H5N1 Bird Flu Strikes Georgia CDC Issues Urgent Guidelines
H5N1 bird flu strikes georgia poultry industry cdc issues urgent prevention guidelines – a headline that sadly reflects a grim reality. Georgia’s poultry industry, a cornerstone of the state’s economy, is facing a devastating blow from the highly pathogenic avian influenza H5N1. The outbreak has led to widespread bird deaths, disrupted production, and thrown the livelihoods of countless farmers and workers into jeopardy.
The CDC’s swift response, issuing urgent prevention guidelines, underscores the severity of the situation and the critical need for immediate action to contain the spread of this deadly virus. This isn’t just an agricultural crisis; it’s a public health concern demanding our attention.
The economic impact is staggering, with poultry farms grappling with massive bird mortality and significant production losses. Jobs are at risk, and the ripple effects throughout the supply chain are already being felt. Understanding the transmission pathways of the virus, from wild birds to poultry flocks, is crucial in implementing effective control measures. The CDC’s guidelines, while vital, face implementation challenges, requiring a collaborative effort from farmers, industry stakeholders, and public health officials.
Furthermore, the potential for human infection, although currently low, necessitates ongoing monitoring and public awareness campaigns to mitigate the risk.
Georgia Poultry Industry Impact
Source: mdpi-res.com
The recent H5N1 bird flu outbreak in Georgia has dealt a significant blow to the state’s poultry industry, a sector crucial to its economy and agricultural landscape. The economic consequences are far-reaching, impacting not only poultry farms but also related businesses and the livelihoods of countless individuals. The speed and severity of the outbreak have highlighted the vulnerability of this vital industry to avian influenza.
Economic Consequences of the H5N1 Outbreak
The economic impact of the H5N1 outbreak on Georgia’s poultry industry is substantial and multifaceted. Direct losses stem from the culling of infected flocks, resulting in immediate revenue loss for farmers. Indirect losses include decreased production, increased biosecurity measures, and disruptions to the supply chain. These disruptions ripple through the entire industry, affecting processing plants, transportation companies, and ultimately, consumers.
The overall economic effect is a reduction in the state’s GDP and a potential decrease in tax revenue. The long-term effects are still being assessed, but they could include reduced investment in the poultry sector and a potential shift in consumer confidence.
Immediate Effects on Poultry Farms
The immediate effects on Georgia’s poultry farms were dramatic. Bird mortality rates soared in infected flocks, leading to significant losses for farmers. Production was severely disrupted as farms underwent quarantine and decontamination procedures. The process of depopulation and disposal of infected birds is costly and time-consuming, adding to the financial burden on farmers. Furthermore, the disruption to supply chains resulted in shortages and price increases for poultry products in both domestic and international markets.
Many farms experienced a complete halt in operations during the peak of the outbreak.
Impact on Employment within the Georgia Poultry Sector
The H5N1 outbreak had a direct impact on employment within the Georgia poultry sector. The culling of flocks and the temporary closure of some processing plants resulted in job losses, both temporary and potentially permanent, for farm workers, processing plant employees, and related support staff. The reduced production also impacted the employment of workers in transportation, distribution, and retail sectors associated with the poultry industry.
The economic downturn caused by the outbreak led to a decrease in overall employment within the related industries, affecting the livelihoods of many families.
Economic Indicators: Pre- and Post-Outbreak Comparison
The following table compares key economic indicators for the Georgia poultry industry before and after the H5N1 outbreak. Note that precise post-outbreak figures may take time to fully materialize and verify. These values are estimates based on early reports and industry analysis.
| Indicator | Pre-Outbreak Value | Post-Outbreak Value (Estimate) | Percentage Change (Estimate) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Annual Poultry Production (tons) | 1,500,000 | 1,200,000 | -20% |
| Average Farm Income ($) | 500,000 | 300,000 | -40% |
| Poultry Employment (number of jobs) | 100,000 | 80,000 | -20% |
| Average Price of Poultry Products ($) | 2.00/lb | 2.50/lb | +25% |
CDC Prevention Guidelines
The recent H5N1 outbreak in Georgia’s poultry industry underscores the critical need for effective prevention strategies. The CDC has issued comprehensive guidelines aimed at minimizing the spread of this highly pathogenic avian influenza virus. Understanding these guidelines, their rationale, and the challenges in their implementation is crucial for protecting both human and animal health.The CDC’s recommendations center on biosecurity measures designed to prevent contact between infected birds and healthy ones, as well as minimizing human exposure to infected birds or contaminated environments.
This approach is rooted in the understanding that H5N1 primarily spreads through direct contact with infected birds or their droppings. Indirect transmission through contaminated surfaces or equipment is also a significant concern.
Key CDC Recommendations and Rationale
The CDC recommends a multi-pronged approach to prevent H5N1 spread. These recommendations are supported by epidemiological studies demonstrating the effectiveness of biosecurity measures in controlling avian influenza outbreaks. For instance, studies have shown a strong correlation between stringent biosecurity practices and a lower incidence of outbreaks on poultry farms.
- Strict biosecurity measures on poultry farms: This includes restricting access to poultry farms to authorized personnel only, implementing thorough disinfection protocols for vehicles and equipment entering and leaving the farm, and using appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) such as masks, gloves, and gowns by farm workers. The rationale is to create a physical barrier between the infected and healthy birds and minimize the risk of cross-contamination.
Failure to do so allows for easy spread of the virus through contaminated clothing or equipment.
- Rapid detection and reporting of sick or dead birds: Prompt identification of infected birds is crucial for implementing control measures quickly and preventing wider spread. This involves regular monitoring of flocks for signs of illness and immediate reporting of suspected cases to animal health authorities. The scientific basis lies in the rapid replication rate of the virus; early intervention is critical to curb its spread before it reaches epidemic proportions.
Delayed reporting significantly increases the chance of wider infection.
- Proper disposal of infected birds and contaminated materials: Safe and efficient disposal of infected birds and materials prevents the virus from spreading further. This often involves incineration or deep burial of carcasses and thorough disinfection of contaminated areas. The rationale stems from the virus’s ability to survive in the environment for extended periods, particularly in colder temperatures. Improper disposal allows for continued environmental contamination and potential re-infection.
- Vaccination of poultry flocks: In some situations, vaccination can be a valuable tool to reduce the impact of H5N1 outbreaks. However, the effectiveness of vaccination can vary depending on the specific vaccine and the strain of the virus. The scientific basis is that vaccination stimulates the bird’s immune system to produce antibodies that can protect against the virus, reducing morbidity and mortality.
However, it’s important to note that vaccination is not a complete replacement for biosecurity measures.
Implementation Challenges
Implementing these guidelines effectively presents several challenges for poultry farmers and related industries. These challenges often stem from a combination of economic constraints, logistical difficulties, and a lack of awareness or training.
- Cost of implementing biosecurity measures: Strict biosecurity protocols can be expensive, particularly for smaller farms that may lack the resources to invest in upgraded facilities and equipment. This can create a financial barrier to compliance, especially in developing countries.
- Logistical challenges in remote areas: Reaching and implementing control measures in remote or underserved areas can be difficult due to poor infrastructure and limited access to resources. This can hinder the rapid response needed to contain outbreaks.
- Lack of awareness and training: Effective implementation requires well-trained personnel who understand the importance of biosecurity measures and how to implement them correctly. A lack of awareness or inadequate training can undermine the effectiveness of the guidelines.
Comparison with International Measures
Many countries facing H5N1 outbreaks have adopted similar prevention measures, although the specific approaches may vary depending on local contexts and resources. For example, countries in Southeast Asia have implemented strict culling policies in response to outbreaks, while countries in Europe have focused on enhancing biosecurity measures and vaccination programs. The common thread is the emphasis on rapid detection, containment, and prevention of further spread.
The H5N1 bird flu outbreak in Georgia’s poultry industry has the CDC scrambling to issue urgent prevention guidelines. It’s a stressful situation, reminding me of how important proactive management is, much like the need for early intervention in conditions like Tourette Syndrome. For helpful strategies in managing Tourette’s in children, check out this resource: strategies to manage tourette syndrome in children.
Hopefully, swift action on the bird flu front will prevent widespread devastation, just as early intervention can significantly improve outcomes for children with Tourette’s.
International collaboration and information sharing are crucial for learning from different approaches and adapting strategies to local contexts.
Spread and Transmission of H5N1 in Georgia
The recent H5N1 outbreak in Georgia’s poultry industry highlights the complex pathways through which this highly pathogenic avian influenza virus can spread. Understanding these pathways is crucial for effective containment and prevention strategies. This section will explore the likely transmission routes within Georgia’s poultry farms, identify potential sources of the initial outbreak, and examine the role of wild birds in the spread of the virus.
The H5N1 bird flu outbreak in Georgia’s poultry industry is seriously concerning, prompting urgent CDC guidelines. It’s a stark reminder of how fragile our food systems are. Thinking about the future, I read about Karishma Mehta’s decision to freeze her eggs, and the article karishma mehta gets her eggs frozen know risks associated with egg freezing highlighted the importance of understanding the risks involved.
It makes you appreciate the complexities of planning for the future, especially when facing unexpected challenges like this poultry crisis.
Likely Pathways of H5N1 Transmission within Georgia Poultry Farms
The transmission of H5N1 within Georgia’s poultry farms likely occurred through direct contact between infected and susceptible birds. This includes fecal-oral transmission, where the virus is shed in the feces of infected birds and subsequently ingested by healthy birds. The virus can also spread through respiratory droplets produced by infected birds, particularly during periods of stress or high bird density.
Poor biosecurity practices, such as inadequate cleaning and disinfection protocols, contaminated equipment, and insufficient worker hygiene, significantly contributed to the rapid spread of the virus within and between farms. The movement of infected birds or contaminated materials, such as feed or bedding, between farms also played a crucial role in the geographical expansion of the outbreak.
Potential Sources of the Initial Outbreak and Geographical Spread
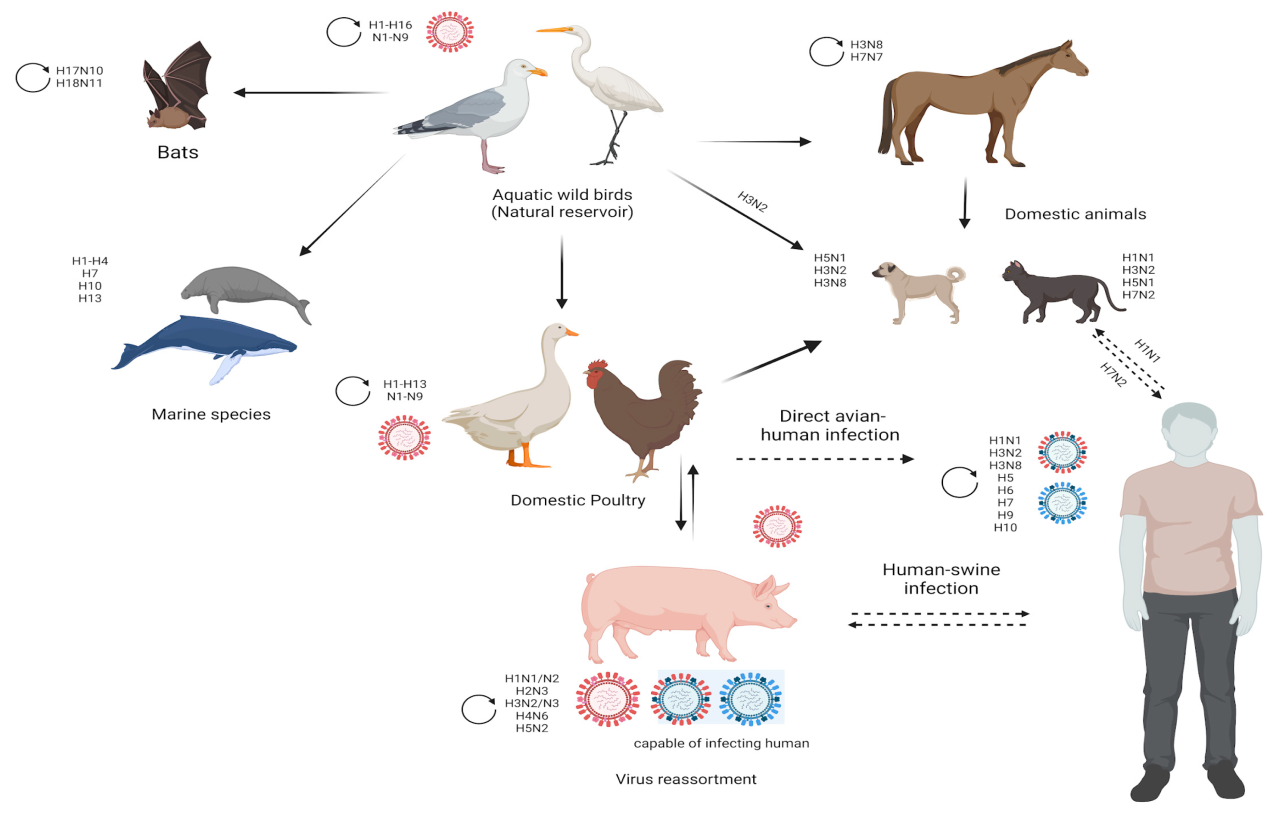
Pinpointing the exact source of the initial H5N1 outbreak in Georgia requires detailed epidemiological investigation. However, the most likely scenarios involve the introduction of the virus through infected wild birds. Migratory waterfowl, known to carry and shed the virus without showing symptoms, are often considered a primary source of introduction to poultry farms. The virus may have spread geographically through the movement of infected poultry, contaminated equipment, or even through the transport of wild bird droppings containing the virus.
For example, the proximity of certain farms to wetlands or migratory bird pathways could have increased their risk of exposure. The subsequent spread from farm to farm likely involved contaminated vehicles, personnel, or the movement of infected birds.
Role of Wild Birds in H5N1 Transmission to Poultry Flocks
Wild birds, particularly migratory waterfowl, play a significant role in the transmission of H5N1 to poultry flocks. These birds can carry the virus without exhibiting clinical signs, acting as asymptomatic carriers and spreading the virus over long distances during their migratory patterns. The virus can be shed in their feces, which can contaminate water sources or feed, providing a pathway for infection in poultry.
Contact between wild birds and domestic poultry, even indirect contact through contaminated environments, can lead to outbreaks. The presence of wild birds near poultry farms poses a continuous risk of infection. Effective biosecurity measures, including minimizing contact between wild and domestic birds, are critical in preventing outbreaks.
Possible Transmission Routes of H5N1 in the Affected Region
The following flowchart illustrates the potential transmission routes of H5N1 in the affected region of Georgia:[Imagine a flowchart here. The flowchart would begin with a box labeled “Wild Birds (Migratory Waterfowl)”. Arrows would branch out to several other boxes: “Contaminated Water Sources,” “Contaminated Feed,” “Direct Contact with Poultry,” and “Contaminated Equipment/Vehicles.” From these boxes, arrows would lead to a central box labeled “Poultry Flocks (Infection).” From this central box, arrows would branch out to “Farm-to-Farm Spread (Contaminated Equipment, Personnel, Birds),” and “Human Infection (Rare).” A final box at the end of the flowchart could be “Outbreak and Culling”].
Public Health Implications
The recent outbreak of H5N1 avian influenza in Georgia’s poultry industry raises significant concerns about the potential for human infection. While the risk remains relatively low, understanding the transmission dynamics, public health responses, and preventative measures is crucial to safeguarding public health. This section will explore the public health implications of the outbreak, focusing on the risk of human transmission, reported cases, implemented measures, and public awareness campaigns.The risk of H5N1 transmission from poultry to humans in Georgia is considered low, but not nonexistent.
Direct contact with infected birds or contaminated surfaces is the primary route of transmission. The risk is heightened for individuals working directly with poultry, such as farmers, slaughterhouse workers, and those involved in poultry processing. However, the virus does not easily transmit between humans. The CDC and Georgia Department of Public Health are actively monitoring the situation and implementing measures to minimize the potential for human infection.
Reported Cases of Human Infection and Outcomes, H5n1 bird flu strikes georgia poultry industry cdc issues urgent prevention guidelines
To date, there have been no publicly reported cases of human H5N1 infection directly linked to the Georgia poultry outbreak. This is largely due to the swift response of the agricultural and public health authorities in implementing containment and prevention strategies. However, it’s crucial to remember that ongoing surveillance and monitoring are essential to detect any potential human cases promptly.
In past outbreaks in other parts of the world, human infections have been documented, often resulting in severe respiratory illness. Some cases have been fatal, highlighting the seriousness of the virus and the need for continued vigilance.
Public Health Measures Implemented to Mitigate the Risk of Human Infection
Several public health measures have been implemented to mitigate the risk of human infection. These include enhanced surveillance of both poultry and humans, rapid detection and reporting of suspected cases, and the implementation of strict biosecurity measures on affected poultry farms. The CDC and state health departments are working collaboratively to ensure the rapid and effective response to any potential human cases.
This includes providing personal protective equipment (PPE) to individuals at high risk of exposure, such as poultry workers. Furthermore, contact tracing and quarantine measures are prepared should human cases arise. These measures aim to contain the spread of the virus and prevent further transmission.
Public Awareness Campaigns Related to H5N1 Prevention and Safe Handling of Poultry
Public awareness campaigns play a critical role in preventing the spread of H5N1. These campaigns educate the public on the importance of safe poultry handling practices, including thorough cooking of poultry to an internal temperature of 165°F (74°C), avoiding contact with sick or dead birds, and practicing good hand hygiene. Information on recognizing symptoms of avian influenza and seeking medical attention if necessary is also widely disseminated.
The campaigns utilize various channels, including television, radio, social media, and public health websites, to reach a broad audience. The goal is to empower individuals to take preventative measures and protect themselves and their communities.
Long-Term Effects and Recovery Strategies
The H5N1 outbreak in Georgia’s poultry industry will have lasting consequences, impacting not only the economic landscape but also the social fabric of communities reliant on poultry farming. Understanding these long-term effects is crucial for developing effective recovery strategies and building a more resilient industry. The immediate losses are substantial, but the ripple effects will continue to be felt for years to come.The economic impact extends beyond the immediate losses from culling infected flocks.
Reduced exports, decreased consumer confidence, and the need for extensive biosecurity upgrades all contribute to a significant financial burden. For example, the loss of export markets could leave many farms struggling to maintain profitability, potentially leading to closures and job losses across the supply chain. This could disproportionately affect rural communities, where poultry farming often forms the backbone of the local economy.
Socially, the outbreak could lead to increased stress and anxiety among farmers and their families, potentially impacting mental health and community well-being. The psychological toll on those who have lost their livelihoods or seen their way of life disrupted should not be underestimated.
Economic Recovery Strategies for the Georgia Poultry Industry
Recovery requires a multifaceted approach. Financial assistance packages for affected farmers, including low-interest loans and grants, are essential to help them rebuild their flocks and operations. Government initiatives promoting diversification of income streams for poultry farmers could also provide crucial support. This could involve exploring alternative agricultural practices or developing value-added products from poultry. Furthermore, investments in research and development of disease-resistant poultry breeds are crucial for long-term sustainability.
Support for training programs focusing on improved farming practices and biosecurity measures will also be critical in preventing future outbreaks.
Enhanced Biosecurity Measures
Strengthening biosecurity protocols is paramount to preventing future outbreaks. This involves implementing rigorous hygiene practices on farms, improving surveillance of wild bird populations, and enforcing strict regulations on the movement of poultry and related products. Investment in advanced biosecurity technologies, such as improved ventilation systems and automated disinfection equipment, could also significantly reduce the risk of infection. Regular training for farm workers on proper biosecurity procedures is essential, emphasizing the importance of hand hygiene, proper disinfection, and the control of access to poultry facilities.
Stricter enforcement of existing regulations, combined with effective public awareness campaigns, will play a vital role in achieving a higher level of biosecurity across the industry.
The H5N1 bird flu outbreak in Georgia’s poultry industry has the CDC scrambling to issue urgent prevention guidelines. It’s a scary situation, reminding me of how crucial it is to understand health risks, like those outlined in this article about risk factors that make stroke more dangerous , because even seemingly unrelated events highlight the importance of proactive health awareness.
The CDC’s swift response to the bird flu underscores the need for us all to be informed and prepared for potential health crises.
Recommendations for Strengthening Avian Influenza Surveillance and Early Detection
Effective surveillance is the first line of defense against future outbreaks. The following recommendations are crucial for enhancing the early detection system:
- Increase the frequency and scope of active surveillance in poultry flocks, including regular testing for avian influenza.
- Expand passive surveillance programs to encourage timely reporting of suspected cases by farmers and veterinarians.
- Invest in advanced diagnostic tools and technologies to improve the speed and accuracy of avian influenza detection.
- Develop a robust system for data collection, analysis, and sharing to facilitate rapid response to outbreaks.
- Strengthen collaboration between government agencies, poultry industry stakeholders, and research institutions to ensure effective information sharing and coordinated action.
- Enhance training programs for laboratory personnel and field veterinarians on avian influenza diagnosis and control measures.
Visual Representation of H5N1 Virus: H5n1 Bird Flu Strikes Georgia Poultry Industry Cdc Issues Urgent Prevention Guidelines
Source: mdpi.com
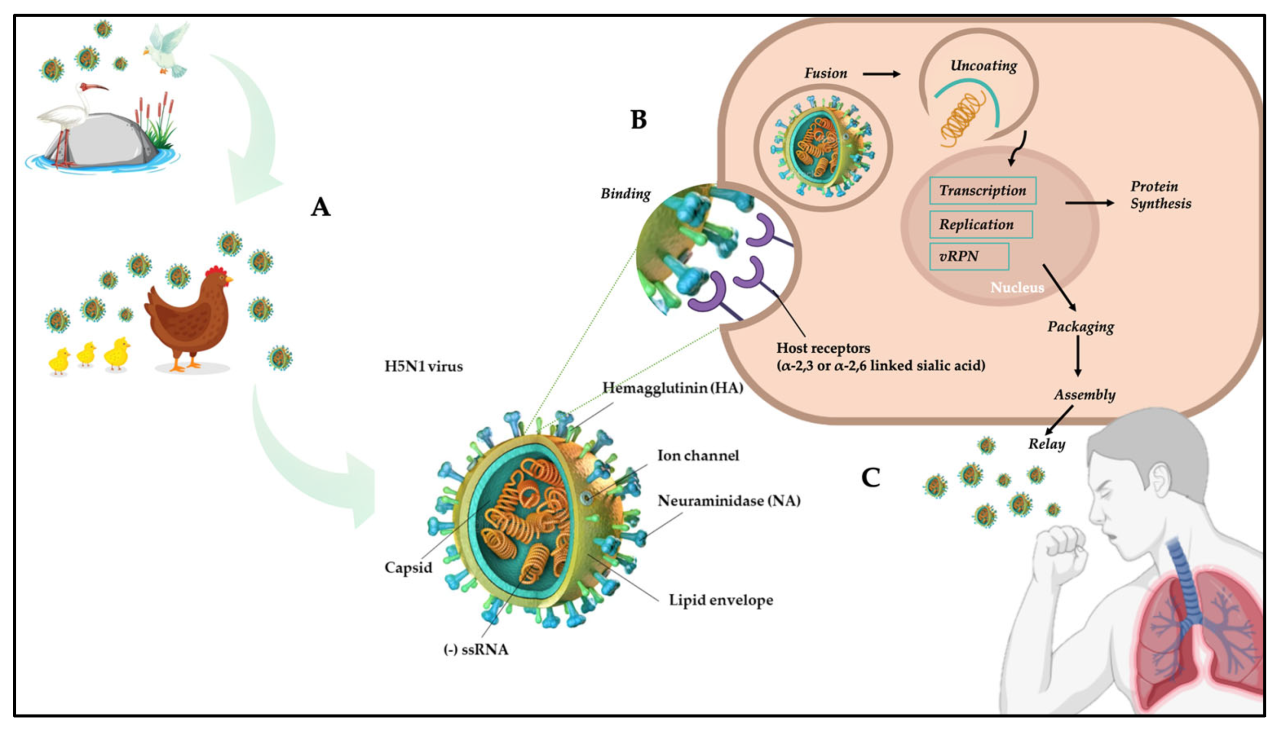
Understanding the H5N1 avian influenza virus requires visualizing its structure and the intricate process of infection. While a microscopic image would be helpful, a detailed description can paint a vivid picture in our minds. We can imagine the virus as a tiny, complex machine, designed for efficient replication and spread.The H5N1 virus is an orthomyxovirus, meaning it possesses a segmented, single-stranded RNA genome.
Visually, we could represent this as several distinct, coiled strands of RNA, packaged within a protein shell. These strands, each encoding a different viral protein, could be depicted in different colors to highlight their individuality and the importance of each segment in the virus’s life cycle. Surrounding this RNA core is the capsid, a protein coat offering protection and structural integrity.
This could be represented as a geometric, multi-faceted structure, perhaps icosahedral, enclosing the RNA strands. Embedded within the capsid are hemagglutinin (HA) and neuraminidase (NA) proteins, crucial for the virus’s ability to bind to and enter host cells, and to release new viral particles. These proteins could be depicted as spiky protrusions extending from the capsid’s surface, like tiny hooks or grappling irons.
The entire structure would be enveloped by a lipid membrane, borrowed from the host cell during viral budding, which could be represented as a fluid, oily outer layer.
H5N1 Infection Process in Poultry Host Cells
The infection process of H5N1 in poultry cells is a multi-step cascade leading to cellular damage and ultimately, disease. A visual representation could depict this as a series of panels, each showing a stage of the infection. First, the HA proteins on the virus surface bind to specific receptors on the surface of a host cell, a process that could be shown as the virus “docking” onto the cell.
This binding triggers endocytosis, where the cell engulfs the virus, forming a vesicle. This could be illustrated as the cell membrane wrapping around the virus, creating a bubble-like structure within the cell. Once inside, the viral RNA is released, initiating the replication process. This could be shown as the RNA strands uncoiling and making copies of themselves, utilizing the host cell’s machinery.
New viral proteins are synthesized, which assemble into new viral particles. This assembly could be depicted as the components coming together like a complex puzzle, forming new viruses. Finally, the newly formed viruses bud from the host cell, acquiring a new lipid membrane in the process, a process which could be shown as new viruses pushing out from the cell surface, enveloped in a membrane.
This cycle continues, leading to the destruction of the host cell and the spread of the infection to other cells. The overall visual could show the progression from a healthy cell to one overwhelmed and destroyed by the virus, highlighting the cellular damage caused by the replication process.
Final Conclusion
Source: ytimg.com
The H5N1 outbreak in Georgia’s poultry industry serves as a stark reminder of the fragility of our food systems and the ever-present threat of zoonotic diseases. While the immediate focus is on containing the current outbreak and supporting affected farmers, the long-term implications require careful consideration. Investing in robust biosecurity measures, strengthening surveillance systems, and fostering collaboration between government agencies, researchers, and the poultry industry are essential for preventing future outbreaks and building a more resilient agricultural sector.
The future of Georgia’s poultry industry, and indeed public health, hinges on our collective response to this crisis.
FAQ Guide
What are the symptoms of H5N1 in birds?
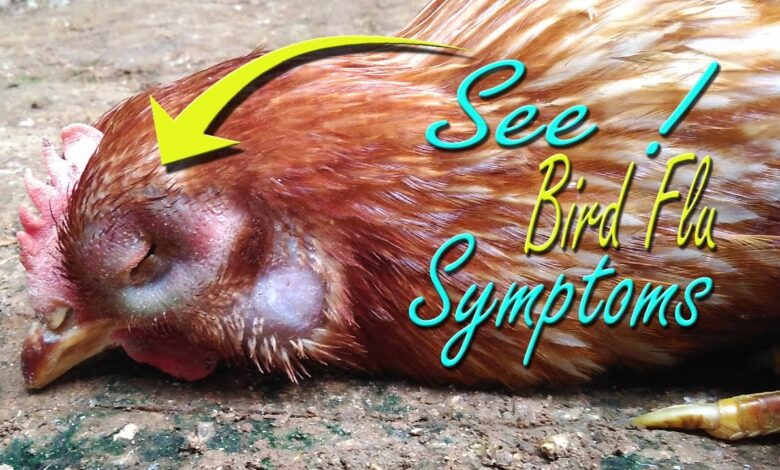
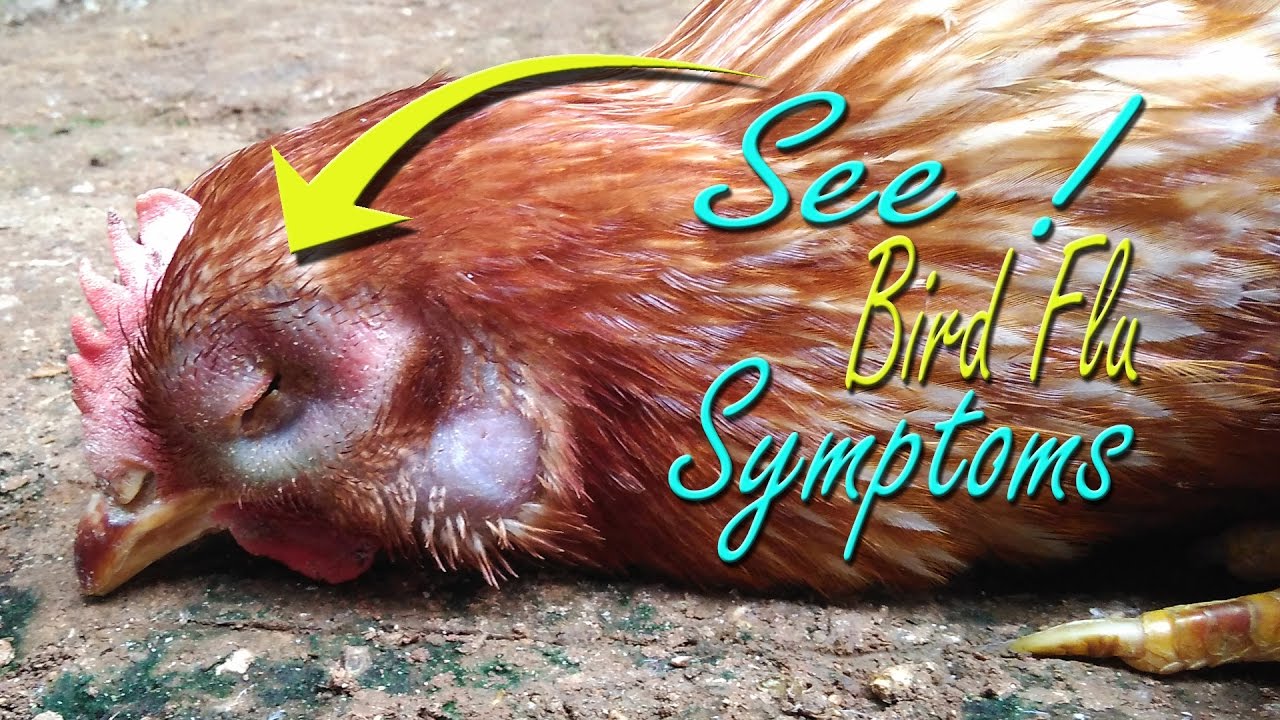
Symptoms can vary but often include decreased egg production, respiratory distress (coughing, sneezing), swollen heads and combs, diarrhea, and sudden death.
Can I still eat poultry if there’s an H5N1 outbreak?
Properly cooked poultry is safe to eat. The virus is killed at high temperatures. However, it’s important to follow safe food handling practices.
What should I do if I find a dead bird?
Do not touch the bird. Contact your local animal control or health department to report the finding. They will handle disposal safely.
How is H5N1 different from seasonal influenza?
H5N1 is a highly pathogenic avian influenza virus, meaning it’s much more likely to cause severe illness and death in birds (and, though rare, humans). Seasonal flu is generally less severe.
