
Pregnancy Signs That Feel Like PMS
Pregnancy signs that feel like premenstrual syndrome (PMS) can be incredibly confusing! That familiar bloat, mood swings, and breast tenderness – is it Aunt Flo or a little one on the way? This post dives deep into the similarities and differences between PMS and early pregnancy symptoms, helping you navigate this potentially tricky territory. We’ll explore the timing of symptoms, unique pregnancy indicators, the role of hormones, and how lifestyle factors can play a part.
Ultimately, understanding these nuances can empower you to make informed decisions about your health.
We’ll break down the common symptoms, showing you how to distinguish between the two, and most importantly, when to seek professional medical advice. We’ll also look at ways to manage the symptoms of both PMS and early pregnancy, focusing on safe and effective strategies. Get ready to unravel the mystery of those early pregnancy symptoms that mimic PMS!
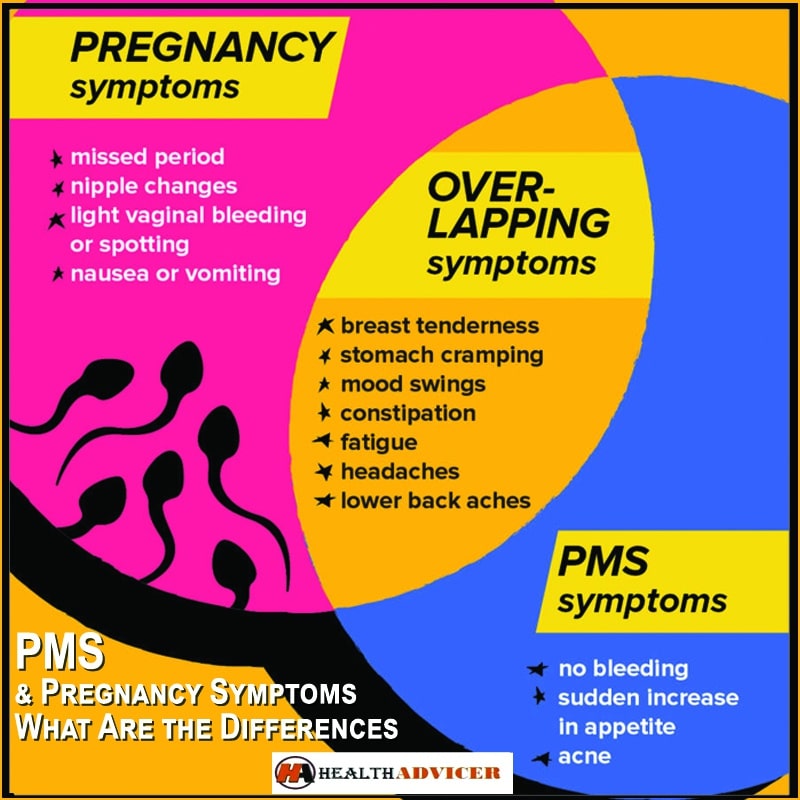
Overlapping Symptoms
The early days of pregnancy can be confusing, especially since many symptoms mirror those of premenstrual syndrome (PMS). This overlap can make it difficult to distinguish between the two, leading to uncertainty and anxiety. Understanding the similarities and differences between PMS and early pregnancy symptoms is crucial for navigating this period. This post will delve into the common symptoms experienced in both conditions, helping you better understand what you might be experiencing.
Both PMS and early pregnancy share a surprising number of symptoms, making early diagnosis challenging. The hormonal fluctuations responsible for PMS are also at play in the initial stages of pregnancy, leading to this overlap. However, the intensity, duration, and underlying causes differ significantly. Let’s explore these shared symptoms in more detail.
Common Symptoms in PMS and Early Pregnancy
Many women experience a range of physical and emotional changes during both PMS and early pregnancy. These shared symptoms often cause confusion, highlighting the need for clear distinctions. The following list details these frequently overlapping symptoms.
A significant number of women experience these symptoms in both PMS and early pregnancy. Understanding the nuances in intensity and duration is key to distinguishing between the two.
| Symptom | PMS Intensity | PMS Duration | PMS Timing | Early Pregnancy Intensity | Early Pregnancy Duration | Early Pregnancy Timing |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Breast tenderness | Mild to moderate | 7-10 days | Days before menstruation | Mild to severe | Weeks | From conception |
| Fatigue | Mild to moderate | 7-10 days | Days before menstruation | Mild to severe | Weeks to months | From conception |
| Mood swings | Mild to moderate | 7-10 days | Days before menstruation | Mild to severe | Weeks to months | From conception |
| Bloating | Mild to moderate | 7-10 days | Days before menstruation | Mild to moderate | Weeks | From conception |
| Nausea | Rare | Short | Days before menstruation | Mild to severe | Weeks to months | From conception, often later) |
| Cramps | Mild to severe | 1-7 days | During menstruation | Mild to moderate | Variable | Early pregnancy (implantation bleeding) |
| Headaches | Mild to moderate | 7-10 days | Days before menstruation | Mild to moderate | Variable | From conception |
| Food cravings/aversions | Mild to moderate | 7-10 days | Days before menstruation | Mild to severe | Weeks to months | From conception |
Symptom Timing and Progression
Differentiating between PMS and early pregnancy symptoms can be tricky because they often overlap. However, understanding the typical timeframe for each can provide valuable clues. While individual experiences vary, recognizing the patterns in symptom onset and duration can help you better understand your body’s signals.The timing of symptom appearance and their progression often differ significantly between PMS and early pregnancy.
This difference in temporal patterns can be a helpful distinguishing factor, though it’s crucial to remember that these are general trends, and exceptions exist.
PMS Symptom Timing
PMS symptoms typically begin a week or two before your period starts and usually resolve within a few days after your period begins. The severity and specific symptoms can vary from cycle to cycle, but the timing remains relatively consistent for each individual. For example, someone experiencing PMS might notice breast tenderness, bloating, mood swings, and food cravings starting around day 21 of a 28-day cycle, with symptoms peaking a few days before menstruation and then subsiding once their period begins.
Early Pregnancy Symptom Timing
Early pregnancy symptoms can begin as early as a week after conception, although this is not typical. Many women don’t notice any symptoms until they miss their period, which is usually around 4-6 weeks after conception. Symptoms may gradually increase in intensity over the first few weeks of pregnancy. For example, a woman might experience mild nausea at week 5, which intensifies to morning sickness by week 8.
Similarly, breast tenderness might be subtle at first and then become more pronounced as pregnancy progresses.
Differentiating Timing of Onset
The key difference in timing lies in the relationship to menstruation. PMS symptoms are closely tied to the menstrual cycle, appearing predictably before and resolving after menstruation. In contrast, early pregnancy symptoms often emergeafter* the expected start of the period. If you experience symptoms similar to PMS but your period is late, pregnancy is a strong possibility. However, irregular cycles can complicate this assessment.
For example, if a woman typically has irregular cycles, she may not notice a missed period, making the timing of symptom onset a less reliable indicator. This highlights the importance of considering other factors along with symptom timing.
Unique Pregnancy Indicators
While many early pregnancy symptoms mirror PMS, certain signs are more strongly suggestive of pregnancy than premenstrual syndrome. These unique indicators often stem from the physiological changes occurring as the fertilized egg implants and the body begins producing pregnancy hormones. Understanding these differences can provide valuable insight and reduce anxiety during the early stages of potential pregnancy.
Differentiating between PMS and early pregnancy can be challenging due to overlapping symptoms. However, certain signs, driven by hormonal shifts specific to pregnancy, are more reliable indicators. These symptoms arise from the implantation of the fertilized egg and the subsequent surge in hormones like human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG).
Implantation Bleeding
Implantation bleeding, a light spotting or bleeding that occurs around the time of a missed period, is a unique indicator of pregnancy. This bleeding differs from a regular menstrual period in that it’s usually lighter, shorter in duration, and often pinkish or brownish rather than bright red. It’s caused by the fertilized egg embedding itself into the uterine wall, which can cause minor blood vessel damage.
This is distinct from a regular menstrual period, which is caused by the shedding of the uterine lining. While not everyone experiences implantation bleeding, its presence, coupled with other symptoms, can be a significant clue.
Breast Changes
While breast tenderness and swelling can occur with PMS, the changes during pregnancy tend to be more intense and persistent. This is due to the hormonal surge that causes significant growth and development of the mammary glands in preparation for breastfeeding. The changes can include increased sensitivity, throbbing sensations, darkening of the areola, and the appearance of Montgomery’s tubercles (small bumps around the nipple).
The intensity and duration of these changes usually surpass what’s typically experienced with PMS.
Increased Basal Body Temperature
A sustained elevation in basal body temperature (BBT) beyond the typical post-ovulation rise is a key indicator. After ovulation, BBT typically rises slightly. However, in pregnancy, this elevated temperature remains high for an extended period, often several weeks. This sustained increase is attributed to the effect of progesterone, a hormone crucial for maintaining pregnancy, on the body’s thermoregulation. Regular BBT charting can be a helpful tool in identifying this pattern.
Positive Pregnancy Test
A positive home pregnancy test, detecting the presence of hCG in urine, is the most definitive indicator of pregnancy. hCG is a hormone produced by the developing placenta, and its presence is uniquely associated with pregnancy. The test detects this hormone, providing a reliable confirmation. While false positives are rare, it’s important to follow up with a blood test for confirmation.
- Implantation Bleeding: Light spotting or bleeding, often pinkish or brownish, around the time of a missed period.
- Intensified Breast Changes: Increased tenderness, swelling, darkening of the areola, and appearance of Montgomery’s tubercles, surpassing typical PMS symptoms.
- Sustained Elevated Basal Body Temperature: A prolonged increase in BBT beyond the typical post-ovulation rise.
- Positive Pregnancy Test: Detection of hCG hormone in urine or blood, confirming pregnancy.
The Role of Hormonal Changes
Understanding the hormonal shifts in your body is crucial to differentiating between PMS and early pregnancy symptoms. Both conditions involve significant hormonal fluctuations, but the types of hormones involved and the timing of these changes differ significantly. This can make it challenging to distinguish between the two, especially in the early stages of pregnancy.Hormonal fluctuations during the menstrual cycle are responsible for the wide array of PMS symptoms experienced by many women.
The cyclical rise and fall of estrogen and progesterone are key players. As the cycle progresses, estrogen and progesterone levels increase, peaking just before ovulation. Following ovulation, progesterone levels remain elevated to prepare the uterine lining for a potential pregnancy. If fertilization doesn’t occur, these hormone levels dramatically drop, triggering menstruation and often resulting in the characteristic PMS symptoms.
Hormonal Changes During the Menstrual Cycle and Their Connection to PMS Symptoms
The sharp decline in estrogen and progesterone just before menstruation is believed to be the primary trigger for many PMS symptoms. This drop can lead to a cascade of effects, including mood swings, irritability, bloating, breast tenderness, and fatigue. Individual sensitivity to these hormonal shifts varies considerably, leading to a broad spectrum of PMS symptom severity. For example, some women might experience only mild bloating, while others may experience severe mood swings and debilitating physical discomfort.
The neurotransmitters in the brain, such as serotonin, are also affected by these hormonal changes, contributing to emotional symptoms.
Hormonal Changes During Early Pregnancy
In contrast to the cyclical hormonal changes of the menstrual cycle, pregnancy introduces a completely new hormonal landscape. After fertilization, the embryo begins producing human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG), a hormone detectable in urine and blood pregnancy tests. hCG levels rise rapidly during the first trimester, stimulating the corpus luteum in the ovary to continue producing progesterone. Progesterone is essential for maintaining the pregnancy by supporting the uterine lining and preventing menstruation.
Estrogen levels also increase significantly throughout pregnancy, contributing to changes in the breasts, uterus, and other bodily systems. These hormonal shifts are responsible for many of the early pregnancy symptoms, some of which overlap with PMS.
Early pregnancy symptoms can be so tricky; that tired feeling, the mood swings, and bloating – it’s all too easy to mistake them for PMS. It got me thinking about how subtle changes in the body can signal bigger things, like the fascinating research I read about can eye test detect dementia risk in older adults.
Similarly, those early pregnancy signs are often subtle, highlighting how important it is to listen to your body and seek professional advice if you’re unsure.
Comparison of Hormonal Profiles in PMS and Early Pregnancy
While both PMS and early pregnancy involve hormonal changes, the key difference lies in the
- types* of hormones involved and the
- direction* of change. PMS is characterized by a sharp
- decrease* in estrogen and progesterone, while early pregnancy involves a
- sustained increase* in progesterone and the introduction of hCG. This fundamental difference highlights the importance of considering the overall hormonal picture, rather than focusing solely on individual symptoms. For instance, while breast tenderness can occur in both conditions, the underlying hormonal mechanisms are distinct. In PMS, it’s linked to the fluctuating estrogen and progesterone; in pregnancy, it’s related to the sustained rise in estrogen and progesterone, often coupled with increased blood flow to the breasts.
The presence of hCG, uniquely elevated during pregnancy, serves as a definitive marker distinguishing it from PMS.
Impact of Lifestyle Factors: Pregnancy Signs That Feel Like Premenstrual Syndrome

Source: ytimg.com
Navigating the often-blurry line between PMS and early pregnancy symptoms can be challenging. Understanding how lifestyle choices influence these symptoms is crucial for self-care and potentially easing discomfort. Stress, diet, and exercise play significant roles in both PMS and early pregnancy, impacting everything from mood swings to bloating.Lifestyle factors significantly affect both PMS and early pregnancy symptoms. While hormonal fluctuations are the primary drivers, external factors can either exacerbate or alleviate the discomfort experienced.
By understanding these influences, women can make informed choices to improve their well-being during these times.
Stress Management Techniques and Their Effects, Pregnancy signs that feel like premenstrual syndrome
Chronic stress elevates cortisol levels, a hormone that can worsen PMS symptoms like irritability, anxiety, and breast tenderness. Similarly, high stress levels in early pregnancy can contribute to nausea, fatigue, and mood changes. Effective stress management techniques, such as yoga, meditation, deep breathing exercises, and spending time in nature, can help regulate cortisol levels and mitigate these symptoms.
For example, studies have shown that regular yoga practice can significantly reduce PMS-related anxiety and depression. Similarly, mindfulness meditation has been linked to improved mood regulation during pregnancy.
Dietary Choices and Nutritional Impact
Diet plays a crucial role in managing both PMS and early pregnancy symptoms. A diet rich in processed foods, sugar, and caffeine can worsen PMS symptoms like bloating, mood swings, and headaches. Similarly, a poor diet during early pregnancy can exacerbate nausea and fatigue. Conversely, a balanced diet rich in whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and lean protein can provide essential nutrients, regulate blood sugar levels, and reduce inflammation, thus alleviating symptoms.
For instance, a diet high in magnesium can help reduce PMS-related cramps, while adequate iron intake is crucial for preventing anemia during pregnancy.
Exercise and Physical Activity Benefits
Regular physical activity is beneficial for both PMS and early pregnancy. Exercise can help regulate hormones, reduce stress, and improve mood. While intense workouts might need to be adjusted during pregnancy, moderate exercise, such as walking, swimming, or prenatal yoga, can alleviate fatigue, improve sleep, and reduce bloating. However, it’s crucial to listen to your body and avoid overexertion, especially during early pregnancy.
A study published in the journal Obstetrics & Gynecology found that moderate exercise during pregnancy was associated with a reduced risk of gestational diabetes and preeclampsia.
Lifestyle Modification Table
| Lifestyle Factor | PMS Symptom Mitigation | Early Pregnancy Symptom Mitigation | Specific Strategies |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stress Management | Reduced irritability, anxiety, mood swings | Reduced anxiety, improved sleep, lessened nausea | Yoga, meditation, deep breathing, spending time in nature |
| Diet | Reduced bloating, improved energy levels, fewer headaches | Lessened nausea, improved digestion, increased energy | Balanced diet rich in whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and lean protein; limiting processed foods, sugar, and caffeine |
| Exercise | Improved mood, reduced bloating, better sleep | Increased energy levels, improved mood, reduced fatigue | Moderate exercise such as walking, swimming, or prenatal yoga; listening to your body and avoiding overexertion |
Seeking Medical Advice
Navigating the early stages of pregnancy, especially when symptoms mimic PMS, can be confusing. Seeking professional medical advice is crucial for confirming pregnancy and ensuring your health and the health of your developing baby. Don’t hesitate to reach out to a healthcare provider if you have any concerns.A woman should consult a healthcare professional if she suspects pregnancy for several vital reasons.
Early confirmation allows for timely access to prenatal care, which is essential for a healthy pregnancy and reduces the risk of complications. Furthermore, a doctor can rule out other potential causes of your symptoms, providing peace of mind and appropriate treatment if needed.
Reasons for Seeking Medical Advice Regarding Pregnancy Symptoms
Several factors highlight the importance of seeking medical attention when experiencing potential pregnancy symptoms. Early detection allows for proactive management of any potential risks, ensuring both maternal and fetal well-being. This also allows for timely interventions if necessary.
- Confirmation of pregnancy: A healthcare professional can perform tests to confirm pregnancy definitively.
- Assessment of overall health: A comprehensive health assessment ensures that you’re in good health to support a pregnancy.
- Detection of potential complications: Early detection of potential complications, such as ectopic pregnancy, can be life-saving.
- Guidance on prenatal care: A healthcare provider can provide personalized advice and guidance on prenatal care, including diet, exercise, and medication.
- Addressing underlying health conditions: Pre-existing health conditions, like diabetes or hypertension, require management during pregnancy.
Steps Involved in Seeking Medical Advice
The process of seeking medical advice for suspected pregnancy or persistent PMS-like symptoms is straightforward. Start by scheduling an appointment with your primary care physician or a gynecologist. Be prepared to discuss your symptoms in detail, including their onset, duration, and severity. Providing a complete medical history will assist your doctor in making an accurate diagnosis.
- Schedule an appointment: Contact your doctor’s office or clinic to schedule an appointment.
- Provide a detailed medical history: Be prepared to share your medical history, including any previous pregnancies, menstrual cycles, and current medications.
- Describe your symptoms: Clearly explain your symptoms, noting their onset, duration, severity, and any other relevant information.
- Undergo necessary tests: Be prepared to undergo any tests recommended by your doctor.
- Discuss treatment options: Discuss any treatment options with your doctor, and ask any questions you may have.
Typical Tests and Procedures for Pregnancy Confirmation
Once you consult a healthcare professional, several tests and procedures can help confirm pregnancy or rule out other conditions. These tests are generally safe and non-invasive, providing reliable results.
- Urine pregnancy test: This is a common and readily available test that detects the presence of human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG), a hormone produced during pregnancy.
- Blood pregnancy test: A blood test can detect even lower levels of hCG than a urine test, providing earlier confirmation of pregnancy.
- Ultrasound: An ultrasound can visualize the gestational sac and fetal pole, confirming pregnancy and providing information about the gestational age.
- Pelvic exam: A pelvic exam can help assess the overall health of the reproductive organs and rule out other conditions.
Visual Representations of Symptom Progression

Source: momjunction.com
Understanding the progression of symptoms is crucial in differentiating between PMS and early pregnancy. While many symptoms overlap, their timing and intensity can offer valuable clues. Visualizing this progression helps clarify the differences. The following descriptions aim to paint a picture of these symptom trajectories.
PMS Symptom Progression
Imagine a graph charting symptom intensity over a typical 28-day menstrual cycle. The baseline, representing minimal discomfort, would sit at the bottom. As ovulation approaches (around day 14), we might see a slight upward tick, representing mild bloating or mood changes. In the week leading up to menstruation (days 21-28), the line sharply ascends. This reflects the peak intensity of PMS symptoms, such as breast tenderness, cramping, irritability, and fatigue.
The types of symptoms vary greatly from person to person, with some experiencing predominantly physical discomfort and others primarily emotional changes. The line then dramatically drops off once menstruation begins, signaling the relief of symptoms. The severity of this peak varies greatly; some women experience mild discomfort, while others experience debilitating symptoms.
Early Pregnancy Symptom Progression
Now, consider a similar graph for early pregnancy symptoms. Instead of a cyclical pattern, we see a more gradual, often less predictable, rise in symptom intensity. Many women report experiencing subtle changes in the first few weeks after conception, such as increased fatigue or nausea, which might appear on the graph as a slow, gentle upward trend. The intensity might fluctuate, but the general direction is upwards.
Unlike PMS, where symptoms typically peak just before menstruation, pregnancy symptoms may gradually intensify over several weeks. The types of symptoms differ as well. While some PMS symptoms like bloating and breast tenderness might also be present in early pregnancy, others, such as nausea (morning sickness) and food aversions, are more strongly associated with pregnancy. The graph would show a continued upward trend for several weeks, although the rate of increase and the specific symptoms experienced will vary significantly from woman to woman.
Some women experience very few symptoms in early pregnancy, resulting in a barely perceptible line on the graph.
Managing Symptoms
Navigating the often-blurry line between PMS and early pregnancy symptoms can be challenging, but effective management strategies exist for both. Understanding the similarities and differences in symptom presentation is key to finding relief and ensuring your well-being. Remember, always consult your doctor for personalized advice, especially if you suspect pregnancy.
Managing PMS Symptoms
PMS symptoms, stemming from hormonal fluctuations during the menstrual cycle, often respond well to lifestyle modifications and over-the-counter remedies. Addressing these symptoms proactively can significantly improve comfort and quality of life.
Lifestyle changes often form the cornerstone of PMS management. Regular exercise, even a moderate amount, can help regulate hormones and reduce stress, a common PMS trigger. Maintaining a balanced diet, rich in whole grains, fruits, and vegetables, and limiting processed foods, caffeine, and alcohol can also alleviate symptoms. Adequate sleep is crucial; aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night.
Stress-reduction techniques like yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises can also be highly beneficial.
Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as ibuprofen or naproxen, can effectively manage cramping and pain. For bloating and water retention, diuretics might offer some relief, but always check with your doctor or pharmacist before using them. Some women find relief with supplements like magnesium or calcium, but again, consult a healthcare professional before starting any new supplements.
Managing Early Pregnancy Symptoms
Early pregnancy symptoms, largely driven by rising hormone levels, require a more cautious approach. While many symptoms overlap with PMS, the management strategies need to consider the developing fetus.
Lifestyle adjustments remain crucial. Maintaining a healthy diet, including folic acid-rich foods, is essential for fetal development. Getting adequate rest and managing stress levels are also vital for both maternal and fetal well-being. Gentle exercise, like walking, is usually encouraged, but strenuous activity should be avoided, especially in the first trimester. Staying well-hydrated is also important.
Over-the-counter medications should be used with caution during pregnancy. While acetaminophen (paracetamol) is generally considered safe for managing pain and fever, ibuprofen and other NSAIDs should be avoided, especially in the later stages of pregnancy, unless specifically advised by a doctor. Always consult your doctor or midwife before taking any medication during pregnancy, even seemingly harmless over-the-counter remedies.
Comparing PMS and Early Pregnancy Symptom Management
While many symptoms overlap, the key difference in managing PMS and early pregnancy symptoms lies in the safety considerations for the developing fetus. For PMS, a wider range of over-the-counter medications and approaches are generally safe, whereas during pregnancy, a more conservative and doctor-approved approach is crucial. The emphasis on nutrition and stress management remains important for both, highlighting the overall importance of a healthy lifestyle.
Last Word
Source: healthadvicer.com
So, while many early pregnancy symptoms mirror PMS, there are key differences to look for. Paying attention to symptom timing, unique indicators like implantation bleeding or missed periods, and understanding the hormonal shifts involved can help you gain clarity. Remember, this information is for educational purposes only, and seeking professional medical advice is crucial if you suspect you might be pregnant.
Take care of yourself, and don’t hesitate to reach out to your doctor with any questions or concerns. Ultimately, understanding your body is the first step towards a healthy and happy journey, whether that journey leads to a period or a positive pregnancy test!
FAQ Insights
What’s the difference between implantation bleeding and a period?
Implantation bleeding is typically lighter and shorter than a regular period, and the blood is often pinkish or brownish rather than bright red. It also occurs earlier in the cycle, around the time of implantation.
Can stress affect both PMS and early pregnancy symptoms?
Absolutely! Stress can exacerbate PMS symptoms and potentially impact early pregnancy symptoms, making them more intense. Stress management techniques are beneficial in both cases.
When should I take a home pregnancy test?
Most home pregnancy tests are accurate from the first day of a missed period. However, some tests can detect pregnancy even earlier.
Is it possible to have PMS and be pregnant simultaneously?
No, you cannot experience PMS and be pregnant at the same time. PMS occurs before ovulation, whereas pregnancy symptoms begin after implantation (following ovulation and fertilization).
