.
How does poor data impact patient safety?
Inaccurate or incomplete data can lead to misdiagnosis, incorrect treatment plans, and medication errors, all of which directly compromise patient safety.
What is the ROI of investing in better data reporting?
The return on investment includes improved efficiency, reduced operational costs, better patient outcomes, and the ability to make more informed strategic decisions.
What are some common barriers to implementing new data systems?
Common barriers include cost, lack of staff training, resistance to change, and integration challenges with existing systems.