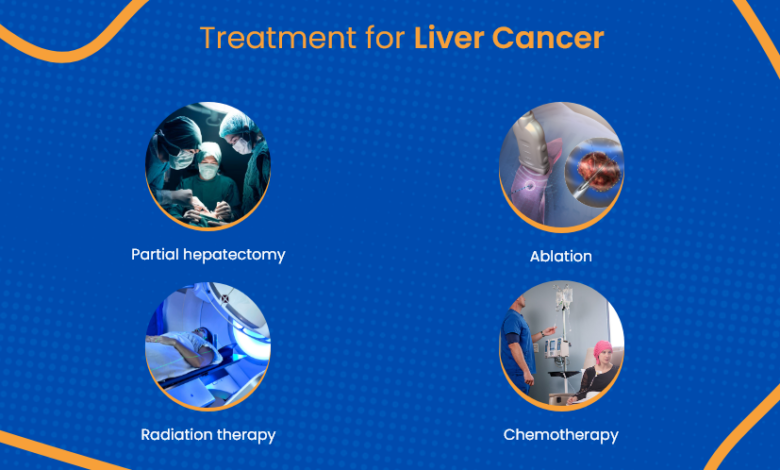
Side Effects of Liver Cancer Treatment & Risk Minimization
Side effects of liver cancer treatment and how to minimise the risk – Side effects of liver cancer treatment and how to minimize the risk are crucial considerations for anyone facing this diagnosis. Liver cancer treatments, while life-saving, often come with a range of side effects, from mild discomfort to serious complications. Understanding these potential side effects and learning proactive strategies to manage them is key to maintaining quality of life throughout the treatment journey.
This post explores common treatments, their associated side effects, and practical steps you can take to minimize their impact, empowering you to navigate this challenging time with greater confidence and control.
We’ll delve into the specifics of various treatments like surgery, chemotherapy, radiation, and immunotherapy, outlining the potential side effects for each. We’ll also discuss lifestyle changes, supportive care options, and effective communication strategies to help you work closely with your healthcare team. Because every individual and every cancer journey is unique, we’ll emphasize the importance of personalized treatment plans and shared decision-making.
We’ll even cover long-term side effects and how to manage them, providing you with a comprehensive understanding of the entire process.
Common Liver Cancer Treatments and Their Associated Side Effects
Liver cancer treatment aims to destroy cancerous cells while minimizing harm to healthy tissues. The approach depends on factors like cancer stage, overall health, and personal preferences. Unfortunately, many treatments come with side effects, ranging from mild discomfort to severe complications. Understanding these side effects and how to manage them is crucial for patients and their caregivers.
Liver Cancer Treatment Modalities and Associated Side Effects
The most common treatments for liver cancer include surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, targeted therapy, and immunotherapy. Each treatment has its own set of potential side effects, varying in severity and frequency. It’s important to remember that not everyone experiences all side effects, and the severity can differ greatly.
| Treatment | Side Effect | Severity | Frequency |
|---|---|---|---|
| Surgery (e.g., resection, transplantation) | Pain | Mild to Moderate | Common |
| Infection | Moderate to Severe | Possible | |
| Bleeding | Moderate to Severe | Possible | |
| Blood clots | Moderate to Severe | Possible | |
| Scar tissue formation | Mild to Moderate | Common | |
| Chemotherapy (e.g., Doxorubicin, 5-fluorouracil) | Nausea and vomiting | Mild to Moderate | Common |
| Hair loss | Mild to Moderate | Common | |
| Fatigue | Mild to Severe | Common | |
| Mouth sores | Mild to Moderate | Common | |
| Reduced blood cell counts (leading to anemia, increased risk of infection, and bleeding) | Moderate to Severe | Possible | |
| Radiation Therapy (e.g., external beam radiation, brachytherapy) | Skin irritation | Mild to Moderate | Common |
| Fatigue | Mild to Moderate | Common | |
| Nausea and vomiting | Mild to Moderate | Possible | |
| Liver damage | Moderate to Severe | Possible | |
| Targeted Therapy (e.g., sorafenib, lenvatinib) | High blood pressure | Mild to Moderate | Common |
| Hand-foot skin reaction | Mild to Moderate | Common | |
| Diarrhea | Mild to Moderate | Common | |
| Fatigue | Mild to Severe | Common | |
| Increased risk of bleeding | Moderate to Severe | Possible | |
| Immunotherapy (e.g., Nivolumab, Ipilimumab) | Fatigue | Mild to Severe | Common |
| Skin rash | Mild to Moderate | Common | |
| Inflammation (colitis, hepatitis) | Moderate to Severe | Possible | |
| Autoimmune effects | Moderate to Severe | Possible |
Mechanisms of Side Effects, Side effects of liver cancer treatment and how to minimise the risk
The side effects of liver cancer treatments stem from the treatments’ mechanisms of action. Surgery, while directly targeting the tumor, can cause pain, bleeding, and infection due to the invasive nature of the procedure. Chemotherapy drugs, designed to kill rapidly dividing cells, also affect healthy cells, leading to hair loss, nausea, and reduced blood cell counts. Radiation therapy damages DNA, causing skin irritation and fatigue, and potentially impacting the liver directly.
Targeted therapies interfere with specific cancer pathways, but can also disrupt normal cellular processes, resulting in side effects like high blood pressure or hand-foot skin reaction. Immunotherapies, while boosting the immune system to fight cancer, can also trigger autoimmune reactions and inflammation. The frequency and severity of these side effects depend on various factors, including the specific treatment, dosage, individual patient factors, and overall health.
Minimizing the Risk of Side Effects During Treatment
Liver cancer treatment, while crucial for combating the disease, often comes with a range of side effects that can significantly impact a patient’s quality of life. Fortunately, proactive measures can be taken to lessen the severity and frequency of these side effects, allowing patients to better manage their treatment journey. This involves a multifaceted approach encompassing lifestyle adjustments, supportive care, and open communication with the healthcare team.
Lifestyle Modifications for Side Effect Mitigation
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle plays a vital role in minimizing the impact of liver cancer treatments. A well-rounded approach combining diet, exercise, and stress management can significantly improve overall well-being and reduce the burden of side effects.Dietary changes can make a substantial difference. A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins helps support the body’s natural healing processes.
Foods high in antioxidants can help combat inflammation often associated with treatment. Conversely, limiting processed foods, sugary drinks, and excessive alcohol consumption is crucial. For example, a diet incorporating foods rich in Vitamin C, like citrus fruits and berries, can help boost the immune system, which is often compromised during treatment. Similarly, incorporating omega-3 fatty acids, found in fatty fish like salmon, can help reduce inflammation.Regular exercise, tailored to individual fitness levels, improves energy levels, strengthens the immune system, and helps manage stress.
Even moderate activity, such as daily walks or gentle yoga, can provide significant benefits. It’s important to consult with a healthcare professional to determine an appropriate exercise plan that aligns with the patient’s physical capabilities and treatment regimen. For instance, a patient undergoing chemotherapy might start with short, low-impact exercises and gradually increase the intensity and duration as tolerated.Stress management techniques are equally important.
Chronic stress can exacerbate side effects and compromise the immune system. Techniques like meditation, deep breathing exercises, and mindfulness practices can help manage stress levels effectively. Joining a support group or engaging in hobbies can also provide emotional support and a sense of normalcy during treatment. A patient might find relief from anxiety through guided meditation apps or by attending regular yoga sessions.
Supportive Care for Side Effect Reduction
Supportive care plays a crucial role in managing side effects. This encompasses a range of medications and therapies designed to alleviate specific symptoms and improve overall comfort.Medications are frequently used to target common side effects. For example, anti-nausea medications can help manage nausea and vomiting often associated with chemotherapy. Pain relievers can alleviate discomfort, and medications can also help manage fatigue, diarrhea, and other symptoms.
The choice of medication depends on the specific side effects experienced and the patient’s overall health status. A multidisciplinary team including oncologists, nurses, and pharmacists work together to develop a personalized supportive care plan.Therapies, such as physical therapy and occupational therapy, can help patients regain strength, improve mobility, and manage functional limitations caused by treatment side effects. Physical therapy can help improve muscle strength and endurance, while occupational therapy can help patients adapt to daily activities and maintain independence.
For instance, physical therapy can help a patient regain strength after surgery, while occupational therapy can help them learn to use adaptive equipment to perform daily tasks.
Effective Communication with the Healthcare Team
Open and honest communication with the healthcare team is essential for effective side effect management. Patients should not hesitate to report any new or worsening symptoms, no matter how minor they may seem. Detailed descriptions of symptoms, including their severity, frequency, and duration, help the healthcare team assess the situation and make appropriate adjustments to the treatment plan or supportive care.
Keeping a detailed journal of symptoms, including dates, times, and severity, can be particularly helpful during appointments. This detailed information enables the healthcare team to accurately monitor the effectiveness of the treatment and interventions.
Specific Side Effects and Management Strategies: Side Effects Of Liver Cancer Treatment And How To Minimise The Risk
Dealing with the side effects of liver cancer treatment is a crucial part of the overall care plan. These side effects can significantly impact a patient’s quality of life, so understanding how to manage them is essential for both physical and emotional well-being. Effective management strategies often involve a combination of medical interventions and lifestyle adjustments tailored to the individual’s needs and the specific side effects experienced.
Nausea and Vomiting Management
Nausea and vomiting are common side effects of many liver cancer treatments, including chemotherapy and radiation therapy. These side effects can lead to dehydration, malnutrition, and a significant reduction in quality of life. Effective management strategies focus on preventing these symptoms and alleviating them when they occur. This often involves a multi-pronged approach.
Anti-emetic medications are the cornerstone of nausea and vomiting management. These medications work by blocking the signals that trigger vomiting in the brain or by directly affecting the digestive system. Examples include ondansetron (Zofran), palonosetron (Aloxi), and aprepitant (Emend). The choice of medication and dosage depends on the severity of the nausea and vomiting and the specific cancer treatment being received.
Sometimes, a combination of anti-emetic medications is used to maximize effectiveness. Additionally, dietary modifications can play a significant role. Eating small, frequent meals, avoiding strong odors, and choosing bland foods can help minimize nausea. Staying well-hydrated is also crucial, and sipping on clear liquids or ice chips throughout the day can help prevent dehydration.
Fatigue and Pain Management
Fatigue and pain are frequently reported side effects of liver cancer and its treatments. Fatigue can range from mild tiredness to debilitating exhaustion, significantly impacting daily activities and overall well-being. Pain can be caused by the tumor itself, the treatment, or other complications.
Managing fatigue often involves a combination of strategies. Rest is crucial, but it’s important to balance rest with gentle exercise to maintain strength and energy levels. A registered dietitian can help develop a nutritional plan to ensure adequate energy intake. Some medications, such as corticosteroids, may help alleviate fatigue, but these should only be used under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
For pain management, a variety of approaches are available, including over-the-counter pain relievers like acetaminophen (Tylenol), prescription pain medications such as opioids, and non-pharmacological methods like heat or cold therapy, massage, and relaxation techniques. A multidisciplinary approach involving a pain specialist, oncologist, and physical therapist often leads to the most effective pain management.
Chemotherapy-Induced Liver Injury Management
Chemotherapy can sometimes damage the liver, leading to chemotherapy-induced liver injury (CILI). This can range from mild elevations in liver enzymes to severe liver failure. Early detection and appropriate management are critical to minimize the risk of serious complications.
Supportive medications play a vital role in managing CILI. These medications help protect the liver, reduce inflammation, and support its function. Examples include corticosteroids, which can help reduce inflammation, and ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA), which helps improve bile flow. In severe cases, hospitalization and more intensive medical interventions may be necessary. Lifestyle adjustments, such as avoiding alcohol and certain medications that can further stress the liver, are also important.
A careful monitoring of liver function tests is essential to track the progress and adjust treatment accordingly. Regular blood tests allow healthcare providers to detect any signs of liver damage early on, allowing for timely intervention and minimizing the risk of long-term complications.
Long-Term Side Effects and Their Management
Source: co.in
Navigating liver cancer treatment means understanding the potential side effects, like fatigue and nausea, and proactively minimizing them. It’s all about managing risks, much like the choices Karishma Mehta faced when she decided to freeze her eggs, as detailed in this article: karishma mehta gets her eggs frozen know risks associated with egg freezing. Open communication with your medical team about your liver cancer treatment is key to identifying and addressing any side effects early on, ensuring the best possible outcome.
The fight against liver cancer often involves aggressive treatments that, while saving lives, can leave lasting impacts on the body. Understanding these long-term side effects and proactively managing them is crucial for maintaining quality of life after treatment. While the immediate side effects are often addressed during treatment, the lingering consequences require ongoing vigilance and careful monitoring. This section explores some of the potential long-term effects and offers strategies for their management.
Cardiovascular Complications
Many liver cancer treatments, particularly chemotherapy and radiation therapy, can damage the heart. This damage can manifest as reduced heart function, an increased risk of heart failure, or abnormal heart rhythms (arrhythmias). Regular monitoring with echocardiograms (ultrasound of the heart) and electrocardiograms (ECG, measuring the heart’s electrical activity) is essential. Lifestyle modifications, such as maintaining a healthy diet, regular exercise (as advised by your doctor), and avoiding smoking, are crucial in mitigating these risks.
In some cases, medication may be necessary to manage heart conditions that develop. For example, beta-blockers might be prescribed to control abnormal heart rhythms.
Kidney Dysfunction
Certain chemotherapy drugs and radiation therapy can negatively impact kidney function. This can lead to reduced kidney filtration, accumulation of toxins in the body, and potentially chronic kidney disease. Regular blood tests to monitor creatinine levels (a marker of kidney function) are vital. Maintaining adequate hydration and avoiding nephrotoxic medications (drugs that are harmful to the kidneys) are crucial.
In advanced cases, dialysis might be necessary to support kidney function. Early detection and proactive management can significantly slow the progression of kidney damage.
Neuropathy
Nerve damage (neuropathy), particularly peripheral neuropathy affecting the hands and feet, is a possible long-term side effect of some chemotherapy drugs. This can cause numbness, tingling, pain, weakness, and loss of coordination. Regular neurological examinations can help detect the onset and progression of neuropathy. Pain management strategies, including medication (such as gabapentin or pregabalin), physical therapy, and lifestyle adjustments, are important.
Protecting the extremities from injury is crucial due to the reduced sensation.
Recommendations for Long-Term Follow-Up Care After Liver Cancer Treatment
It’s vital to have a comprehensive plan for long-term follow-up care after liver cancer treatment. This involves regular monitoring and proactive management of potential long-term side effects.
Here are some key recommendations:
- Regular check-ups with your oncologist and other specialists (cardiologist, nephrologist, neurologist, as needed).
- Routine blood tests to monitor liver function, kidney function, and blood counts.
- Periodic imaging studies (e.g., CT scans, MRI scans) to detect recurrence or monitor for new problems.
- Lifestyle modifications, including a healthy diet, regular exercise (as tolerated), stress management, and avoidance of smoking and excessive alcohol consumption.
- Prompt reporting of any new or worsening symptoms to your healthcare team.
- Participation in support groups or counseling to address emotional and psychological challenges.
Individualized Treatment Plans and Risk Mitigation
Source: mdpi.com
Liver cancer treatments, while life-saving, often bring nasty side effects like fatigue and nausea. Minimizing these risks involves a holistic approach, including a healthy diet. Understanding nutritional needs is key, and that’s where this article comes in: are women and men receptive of different types of food and game changing superfoods for women , as tailoring your diet to your gender can significantly impact your recovery.
Focusing on nutrient-rich foods can help bolster your immune system during and after treatment, making a real difference in managing those pesky side effects.
Liver cancer treatment is not a one-size-fits-all approach. The best course of action depends heavily on individual circumstances, ensuring a personalized plan is crucial for maximizing effectiveness and minimizing the potential for debilitating side effects. This personalized approach considers several key factors to tailor treatment and risk mitigation strategies.The choice of treatment and the likelihood of experiencing side effects are significantly influenced by a patient’s age, overall health, and the specific type and stage of their liver cancer.
Older patients, for example, might be more susceptible to the toxicities of certain chemotherapy regimens, necessitating a careful consideration of the balance between treatment benefits and potential side effects. Similarly, patients with pre-existing conditions like heart or kidney disease require a modified approach to avoid exacerbating these issues. The type of liver cancer (hepatocellular carcinoma, cholangiocarcinoma, etc.) also dictates the most effective treatment options, each carrying its own unique profile of potential side effects.
For instance, surgical resection, while highly effective for early-stage cancers, carries risks of bleeding, infection, and bile duct injury. Targeted therapies, on the other hand, may cause fatigue, skin rashes, or hand-foot syndrome.
Factors Influencing Treatment Choice and Side Effect Risk
Age, overall health status (including presence of other medical conditions), the specific type and stage of liver cancer, and the patient’s personal preferences all play a crucial role in selecting the most appropriate treatment strategy. A thorough assessment of these factors is essential for creating a tailored treatment plan that optimizes the chances of success while minimizing potential harm.
Younger patients with good overall health might tolerate more aggressive treatment regimens, whereas older patients with comorbidities may benefit from less intensive approaches. Early-stage cancers often respond well to surgery or localized therapies, whereas advanced cancers might require systemic treatments like chemotherapy, targeted therapy, or immunotherapy, each with its own set of potential side effects.
Shared Decision-Making in Treatment Planning
Shared decision-making is paramount in the development of a liver cancer treatment plan. This collaborative approach involves open communication and mutual agreement between the patient and their healthcare team (oncologist, hepatologist, surgeon, etc.). The patient’s values, preferences, and understanding of the risks and benefits of each treatment option are central to this process. The healthcare team provides evidence-based information, explaining the potential benefits, risks, and side effects associated with different treatments.
Together, they collaboratively select a treatment plan that best aligns with the patient’s individual needs and goals. This shared decision-making process empowers patients to actively participate in their care, leading to increased satisfaction and improved adherence to the treatment plan.
Hypothetical Patient Profile and Tailored Treatment Plan
Let’s consider a hypothetical case: A 60-year-old male patient, Mr. Jones, is diagnosed with stage II hepatocellular carcinoma. He has a history of hypertension, well-controlled with medication. His overall health is otherwise good. His oncologist, after a thorough assessment, proposes a combination of surgical resection followed by adjuvant targeted therapy.
The surgical resection aims to remove the cancerous tumor, while the targeted therapy helps prevent recurrence.To mitigate the risk of side effects, a multi-pronged approach is implemented. Pre-operative nutritional support is provided to improve his overall health and enhance his ability to tolerate surgery. During surgery, meticulous surgical techniques are employed to minimize bleeding and other complications.
Post-operatively, he receives close monitoring for signs of infection or bile duct injury. For the targeted therapy, the oncologist carefully monitors his blood counts and liver function tests to detect and manage potential side effects such as fatigue and skin rash. He is also provided with strategies for managing fatigue, such as pacing activities and getting adequate rest.
Furthermore, the patient is educated on the importance of reporting any new or worsening symptoms to his healthcare team promptly. This proactive approach, combining careful treatment selection and vigilant monitoring, aims to optimize the effectiveness of treatment while minimizing the impact of potential side effects.
Nutritional Considerations for Minimizing Side Effects
Source: actchealth.com
Dealing with the side effects of liver cancer treatment can be tough, requiring careful management and proactive strategies to minimize risks. It’s all about finding the right balance, much like the approach needed for managing other challenging conditions, such as the effective techniques outlined in this helpful article on strategies to manage Tourette syndrome in children. Understanding the potential side effects and working closely with your medical team is key to navigating this journey and improving your quality of life during and after treatment.
Proper nutrition plays a vital role in supporting your body’s ability to cope with the challenges of liver cancer treatment and recovery. A well-balanced diet can help minimize side effects, improve your energy levels, and strengthen your immune system, ultimately improving your overall quality of life during and after treatment. This is not about a quick fix, but a long-term strategy for better health outcomes.Maintaining a healthy weight is also crucial.
Both undernutrition and obesity can negatively impact treatment response and recovery. Consult with a registered dietitian or oncology nutritionist for personalized guidance. They can help you create a meal plan tailored to your specific needs and preferences, taking into account any dietary restrictions or limitations imposed by your treatment.
Sample Meal Plan Supporting Liver Health
The following sample meal plan provides a general guideline. Remember, individual needs vary, and it’s crucial to consult with a healthcare professional for personalized dietary advice. Portion sizes should be adjusted to meet your individual caloric needs.
| Meal | Food Items | Nutritional Benefits | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Breakfast | Oatmeal with berries and nuts, a glass of green tea | Fiber, antioxidants, healthy fats, sustained energy release | Choose whole grain oats for added fiber. Limit added sugar. |
| Lunch | Grilled salmon with quinoa and steamed broccoli | High-quality protein, omega-3 fatty acids, fiber, vitamins | Salmon is a good source of protein and healthy fats. Quinoa provides complete protein and fiber. |
| Dinner | Lentil soup with whole-wheat bread | Plant-based protein, fiber, iron, and various vitamins and minerals | Lentils are a great source of plant-based protein. Choose whole-wheat bread for added fiber. |
| Snacks | Greek yogurt with fruit, a handful of almonds, vegetable sticks with hummus | Protein, calcium, healthy fats, vitamins, and minerals | Choose plain Greek yogurt and add fruit for natural sweetness. |
Dietary Supplements and Liver Function
Dietary supplements can play a supporting role in liver health, but it’s crucial to use them cautiously and under the guidance of your healthcare team. Some supplements, like milk thistle, have shown promise in supporting liver function, but more research is needed to confirm their effectiveness in liver cancer patients. Crucially, many supplements can interact negatively with cancer medications, potentially reducing their effectiveness or increasing side effects.
Always inform your doctor or pharmacist about any supplements you are considering taking, including vitamins and herbal remedies, to avoid potential complications. Self-treating with supplements without medical supervision is strongly discouraged. The potential benefits must be carefully weighed against the risks of adverse interactions.
Final Review
Navigating liver cancer treatment and its associated side effects can feel overwhelming, but remember you’re not alone. By understanding the potential challenges and actively participating in your care, you can significantly improve your experience and outcome. This journey requires a proactive approach, open communication with your healthcare team, and a commitment to self-care. Prioritizing your well-being, both physically and emotionally, is crucial throughout this process.
Remember to leverage the resources available to you, including support groups and healthcare professionals, to build a strong support network that can help you navigate this journey with resilience and hope.
Q&A
What are some common mild side effects of liver cancer treatment?
Mild side effects can include fatigue, nausea, hair loss, and changes in appetite. These are often manageable with lifestyle adjustments and over-the-counter medications.
How can I cope with fatigue during treatment?
Prioritize rest, break down tasks into smaller parts, eat a balanced diet, and consider gentle exercise like walking when you feel up to it. Talk to your doctor about fatigue management strategies.
Are there any dietary supplements that can help manage side effects?
Always discuss supplements with your doctor before taking them, as they can interact with medications. Some supplements might support liver health, but it’s crucial to have professional guidance.
What should I do if I experience severe side effects?
Contact your healthcare team immediately. Severe side effects require prompt medical attention to prevent complications.
How often should I have follow-up appointments after treatment?
Follow-up schedules vary depending on your individual situation. Your doctor will recommend a plan based on your specific needs and risk factors.
