North Carolina Expand Medicaid A Deep Dive
North Carolina expand Medicaid: This phrase has become a battle cry, a hope, and a source of intense debate across the state. Will expanding Medicaid coverage truly benefit North Carolinians, or will it strain the state budget and lead to unintended consequences? This isn’t just about healthcare; it’s about the economy, politics, and the future of access to vital medical services for thousands.
Let’s delve into the complexities of this crucial issue.
The current Medicaid system in North Carolina serves a significant portion of the population, but leaves many vulnerable individuals without coverage. Proposed expansions aim to bridge this gap, potentially offering health insurance to hundreds of thousands more. However, the financial implications, both positive and negative, are significant and require careful consideration. We’ll explore the projected economic impact, examine the political landscape, and weigh the potential benefits against the challenges.
The Current State of Medicaid in North Carolina

Source: nyt.com
North Carolina’s Medicaid program, officially known as NC Medicaid, provides healthcare coverage to millions of low-income residents. Understanding its current structure, eligibility, and funding is crucial for anyone interested in the state’s healthcare landscape. This overview will detail the key aspects of the program.
Medicaid Eligibility Requirements in North Carolina
Eligibility for NC Medicaid is complex and depends on several factors, including income, household size, age, disability status, and pregnancy. Generally, individuals and families must fall below a certain income threshold to qualify. Specific requirements vary based on the individual’s circumstances and the specific Medicaid program they apply for. For example, children may have different income limits than adults, and pregnant women have separate eligibility pathways.
Further, some individuals may qualify for Medicaid expansion under the Affordable Care Act (ACA), while others may be eligible through traditional Medicaid programs. The North Carolina Department of Health and Human Services (NCDHHS) website provides the most up-to-date and detailed eligibility information.
Services Covered Under NC Medicaid
NC Medicaid covers a broad range of healthcare services, aiming to provide comprehensive medical care to its enrollees. These services include doctor visits, hospital care, prescription drugs, mental health services, substance abuse treatment, and dental care. The specific services covered can vary depending on the individual’s plan and program. While NC Medicaid strives for comprehensive coverage, there may be limitations or restrictions on certain services or medications.
The specifics of covered services are subject to change, so consulting the NCDHHS website for the most current information is recommended.
Funding Mechanisms for NC Medicaid
NC Medicaid’s funding is a shared responsibility between the state and federal governments. The federal government contributes a significant portion of the funding, with the state covering the remaining amount. The specific contribution percentages vary based on federal guidelines and state budget allocations. Additional funding may come from various other sources, including managed care organizations (MCOs) that administer the Medicaid program for many enrollees.
These MCOs manage the care provided to Medicaid recipients and are paid a capitated rate, a fixed amount per enrollee per month, by the state. This complex funding system requires ongoing negotiation and adjustments between state and federal authorities.
Summary of NC Medicaid: Eligibility, Coverage, Funding, and Limitations
| Eligibility Criteria | Covered Services | Funding Source | Current Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Low income, age, disability, pregnancy; specific criteria vary by program. | Doctor visits, hospital care, prescription drugs, mental health services, substance abuse treatment, dental care (with variations based on plan and program). | Federal and state government, managed care organizations (MCOs). | Specific services may have limitations or restrictions; coverage can vary depending on the individual’s plan and program; access to specialists or certain treatments may be challenging in some areas. |
Proposed Expansion Plans
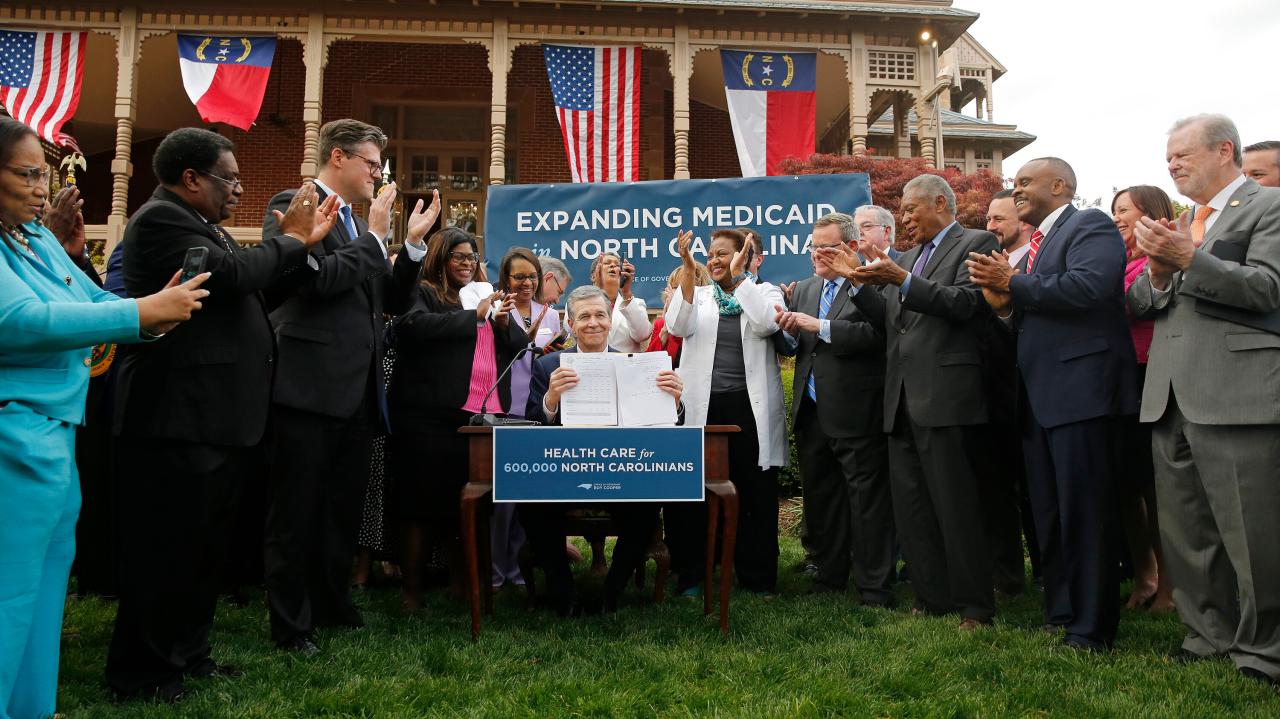
North Carolina’s proposed Medicaid expansion represents a significant shift in the state’s healthcare landscape. The plan aims to extend coverage to hundreds of thousands of low-income adults, addressing a long-standing gap in access to essential medical services. This expansion is not simply an increase in numbers; it’s a potential restructuring of the state’s healthcare system, impacting everything from hospital budgets to individual health outcomes.The core of the proposed expansion involves extending Medicaid eligibility to non-disabled adults earning up to 138% of the federal poverty level.
This aligns with the Affordable Care Act’s original intent, offering a safety net for those who fall into the “coverage gap”—earning too much for traditional Medicaid but too little to afford private insurance. The plan also includes provisions for workforce development within the healthcare sector to accommodate the influx of new enrollees and maintain quality of care. Funding mechanisms involve a combination of federal and state dollars, with a significant portion covered by the federal government.
Key Features of the Proposed Expansion
The proposed expansion isn’t a monolithic entity; it incorporates several key features designed to address specific concerns and maximize its impact. These features include not only the expansion of eligibility to adults but also specific provisions for care coordination, preventative services, and behavioral health integration. This integrated approach aims to improve the overall health and well-being of newly enrolled individuals, preventing more costly healthcare interventions down the line.
The plan also incorporates robust reporting mechanisms to track enrollment numbers, utilization rates, and overall effectiveness.
Projected Impact on the Uninsured Population
The projected impact on North Carolina’s uninsured population is substantial. Estimates suggest that expanding Medicaid could cover upwards of 600,000 individuals currently lacking health insurance. This influx of newly insured individuals could dramatically reduce the number of individuals facing medical debt, improve access to preventative care, and ultimately reduce the overall strain on the state’s healthcare system. For example, a study conducted by the [insert credible source, e.g., a reputable university or think tank] suggests that similar expansions in other states have led to a significant reduction in hospital emergency room visits for non-emergency conditions.
This shift reflects the ability of individuals with insurance to access routine and preventative care, thus preventing more costly emergency room interventions.
Comparison with Other State Models
North Carolina’s proposed expansion shares similarities with other states that have successfully expanded Medicaid. Many states have adopted a similar eligibility threshold of 138% of the federal poverty level. However, the specific implementation details, such as the level of state-level cost-sharing and the design of care coordination programs, can vary considerably. For instance, some states have opted for more robust managed care programs, while others have maintained a fee-for-service model.
North Carolina’s proposed model incorporates elements of both, reflecting a compromise between cost-containment and access to care. By comparing the outcomes in these different models, policymakers can better refine the North Carolina plan and maximize its positive effects.
Potential Benefits and Drawbacks
The potential benefits and drawbacks of the proposed expansion require careful consideration.
- Benefits: Increased access to healthcare for low-income adults, reduced uncompensated care costs for hospitals, improved public health outcomes, potential economic stimulus through increased healthcare employment.
- Drawbacks: Increased state budget expenditures (though partially offset by federal funding), potential strain on the healthcare workforce, concerns about the quality of care under expanded coverage, potential for increased administrative costs.
It is crucial to understand that these are potential outcomes, and the actual results will depend on the effective implementation and ongoing monitoring of the program. Rigorous evaluation is essential to identify and address any unforeseen challenges.
Economic Impacts of Expansion
Medicaid expansion in North Carolina carries significant economic implications, impacting both the state’s budget and its overall economic health. Understanding these potential benefits and costs is crucial for a comprehensive assessment of the expansion’s feasibility and long-term effects. The debate often centers around the balance between increased healthcare access and potential increases in state spending.Potential Economic Benefits of Medicaid Expansion
Increased Healthcare Access and Improved Health Outcomes
Expanding Medicaid would provide health insurance coverage to hundreds of thousands of low-income North Carolinians currently uninsured. This increased access would lead to preventative care, earlier diagnosis and treatment of chronic conditions, and ultimately, better overall health outcomes. Studies have consistently shown that increased access to healthcare leads to reduced hospitalizations and emergency room visits, which translates to cost savings in the long run.
For example, a study by the Kaiser Family Foundation showed that Medicaid expansion in other states has led to significant reductions in uninsured rates and improvements in access to care. This improved health status also contributes to a more productive workforce, reducing lost workdays due to illness.
Job Creation and Economic Growth
The influx of federal funds associated with Medicaid expansion would stimulate the state’s economy. This injection of capital would create jobs in the healthcare sector, including nurses, doctors, administrators, and support staff. Furthermore, increased economic activity in the healthcare industry would have a ripple effect, boosting related sectors like pharmaceuticals and medical equipment. The increased consumer spending power resulting from improved health and employment would further stimulate economic growth across various sectors.
A similar effect was observed in states that expanded Medicaid earlier, with reports of significant job creation in the healthcare and related industries.Potential Economic Costs of Medicaid Expansion
Increased State Spending
While the federal government covers a significant portion of Medicaid expansion costs, the state of North Carolina would still be responsible for a share of the expenses. This increased state spending would necessitate careful budgeting and potential adjustments to other state programs or revenue sources. The exact amount of state spending would depend on factors such as the number of newly enrolled individuals and the utilization of healthcare services.
It’s important to note that this increased spending needs to be weighed against the potential long-term cost savings from reduced hospitalizations and improved health outcomes.
Potential Tax Increases
To offset the increased state spending associated with Medicaid expansion, the state might need to consider raising taxes or making cuts in other areas of the budget. This could involve increases in existing taxes or the implementation of new taxes. The specifics of any tax increases would depend on the state’s fiscal situation and political priorities. This aspect is often a point of contention in the debate surrounding Medicaid expansion.Projected Impact on the State’s Budget
North Carolina’s Medicaid expansion is a huge deal, impacting thousands. It’s interesting to consider how this expansion might affect major healthcare players like Elevance Health, whose recent Q1 earnings were influenced by a cyberattack and changes in Medicaid and Medicare Advantage participation, as reported in this article: elevance health earnings q1 change cyberattack medicaid medicare advantage. The ripple effects of this expansion on companies like Elevance will be fascinating to watch unfold in the coming months.
Projected Costs and Benefits
The projected impact of Medicaid expansion on North Carolina’s budget is a complex issue with varying estimates from different sources. However, many analyses project a net positive economic impact over the long term, despite the initial increase in state spending. For instance, a study by the UNC Center for Health Policy and Healthcare Research could be cited (though specific data would need to be inserted here from the actual study).
This study might illustrate how the long-term cost savings from reduced hospitalizations and improved health outcomes outweigh the initial increase in state spending. Conversely, opposing viewpoints might emphasize the short-term fiscal strain and potential negative impact on other state programs.
Visual Representation of Projected Economic Impacts
Imagine a bar graph. The X-axis represents time (e.g., years 1-10 post-expansion). The Y-axis represents dollars (in billions). Two bars are shown for each year: one representing projected state costs (initially higher, gradually leveling off), and another representing projected state savings (from reduced healthcare utilization, initially lower, gradually increasing). A third line would represent the net effect (costs minus savings), showing an initial negative value that eventually becomes positive, demonstrating a net positive economic impact over the long term.
The graph would visually demonstrate that while initial costs are higher, long-term savings from improved health outcomes eventually outweigh these costs. The exact figures on the graph would, of course, depend on the specific projections used.
Political and Social Considerations
Medicaid expansion in North Carolina is far from a simple budgetary issue; it’s deeply entangled in the state’s political landscape and social fabric. The debate reflects broader national tensions surrounding healthcare access, government spending, and the role of the federal government. Understanding these interwoven political and social factors is crucial to grasping the complexities surrounding the ongoing discussion.The arguments for and against expansion are often framed in starkly contrasting terms, reflecting deep-seated ideological differences.
This makes finding common ground a significant challenge, even as the potential benefits become increasingly apparent.
Key Political Actors and Stakeholders
The debate over Medicaid expansion in North Carolina involves a complex web of political actors and stakeholders. Governor Roy Cooper, a Democrat, has consistently advocated for expansion, viewing it as a crucial step towards improving the health and well-being of North Carolinians. Republican lawmakers, however, have generally opposed expansion, citing concerns about the state budget and the potential long-term financial implications.
Powerful lobbying groups, such as the North Carolina Hospital Association (supporting expansion) and conservative think tanks (opposing expansion), also play significant roles, influencing legislative agendas and public opinion through advocacy campaigns and media outreach. Furthermore, the healthcare industry itself—including hospitals, doctors, and insurance companies—has a vested interest in the outcome, with their positions often aligning with their financial interests.
Finally, the public, particularly low-income individuals and families who would directly benefit from expansion, are key stakeholders whose voices are crucial in shaping the political narrative.
Arguments For and Against Medicaid Expansion
Proponents of Medicaid expansion argue that it would significantly improve the health of thousands of low-income North Carolinians, leading to better health outcomes and reduced healthcare costs in the long run. They cite studies demonstrating that expanded access to care leads to earlier diagnosis and treatment of chronic conditions, preventing costly hospitalizations and emergency room visits. Furthermore, expansion is seen as a vital step towards reducing health disparities, ensuring equitable access to healthcare for all residents regardless of socioeconomic status.
Opponents, however, express concerns about the fiscal impact of expansion on the state budget, arguing that the state would be responsible for a portion of the costs, even with federal matching funds. They also raise concerns about the potential increase in demand for healthcare services and the capacity of the state’s healthcare system to handle the influx of newly insured individuals.
These arguments frequently center on the belief that the free market is the most efficient way to allocate healthcare resources.
Potential Social Impacts of Medicaid Expansion
Medicaid expansion holds the potential to significantly improve the health and well-being of North Carolinians, particularly those in low-income communities. Increased access to preventative care, such as screenings and vaccinations, would lead to earlier detection and treatment of diseases, reducing morbidity and mortality rates. Improved access to mental healthcare and substance abuse treatment services would also address significant public health challenges.
Expansion could lead to reduced rates of chronic diseases like diabetes and heart disease, and decrease infant and maternal mortality. The economic benefits of a healthier workforce, reduced healthcare costs, and increased productivity are also significant potential outcomes. By reducing health disparities, Medicaid expansion would contribute to a more equitable and just society. For example, improved access to prenatal care could lead to better birth outcomes for mothers and babies in underserved communities, addressing systemic inequalities.
Political and Social Challenges to Medicaid Expansion
The path to Medicaid expansion in North Carolina faces several significant political and social challenges:
- Persistent Political Polarization: The deeply partisan nature of the debate makes finding bipartisan consensus difficult.
- Fiscal Concerns: Concerns about the state’s financial responsibility for a portion of the expansion costs remain a major obstacle.
- Concerns about Healthcare System Capacity: Questions about the state’s ability to handle an increased demand for healthcare services persist.
- Public Opinion: While support for expansion exists, it’s not uniformly strong across all demographics, hindering broad-based political momentum.
- Lobbying Efforts: Powerful lobbying groups on both sides of the issue actively influence the legislative process.
Potential Implementation Strategies: North Carolina Expand Medicaid

Source: oralhealthnc.org
Medicaid expansion in North Carolina presents several implementation strategies, each with its own set of advantages, disadvantages, and challenges. Careful consideration of these factors is crucial for a successful and sustainable program. The choice of strategy will significantly impact the speed, cost-effectiveness, and overall impact of the expansion.
Phased Rollout, North carolina expand medicaid
A phased rollout involves gradually expanding Medicaid eligibility over a period of time, perhaps by age group or income bracket. This approach allows for a more manageable implementation process, reducing the immediate strain on the state’s healthcare system and administrative capacity. For example, North Carolina could begin by expanding coverage to adults under 65 with incomes up to 100% of the Federal Poverty Level (FPL), then gradually increase the income threshold over several years.
This strategy minimizes initial costs and allows for adjustments based on early experiences. However, it delays full coverage for eligible individuals, which could lead to continued health disparities.
Streamlined Application Process
A key component of successful implementation is a streamlined and user-friendly application process. This involves simplifying the paperwork, utilizing online applications, and providing adequate support to applicants. This strategy aims to maximize enrollment and ensure that eligible individuals are able to access coverage without unnecessary hurdles. For example, the state could partner with community organizations to provide assistance with applications and address any technical difficulties.
Challenges include the need for significant upfront investment in technology and training, as well as the potential for errors or delays in processing applications.
Increased Provider Network Participation
Expanding Medicaid coverage requires sufficient providers willing to accept Medicaid patients. Incentivizing participation, such as increasing reimbursement rates or offering financial assistance for infrastructure improvements, is vital. This strategy aims to ensure that expanded coverage translates into accessible healthcare services. For instance, the state could offer bonuses to providers who agree to accept a certain number of Medicaid patients or invest in telehealth infrastructure to increase access in underserved areas.
Challenges here involve securing sufficient funding for these incentives and ensuring that the increased reimbursement rates are sustainable in the long term.
Robust Outreach and Education Campaign
Effective outreach and education are essential for ensuring that eligible individuals are aware of the expansion and how to enroll. This involves a multi-pronged approach using various media channels and community partnerships to reach diverse populations. For instance, North Carolina could launch a public awareness campaign using television, radio, print, and social media, alongside community events and partnerships with trusted organizations.
Challenges in this strategy include effectively targeting specific populations, overcoming language barriers, and combating misinformation.
Implementation Plan: A Step-by-Step Approach
A successful Medicaid expansion program requires a well-defined implementation plan. This plan should Artikel the following steps:
1. Needs Assessment Thoroughly assess the state’s healthcare needs and identify the specific challenges and opportunities related to Medicaid expansion.
2. Budget Allocation Secure adequate funding for expansion, considering both state and federal contributions. This includes funding for administration, provider reimbursement, and outreach.
3. System Development Develop a robust IT system to manage enrollment, claims processing, and provider payments.
4. Provider Recruitment Implement strategies to increase the number of providers willing to accept Medicaid patients.
North Carolina’s Medicaid expansion is a huge deal for the state, potentially impacting healthcare access for hundreds of thousands. The appointment of rfk jr confirmed hhs secretary robert f kennedy jr as HHS Secretary could significantly influence the federal government’s role in such expansions, and therefore, the ultimate success of the North Carolina initiative. It’ll be interesting to see how his policies affect the funding and implementation of expanded Medicaid in the state.
5. Outreach and Enrollment Launch a comprehensive outreach and enrollment campaign to ensure that eligible individuals are aware of the expansion and can easily access coverage.
6. Monitoring and Evaluation Continuously monitor the program’s performance and make adjustments as needed to optimize its effectiveness and sustainability. This includes tracking enrollment rates, healthcare utilization, and health outcomes.
Impact on Healthcare Providers
Medicaid expansion in North Carolina would significantly reshape the healthcare landscape, particularly impacting the state’s healthcare providers. The influx of newly insured individuals would lead to increased patient volume, potentially altering provider workloads, revenue streams, and the overall accessibility of care. Understanding these potential impacts is crucial for planning and adapting to the changes that expansion would bring.
The expansion’s effect on healthcare providers is multifaceted and depends on various factors, including the provider’s specialty, location, and existing patient base. While some providers might experience increased financial stability, others might face challenges in adapting to the increased demand and potential changes in reimbursement rates.
Provider Reimbursement Rates
Medicaid reimbursement rates in North Carolina are currently lower than those of private insurance, often leading to financial strain for providers, particularly those serving a high proportion of Medicaid patients. Expansion would increase the number of Medicaid patients, and while the federal government would cover a significant portion of the costs, the state’s reimbursement rates would still play a crucial role in provider participation.
Some estimates suggest that even with expansion, reimbursement rates might remain below the cost of providing care for some services, potentially creating a financial incentive for providers to limit Medicaid patients or even to stop participating in the program altogether. For example, rural hospitals, already struggling financially, might find it even harder to sustain themselves with a higher proportion of lower-reimbursing Medicaid patients.
Conversely, larger hospital systems with greater financial resources might be better positioned to absorb the increased volume of patients.
Access to Care for Medicaid Beneficiaries
Increased access to care is a primary goal of Medicaid expansion. With more individuals gaining coverage, the demand for healthcare services would undoubtedly rise. This could lead to longer wait times for appointments, especially in areas with limited provider capacity, such as rural communities or underserved urban areas. However, the expansion could also incentivize providers to increase their capacity by hiring more staff, expanding facilities, or adopting more efficient operational models.
For example, the establishment of more community health clinics in underserved areas could improve access for newly insured individuals.
North Carolina’s Medicaid expansion is a huge step forward for access to healthcare, especially for our aging population. This improved access is crucial because early detection of health issues is key to better outcomes, and I recently read an interesting article about how can eye test detect dementia risk in older adults. Early diagnosis of conditions like dementia through simple eye tests could significantly benefit those newly covered under the expanded Medicaid program, leading to better quality of life and more effective management of the disease.
Ultimately, expanding Medicaid means more people can access these vital preventative measures.
Projected Impact on Different Provider Types
The impact of Medicaid expansion will vary across different types of healthcare providers. To illustrate this, consider the following table:
| Type of Provider | Projected Impact | Changes in Reimbursement | Potential Challenges |
|---|---|---|---|
| Primary Care Physicians | Increased patient volume; potential for increased revenue with higher patient load, but potentially offset by lower reimbursement rates. | Likely slight increase, but may remain below cost of care for some services. | Increased workload, potential for longer wait times, need for additional staff. |
| Specialty Physicians (e.g., Cardiology, Oncology) | Increased demand for services, particularly for preventative care and chronic disease management. | Similar to primary care, likely slight increase, but may not fully cover costs. | Potential for longer wait times for appointments, need for increased capacity. |
| Rural Hospitals | Increased patient volume, but potentially strained finances due to lower Medicaid reimbursement rates. | Potential for slight increase, but may not be sufficient to offset financial losses. | Financial sustainability concerns, potential for service reductions or closures. |
| Mental Health Providers | Significant increase in demand for services, addressing unmet needs of the newly insured population. | Potential for increased demand, but reimbursement rates may remain a concern. | Need for additional workforce training and resources, ensuring adequate staffing levels. |
Summary
The debate surrounding North Carolina Medicaid expansion is far from over. While the potential benefits – improved health outcomes, economic growth, and reduced health disparities – are compelling, the financial and political hurdles remain substantial. Ultimately, the decision will hinge on a careful balancing act, weighing the needs of the uninsured against the concerns of taxpayers and policymakers.
The path forward requires open dialogue, data-driven analysis, and a commitment to finding solutions that serve the best interests of all North Carolinians.
Expert Answers
What are the main arguments against Medicaid expansion in North Carolina?
Opponents often cite concerns about increased state spending and the potential impact on the state budget. There are also concerns about the long-term sustainability of the program and potential administrative challenges.
How would Medicaid expansion affect taxes in North Carolina?
The potential impact on taxes is a complex issue. While federal funds would cover a significant portion of the cost, the state would still need to contribute, potentially leading to tax increases or cuts in other areas of the budget. The exact impact is subject to ongoing debate and projections.
What types of services would be covered under expanded Medicaid?
Expanded Medicaid would likely cover a broad range of services, including doctor visits, hospital care, prescription drugs, and mental health services. The specific services covered could vary based on the final plan adopted by the state.