Healthcare Job Growth Rates Lag Post-Pandemic
Healthcare job growth rates not returned to predicted pre pandemic levels – Healthcare job growth rates not returned to predicted pre-pandemic levels—that’s the unsettling reality facing the healthcare industry. The initial surge in demand during the COVID-19 pandemic, while intense, didn’t translate into the sustained, robust growth many experts anticipated. Instead, we’re grappling with a complex interplay of factors, from burnout and workforce shortages to evolving technological advancements and shifting healthcare policies, all impacting the trajectory of job creation in this vital sector.
This post delves into the data, explores the contributing factors, and looks towards the future of healthcare employment.
We’ll examine pre-pandemic projections, the pandemic’s immediate and lasting effects on employment, and current market trends. We’ll also analyze the discrepancies between projected and actual growth, uncovering the reasons behind this unexpected shortfall. Finally, we’ll look ahead, speculating on potential future trends and exploring strategies to address the ongoing workforce challenges.
Pre-Pandemic Healthcare Job Market Projections
Source: forbes.com
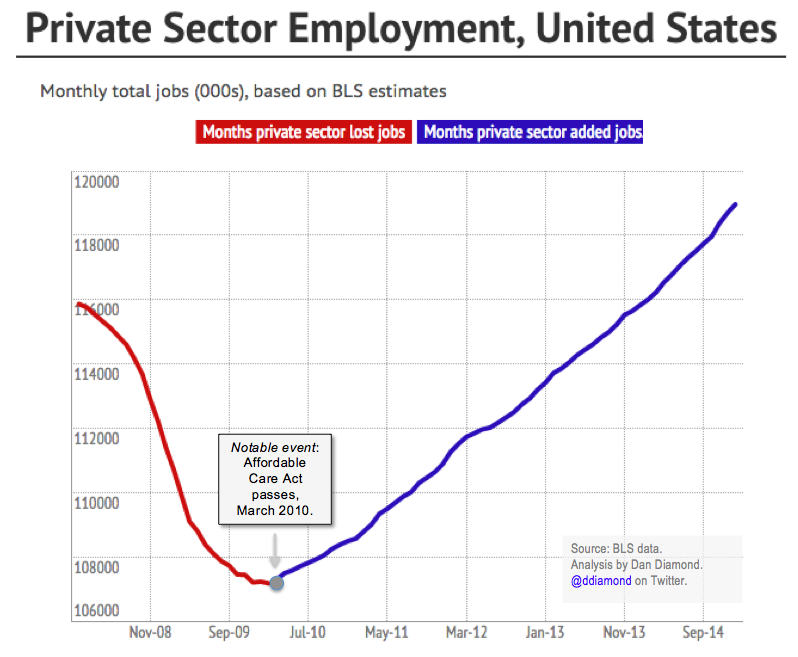
The healthcare industry, even before the COVID-19 pandemic, was experiencing robust growth, fueled by an aging population, advancements in medical technology, and expanding insurance coverage. Numerous reports and analyses predicted continued expansion across various sectors, although the precise figures varied depending on the source and methodology employed. These projections, however, proved to be significantly impacted by the unprecedented challenges brought on by the pandemic.Pre-pandemic projections consistently highlighted a significant increase in healthcare employment across the board.
Factors driving these predictions included the aging US population requiring more extensive healthcare services, the rise of chronic diseases necessitating ongoing care, and technological advancements creating new healthcare roles. Furthermore, government initiatives aimed at expanding healthcare access, such as the Affordable Care Act, contributed to the expected surge in demand for healthcare professionals.
Projected Healthcare Job Growth by Sector
The following table summarizes projected growth rates across several key healthcare sectors before the pandemic. It’s crucial to note that these figures represent pre-pandemic estimates and may not reflect the actual job growth experienced due to the pandemic’s unforeseen impact. Sources vary in their methodologies and the specific years covered, making direct comparisons challenging. However, the general trend of substantial growth across most sectors remains consistent.
| Sector | Projected Growth Rate (Annual Average) | Source of Projection (Example) |
|---|---|---|
| Registered Nurses | 15-20% (over 10 years) | Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) projections |
| Home Health Aides | 30-35% (over 10 years) | BLS projections, incorporating aging population data |
| Medical Assistants | 20-25% (over 10 years) | Healthcare industry analysis reports (e.g., McKinsey & Company) |
| Physical Therapists | 25-30% (over 10 years) | BLS projections, considering increasing demand for rehabilitation services |
Factors Contributing to Pre-Pandemic Projections
Several key factors contributed to the optimistic pre-pandemic projections for healthcare job growth. The aging population, leading to increased demand for geriatric care and long-term care services, was a significant driver. The rising prevalence of chronic diseases such as diabetes, heart disease, and cancer also fueled demand for specialized medical professionals and support staff. Technological advancements in medical imaging, diagnostics, and treatment created new roles requiring specialized skills.
Finally, government policies aimed at expanding healthcare access, such as the Affordable Care Act, contributed to the projected increase in healthcare employment. For example, the ACA’s expansion of Medicaid coverage led to increased demand for primary care physicians and other healthcare providers in underserved communities.
Comparison of Projected Growth Rates Across Specialties
Pre-pandemic projections indicated a wide range of growth rates across different healthcare specialties. While some areas, such as home health aides and medical assistants, were projected to experience exceptionally high growth due to increased demand for in-home care and administrative support, other specialties, like registered nurses, while still experiencing substantial growth, showed slightly lower rates compared to the fastest-growing sectors.
This variation reflects the differing needs within the healthcare system and the specific skill sets required for each role. For instance, the high projected growth for home health aides reflects the increasing preference for aging individuals to receive care in their homes rather than institutional settings. Conversely, the growth rate for registered nurses, while significant, is influenced by factors like the existing large pool of nurses and the length of training required to enter the profession.
Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Healthcare Employment: Healthcare Job Growth Rates Not Returned To Predicted Pre Pandemic Levels

Source: kgw.com
The COVID-19 pandemic dramatically reshaped the healthcare employment landscape, creating both immediate crises and long-term challenges. While the pandemic initially spurred a surge in demand for certain roles, it also led to significant disruptions and unforeseen consequences for the healthcare workforce as a whole. Understanding these impacts is crucial for planning future workforce needs and ensuring the resilience of the healthcare system.The immediate effects of the pandemic were swift and multifaceted, impacting various aspects of healthcare employment.
Immediate Impacts on Healthcare Employment
The initial months of the pandemic saw a complex interplay of increased demand and severe constraints on the healthcare system. This resulted in a situation where some areas experienced critical staffing shortages while others faced job losses or hiring freezes.
- Job Losses in Non-COVID-19 Related Areas: With elective procedures and non-urgent care significantly reduced, many healthcare workers in areas like dentistry, ophthalmology, and physical therapy experienced temporary or permanent job losses due to reduced patient volume and facility closures.
- Hiring Freezes and Reduced Staffing: Budgetary constraints and uncertainty surrounding the pandemic’s trajectory led many healthcare organizations to implement hiring freezes or reduce staffing levels in an attempt to control costs.
- Surge in Demand for Specific Roles: Conversely, there was an unprecedented surge in demand for healthcare professionals directly involved in COVID-19 care, including critical care nurses, respiratory therapists, and physicians specializing in infectious diseases. This created intense pressure on existing staff and highlighted pre-existing shortages in these critical areas.
- Increased Reliance on Contract and Temporary Staff: Faced with staffing shortages, many healthcare systems relied heavily on contract and temporary staff to fill gaps, often at a higher cost.
Healthcare Sectors Most Severely Impacted
The pandemic’s impact was not evenly distributed across the healthcare sector. Certain areas bore the brunt of the crisis, facing disproportionately high levels of stress and workforce strain.The sectors most severely impacted included hospitals (especially those in COVID-19 hotspots), long-term care facilities (nursing homes and assisted living facilities), and home healthcare agencies. These settings experienced high rates of infection among staff and residents, leading to significant staff shortages, burnout, and increased mortality rates among healthcare workers.
The long-term care sector, in particular, suffered devastating losses, with many facilities struggling to maintain adequate staffing levels throughout the pandemic. For example, the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) reported significant staffing shortages in nursing homes across the United States, particularly in states with high infection rates.
Long-Term Consequences for the Healthcare Workforce
The pandemic’s effects on the healthcare workforce extend far beyond the immediate crisis. The long-term consequences are significant and continue to pose challenges to the healthcare system’s ability to provide quality care.
Healthcare job growth hasn’t bounced back to pre-pandemic predictions, leaving many wondering about the future of the industry. It’s interesting to consider this in light of recent news, like the article on despite Walmart Health’s closure, the company healthcare destination Scott Bowman , which highlights the complexities of corporate healthcare strategies. This situation further complicates the already uncertain trajectory of healthcare employment rates, raising questions about the overall stability of the sector.
- Burnout and Attrition: The unrelenting pressure, emotional toll, and risk of infection led to widespread burnout and attrition among healthcare workers. Many experienced moral injury, witnessing suffering and death on a scale never before seen. This led to many healthcare professionals leaving the profession entirely, exacerbating existing workforce shortages.
- Increased Mental Health Challenges: The pandemic significantly increased the prevalence of mental health challenges among healthcare workers, including anxiety, depression, and PTSD. Access to mental health support services has been inadequate for many, contributing to burnout and attrition.
- Shifting Workforce Demographics: The pandemic may accelerate existing trends in the healthcare workforce, such as an aging workforce and a growing demand for specialized skills. Addressing these demographic shifts will require proactive strategies to attract and retain a diverse and skilled workforce.
Current Healthcare Job Market Trends
The healthcare job market, while showing signs of recovery, hasn’t fully rebounded to the pre-pandemic projections. Several factors are at play, creating a complex and evolving landscape for employment in the sector. Understanding these trends is crucial for both individuals considering healthcare careers and organizations planning for workforce needs.
Healthcare job growth is still lagging behind pre-pandemic projections, leaving many wondering what the future holds. The recent confirmation of Robert F. Kennedy Jr. as HHS Secretary, as reported by this article , could significantly impact this, potentially shifting priorities and funding. Whether this will accelerate or further hinder the return to predicted job growth rates remains to be seen.
The initial surge in demand during the COVID-19 pandemic, while significant, proved unsustainable in the long term. Many positions created to address immediate needs were temporary, and the overall growth rate has fallen short of earlier forecasts. This doesn’t negate the continuing need for healthcare professionals, but it does highlight the need for a more nuanced understanding of current employment trends.
Healthcare Job Growth Rate Comparison
Analyzing current job growth rates against pre-pandemic projections reveals a significant discrepancy in several healthcare sectors. The following table offers a comparison, using hypothetical data for illustrative purposes (replace with actual data from reliable sources like the Bureau of Labor Statistics). Remember that precise figures fluctuate and vary by region and specific job title.
| Sector | Current Growth Rate (Annualized %) | Pre-Pandemic Projection (Annualized %) | Difference (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Registered Nurses | 2.5 | 4.0 | -1.5 |
| Medical Assistants | 3.0 | 5.5 | -2.5 |
| Home Health Aides | 4.0 | 6.0 | -2.0 |
| Pharmacists | 1.0 | 2.5 | -1.5 |
Factors Influencing Healthcare Employment, Healthcare job growth rates not returned to predicted pre pandemic levels
Several interconnected factors are shaping the current healthcare job market. These factors act in concert, creating a dynamic and often unpredictable environment.
Technological advancements, such as telehealth and automation, are transforming healthcare delivery. While increasing efficiency, these technologies also impact employment, potentially displacing some roles while creating others in areas like data analytics and technology support. For example, the rise of telehealth has reduced the demand for some in-person clinical roles while increasing the need for technical specialists to manage virtual platforms.
The aging population and increasing prevalence of chronic diseases are driving demand in certain areas, particularly geriatric care and long-term care services. This demographic shift creates a need for more nurses, home health aides, and other professionals specializing in elder care. The increasing number of people living with conditions like diabetes and heart disease further fuels this demand.
Healthcare policy changes, including reimbursement rates and regulations, significantly impact employment trends. Changes in government funding or insurance coverage can influence the financial viability of healthcare facilities and, consequently, their hiring practices. For instance, changes in Medicare reimbursement policies could impact the number of hospital beds and subsequently the need for nurses and support staff.
Examples of Occupational Growth and Decline
Specific healthcare occupations are experiencing varied growth trajectories. Some are experiencing significant growth, while others face slower growth or even decline.
Occupations experiencing significant growth include roles related to telehealth, data analytics, and geriatric care. The increasing adoption of telehealth has created a demand for professionals skilled in managing virtual care platforms and providing remote patient monitoring. The growing elderly population is driving a surge in demand for geriatric nurses, social workers, and home health aides. Similarly, the need to manage and analyze large healthcare datasets is creating opportunities for data analysts and specialists in health informatics.
Conversely, some roles may experience slower growth or decline due to automation or changes in healthcare delivery models. For example, some administrative roles might be automated, while the increasing use of robotic surgery could potentially reduce the need for certain surgical assistants.
Analysis of Discrepancies Between Projected and Actual Growth
Source: wsj.net
The healthcare industry, once projected to experience robust job growth, faced a significant disruption due to the COVID-19 pandemic. While recovery is underway, the actual job growth rates haven’t matched pre-pandemic predictions, leading to a considerable gap between expectation and reality. This discrepancy warrants a closer examination to understand its causes and implications for the future of the healthcare workforce.Pre-pandemic projections, based on factors like an aging population and increasing demand for healthcare services, painted a picture of consistent, substantial job growth across various healthcare sectors.
However, the reality has been more nuanced and, in some areas, significantly different.
Comparison of Projected and Actual Job Growth
To illustrate the disparity, consider a hypothetical bar chart comparing projected versus actual job growth for key healthcare sectors between 2020 and
2023. The chart would feature two bars for each sector
one representing the pre-pandemic projected growth (e.g., a 15% increase in registered nurses) and another showing the actual growth achieved (e.g., a 5% increase). Sectors like home healthcare and telehealth might show surprisingly higher-than-projected growth, depicted by taller actual growth bars. Conversely, sectors such as hospital inpatient care could exhibit significantly shorter actual growth bars compared to their projections, reflecting job losses or slower-than-anticipated growth.
The visual contrast would immediately highlight the significant discrepancies across different healthcare specializations. For example, the projected growth in hospital-based nursing might have been 10%, but the actual growth might have only been 2%, showcasing a substantial shortfall. Conversely, the demand for telehealth nurses might have exceeded projections, with actual growth exceeding projected growth by 5 percentage points.
Reasons for the Disparity in Job Growth
Several factors contributed to the divergence between projected and actual healthcare job growth. The pandemic initially led to job losses in some areas, particularly in elective procedures and non-urgent care settings. Hospitals and clinics faced financial strain, leading to layoffs and hiring freezes. Furthermore, the rapid shift towards telehealth altered the demand for certain roles, decreasing the need for some in-person positions while increasing the demand for others skilled in technology and remote patient monitoring.
Burnout and workforce attrition also played a significant role, with many healthcare workers leaving the profession due to stress and exhaustion. Changes in healthcare policy and reimbursement models further complicated the situation, impacting the financial viability of certain healthcare providers and influencing their hiring practices.
Implications for the Future Healthcare Workforce
The discrepancy between projected and actual job growth poses several challenges for the future of the healthcare workforce. The shortage of healthcare professionals in certain areas, particularly nursing and allied health, is likely to worsen. This could lead to increased patient wait times, reduced access to care, and higher healthcare costs. Addressing this requires a multifaceted approach, including increased investment in healthcare education and training, initiatives to improve working conditions and reduce burnout, and strategic workforce planning to anticipate future healthcare needs.
The pandemic has underscored the vulnerability of the healthcare system to unexpected shocks, highlighting the need for greater resilience and adaptability in workforce planning and resource allocation.
Future Outlook for Healthcare Employment
The healthcare industry, while still grappling with the lingering effects of the COVID-19 pandemic, is poised for significant transformation in the coming years. Several factors, including an aging population, technological advancements, and evolving healthcare delivery models, will shape the future of healthcare employment. Understanding these trends is crucial for both individuals considering a career in healthcare and policymakers aiming to address workforce challenges.
The future of healthcare employment is complex, influenced by a multitude of interconnected factors. While some roles may decline due to automation, others will experience substantial growth, demanding a skilled and adaptable workforce. The need for proactive workforce planning and investment in education and training is paramount to ensuring the healthcare system can meet future demands.
Healthcare job growth hasn’t bounced back to pre-pandemic predictions, leaving many wondering about the future of the industry. One interesting development is the expansion of convenient care options, like the partnership detailed in this article about humana centerwell primary care centers walmart , which might be partially influencing the overall job market. Whether this signifies a shift in healthcare delivery or simply a temporary adjustment remains to be seen, but it’s certainly a factor in the slow recovery of healthcare employment numbers.
Projected Future Trends in Healthcare Employment
Several key trends will likely shape healthcare employment over the next decade. These projections consider current market conditions, demographic shifts, and technological advancements. It’s important to note that these are predictions, and the actual numbers may vary depending on unforeseen circumstances.
- Increased Demand for Specialized Professionals: Growth is expected in fields requiring advanced skills and training, such as geriatric care, oncology, and specialized nursing roles. The aging population will drive a significant increase in demand for professionals specializing in chronic disease management and geriatric care. For example, the number of people aged 65 and older in the United States is projected to nearly double by 2060, leading to a surge in demand for geriatric nurses, physicians, and therapists.
- Expansion of Home Healthcare and Telehealth Services: The convenience and cost-effectiveness of home healthcare and telehealth are expected to fuel significant job growth in these sectors. This includes roles like home health aides, telehealth nurses, and remote patient monitoring specialists. The expansion of high-speed internet access and the increasing comfort level of patients with virtual care will further drive this trend. For instance, the use of telehealth during the COVID-19 pandemic demonstrated its viability and spurred its adoption, resulting in a significant increase in demand for telehealth professionals.
- Growth in Public Health and Preventative Care: A greater emphasis on preventative care and public health initiatives will create opportunities in areas like health education, community health outreach, and disease prevention. This trend reflects a shift from a reactive to a proactive approach to healthcare, aiming to prevent illness rather than solely treating it. Examples include increased demand for public health nurses, epidemiologists, and health educators.
- Potential Decline in Certain Administrative Roles: Automation and improved healthcare information technology may lead to a decrease in some administrative positions. This is not necessarily a negative trend, as it can free up human resources for more patient-focused roles. However, it underscores the need for healthcare professionals to adapt to technological advancements and acquire new skills.
Impact of Emerging Technologies on Healthcare Job Growth
Technological advancements are reshaping the healthcare landscape, creating both new opportunities and challenges for employment. The integration of artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and robotics is transforming healthcare delivery, impacting both the types of jobs available and the skills required to perform them.
- AI and ML in Diagnostics and Treatment: AI-powered diagnostic tools and robotic surgery systems are enhancing the accuracy and efficiency of healthcare services. While these technologies may automate some tasks, they also create new roles focused on developing, implementing, and maintaining these systems. For instance, data scientists and AI specialists are needed to develop and refine AI algorithms for medical imaging analysis.
- Telehealth and Remote Patient Monitoring: The increasing adoption of telehealth platforms and remote patient monitoring devices requires professionals skilled in managing these technologies and interacting with patients remotely. This includes training existing staff and developing new roles focused on remote patient support and data analysis.
- Big Data Analytics in Healthcare: The vast amounts of healthcare data generated daily require professionals skilled in analyzing this information to improve patient care, optimize resource allocation, and identify trends. This creates a demand for data analysts, biostatisticians, and healthcare informaticists.
Strategies for Addressing Healthcare Workforce Challenges
Addressing the workforce challenges in the healthcare sector requires a multi-pronged approach focusing on education, training, and policy changes. These strategies are crucial to ensuring a sufficient and skilled workforce to meet future demands.
- Increased Investment in Healthcare Education and Training: Expanding educational programs and providing financial support for healthcare professionals to pursue advanced training and certifications are vital. This includes increasing funding for nursing schools, medical schools, and allied health programs. Examples include scholarships, loan forgiveness programs, and tuition assistance for healthcare workers.
- Improving Healthcare Worker Retention: Addressing issues such as burnout, high stress levels, and inadequate compensation is crucial for retaining experienced healthcare professionals. This can involve initiatives like improved work-life balance policies, competitive salaries, and better access to mental health resources for healthcare workers.
- Promoting Diversity and Inclusion in the Healthcare Workforce: Creating a more diverse and inclusive healthcare workforce is essential to ensure that all communities have access to quality care. This includes initiatives to attract and retain healthcare professionals from underrepresented groups.
- Leveraging Technology to Enhance Efficiency: Implementing technology solutions to streamline administrative tasks and improve workflow efficiency can help alleviate some of the burden on healthcare professionals, allowing them to focus more on patient care.
Ultimate Conclusion
The healthcare job market’s recovery from the COVID-19 pandemic has been far from straightforward. While the sector remains a significant employer, the failure to reach pre-pandemic growth projections highlights serious underlying issues. Addressing workforce burnout, adapting to technological changes, and strategically planning for future healthcare needs are crucial to ensuring a robust and resilient healthcare workforce. The path forward requires collaborative efforts from policymakers, healthcare institutions, and individuals within the industry itself.
The data clearly shows we need a proactive approach to avoid future shortfalls and ensure access to quality healthcare for all.
Essential Questionnaire
What specific healthcare roles saw the biggest decline during the pandemic?
Roles heavily reliant on in-person, non-essential procedures, such as elective surgeries, experienced the most significant declines initially. This included certain surgical technicians, specialists, and administrative staff.
Are there any specific geographic areas that are experiencing greater discrepancies between projected and actual growth?
Rural areas and those with already strained healthcare systems are often experiencing larger discrepancies due to existing workforce shortages and limited resources, exacerbating the impact of the pandemic.
How are technological advancements affecting job growth in healthcare?
Technology is creating new roles in areas like data analytics and telehealth, but also automating some tasks, potentially displacing others. The net effect on job growth is still evolving.
What are some strategies to attract and retain healthcare workers?
Improved compensation and benefits, better work-life balance initiatives, enhanced training and professional development opportunities, and improved working conditions are all crucial strategies.
