Medicare Solvency House Budget Committee Report
Medicare solvency house budget committee – Medicare Solvency: House Budget Committee Report – The future of Medicare is a hot topic, and the House Budget Committee’s recent report throws a lot of fuel on the fire. They’ve crunched the numbers, projected potential insolvency dates, and offered up some pretty bold policy recommendations. This isn’t just dry data; it’s a direct reflection of the ongoing battle over healthcare costs, an aging population, and the very real possibility of a system facing collapse.
Get ready to dive into the details and see what’s really at stake.
This post will unpack the key findings of the House Budget Committee’s report on Medicare solvency. We’ll explore their projections, examine the factors driving the projected crisis, analyze their proposed solutions, and compare their findings to other analyses. We’ll also look at the public and political reactions to this critical report. Buckle up; it’s going to be a fascinating (and potentially alarming) ride.
Medicare Solvency Projections from the House Budget Committee
Source: kff.org
The Medicare solvency debate raging in the House Budget Committee is incredibly complex, touching on so many aspects of senior care. A key concern is the rising cost of treating age-related diseases, and understanding early detection methods is crucial. This is why I found a recent article on whether an eye test can detect dementia risk in older adults, can eye test detect dementia risk in older adults , incredibly interesting.
Early detection could significantly impact long-term care costs, a major factor in the Medicare solvency discussion.
The House Budget Committee plays a crucial role in assessing the long-term financial health of Medicare, regularly releasing reports that project the program’s solvency. These projections are vital for informing policy decisions and guiding discussions about necessary reforms. Understanding the methodology and assumptions behind these projections is key to interpreting their implications.
Timeline of House Budget Committee Reports on Medicare Solvency
The House Budget Committee has consistently produced reports on Medicare’s financial outlook over the past decade. While specific report titles and release dates vary, a general pattern emerges of annual or biennial updates reflecting changes in economic conditions, healthcare utilization, and legislative actions. These reports often incorporate updated actuarial analyses from the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS), which provides the underlying data and projections for many of the Committee’s findings.
Access to the specific reports requires searching the House Budget Committee’s website for relevant years. The reports typically include detailed tables and graphs illustrating various scenarios for Medicare’s future.
Key Assumptions in House Budget Committee Medicare Solvency Models, Medicare solvency house budget committee
The House Budget Committee’s Medicare solvency models rely on several key assumptions that significantly influence the projected insolvency dates. These assumptions often include projections for: healthcare utilization rates (e.g., growth in physician visits, hospital admissions, and prescription drug use); future healthcare costs (e.g., inflation rates for medical services and prescription drugs); economic growth (influencing tax revenues available to fund Medicare); enrollment growth (projecting the number of beneficiaries); and the impact of future legislation (including changes to Medicare benefits or payment rates).
The Committee often explicitly states the assumptions used in their reports, enabling analysts to assess the sensitivity of the projections to changes in these parameters. For instance, a faster-than-expected rise in healthcare costs would likely accelerate the projected insolvency date.
Methodologies for Forecasting Medicare Spending and Revenue
The Committee employs sophisticated actuarial models to forecast future Medicare spending and revenue. These models typically involve analyzing historical trends, applying statistical techniques to project future growth, and incorporating the assumptions mentioned previously. The models account for different components of Medicare spending, such as Part A (hospital insurance), Part B (medical insurance), and Part D (prescription drug insurance).
Revenue projections typically consider payroll taxes, general fund contributions, and beneficiary premiums. The models aim to capture the complex interplay between these factors and their impact on the program’s financial sustainability. The specific details of the methodologies are usually described in the committee’s reports, offering transparency into their analytical approach.
Medicare Insolvency Scenarios from the House Budget Committee
The following table summarizes different scenarios presented by the House Budget Committee regarding potential Medicare insolvency dates. Note that these are illustrative examples and actual figures will vary based on the specific report and its underlying assumptions. The insolvency date refers to the point when the Medicare trust funds are projected to be depleted, requiring additional funding from general revenues or benefit cuts to maintain operations.
| Scenario | Assumptions | Projected Insolvency Date | Key Factors |
|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline Scenario | Moderate growth in healthcare costs and utilization, stable economic growth | 2028 | Aging population, rising healthcare costs |
| Optimistic Scenario | Slow growth in healthcare costs, strong economic growth | 2035 | Technological advancements leading to cost savings, increased productivity |
| Pessimistic Scenario | Rapid growth in healthcare costs, slower economic growth | 2026 | Unforeseen medical breakthroughs driving up costs, economic downturn |
| Policy Reform Scenario | Implementation of cost-containment measures | 2040 | Successful implementation of cost-saving policies, reduced healthcare utilization |
Factors Affecting Medicare Solvency as Highlighted by the House Budget Committee
The House Budget Committee’s analysis of Medicare’s financial outlook paints a concerning picture, highlighting several key factors driving the projected shortfall. Understanding these factors is crucial for developing effective strategies to ensure the long-term viability of the program. This analysis focuses on the three most significant contributors to Medicare’s financial challenges, as identified by the committee.
Rising Healthcare Costs
The relentless increase in healthcare costs is arguably the most significant threat to Medicare’s solvency. These rising costs encompass a wide range of factors, including the increasing prices of prescription drugs, advanced medical technologies, and the complexity of modern medical treatments. For example, the cost of cancer treatments has skyrocketed in recent years, placing a substantial strain on Medicare’s budget.
Furthermore, the aging population requires more healthcare services, exacerbating the problem. Without effective cost-containment measures, Medicare’s expenses will continue to outpace its revenue streams, leading to a growing deficit. The committee’s projections likely incorporate various modeling scenarios reflecting different rates of cost growth, and the results would significantly differ based on those assumptions. For instance, a scenario assuming a 1% slower annual growth rate in healthcare costs would significantly improve Medicare’s long-term financial outlook compared to a scenario with a higher growth rate.
The Impact of an Aging Population
The United States is experiencing a demographic shift with a rapidly growing elderly population. This trend directly impacts Medicare’s financial health because older individuals tend to utilize significantly more healthcare services than younger individuals. The increasing number of beneficiaries places immense pressure on Medicare’s resources, requiring greater spending on hospitalizations, physician visits, and prescription drugs. The committee’s projections likely incorporate demographic data from the Census Bureau and other reliable sources to model the future size and healthcare utilization patterns of the Medicare beneficiary population.
For example, the committee might use actuarial models to predict the number of individuals who will reach Medicare eligibility age in the coming decades and estimate their average healthcare spending based on historical trends and future projections.
Analysis of Healthcare Reform Proposals
The House Budget Committee’s report likely includes an assessment of various healthcare reform proposals and their potential impact on Medicare’s solvency. This analysis might compare different policy options, such as negotiating drug prices, expanding preventive care, or implementing value-based care models. The committee’s analysis would likely involve sophisticated cost-benefit modeling, considering both the immediate and long-term effects of each proposal on Medicare spending and revenue.
For example, a proposal to negotiate drug prices might lead to lower short-term costs but could also have unintended consequences, such as limiting access to innovative medications or slowing down pharmaceutical innovation. The committee’s analysis would weigh these trade-offs to determine the overall impact on Medicare’s financial sustainability.
Policy Recommendations from the House Budget Committee Regarding Medicare Solvency: Medicare Solvency House Budget Committee
Source: kff.org
The House Budget Committee’s deliberations on Medicare solvency are crucial, impacting future healthcare access. These long-term planning discussions got me thinking about personal choices impacting future family planning, like actress Karishma Mehta’s decision to freeze her eggs, as detailed in this article karishma mehta gets her eggs frozen know risks associated with egg freezing. Ultimately, both the committee’s work and individual reproductive choices highlight the importance of planning for the future, albeit on vastly different scales.
The House Budget Committee, tasked with overseeing the federal budget, has proposed several policy changes to address the projected insolvency of Medicare. These proposals aim to curb rising costs and ensure the long-term viability of the program while minimizing negative impacts on beneficiaries. The committee’s recommendations are complex and often involve trade-offs between cost savings and program access.
Understanding these proposals is crucial for informed discussion about the future of Medicare.
Proposed Policy Changes and Their Impacts
The House Budget Committee’s proposed solutions are multifaceted, aiming to address both spending and revenue issues within the Medicare system. These proposals often involve adjustments to reimbursement rates for healthcare providers, changes to beneficiary premiums and cost-sharing, and modifications to the eligibility criteria. The potential impact on beneficiaries and the federal budget varies significantly depending on the specific proposal.
Detailed Description of Policy Changes
The committee’s recommendations often include a combination of approaches. For example, one common strategy involves negotiating lower drug prices. This could be achieved through various mechanisms, including allowing Medicare to negotiate directly with pharmaceutical companies for lower prices on certain drugs, or implementing a system of price controls. The impact on beneficiaries would be lower prescription drug costs, but the pharmaceutical industry might face reduced profitability, potentially impacting innovation.
The federal budget would see savings from reduced drug expenditures.Another frequently suggested approach involves modifying the Medicare Advantage program. This could involve adjustments to the payment rates for Medicare Advantage plans, or changes to the types of benefits offered. Beneficiaries might experience changes to their plan options or premiums. Budget impacts could range from savings through lower payment rates to increased costs if changes lead to higher enrollment or increased plan benefits.Finally, proposals to increase the eligibility age for Medicare are often debated.
Raising the eligibility age would reduce the number of individuals receiving benefits, resulting in substantial budget savings. However, this would delay access to critical healthcare coverage for older Americans, potentially leading to negative health outcomes and increased costs in other healthcare sectors.
Comparative Analysis of Policy Proposals
The following table provides a comparative overview of the pros and cons of some of the key policy proposals, along with their projected budget impact. Note that these projections are estimates and can vary depending on several factors, including economic conditions and healthcare utilization rates.
| Policy | Pros | Cons | Projected Budget Impact (Illustrative Example) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Negotiated Drug Prices | Lower drug costs for beneficiaries, significant budget savings | Potential impact on pharmaceutical innovation, potential for drug shortages | $100 billion savings over 10 years (hypothetical) |
| Medicare Advantage Payment Rate Adjustments | Potential for budget savings, potential for improved plan efficiency | Could lead to reduced benefits or higher premiums for beneficiaries, potential for reduced access to care | $50 billion savings over 10 years (hypothetical) |
| Increased Medicare Eligibility Age | Significant budget savings | Delayed access to healthcare for older Americans, potential for increased costs in other healthcare sectors | $200 billion savings over 10 years (hypothetical) |
Comparison with Other Analyses of Medicare Solvency
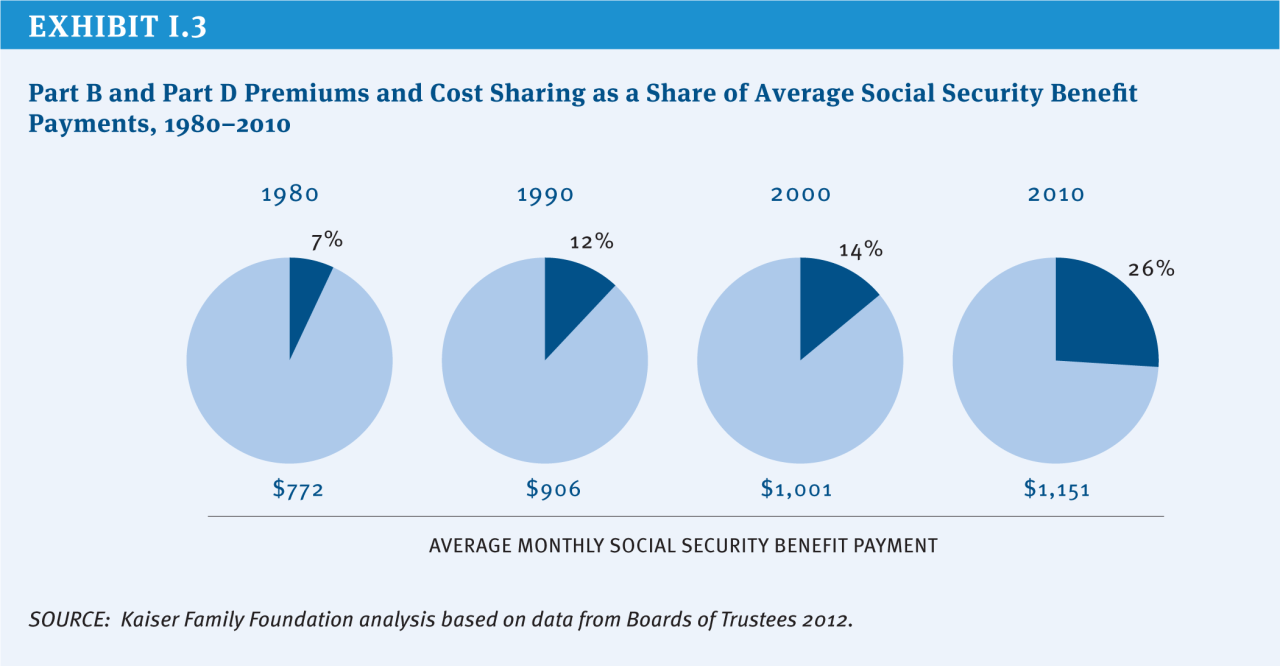
Source: kff.org
The House Budget Committee’s analysis of Medicare solvency is just one piece of the puzzle. Understanding its conclusions requires comparing them to the findings of other respected organizations, primarily the Congressional Budget Office (CBO) and the Medicare Trustees. These groups, while employing different methodologies and assumptions, offer valuable perspectives that help paint a more complete picture of the challenges facing Medicare’s long-term financial stability.
Discrepancies in their projections highlight the inherent uncertainties in long-term forecasting and the sensitivity of results to underlying assumptions.The CBO and the Medicare Trustees, for instance, often arrive at somewhat different projections for the depletion of Medicare’s trust funds, even when using similar data sets. This difference isn’t necessarily a sign of flawed analysis, but rather a reflection of the complexities involved in predicting healthcare costs decades into the future.
Factors like technological advancements, demographic shifts, and changes in healthcare utilization patterns are inherently difficult to predict with complete accuracy.
Key Assumptions and Methodologies
Understanding the differences in projections necessitates examining the underlying assumptions and methodologies employed by these various organizations. The differences in these foundational elements often explain the divergence in their conclusions. A detailed comparison helps to clarify the strengths and limitations of each approach.
- Discount Rate: The House Budget Committee, CBO, and the Medicare Trustees all use discount rates to calculate the present value of future costs. However, the specific rates used can vary, significantly impacting the projected financial burden on Medicare. A higher discount rate, for example, reduces the present value of future costs, making the program appear financially healthier than it might be under a lower discount rate.
This is because a higher discount rate places less weight on future costs.
- Healthcare Cost Growth Projections: The biggest source of disagreement often lies in projecting future healthcare costs. The House Budget Committee, the CBO, and the Medicare Trustees each utilize different models and data to estimate future healthcare spending growth. These models incorporate varying assumptions about factors like the adoption of new technologies, the effectiveness of cost-containment measures, and the rate of medical innovation.
Even small differences in these assumptions can lead to vastly different long-term projections. For example, a slightly higher projected growth rate in prescription drug costs can dramatically alter the long-term solvency outlook.
- Economic Growth Assumptions: Future economic growth is another critical factor. Stronger economic growth can lead to higher tax revenues, easing the financial strain on Medicare. Conversely, slower economic growth can exacerbate the program’s financial challenges. Different organizations use varying models and assumptions regarding future economic growth, leading to differing projections of Medicare’s financial health. The impact of a recession, for example, can be significant in these models.
Implications for Policymaking
The discrepancies between the analyses conducted by the House Budget Committee, the CBO, and the Medicare Trustees highlight the uncertainties inherent in long-term fiscal projections. Policymakers must carefully consider the range of possible outcomes when formulating policy responses to Medicare’s financial challenges. Relying solely on one analysis risks overlooking crucial aspects of the problem and potentially leading to ineffective or even counterproductive policies.
A robust policy response requires a comprehensive understanding of the various perspectives and a willingness to acknowledge the limitations of any single projection. For example, a policy based solely on the most optimistic projection might prove inadequate if the actual costs exceed expectations, leading to a financial crisis down the line. Conversely, a policy based on the most pessimistic projection might impose unnecessary burdens on beneficiaries and taxpayers.
A balanced approach that considers the full spectrum of possibilities is crucial for effective and sustainable Medicare reform.
Public Perception and Political Implications
The House Budget Committee’s report on Medicare solvency has generated a mixed response, sparking considerable public and media attention, and fueling intense political debate. The report’s projections, often framed in terms of impending crises, have resonated with some segments of the population concerned about the future of the program, while others have questioned the methodology and the underlying assumptions.
The media coverage has been varied, ranging from alarmist headlines emphasizing the urgency of the situation to more nuanced analyses considering the complexities of the issue.
Public Reception of the Report
Public reaction to the House Budget Committee’s findings has been largely polarized, reflecting existing partisan divisions. Conservative media outlets have tended to highlight the report’s warnings of impending insolvency, using this to advocate for significant reforms, often involving privatization or market-based solutions. Liberal outlets, on the other hand, have focused on the report’s limitations, arguing that its projections rely on pessimistic assumptions and that alternative policy options, such as expanding eligibility or increasing taxes on high earners, have not been adequately explored.
Public opinion polls have shown a fluctuating level of concern about Medicare’s financial future, with the level of concern often tied to broader economic anxieties and the political climate. For example, during periods of economic uncertainty, concern about Medicare solvency tends to rise.
Political Implications of the Analysis and Recommendations
The committee’s analysis and recommendations have become a key battleground in the ongoing political debate over the role of government in healthcare. The report’s findings have been used by Republicans to push for market-based reforms, such as raising the eligibility age, increasing premiums, or introducing private insurance options into the Medicare system. Democrats, conversely, have emphasized the need for increased funding and the protection of existing benefits, often proposing tax increases on higher earners or corporations to address the funding shortfall.
The political implications extend beyond immediate legislative action; the report’s findings are likely to shape future election campaigns and influence public policy debates for years to come. The framing of the issue – whether as a looming crisis requiring immediate drastic action or as a manageable challenge requiring incremental adjustments – has significant consequences for the political strategies employed by both parties.
The House Budget Committee’s wrestling with Medicare solvency is a huge challenge, and recent Supreme Court decisions only add to the complexity. The implications of the ruling where the scotus overturns chevron doctrine healthcare are still unfolding, but it’s clear this will significantly impact the regulatory landscape and, therefore, the future financial stability of Medicare. This makes the committee’s work even more critical in finding sustainable solutions.
Examples of Public Discourse and Political Debates
Several high-profile examples illustrate the political divisions surrounding Medicare solvency. The debate over raising the eligibility age has been particularly contentious, with Republicans arguing that it is a necessary measure to ensure the program’s long-term viability and Democrats countering that it would disproportionately harm vulnerable populations. Similarly, proposals to increase premiums or introduce cost-sharing mechanisms have faced strong opposition from seniors’ advocacy groups and Democratic lawmakers.
The political discourse is often characterized by competing narratives, with each side emphasizing different aspects of the problem and proposing solutions that align with their broader ideological perspectives. For example, debates about the role of private insurers in Medicare often highlight the fundamental disagreements about the ideal balance between public and private healthcare provision.
Visual Representation of Political Viewpoints
Imagine a two-dimensional graph. The horizontal axis represents the degree of government intervention in Medicare (from minimal intervention on the left to extensive government control on the right). The vertical axis represents the level of cost-control measures (from minimal measures at the bottom to aggressive cost-control measures at the top). A point plotted far to the right and high on the graph would represent a policy position advocating for extensive government control and aggressive cost-control, perhaps through expanded government negotiation of drug prices and stricter regulations.
This might be associated with a liberal or progressive viewpoint. A point plotted far to the left and low on the graph would represent a policy position favoring minimal government intervention and limited cost-control, perhaps through market-based reforms and increased reliance on private insurance. This might be associated with a conservative viewpoint. Points in between represent a spectrum of policy options, each reflecting different combinations of government involvement and cost-control strategies.
The positions of various political actors and advocacy groups could be plotted on this graph to visually illustrate the range of viewpoints on the issue of Medicare solvency.
Ultimate Conclusion
The House Budget Committee’s report on Medicare solvency paints a stark picture, highlighting the urgent need for action. While their projections are concerning, their proposed solutions offer a pathway forward, albeit one fraught with political and economic challenges. The debate over Medicare’s future is far from over, and the committee’s work serves as a crucial starting point for a much-needed national conversation.
Understanding the complexities of this issue is essential for everyone, and hopefully, this deep dive sheds some light on the path ahead.
FAQ Summary
What are the biggest criticisms of the House Budget Committee’s report?
Criticisms often center on the assumptions used in their models, particularly regarding future healthcare cost growth and the effectiveness of proposed policy changes. Some argue the report is overly pessimistic, while others find it lacks sufficient detail on the potential impact on specific beneficiary groups.
How does the committee’s report compare to the projections from the Medicare Trustees?
There are often areas of agreement and disagreement between the House Budget Committee and the Medicare Trustees. Differences often stem from varying assumptions about future healthcare costs, economic growth, and the impact of policy changes. Comparing the reports side-by-side is crucial for a comprehensive understanding.
What role does lobbying play in shaping the committee’s recommendations?
The influence of lobbying groups representing healthcare providers, pharmaceutical companies, and senior citizen advocacy organizations can significantly impact the committee’s recommendations. Understanding these influences is vital to assessing the objectivity of the report and the potential biases in proposed solutions.