Private Equity Healthcare Senate Report Key Findings
Private equity healthcare senate report reveals a complex picture of private equity’s influence on the healthcare industry. The report delves into the investment strategies employed by these firms, examining their impact on healthcare access, quality of care, and the overall cost of healthcare. It also scrutinizes the regulatory landscape and proposes legislative recommendations to address potential negative consequences.
This report sparks crucial conversations about the balance between private investment and public health.
The Senate report meticulously details its methodology, drawing on a wide range of data sources to paint a comprehensive picture. It highlights concerns such as increased prices for services, potential reductions in the quality of care due to cost-cutting measures, and the challenges in ensuring equitable access to healthcare for all patients. The report doesn’t shy away from presenting a critical analysis of private equity’s role, prompting a vital dialogue about responsible investment in the healthcare sector.
Senate Report Overview
Source: workweek.com
The Senate report on private equity’s influence on healthcare is pretty eye-opening, highlighting potential cost increases. Ironically, while reading it, my wrist started acting up – classic carpal tunnel! Thankfully, I found some helpful info on non-surgical treatments, like those detailed at ways to treat carpal tunnel syndrome without surgery , which gave me a much-needed break.
Back to the report though – the implications for patient access are really concerning.
The recent Senate report on private equity’s influence in the healthcare sector has ignited a significant debate. It delves into the complex relationship between private equity firms and the provision of healthcare services, raising serious concerns about the potential for increased costs, reduced quality of care, and compromised patient access. This overview summarizes the report’s key findings, methodology, and recommendations.
Key Findings of the Senate Report
The report’s central finding is that private equity investment in healthcare has led to a noticeable increase in prices for essential services. This price inflation is often not accompanied by commensurate improvements in quality or efficiency. The report identifies specific instances where private equity-owned healthcare providers have implemented aggressive cost-cutting measures, resulting in staff reductions, reduced benefits, and a deterioration of patient care.
Further, the report highlights concerns about the lack of transparency in pricing practices within private equity-owned healthcare facilities.
Concerns Raised by the Report
The Senate report expresses significant concern over several key areas. First, it points to the potential for conflicts of interest, where profit maximization for private equity firms may overshadow the provision of quality patient care. Second, the report highlights the opacity surrounding the financial dealings of private equity-owned healthcare providers, making it difficult to assess their true impact on healthcare costs and quality.
Third, the report examines the potential for private equity to consolidate market power, leading to reduced competition and ultimately higher prices for consumers. Finally, the report expresses worry about the lack of robust regulatory oversight of private equity activity in the healthcare sector.
Methodology and Data Sources
The report utilized a mixed-methods approach, combining quantitative and qualitative data analysis. Quantitative data included financial records from private equity-owned healthcare providers, market share data, and publicly available information on healthcare costs and quality. Qualitative data was gathered through interviews with healthcare professionals, patients, and industry experts. The report also analyzed existing literature on the impact of private equity on various sectors, including healthcare.
Data sources included SEC filings, Medicare and Medicaid data, and state regulatory filings.
Legislative Recommendations
The Senate report proposes several legislative recommendations to mitigate the negative impacts of private equity in healthcare. These include enhanced transparency requirements for private equity-owned healthcare providers, stricter antitrust enforcement to prevent market consolidation, and increased regulatory oversight to ensure patient safety and affordability. The report also recommends increased funding for healthcare consumer protection agencies and the strengthening of existing whistleblower protection laws.
Comparison with Previous Research
The following table compares the findings of the Senate report with previous research on private equity’s impact on healthcare:
| Aspect | Senate Report Findings | Previous Research Findings (Summary) | Discrepancies/Similarities |
|---|---|---|---|
| Price Increases | Significant price increases observed in PE-owned facilities. | Studies show mixed results, some indicating price increases, others showing no significant impact. | Some studies support the report’s findings, others do not, highlighting the complexity of the issue. |
| Quality of Care | Concerns raised about reduced quality due to cost-cutting measures. | Some research suggests a negative correlation between PE ownership and quality metrics, others find no clear link. | This area requires further research to establish a definitive causal relationship. |
| Market Consolidation | Concerns about increased market concentration and reduced competition. | Existing research generally supports the concern of increased market concentration due to PE activity. | The report’s findings align with the broader literature on this aspect. |
| Transparency | Lack of transparency in financial practices highlighted. | Limited research directly addresses transparency in PE-owned healthcare; this is a key area for future study. | The report identifies a significant gap in existing research and calls for increased transparency. |
Private Equity Investment Strategies in Healthcare
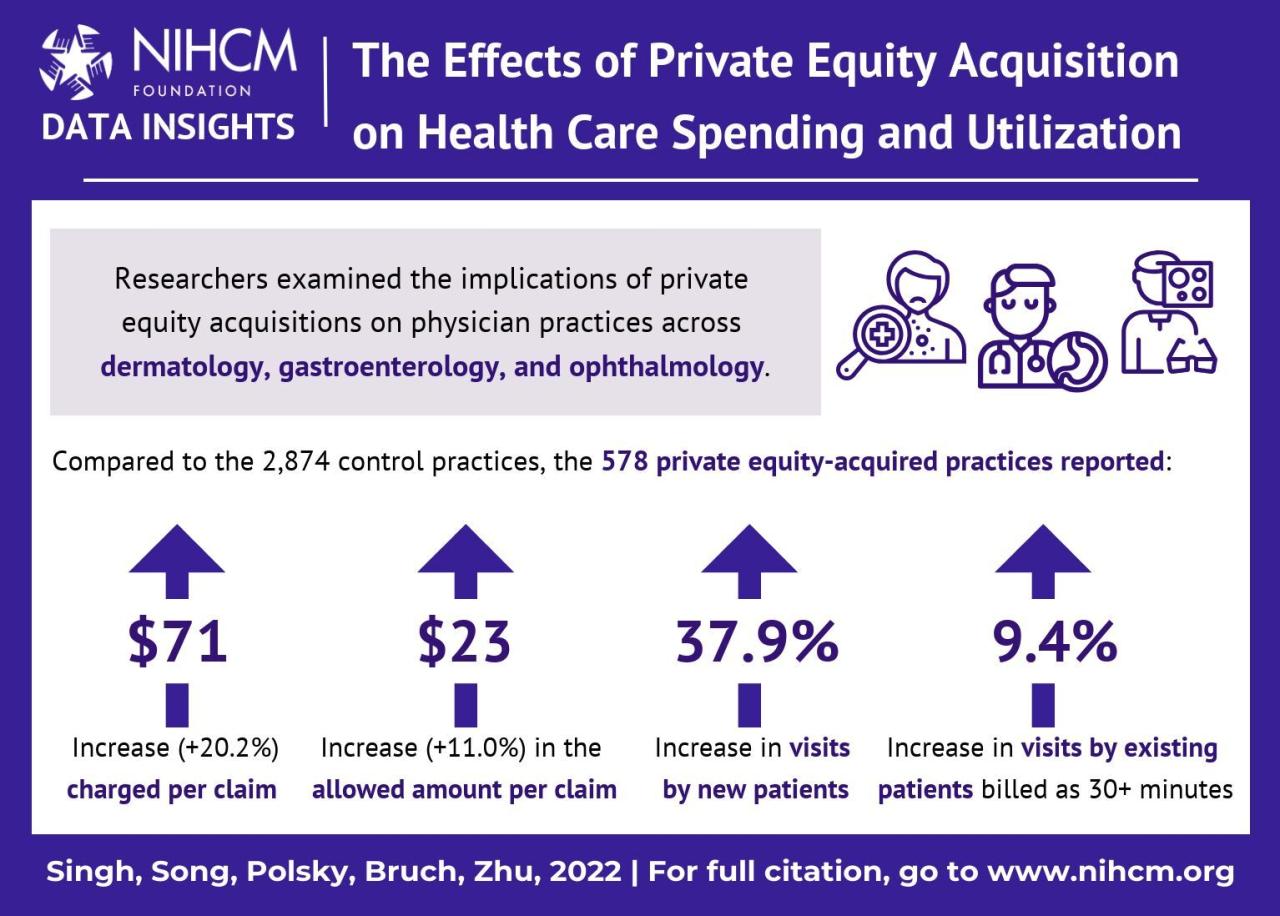
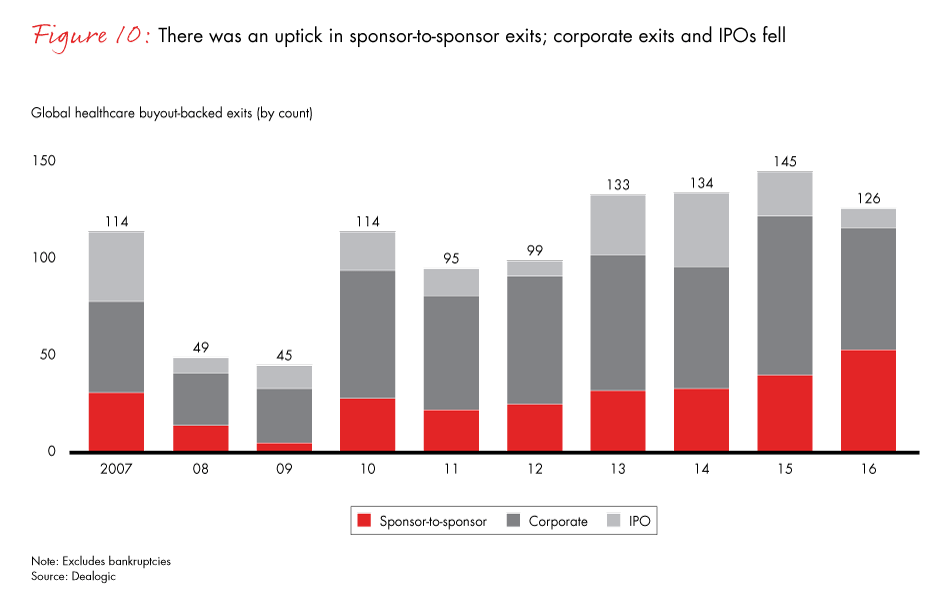
Source: nihcm.org
Private equity firms employ a range of strategies to capitalize on the growth and profitability within the healthcare sector. These strategies often involve significant financial leverage and a focus on operational improvements to enhance returns before ultimately exiting the investment. Understanding these strategies is crucial to assessing the impact of private equity on the healthcare landscape.
Common Private Equity Investment Strategies in Healthcare
Private equity firms utilize several key strategies when investing in healthcare. These strategies are often tailored to the specific target company and market conditions. A common approach is to acquire underperforming or undervalued healthcare businesses, implement operational improvements, and then sell them at a higher valuation. Another strategy involves consolidating fragmented markets, creating larger, more efficient entities.
Finally, some firms focus on growth equity investments, providing capital to promising companies to fuel expansion.
Healthcare Sectors Targeted by Private Equity
Private equity investments span a broad range of healthcare sectors. Hospitals and hospital systems are frequent targets, with private equity firms often seeking to improve operational efficiency and increase profitability through consolidation or cost-cutting measures. Physician practices, particularly in specialties like dermatology, ophthalmology, and gastroenterology, are also attractive investment opportunities due to their recurring revenue streams and potential for scale.
The medical equipment and technology sector is another area of significant private equity activity, with firms investing in companies developing innovative medical devices and software. Finally, home health and hospice care are increasingly attractive due to the aging population and growing demand for these services.
Financial Implications of Private Equity Investments in Healthcare: Leverage and Debt
Private equity firms frequently utilize significant leverage in their healthcare investments. This means they use a substantial amount of borrowed money to finance acquisitions, amplifying potential returns but also increasing financial risk. The high levels of debt incurred can influence operational decisions, potentially leading to cost-cutting measures that may impact the quality of care or employee compensation. The use of debt also creates a pressure to generate quick returns to repay the loans.
For example, a private equity firm might acquire a hospital system using a high debt-to-equity ratio, then implement cost-cutting measures to improve profitability and repay the debt within a defined timeframe.
Portfolio Management and Exit Strategies in Private Equity Healthcare Investments
Effective portfolio management is critical for private equity firms in healthcare. This involves actively monitoring the performance of their investments, providing operational support to portfolio companies, and implementing strategies to enhance value. Exit strategies typically involve selling the portfolio company to a strategic buyer (another healthcare company, for example) or through an initial public offering (IPO). The timing of the exit is crucial and depends on factors such as market conditions and the portfolio company’s performance.
A successful exit strategy translates to substantial returns for the private equity firm.
Typical Investment Lifecycle of a Private Equity Firm in the Healthcare Sector
The following flowchart illustrates the typical investment lifecycle:[Diagram description: The flowchart would begin with “Investment Sourcing and Due Diligence,” leading to “Acquisition and Integration.” This would then branch into “Portfolio Company Management and Value Enhancement,” which includes operational improvements, strategic planning, and financial restructuring. From “Portfolio Company Management,” the flow would continue to “Exit Strategy,” showing paths for “Sale to Strategic Buyer,” “IPO,” or “Recapitalization.” Each stage would have a brief description of the activities involved.
The final stage would be “Return of Capital to Investors.”]
Impact on Healthcare Access and Quality: Private Equity Healthcare Senate Report
This section delves into the Senate report’s findings on how private equity investment in healthcare affects patient access to care and the overall quality of services. The report examines a complex interplay of factors, highlighting both potential benefits and significant drawbacks associated with this type of investment. A nuanced understanding of these impacts is crucial for policymakers seeking to shape regulations and ensure a robust and equitable healthcare system.The report’s assessment of private equity’s impact on healthcare access paints a mixed picture.
While some investments may lead to improved efficiency and expansion of services in underserved areas, the report also points to instances where increased focus on profitability has resulted in reduced access for certain patient populations. For example, the closure of less profitable facilities or the prioritization of higher-reimbursement procedures can limit access for individuals relying on specific services or located in particular geographic areas.
The report emphasizes the need for a thorough investigation into these discrepancies to determine the overall net effect.
Private Equity’s Influence on Healthcare Service Quality
The report analyzes the correlation between private equity ownership and changes in the quality of healthcare services. It acknowledges that some private equity firms may invest in improving infrastructure and technology, potentially leading to better patient outcomes. However, a significant concern raised is the potential for cost-cutting measures that compromise quality. This could manifest in reduced staffing levels, decreased investment in training and development for healthcare professionals, or the adoption of less rigorous quality control measures.
The report cites several instances where private equity-owned facilities experienced a decline in patient satisfaction scores and an increase in adverse events, suggesting a need for stricter oversight and accountability.
Comparison with Alternative Perspectives
The report’s findings are compared with various alternative perspectives on private equity’s influence on healthcare outcomes. Some argue that private equity investments stimulate innovation and efficiency, leading to improved quality and affordability. Others maintain that the primary focus on profit maximization invariably leads to compromised care. The report attempts to synthesize these conflicting views by examining specific case studies and employing statistical analysis to identify trends and correlations.
The Senate’s report on private equity’s influence in healthcare is raising serious questions about affordability and access. It’s a complex issue, and the potential impact of whoever leads the HHS is huge. For example, Robert F. Kennedy Jr.’s recent progress, as reported in this article, rfk jr clears key hurdle on path to hhs secretary , could significantly alter the regulatory landscape surrounding these concerns.
Ultimately, the Senate report’s findings will need careful consideration regardless of who holds the HHS Secretary position.
It concludes that while some positive impacts exist, the potential negative consequences warrant close scrutiny and the implementation of appropriate regulatory safeguards.
Potential Negative Consequences of Private Equity Investment
The report highlights several potential negative consequences associated with private equity investment in healthcare, including increased prices and reduced care. Increased prices can stem from various factors, such as the consolidation of healthcare providers, leading to reduced competition and higher charges for services. Reduced care can result from cost-cutting measures, including staff reductions, limitations on access to certain treatments, and a shift towards procedures with higher reimbursement rates, regardless of patient need.
The report stresses the importance of considering these potential downsides when evaluating the overall impact of private equity involvement in the healthcare sector.
The recent private equity healthcare senate report highlighted some concerning trends in healthcare access. It made me think about the challenges faced by families, like the need for consistent, specialized care; for example, finding effective strategies to manage Tourette Syndrome in children can be a huge hurdle. This lack of accessible, affordable care underscores the broader issues raised in the senate report regarding equitable healthcare provision.
Strategies to Mitigate Negative Impacts
To mitigate the potential negative impacts of private equity investment on healthcare access and quality, the report suggests several strategies.
- Strengthening regulatory oversight to ensure compliance with quality standards and prevent anti-competitive practices.
- Implementing stricter transparency requirements to provide greater visibility into the financial practices and operational decisions of private equity-owned healthcare providers.
- Promoting greater accountability for private equity firms regarding their impact on patient access and healthcare outcomes.
- Investing in independent research and data collection to monitor the effects of private equity investment on various aspects of healthcare delivery.
- Enhancing public awareness of the potential risks and benefits associated with private equity investment in healthcare.
Regulatory and Policy Implications
The Senate report’s examination of private equity’s role in healthcare reveals a complex interplay between financial investment and the delivery of care. Understanding the regulatory landscape and the report’s proposed changes is crucial for ensuring both the financial viability of the healthcare system and equitable access to quality care. This section will delve into the current regulatory environment, the rationale behind the report’s recommendations, and the potential challenges in their implementation.The current regulatory landscape surrounding private equity investment in healthcare is fragmented and often lacks the specificity needed to address the unique challenges posed by these investments.
Existing regulations, primarily focused on antitrust and fraud prevention, often prove insufficient to capture the potential negative consequences of private equity’s focus on maximizing returns. This lack of tailored oversight has led to concerns about increased healthcare costs, reduced access to care, and compromised quality of services in certain sectors. The varied state-level regulations further complicate the issue, creating an uneven playing field and hindering consistent enforcement.
Rationale Behind Legislative Recommendations
The Senate report’s legislative recommendations stem from a need for greater transparency and accountability in private equity’s healthcare investments. The report argues that stricter regulations are necessary to mitigate the potential for profit-driven practices to negatively impact patient care. Key recommendations likely include enhanced disclosure requirements for private equity firms operating in the healthcare sector, stricter oversight of mergers and acquisitions, and increased scrutiny of pricing practices to prevent excessive cost increases.
The ultimate goal is to establish a regulatory framework that balances the benefits of private investment with the paramount need to protect patients and ensure the integrity of the healthcare system.
Challenges in Implementing Proposed Regulatory Changes
Implementing the proposed regulatory changes will present significant challenges. Firstly, navigating the complex legal and political landscape will require careful consideration of the potential impacts on various stakeholders, including private equity firms, healthcare providers, and patients. Secondly, crafting effective regulations that are both stringent enough to address the identified concerns and flexible enough to accommodate the dynamic nature of the healthcare industry will be a considerable undertaking.
Thirdly, robust enforcement mechanisms will be crucial to ensure compliance and prevent circumvention of the new regulations. The potential for legal challenges from private equity firms further complicates the implementation process. The experience of implementing similar regulations in other sectors can offer valuable lessons, but the unique characteristics of healthcare require careful adaptation.
Comparison with Regulations in Other Sectors
The proposed regulations for private equity in healthcare can be compared to those in other sectors, such as finance and telecommunications, where private equity investment has also drawn scrutiny. For instance, the Dodd-Frank Act, enacted in response to the 2008 financial crisis, introduced stricter regulations for financial institutions, including enhanced oversight and increased transparency. Similarly, regulations in the telecommunications sector aim to prevent monopolies and ensure fair competition.
However, the healthcare sector’s unique characteristics, particularly its significant impact on public health and the ethical considerations surrounding patient care, necessitate a tailored regulatory approach, rather than a simple replication of existing models. Learning from the successes and failures of regulations in other sectors will be crucial in developing an effective framework for healthcare.
Influence on Future Healthcare Policy Debates
The findings of the Senate report are poised to significantly influence future healthcare policy debates. The report’s detailed analysis of private equity’s impact on healthcare access, quality, and costs will likely fuel ongoing discussions about the appropriate role of private investment in the healthcare system. The report’s recommendations will serve as a blueprint for future legislative initiatives, prompting policymakers to consider more robust regulatory frameworks to address concerns about cost inflation, reduced access to care, and compromised quality of services.
The report’s findings will also likely contribute to a broader conversation about the balance between market-based solutions and public regulation in the healthcare sector, shaping the trajectory of healthcare policy for years to come. For example, the debate around Medicare for All will likely incorporate considerations raised by the report’s analysis of private equity’s influence on cost and access.
Public Perception and Media Coverage
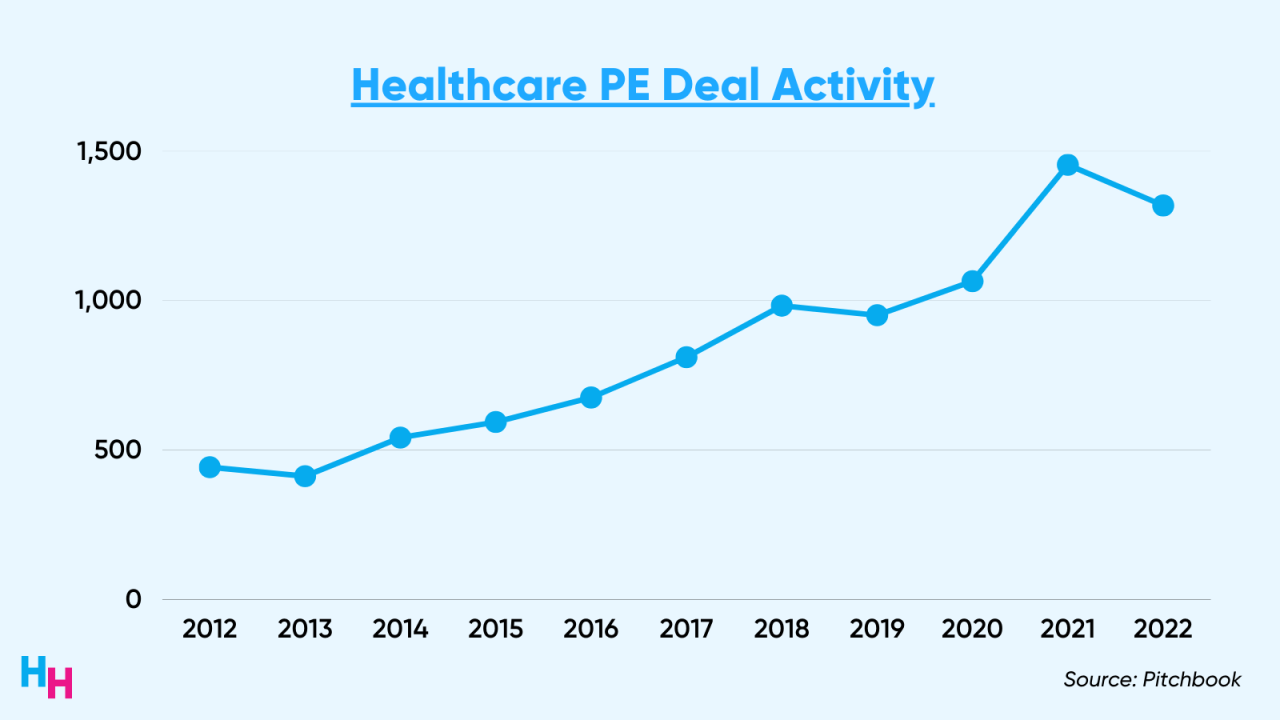
Source: bain.com
The Senate report on private equity’s role in healthcare has ignited a complex public debate. Public perception is largely negative, fueled by concerns about rising healthcare costs, reduced access to care, and the prioritization of profit over patient well-being. This perception is shaped not only by the report’s findings but also by a long history of media portrayals of private equity, often depicting it as a force that extracts value from businesses at the expense of employees and consumers.The report’s release prompted widespread media coverage, varying significantly in tone and framing across different outlets.
This variation reflects the diverse perspectives of stakeholders involved.
Media Coverage Examples and Tone Analysis
News outlets ranging from major national newspapers like the New York Times and the Wall Street Journal to specialized healthcare publications and local news channels covered the Senate report. The New York Times, for example, often framed the issue around the potential negative impact on patient care and access, citing specific examples from the report and including interviews with affected patients and providers.
In contrast, the Wall Street Journal’s coverage sometimes presented a more balanced perspective, acknowledging the potential benefits of private equity investment in healthcare innovation while also highlighting concerns about cost and access. Conservative outlets tended to downplay the negative consequences, emphasizing the potential for increased efficiency and investment, while more liberal outlets focused on the negative impacts on patients and the healthcare system as a whole.
This difference in framing reflects the political polarization surrounding the issue.
Key Stakeholders and Their Perspectives
Several key stakeholders are deeply involved in this debate. Patients are primarily concerned about access to affordable, high-quality care. Providers, including doctors, nurses, and hospital administrators, are worried about the potential for increased workloads, reduced resources, and pressure to prioritize profits over patient needs. Private equity investors, on the other hand, emphasize their role in providing capital for healthcare innovation, improving efficiency, and ultimately benefiting patients.
Government regulators and policymakers are tasked with balancing the need to encourage investment in the healthcare sector with the need to protect patients and ensure equitable access to care.
Visual Representation of Stakeholder Perspectives, Private equity healthcare senate report
Imagine a Venn diagram. One circle represents the perspective of patients and providers, largely focused on access, affordability, and quality of care. Another circle represents the perspective of private equity investors, focused on profitability, efficiency, and return on investment. A third, smaller circle represents the government regulators, aiming to find common ground between these competing interests. The overlap between the patient/provider circle and the government circle represents the shared goal of ensuring equitable access to quality healthcare.
The overlap between the investor circle and the government circle represents the shared interest in promoting innovation and investment in healthcare. The lack of significant overlap between the patient/provider circle and the investor circle illustrates the potential conflict between profit maximization and patient well-being. This visual representation highlights the complex interplay of interests and the challenges in finding a solution that satisfies all stakeholders.
Last Word
Ultimately, the private equity healthcare senate report serves as a crucial call to action. It underscores the need for greater transparency and accountability in private equity investments within healthcare, emphasizing the critical importance of safeguarding patient access and quality of care. The report’s findings and recommendations will undoubtedly shape future policy debates and regulatory frameworks, influencing how private equity operates within this vital sector.
The ongoing discussion surrounding this report will be critical in shaping the future of healthcare.
FAQ Guide
What specific types of healthcare providers are most frequently targeted by private equity firms?
Private equity firms often target hospitals, physician practices, medical equipment companies, and other healthcare service providers.
How does the report define “quality of care” and how is it measured?
The report likely uses a multifaceted definition of quality of care, encompassing factors such as patient outcomes, staff-to-patient ratios, and patient satisfaction scores. Specific metrics used would be detailed within the report itself.
What are some examples of alternative perspectives on private equity’s impact on healthcare?
Some argue that private equity investments can improve efficiency and bring needed capital to healthcare providers, leading to better outcomes. Others maintain that the focus on profit maximization can compromise quality and access.
What international examples of regulation are cited in the report for comparison?
The report may draw comparisons to regulations in other countries that have already addressed similar concerns regarding private equity investment in sensitive sectors. These examples would be detailed in the regulatory implications section.