Medicare Advantage Denials AI, Prior Auth, Senate Scrutiny
Medicare advantage denials prior authorization ai senate – Medicare Advantage Denials: Prior Authorization, AI, and Senate Scrutiny – it sounds like a mouthful, right? But it’s a crucial issue impacting millions of seniors. This post dives into the complex world of Medicare Advantage denials, exploring how prior authorization processes are impacting access to care, the potential of AI to streamline (or complicate!) things, and the increasing scrutiny from the Senate.
Get ready to unravel this tangled web!
We’ll look at the common reasons for denials, the struggles faced by beneficiaries navigating the system, and the perspectives of healthcare providers caught in the middle. We’ll also examine potential legislative changes and explore the ethical considerations of using AI in healthcare decision-making, especially when it comes to potentially life-altering denials.
Medicare Advantage Denials Overview
Navigating the Medicare Advantage system can be complex, and unfortunately, denials of claims are a common frustration for beneficiaries. Understanding the reasons behind these denials and the appeals process is crucial for ensuring access to necessary healthcare services. This overview aims to clarify the current landscape of Medicare Advantage denials and provide some insight into the process.Medicare Advantage denials represent a significant issue for many seniors and individuals with disabilities relying on these plans for their healthcare coverage.
The high rate of denials often stems from the intricate nature of the plans themselves, coupled with sometimes unclear communication between providers, insurers, and beneficiaries. The financial consequences of denials can be substantial, impacting both the individual and the healthcare system as a whole.
Common Reasons for Medicare Advantage Denials, Medicare advantage denials prior authorization ai senate
Several factors frequently contribute to Medicare Advantage claim denials. These reasons often involve issues with pre-authorization, coding errors, out-of-network care, and benefit limitations. Understanding these common causes can help beneficiaries proactively prevent denials and streamline the appeals process if one occurs.
- Lack of Pre-authorization: Many procedures and services require prior authorization from the Medicare Advantage plan. Failure to obtain this authorization before receiving the service is a leading cause of denial.
- Incorrect Coding: Medical billing codes must be precise and accurate. Incorrect or incomplete coding can lead to claims being rejected or processed incorrectly.
- Out-of-Network Care: Receiving care from a provider who is not part of the plan’s network often results in significantly higher costs and potential denials, unless there are specific exceptions in place.
- Benefit Limitations: Medicare Advantage plans have specific benefit limitations, such as the number of visits or types of services covered. Exceeding these limits can lead to denial of further services.
- Missing or Incomplete Documentation: Claims require complete and accurate documentation to support the medical necessity of the services provided. Missing information can result in a denial.
The Beneficiary’s Experience with a Denied Claim
When a claim is denied, the beneficiary typically receives a formal notification explaining the reason for the denial. This notification usually includes information about the appeals process, outlining the steps to take to challenge the denial. The appeals process can be lengthy and complex, often involving multiple levels of review and documentation. Beneficiaries may need to gather additional medical records, complete forms, and communicate with both their provider and the Medicare Advantage plan.
The process can be daunting, particularly for individuals unfamiliar with healthcare insurance regulations. Many plans offer assistance programs to help beneficiaries navigate this process, but accessing these resources may require proactive engagement on the part of the beneficiary.
The Role of Prior Authorization in Medicare Advantage
Prior authorization, a process requiring pre-approval from your insurance provider before receiving certain medical services, plays a significant role in the Medicare Advantage landscape. Its implementation is a complex balancing act, aiming to control healthcare costs while ensuring patients have timely access to necessary care. Understanding its nuances is crucial for both beneficiaries and healthcare providers.Prior authorization’s primary purpose is cost containment.
By requiring pre-approval for specific procedures, medications, and treatments, Medicare Advantage plans aim to limit the use of expensive or potentially unnecessary services. This strategy, while controversial, is intended to help keep premiums lower and benefit the overall financial stability of the plans. The hope is that by carefully evaluating the necessity of each service, the plans can prevent wasteful spending and channel resources towards more effective and cost-efficient care.
Impact of Prior Authorization on Patient Access to Care
Prior authorization processes can significantly impact patient access to timely and appropriate care. The added administrative burden, involving paperwork and delays in obtaining approval, can create obstacles for patients seeking necessary treatment. For example, a patient needing a specialist referral might experience delays while waiting for authorization, potentially worsening their condition in the meantime. The complexity of the process can also lead to frustration and confusion, particularly for patients already dealing with health issues.
While intended to save money, prior authorization’s impact on patient experience is a significant area of concern and ongoing debate.
Comparison of Prior Authorization Processes Across Medicare Advantage Plans
Prior authorization requirements vary considerably across different Medicare Advantage plans. The specific procedures requiring pre-approval, the documentation needed, and the timelines for approval differ based on the plan’s design and network of providers. Some plans might have stricter requirements than others, resulting in varying levels of access to care. This lack of standardization creates challenges for both patients and providers navigating the system.
Transparency in the specifics of each plan’s prior authorization process is crucial for informed decision-making.
Prior Authorization Requirements for Common Procedures
The following table compares prior authorization requirements for three common procedures across five hypothetical Medicare Advantage plans (Plan A, Plan B, Plan C, Plan D, Plan E). Note that these are examples and actual requirements vary significantly among real plans. Always consult your specific plan’s benefit materials for accurate information.
| Procedure | Plan A | Plan B | Plan C | Plan D | Plan E |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MRI of the Knee | Required | Required (with specific referral) | Not Required | Required (pre-certification only) | Required (for certain diagnoses) |
| Prescription for Brand Name Drug X | Required (generic alternative must be tried first) | Required (step therapy required) | Not Required (if in formulary) | Required (quantity limits apply) | Required (prior authorization for 3-month supply) |
| Cardiac Catheterization | Required (extensive documentation needed) | Required (specialist referral and pre-admission review) | Not Required (in-network cardiologist) | Required (concurrent review during procedure) | Required (utilization management review) |
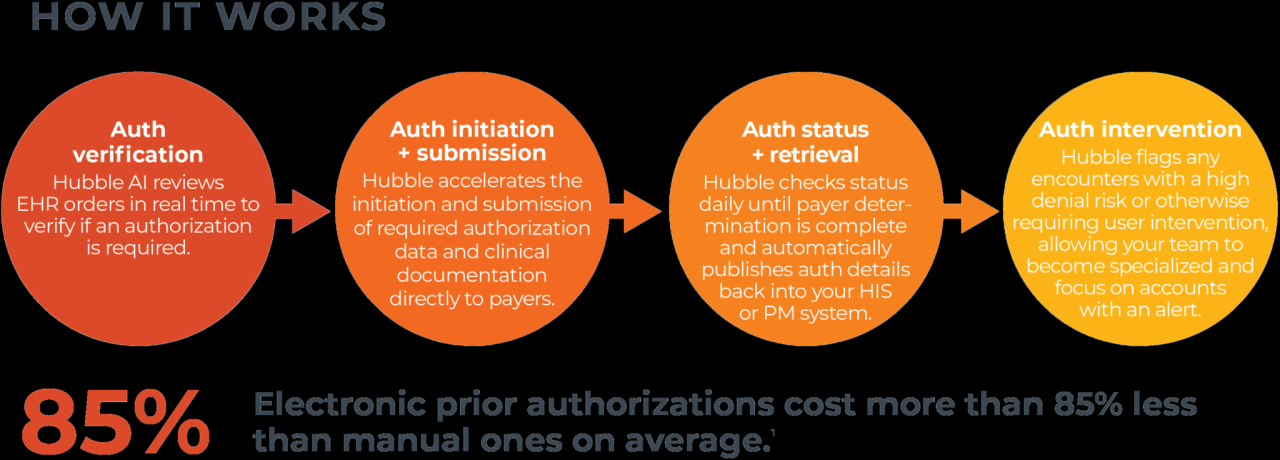
The Potential of AI in Prior Authorization for Medicare Advantage
The prior authorization process for Medicare Advantage plans is notoriously cumbersome, leading to delays in care and frustration for both patients and providers. However, the application of artificial intelligence (AI) offers a transformative opportunity to streamline this process, potentially improving efficiency and patient outcomes. AI’s ability to analyze vast amounts of data and identify patterns can significantly reduce the administrative burden associated with prior authorizations.AI could streamline the prior authorization process by automating many of the currently manual tasks.
This includes tasks such as data entry, form completion, and eligibility verification. Furthermore, AI algorithms can analyze patient medical history, treatment plans, and clinical guidelines to assess the medical necessity of requested services, potentially speeding up the decision-making process. By identifying patterns and predicting outcomes, AI can even help to proactively identify situations where prior authorization might be unnecessary, further reducing delays.
AI-Driven Prior Authorization: Benefits for Patients and Providers
The benefits of AI-driven prior authorization extend to both patients and providers. For patients, this means faster access to necessary care, reduced administrative burden, and less time spent navigating complex insurance processes. For providers, AI can free up valuable time and resources, allowing them to focus on patient care rather than paperwork. This increased efficiency can lead to improved practice productivity and reduced administrative costs.
Imagine a scenario where a provider submits a prior authorization request, and the AI system instantly approves it based on the patient’s history and established treatment guidelines – this is the potential of AI in this context.
Challenges and Risks of AI in Prior Authorization
Despite the significant potential, several challenges and risks are associated with the use of AI in prior authorization. Data privacy and security are paramount concerns. AI systems require access to sensitive patient data, and robust security measures are crucial to prevent breaches and protect patient confidentiality. Another challenge lies in ensuring the accuracy and fairness of AI algorithms.
The Senate’s investigation into Medicare Advantage denials and the role of AI in prior authorization is really making waves. It got me thinking about leadership changes in the healthcare industry, especially with the news that Terry Shaw is retiring as AdventHealth CEO – check out this article on his retirement adventhealth ceo retire terry shaw – and how that might impact the system’s response to these issues.
Ultimately, the Medicare Advantage denials debate highlights the urgent need for systemic reform.
Bias in the data used to train AI models can lead to discriminatory outcomes, potentially denying necessary care to certain patient populations. The potential for algorithmic errors leading to incorrect denials is also a significant concern. Rigorous testing and validation are crucial to mitigate these risks. Furthermore, the integration of AI systems into existing healthcare IT infrastructure can be complex and costly.
Ethical Considerations in AI-Driven Healthcare Decision-Making
The use of AI in healthcare decision-making, particularly concerning denials, raises several important ethical considerations. Transparency is crucial. Providers and patients need to understand how AI systems arrive at their decisions. Accountability is another key factor. Clear lines of responsibility must be established when AI systems make errors or result in denials.
The Senate’s debate on using AI to streamline Medicare Advantage prior authorization denials is crucial. Access to timely care is paramount, and the impact on patient outcomes is a major concern. This is especially relevant considering the expansion of convenient care options like the Humana Centerwell primary care centers located in Walmart stores, humana centerwell primary care centers walmart , which could be affected by inefficient prior authorization processes.
Ultimately, improving the AI system should lead to faster approvals and better patient experiences.
Furthermore, ensuring fairness and equity in AI-driven decision-making is paramount. AI algorithms should not perpetuate existing health disparities or discriminate against certain patient populations. The potential for dehumanization of care due to reliance on AI systems also requires careful consideration. Establishing clear guidelines and ethical frameworks is crucial to address these concerns and ensure responsible implementation of AI in prior authorization for Medicare Advantage.
Senate Scrutiny and Regulatory Implications

Source: coherehealth.com
The increasing use of prior authorization in Medicare Advantage plans, coupled with the growing implementation of AI in this process, has drawn significant scrutiny from the Senate. Concerns about denials, delays in care, and the potential for bias in automated systems have fueled investigations and hearings, leading to calls for greater transparency and accountability. This section examines the legislative landscape and potential regulatory changes arising from this heightened attention.Recent Senate investigations have focused on the high rates of Medicare Advantage denials and the impact on beneficiaries’ access to necessary care.
Hearings have featured testimony from patients detailing their struggles to obtain timely and appropriate medical services due to prior authorization requirements. These investigations are not solely focused on AI, but the technology’s role in automating these decisions is a major point of discussion. The investigations aim to understand whether these automated systems are exacerbating existing problems or introducing new ones, such as algorithmic bias.
Senate Concerns Regarding Medicare Advantage and Prior Authorization
Senators have expressed deep concerns about several key aspects of Medicare Advantage and prior authorization. These concerns extend beyond the simple denial rate and delve into the systemic issues contributing to the problem. For example, the lack of transparency in the denial process, the burden placed on both providers and patients in navigating the complexities of prior authorization, and the potential for financial incentives that might lead to unnecessary denials are all areas of significant worry.
Specific examples include the difficulty for patients to understand the reasons for denial, the time-consuming appeals process, and the potential for bias in the application of prior authorization criteria.
Potential Legislative Changes and Regulatory Actions
The potential for legislative and regulatory changes to address the issues surrounding Medicare Advantage denials and the role of AI in prior authorization is substantial. Several proposals are under consideration, and these can be broadly categorized based on their approach.The potential legislative proposals can be categorized as follows:
- Increased Transparency and Accountability: These proposals focus on improving transparency in the prior authorization process by requiring clearer explanations for denials, standardized appeals processes, and public reporting of denial rates by plan. This category aims to empower patients and providers with more information to navigate the system effectively. One example might involve mandating a plain-language explanation of denials, easily understood by the average patient, not just medical professionals.
- Streamlining the Prior Authorization Process: This category includes proposals designed to make the prior authorization process more efficient and less burdensome. This might involve exploring the use of AI to streamline legitimate requests, but with stringent oversight and safeguards against bias and inappropriate denials. Examples include exploring the use of predictive modeling to identify requests that are likely to be approved and automating those approvals, while still requiring human review for more complex cases.
- Strengthening Oversight and Enforcement: These proposals would strengthen oversight of Medicare Advantage plans and enhance enforcement of existing regulations related to prior authorization. This might include increasing penalties for plans with high denial rates or those found to be engaging in abusive practices. For instance, increased audits and investigations of plans with a disproportionately high number of denials could deter unfair practices.
- AI-Specific Regulations: Given the increasing use of AI in prior authorization, proposals are emerging that specifically address the unique challenges posed by this technology. This could include regulations requiring algorithmic transparency, bias detection and mitigation strategies, and human-in-the-loop oversight to ensure fairness and accuracy in AI-driven decisions. A real-world example could be a requirement for AI systems to provide an explanation for their decisions, similar to how a human reviewer would explain a denial.
Impact on Beneficiaries

Source: rapidload-cdn.io
Medicare Advantage denials, often stemming from prior authorization requirements, have a significant and multifaceted impact on beneficiaries, affecting both their health and their financial well-being. These denials create unnecessary stress and barriers to accessing timely and appropriate medical care.The consequences of denied claims extend far beyond a simple inconvenience. For many seniors, already navigating complex health issues and often living on fixed incomes, a denied claim can trigger a cascade of negative effects.
Delayed or forgone treatment can lead to worsening health conditions, increased hospitalizations, and ultimately, higher overall healthcare costs. Financially, the burden of unexpected medical bills can be devastating, potentially forcing difficult choices between essential needs and medical care.
The Senate’s scrutiny of Medicare Advantage denials, particularly those involving AI-driven prior authorization, is raising serious questions about patient access to care. This issue becomes even more complex when considering the scale of large healthcare systems like the lifepoint health ascension saint thomas joint venture , whose operations could be significantly impacted by stricter regulations on prior authorization.
Ultimately, the debate over AI in Medicare Advantage hinges on balancing cost savings with the potential for denials to negatively affect patient health outcomes.
Denied Claims and Health Outcomes
Denied claims directly impact a beneficiary’s health. For example, a denial for a necessary medication could lead to uncontrolled chronic conditions like diabetes or hypertension, resulting in serious complications. Similarly, delaying a crucial diagnostic test due to a prior authorization denial might mean a delayed cancer diagnosis, reducing the chances of successful treatment. The financial strain of dealing with a denial can also exacerbate existing health problems, leading to increased stress and anxiety, which negatively impact overall health.
Consider a scenario where a beneficiary needs a specialized therapy for rehabilitation after a stroke. If their prior authorization is denied, the delay in receiving the therapy could lead to prolonged recovery time, permanent disability, and a lower quality of life.
A Hypothetical Scenario Illustrating the Challenges of a Denied Claim
Imagine Mrs. Eleanor Vance, a 72-year-old retiree with a history of heart disease. Her cardiologist recommends a specialized cardiac rehabilitation program, which requires prior authorization from her Medicare Advantage plan. The authorization request is submitted, but weeks pass without a response. Repeated calls to the insurance company are met with long hold times and unhelpful customer service representatives.
Finally, the claim is denied, citing “lack of medical necessity.” Mrs. Vance is devastated. She struggles to understand the rationale behind the denial and is now faced with the daunting task of appealing the decision, a process she finds confusing and overwhelming. She worries about the impact on her health, as the rehabilitation program is crucial for her recovery.
The financial burden of potentially paying for the program out-of-pocket adds to her stress and anxiety.
Emotional and Logistical Burdens on Beneficiaries
Navigating a denied claim places an immense emotional and logistical burden on beneficiaries. The emotional toll includes frustration, anxiety, anger, and feelings of helplessness. The logistical burden involves numerous phone calls, faxes, and potentially appeals processes, all while dealing with the stress of their health condition. This often falls disproportionately on family members who may have to assist with the process, adding further stress to their lives.
The uncertainty surrounding the outcome of the appeal process can create prolonged periods of stress and anxiety, significantly impacting their mental and emotional well-being. The sheer complexity of the process, involving medical jargon, insurance policies, and bureaucratic procedures, often leaves beneficiaries feeling overwhelmed and disempowered.
Provider Perspectives: Medicare Advantage Denials Prior Authorization Ai Senate
The prior authorization process for Medicare Advantage plans presents significant challenges for healthcare providers, impacting their workflows, administrative burden, and ultimately, the patient-provider relationship. The variations in requirements across different plans exacerbate these issues, creating a complex and often frustrating landscape for those delivering care.The administrative burden imposed by prior authorization varies significantly depending on the specific Medicare Advantage plan.
Some plans have streamlined processes with user-friendly online portals and relatively straightforward requirements, while others demand extensive documentation, multiple attempts at submission, and lengthy wait times for approvals. This inconsistency forces providers to invest significant resources in navigating the unique requirements of each plan, diverting time and staff away from direct patient care. Smaller practices, in particular, often lack the administrative infrastructure to manage this complexity effectively, potentially leading to delays in treatment and financial hardship.
Administrative Burden and Resource Allocation
The administrative tasks associated with prior authorization consume considerable resources for healthcare providers. This includes the time spent completing and submitting forms, following up on pending requests, and appealing denials. Staff time dedicated to these tasks could otherwise be used for patient care, leading to decreased efficiency and potentially impacting the quality of care delivered. The cost of employing additional staff or investing in specialized software to manage prior authorization further adds to the financial burden on providers.
For example, a small cardiology practice might dedicate one full-time employee solely to managing prior authorizations for multiple Medicare Advantage plans, representing a significant portion of their operating budget.
Impact on Provider-Patient Relationships
Delays in treatment caused by prior authorization denials can negatively affect the provider-patient relationship. Patients become frustrated by the lengthy wait times and the perceived obstacles to accessing necessary care. This frustration can manifest as decreased trust in the provider, leading to a decline in patient satisfaction and potentially impacting adherence to treatment plans. Providers, in turn, feel constrained by the administrative hurdles, potentially affecting their ability to provide optimal care and build strong relationships with their patients.
A patient needing a crucial medication might experience a delay in receiving it due to a denial, leading to a deterioration in their health and a breakdown in the trust they placed in their doctor.
Denial Rates and Financial Implications
High denial rates significantly impact provider revenue and financial stability. When a prior authorization is denied, the provider may not receive reimbursement for the service, leading to financial losses. This is particularly problematic for providers who rely heavily on Medicare Advantage patients for their revenue stream. Furthermore, the time and resources spent on appeals further compound these financial losses.
A high volume of denials can threaten the viability of a practice, especially for those with limited financial reserves. For instance, a small rural clinic might face closure if a significant portion of their Medicare Advantage claims are repeatedly denied, creating a healthcare access crisis in the community.
Future Directions
The intersection of AI and Medicare Advantage prior authorization is still in its nascent stages, presenting a wealth of opportunities for improvement and innovation. Further development and refinement of AI algorithms, coupled with a focus on transparency and fairness, can significantly reshape the prior authorization landscape, ultimately benefiting both providers and beneficiaries.The potential for AI to streamline and improve the prior authorization process is immense.
This includes not only reducing administrative burdens but also leading to more timely and accurate decisions, ultimately enhancing patient care. Several key areas demand attention to fully realize this potential.
AI Algorithm Refinement and Expansion
Current AI systems primarily focus on automating the review of prior authorization requests. Future development should incorporate more sophisticated algorithms capable of predicting the likelihood of approval based on a wider range of factors, including patient history, clinical guidelines, and treatment efficacy data. This predictive capability can lead to a more proactive approach, potentially pre-approving certain treatments or flagging cases requiring immediate human review.
For instance, an AI system could identify patterns indicating a high probability of denial for a specific procedure in a particular region, allowing for proactive interventions to address potential issues before the request is even submitted.
Enhanced Transparency and Fairness
Transparency is crucial to building trust and ensuring fairness in the prior authorization process. Future systems should provide clear and concise explanations for both approvals and denials, detailing the specific criteria used in the decision-making process. This could involve the development of user-friendly dashboards displaying relevant data points and allowing providers to understand the reasoning behind each decision.
Furthermore, mechanisms for appealing denials should be simplified and streamlined, ensuring equitable access to review and reconsideration. For example, a system could provide a standardized appeals process with clear timelines and access to independent review boards.
Improved Patient Outcomes Through Denial Management
Effective management of denials is vital for ensuring timely access to necessary care. Future AI systems could play a crucial role in this process by proactively identifying potential denial risks and offering solutions to mitigate them. This might involve suggesting alternative treatments, providing guidance on documentation requirements, or facilitating communication between providers and payers. Imagine a system that automatically alerts a provider when a prescription is likely to be denied due to missing information, allowing them to rectify the issue before the patient experiences a delay in treatment.
This proactive approach would significantly improve patient outcomes by reducing the time and frustration associated with navigating the prior authorization process.
Outcome Summary
Source: waystar.com
The intersection of Medicare Advantage denials, prior authorization, AI, and Senate oversight presents a complex challenge. While AI offers the potential to streamline processes and improve efficiency, ethical concerns and the risk of exacerbating existing inequalities must be carefully addressed. The ongoing Senate scrutiny highlights the need for greater transparency, accountability, and ultimately, a system that prioritizes patient access to necessary care.
The fight for fair and equitable access to healthcare for Medicare Advantage beneficiaries is far from over, and staying informed is crucial.
General Inquiries
What are the most common reasons for Medicare Advantage denials?
Common reasons include lack of prior authorization, services not considered medically necessary, or incorrect coding.
How can I appeal a Medicare Advantage denial?
The process varies by plan, but generally involves filing an appeal with your Medicare Advantage plan and potentially escalating to a higher level of review.
What specific role does the Senate play in addressing these denials?
The Senate conducts oversight hearings, investigates complaints, and can propose legislation to reform Medicare Advantage and prior authorization processes.
What are the potential downsides of using AI in prior authorization?
Potential downsides include algorithmic bias, lack of transparency, and the potential for increased denials based on flawed algorithms.





