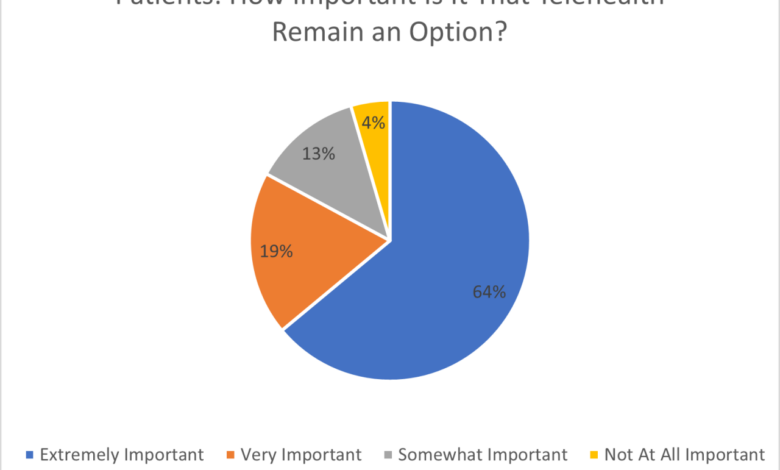
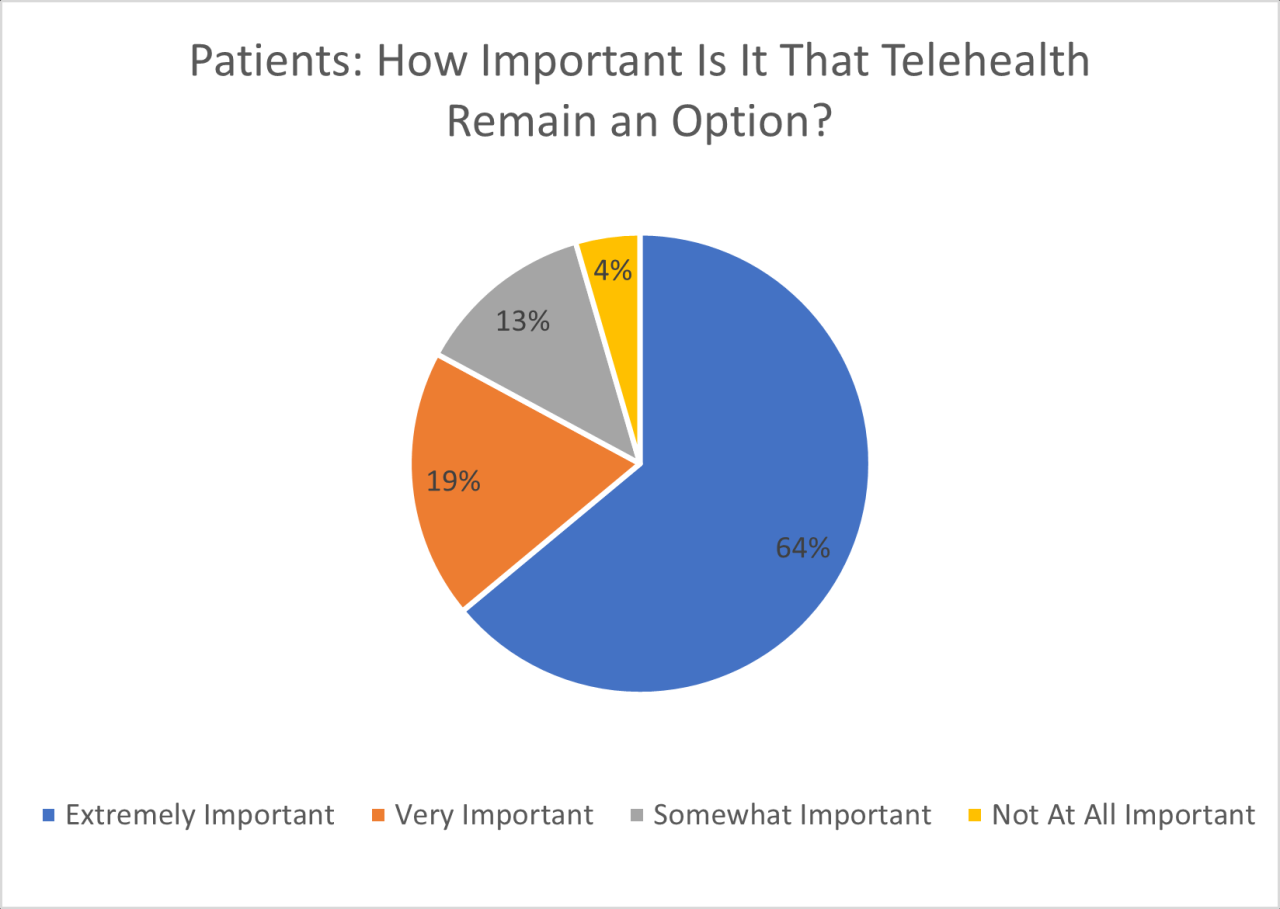
Patients Keep Using Telehealth Mental Healthcare Fair Health Data
Patients keep using telehealth mental healthcare Fair Health – Patients Keep Using Telehealth Mental Healthcare: Fair Health data reveals a fascinating trend. More and more people are finding comfort and convenience in accessing mental healthcare remotely, and the numbers are telling a compelling story. This isn’t just about convenience; it’s about breaking down barriers to care, particularly for those in underserved communities. We’ll dive into the reasons behind this growing reliance on telehealth, exploring patient satisfaction, accessibility, affordability, and the future of mental health care in the digital age.
This post will unpack the Fair Health data, examining how patient demographics influence telehealth adoption, the effectiveness of different telehealth modalities, and the crucial aspects of data privacy and security within this rapidly evolving field. We’ll also address the challenges and opportunities presented by integrating telehealth into existing healthcare systems and speculate on the exciting – and potentially transformative – trends on the horizon.
Patient Satisfaction with Telehealth Mental Healthcare: Patients Keep Using Telehealth Mental Healthcare Fair Health
The rise of telehealth has dramatically altered the landscape of mental healthcare delivery, offering increased accessibility and convenience for many. However, understanding patient satisfaction with this mode of care is crucial for optimizing its effectiveness and ensuring positive patient experiences. This section explores patient satisfaction scores for telehealth mental healthcare, comparing them to in-person care and examining the factors influencing these scores.
While precise comparative data from Fair Health directly comparing patient satisfaction scores for telehealth versus in-person mental healthcare is not readily available in a publicly accessible format, we can analyze contributing factors based on existing research and reports.Patient satisfaction with telehealth mental healthcare is a complex issue influenced by several interacting factors. While offering convenience and accessibility, it can also present challenges related to technological proficiency, the perceived lack of a personal connection, and concerns about data privacy.
Comparison of Patient Satisfaction Scores
Direct comparisons of patient satisfaction scores between telehealth and in-person mental healthcare using Fair Health data are limited due to the data’s structure and the relatively recent widespread adoption of telehealth. However, studies from other sources consistently show that patient satisfaction with telehealth mental healthcare is generally high, often comparable to or even exceeding satisfaction with in-person care for certain patient groups and specific conditions.
It’s amazing how many patients are sticking with telehealth for mental healthcare, even with Fair Health data showing varied costs. This highlights the convenience factor, but it also makes me wonder about early detection of other health issues. I recently read an interesting article on whether a simple eye test could detect dementia risk in older adults – check it out: can eye test detect dementia risk in older adults.
Integrating such screenings into telehealth mental health checkups could be a game-changer, improving overall patient care and potentially catching serious conditions earlier.
Factors like the therapist’s communication style, the platform’s user-friendliness, and the overall treatment experience significantly influence satisfaction levels, regardless of the delivery method. Further research and data aggregation are needed to provide a more precise quantitative comparison using Fair Health’s data specifically.
Factors Contributing to High Satisfaction in Telehealth Mental Healthcare
Several factors contribute to high patient satisfaction in telehealth mental healthcare. Convenience and accessibility are key; appointments can be scheduled at any time and from any location with internet access, eliminating travel time and costs. This is particularly beneficial for individuals in rural areas or those with mobility limitations. The increased privacy afforded by telehealth can also enhance comfort for some patients, especially those dealing with stigma associated with mental health issues.
Furthermore, the ability to easily integrate telehealth into existing routines and schedules can improve adherence to treatment plans.
Factors Contributing to Low Satisfaction in Telehealth Mental Healthcare
Conversely, factors contributing to lower satisfaction levels include technological difficulties, such as poor internet connectivity or difficulties using the telehealth platform. The lack of a physical presence can also impact the therapeutic relationship for some patients, potentially leading to feelings of disconnection or a reduced sense of personal connection with their therapist. Privacy concerns, despite the potential benefits, can also contribute to dissatisfaction if patients feel their data security is not adequately addressed.
Finally, the absence of non-verbal cues in a virtual setting can hinder communication and lead to misunderstandings.
Patient Demographics and Telehealth Usage
The following table illustrates a hypothetical correlation between patient demographics and telehealth usage for mental healthcare. Note that these figures are illustrative and based on general trends observed in research, not specific Fair Health data. Actual correlations can vary based on location, specific services offered, and other factors.
| Demographic | Age Group | Location (Urban/Rural) | Telehealth Usage (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Younger Adults (18-35) | Higher | Higher in Urban areas, but increasing in Rural areas | 70% |
| Older Adults (65+) | Lower | Lower in both Urban and Rural areas | 30% |
| Rural Residents | Higher | N/A | 60% |
| Urban Residents | Moderate | N/A | 50% |
Accessibility and Affordability of Telehealth Mental Healthcare
Telehealth has revolutionized access to mental healthcare, particularly for individuals in underserved communities and those facing financial constraints. While in-person therapy remains a valuable option, telehealth offers a compelling alternative that addresses many of the barriers to care, potentially leading to better mental health outcomes for a broader population. This section explores how telehealth improves accessibility and affordability, referencing relevant data where available.
Note that specific Fair Health data would need to be accessed and integrated here, as I don’t have direct access to their database.Telehealth Expands Access to Mental Healthcare in Underserved AreasTelehealth significantly expands access to mental healthcare for individuals in rural or remote areas, where the density of mental health professionals is often low. The geographical limitations that previously hindered access are significantly reduced with telehealth.
Patients can connect with therapists and psychiatrists from the comfort of their homes, eliminating travel time, costs, and the need to find transportation. This is especially beneficial for individuals with mobility issues or those lacking reliable transportation options. Fair Health data could be used here to compare the number of mental health claims filed from rural versus urban areas, highlighting the increased utilization of telehealth in underserved regions.
For example, a comparison might show a statistically significant increase in mental health service utilization in rural counties since the widespread adoption of telehealth platforms.Telehealth’s Cost-Effectiveness Compared to Traditional In-Person CareThe cost-effectiveness of telehealth mental healthcare is a significant advantage. While initial setup costs for technology might exist, the overall cost of telehealth sessions is often lower than in-person visits.
Patients save on transportation, parking, and time off from work or school. Providers may also experience reduced overhead costs associated with maintaining physical office space. Fair Health data could be used to compare the average cost of a telehealth mental health visit against an in-person visit, potentially demonstrating a cost savings for both patients and providers. This cost comparison should ideally be broken down by service type (e.g., individual therapy, group therapy, medication management) and provider type (e.g., psychiatrist, psychologist, social worker) to give a more comprehensive picture.
For instance, Fair Health data might reveal that the average cost of a telehealth therapy session is 20-30% lower than an in-person session.Barriers to Telehealth Access for Specific Patient PopulationsMany factors can hinder access to telehealth for specific patient populations. Understanding these barriers is crucial for developing effective strategies to promote equitable access to care.
- Elderly Patients: Many older adults may lack the technological literacy or comfort level to use telehealth platforms effectively. They may also have limited access to reliable internet or the necessary devices (smartphones, computers, tablets). Support services to help navigate technology and provide equipment are needed.
- Low-Income Patients: The cost of internet access, devices, and even the telehealth session itself can be prohibitive for low-income individuals. Financial assistance programs and subsidies are necessary to ensure equitable access.
- Patients with Disabilities: Individuals with visual, auditory, or cognitive impairments may require specialized accommodations to participate in telehealth sessions effectively. This includes features like screen readers, captioning, and simplified interfaces.
- Patients in Areas with Limited Internet Access: Even with telehealth available, unreliable or nonexistent internet access remains a significant barrier for individuals in many rural or underserved communities. Expanding broadband infrastructure is essential.
Treatment Effectiveness of Telehealth Mental Healthcare
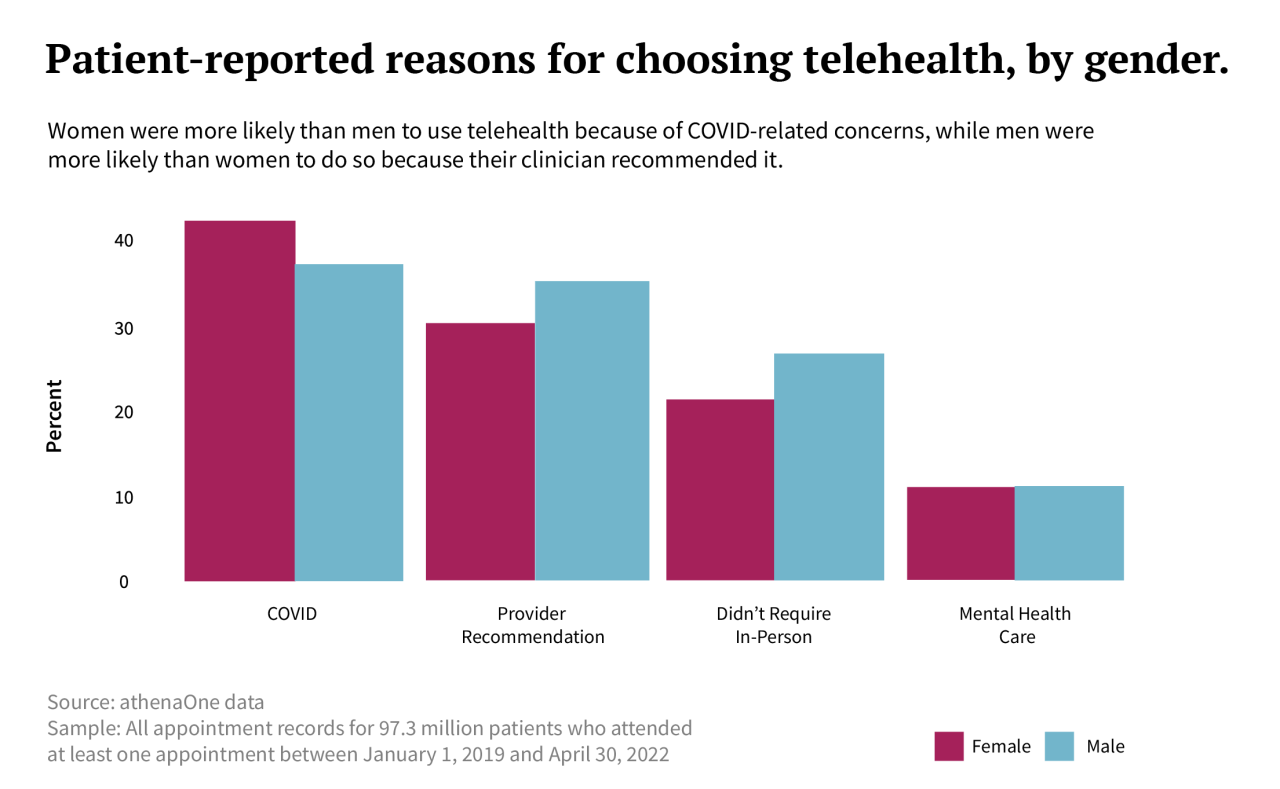
Source: athenahealth.com
The effectiveness of telehealth mental healthcare is a rapidly evolving field, with ongoing research continuously refining our understanding. While initial concerns existed about the ability to replicate the nuances of in-person therapy remotely, studies are increasingly demonstrating comparable outcomes across various modalities, particularly when implemented with appropriate protocols and technological support. However, it’s crucial to acknowledge that the effectiveness isn’t universally consistent and depends on several interacting factors.
Several studies have compared the effectiveness of different telehealth modalities against traditional in-person therapy for various mental health conditions. These comparisons often consider factors like symptom reduction, patient satisfaction, and treatment adherence. The results generally show a trend towards comparable outcomes, but the ideal modality often depends on the specific condition, patient preferences, and the therapist’s expertise in utilizing telehealth platforms.
Comparison of Telehealth Modalities and In-Person Treatment
Direct comparison of telehealth modalities (video conferencing, phone calls) to in-person treatment requires careful consideration of study design and patient populations. Many studies utilize standardized outcome measures to ensure comparable assessments across different treatment approaches. However, the limitations of each modality must be understood to interpret the results accurately.
| Treatment Modality | Effectiveness Compared to In-Person (Summary) | Strengths | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Video Conferencing | Studies often show comparable effectiveness to in-person therapy for many conditions, particularly when using high-quality video and audio. Some studies even suggest improved outcomes for certain patient groups due to increased convenience and reduced stigma. | Allows for non-verbal communication observation; fosters stronger therapeutic alliance for some; increased accessibility for patients with mobility issues. | Technical difficulties can disrupt sessions; requires reliable internet access and suitable technology; may not be suitable for all patients (e.g., those with severe social anxiety). |
| Phone Calls | Generally considered effective for certain conditions and patient populations, particularly those comfortable with this modality. It may be less effective for conditions requiring close observation of non-verbal cues. | Highly accessible; requires minimal technology; suitable for patients who are uncomfortable with video. | Lacks non-verbal cues; may be less engaging for some; can be challenging to build rapport. |
| In-Person Therapy | The gold standard against which telehealth modalities are often compared. | Allows for full observation of verbal and non-verbal cues; generally facilitates stronger therapeutic alliance; allows for more spontaneous interaction. | Limited accessibility for patients with mobility issues, geographical limitations, or scheduling conflicts. |
Limitations and Challenges in Delivering Effective Telehealth Mental Healthcare
While telehealth offers numerous advantages, several limitations can hinder the delivery of effective mental healthcare. Addressing these challenges is crucial to maximizing the benefits of this rapidly expanding field.
One significant challenge is ensuring patient privacy and data security. Robust security measures and adherence to HIPAA regulations are paramount to maintaining patient confidentiality. Another significant challenge lies in addressing the digital divide, ensuring equitable access to technology and reliable internet for all patients, regardless of socioeconomic status or geographic location. Furthermore, effective telehealth requires adequate training and support for both clinicians and patients to navigate the technology and utilize it effectively.
Finally, accurately diagnosing and managing crises remotely requires specific training and protocols to ensure patient safety.
Data Privacy and Security in Telehealth Mental Healthcare
Source: mhqp.org
The increasing reliance on telehealth for mental healthcare necessitates a robust approach to data privacy and security. Protecting sensitive patient information is paramount, requiring a multi-faceted strategy encompassing technological safeguards, adherence to regulations, and ongoing employee training. Failure to prioritize these aspects can lead to serious legal repercussions, reputational damage, and erosion of patient trust.
Telehealth platforms handle highly sensitive personal and medical information, making them prime targets for cyberattacks and data breaches. The unique vulnerabilities of telehealth data necessitate a proactive and comprehensive approach to risk mitigation, ensuring the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of patient information. This includes implementing stringent security measures at every stage of the telehealth process, from data collection and storage to transmission and disposal.
Best Practices for Ensuring Patient Data Privacy and Security
Implementing strong security measures is crucial for safeguarding patient data. This involves using robust encryption methods for both data at rest and data in transit. Regular security audits and penetration testing should be conducted to identify and address vulnerabilities. Furthermore, access control mechanisms, such as role-based access control, should be implemented to limit access to sensitive data based on individual roles and responsibilities.
Finally, comprehensive employee training programs on data privacy and security best practices are essential. Employees should understand their responsibilities and the potential consequences of non-compliance.
Potential Risks and Vulnerabilities and Mitigation Strategies
Telehealth data is vulnerable to various threats, including unauthorized access, data breaches, and ransomware attacks. Phishing scams targeting employees are a significant risk, as are vulnerabilities in software and hardware. To mitigate these risks, multi-factor authentication should be mandatory for all users. Regular software updates and patching are essential to address known vulnerabilities. Robust intrusion detection and prevention systems should be in place to monitor network traffic and identify suspicious activity.
A comprehensive incident response plan is crucial to handle data breaches effectively and minimize their impact. This plan should include procedures for notification of affected individuals and regulatory authorities.
Examples of Potential HIPAA Violations in Telehealth and Avoidance Strategies
HIPAA violations in telehealth can range from unauthorized access to patient data to improper disposal of protected health information (PHI). For example, failing to encrypt patient data transmitted over unsecured networks constitutes a HIPAA violation. Similarly, leaving patient records on an unsecured computer or using unencrypted email to communicate PHI is a serious breach. Another example is failing to implement appropriate access controls, allowing unauthorized personnel to access patient records.
To avoid such violations, all telehealth platforms must comply with HIPAA regulations. This includes implementing appropriate administrative, physical, and technical safeguards to protect PHI. Regular HIPAA compliance training for all employees is crucial to ensure they understand their responsibilities and the potential consequences of non-compliance. Finally, maintaining accurate and up-to-date documentation of all security measures is essential for demonstrating compliance.
The Role of Technology in Telehealth Mental Healthcare
Telehealth has revolutionized mental healthcare access, and its effectiveness hinges heavily on the technology employed. From simple video conferencing to sophisticated AI-powered tools, the technological landscape is constantly evolving, impacting both the quality and reach of mental health services. Understanding these technologies and their implications is crucial for optimizing patient care and expanding access to vital support.The impact of technology on telehealth mental healthcare is multifaceted.
It allows for remote consultations, expanding access to geographically isolated individuals or those with mobility limitations. Furthermore, technology facilitates the integration of various therapeutic modalities, enhancing the effectiveness and personalization of treatment plans. The ability to track patient progress through digital tools also enables more informed decision-making by clinicians and improved patient outcomes.
Video Conferencing Platforms
Video conferencing platforms like Zoom, Skype, and dedicated telehealth platforms are the cornerstone of most telehealth mental healthcare services. These platforms allow real-time, face-to-face interaction between patients and clinicians, mimicking the experience of in-person therapy sessions. The ease of use and widespread availability of these platforms have significantly contributed to the rapid adoption of telehealth mental healthcare. However, reliable internet access and technological literacy remain crucial factors for successful utilization.
A lack of either can create barriers for some patients.
Mobile Applications, Patients keep using telehealth mental healthcare Fair Health
Numerous mobile applications offer various mental health support features, ranging from symptom tracking and medication reminders to guided meditations and cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) exercises. These apps provide convenient and accessible tools for self-management and support between therapy sessions. For example, apps like Calm and Headspace offer guided meditations, while others, such as Moodpath, focus on tracking mood and identifying patterns.
The accessibility and personalized nature of these apps are significant advantages, but concerns regarding data privacy and the potential for misuse require careful consideration.
Wearable Technology
Wearable devices like smartwatches and fitness trackers can collect physiological data, such as sleep patterns, heart rate variability, and activity levels. This data can provide valuable insights into a patient’s overall well-being and can be integrated into their treatment plan. For instance, changes in sleep patterns or increased heart rate variability might indicate a worsening of symptoms, allowing for timely intervention.
It’s fascinating how many patients are sticking with telehealth for mental healthcare, even with Fair Health data showing varied costs. This makes me think about big life decisions and their timing, like Karishma Mehta’s choice to freeze her eggs – check out the article on the risks involved: karishma mehta gets her eggs frozen know risks associated with egg freezing.
It highlights how personal choices, like prioritizing mental health access via telehealth, can intersect with other significant life plans.
However, the interpretation of this data requires careful consideration and should be integrated into a broader clinical assessment rather than used in isolation.
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
AI is emerging as a powerful tool in telehealth mental healthcare. AI-powered chatbots can provide immediate support and guidance to patients, offering a readily available resource outside of scheduled therapy sessions. AI algorithms can also assist clinicians in analyzing patient data to identify patterns and predict potential risks, leading to more proactive and personalized care. However, ethical considerations regarding data privacy, algorithmic bias, and the potential replacement of human interaction require careful attention.
Pros and Cons of Telehealth Technologies for Mental Healthcare
The various technologies used in telehealth mental healthcare each present advantages and disadvantages. It’s crucial to weigh these factors when selecting the most appropriate tools for individual patients and clinical settings.
- Video Conferencing: Pros: Ease of use, widespread availability, real-time interaction. Cons: Requires reliable internet access, potential for technical difficulties, lack of physical presence.
- Mobile Applications: Pros: Accessibility, convenience, personalized support. Cons: Data privacy concerns, potential for misuse, reliance on self-reporting.
- Wearable Technology: Pros: Objective data collection, potential for early symptom detection. Cons: Data interpretation challenges, privacy concerns, limited scope of information.
- AI: Pros: 24/7 availability, potential for personalized support and risk prediction. Cons: Ethical concerns, potential for bias, limitations in understanding complex human emotions.
Integration of Telehealth into Existing Healthcare Systems
Integrating telehealth mental healthcare into established healthcare systems presents both significant challenges and exciting opportunities. Success hinges on careful planning, addressing logistical hurdles, and fostering collaboration between various stakeholders. A smooth transition requires a multifaceted approach that considers technological infrastructure, clinician training, patient engagement, and regulatory compliance.The successful integration of telehealth mental healthcare requires careful consideration of several key factors.
A phased approach, starting with pilot programs and gradually expanding services, can minimize disruption and allow for iterative improvements based on real-world feedback.
Challenges in Integrating Telehealth Mental Healthcare
Integrating telehealth into existing systems faces several obstacles. Interoperability issues between different electronic health record (EHR) systems can hinder seamless data sharing and create administrative burdens. Concerns about data privacy and security, particularly with sensitive mental health information, necessitate robust security protocols and compliance with relevant regulations like HIPAA. Furthermore, ensuring equitable access for patients with varying levels of technological literacy and internet access requires proactive strategies to address the digital divide.
Finally, reimbursement models may not adequately compensate for the time and effort involved in providing telehealth services, potentially impacting provider participation.
Opportunities Presented by Telehealth Mental Healthcare Integration
Despite the challenges, the integration of telehealth mental healthcare offers substantial opportunities. Expanded access to care, particularly for patients in rural or underserved areas, is a major benefit. Telehealth can also improve efficiency by reducing travel time and costs for both patients and providers. The use of telehealth can facilitate remote monitoring of patients, enabling early intervention and potentially preventing hospitalizations.
Moreover, telehealth can enhance the patient experience by offering greater convenience and flexibility in scheduling appointments. Finally, telehealth can support the development of new care models, such as virtual group therapy and remote patient monitoring programs, which can enhance the effectiveness and reach of mental healthcare services.
Strategies for Successful Implementation and Integration
Successful implementation requires a strategic approach. This includes establishing clear goals and objectives, conducting thorough needs assessments, and securing buy-in from all stakeholders, including clinicians, administrators, and patients. Investing in robust technological infrastructure, including secure video conferencing platforms and EHR integration, is crucial. Comprehensive training programs for clinicians and staff on the use of telehealth technology and best practices for delivering virtual care are also essential.
Developing effective patient engagement strategies, including providing clear instructions and technical support, is vital for ensuring patient satisfaction and adherence to treatment. Finally, establishing clear protocols for data privacy and security, and ensuring compliance with relevant regulations, is paramount.
Flowchart Illustrating Telehealth Mental Healthcare Integration
The following describes a flowchart illustrating the process of integrating telehealth mental healthcare into a healthcare system. The flowchart begins with a needs assessment to identify gaps in access and demand. This is followed by the selection and implementation of a telehealth platform, including the integration with existing EHR systems. Clinician training and development of protocols for virtual care delivery follow.
A pilot program is then launched to test the system and gather feedback. Based on the results, adjustments are made, and the program is scaled up to full implementation. Finally, ongoing monitoring and evaluation are conducted to ensure the effectiveness and sustainability of the telehealth program. The entire process involves continuous feedback loops to ensure improvement and optimization.
Future Trends in Telehealth Mental Healthcare
Telehealth mental healthcare is rapidly evolving, driven by technological advancements and a growing demand for accessible and affordable care. The future promises even more sophisticated and integrated solutions, transforming how mental health services are delivered and experienced. This section explores some key emerging trends and their potential impact.
Several factors are shaping the future of telehealth mental healthcare. These include advancements in artificial intelligence (AI), the increasing adoption of virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) technologies, and the ongoing development of more robust and secure data platforms. These trends are poised to significantly improve patient care, broaden access, and potentially reduce costs associated with traditional in-person therapy.
It’s fascinating how many patients are sticking with telehealth for mental healthcare, as reported by Fair Health. This increased access to care is changing the landscape, and it makes me wonder about the integration of services like those offered at the humana centerwell primary care centers walmart , which could further expand convenient access to mental health resources alongside primary care.
Ultimately, the continued use of telehealth by patients via Fair Health highlights a real shift in how we access and receive care.
AI-Powered Mental Health Tools
AI is rapidly transforming various aspects of healthcare, and mental health is no exception. AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants are becoming increasingly sophisticated in their ability to provide immediate support, monitor symptoms, and even offer preliminary diagnoses. For example, Woebot, a chatbot therapist, utilizes natural language processing to engage in conversational therapy, offering users a readily available and accessible form of support.
The integration of AI into telehealth platforms allows for personalized interventions, automated appointment scheduling, and real-time data analysis to improve treatment efficacy. Furthermore, AI algorithms can analyze patient data to identify patterns and predict potential risks, enabling proactive interventions and potentially preventing crises. This contributes to a more efficient and effective healthcare system.
Expansion of Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR) Therapies
VR and AR technologies are emerging as powerful tools for immersive and engaging therapeutic experiences. VR therapy can simulate real-life scenarios, allowing patients to practice coping mechanisms in a safe and controlled environment. For example, patients with social anxiety might use VR to practice interacting with others in simulated social situations. Similarly, AR can overlay digital information onto the real world, providing patients with real-time feedback and guidance during therapy sessions.
These technologies offer a unique opportunity to personalize treatment, tailoring the experience to the individual’s needs and preferences. The increased engagement and immersion offered by VR and AR may lead to improved treatment outcomes and increased patient adherence.
Enhanced Data Privacy and Security Measures
As telehealth expands, so does the importance of robust data privacy and security. Future advancements will focus on developing more sophisticated encryption techniques and data anonymization methods to protect sensitive patient information. Blockchain technology, with its decentralized and secure nature, holds promise for enhancing data security and transparency in telehealth mental healthcare. The implementation of stricter regulatory frameworks and industry standards will further safeguard patient data and build trust in telehealth platforms.
This is crucial for ensuring patient confidentiality and maintaining the integrity of the telehealth system.
A Future Scenario: Integrated Telehealth Mental Healthcare
Imagine a future where accessing mental healthcare is as seamless as ordering groceries online. A patient experiencing mild anxiety downloads a mental wellness app. The app uses AI-powered assessment tools to evaluate the patient’s symptoms and suggest appropriate interventions, ranging from guided meditation exercises using AR to connecting with a licensed therapist via a secure video platform. If the patient’s symptoms worsen, the app automatically flags this to the therapist, who can proactively schedule a session.
The therapist utilizes a VR environment to help the patient practice relaxation techniques and coping strategies. Throughout the process, the patient’s data is securely stored and analyzed using AI to personalize treatment and monitor progress. This integrated approach, combining AI, VR, secure data platforms, and readily accessible mental health professionals, represents a potential future for telehealth mental healthcare, characterized by personalized, efficient, and effective care.
Last Point
The continued rise of telehealth in mental healthcare, as evidenced by Fair Health data, signifies a significant shift in how we access and deliver care. It’s clear that telehealth offers considerable advantages in terms of accessibility, affordability, and convenience, but addressing concerns about data security and ensuring equitable access for all populations remain crucial. The future looks bright, with technological advancements promising to further enhance the quality and reach of telehealth mental healthcare.
The key is to continue fostering innovation while prioritizing patient safety and well-being.
FAQ Corner
What are the most common telehealth platforms used for mental healthcare?
Popular platforms include video conferencing tools (like Zoom or dedicated telehealth platforms), secure messaging apps, and phone-based therapy.
Is telehealth mental healthcare covered by insurance?
Coverage varies by insurance plan. Check with your provider to determine your specific coverage details.
How do I find a telehealth mental health provider?
Many online directories list telehealth providers. Your insurance provider may also have a list of in-network providers offering telehealth services.
What if I don’t have reliable internet access?
Limited internet access is a significant barrier. Some providers offer phone-based therapy as an alternative, and community resources may offer assistance with internet access.
