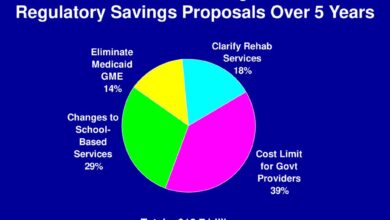
Nonprofit Hospitals Charity Care Spending Drops
Nonprofit hospitals charity care spending drops – it’s a headline that’s raising serious questions about the future of healthcare access for vulnerable populations. We’re seeing a worrying trend, a decline in the crucial funding that helps those who can least afford it get the medical care they desperately need. This isn’t just about numbers on a spreadsheet; it’s about real people facing real hardship.
This post dives into the reasons behind this decline, explores potential solutions, and examines the broader implications for our communities.
The decrease in charity care spending isn’t happening in a vacuum. Rising healthcare costs, increasingly complex regulations, and evolving hospital operational challenges are all playing a significant role. We’ll unpack these factors, examining both internal hospital issues and broader market forces, to understand the full picture. We’ll also look at innovative strategies for securing alternative funding sources and improving the efficiency of existing resources.
The goal? To ensure that those who rely on nonprofit hospitals for care continue to receive it, even in the face of these significant financial pressures.
Impact of Reduced Charity Care Spending
The decline in charity care spending by nonprofit hospitals is a deeply concerning trend with far-reaching consequences for vulnerable populations and the overall health of communities. This reduction not only impacts individuals’ access to vital medical services but also creates ripple effects throughout the local economy. Understanding the magnitude of this issue is crucial to developing effective solutions.
Consequences for Vulnerable Populations
Decreased charity care directly harms individuals who lack the financial resources to afford healthcare. This includes the uninsured, the underinsured, and those with chronic illnesses requiring ongoing, expensive treatment. Without access to subsidized care, these individuals may delay or forgo necessary medical attention, leading to worsening health conditions, increased hospitalizations later on (at a higher cost), and even premature mortality.
The most vulnerable – the elderly, children, and those with pre-existing conditions – are disproportionately affected. A lack of preventative care further exacerbates the problem, leading to more expensive emergency room visits instead of proactive management.
Economic Effects on Communities
The economic impact of reduced charity care extends beyond the individual patient. Nonprofit hospitals are major employers and significant contributors to the local economy. When these hospitals reduce their charity care, the resulting increase in uncompensated care shifts the financial burden to other areas, potentially leading to higher taxes, reduced hospital services, and job losses within the healthcare system.
Furthermore, a sicker population translates to reduced workforce productivity and increased reliance on social safety nets, placing further strain on community resources. This creates a negative feedback loop where the economic health of the community is directly linked to the access to affordable healthcare.
Comparison of Charity Care Spending Over Time
Comparing current charity care spending to previous years reveals a significant downward trend. While precise figures vary depending on the hospital and geographic location, many nonprofit hospitals have reported reductions of 10-20% or more in the past five years. Several factors contribute to this decrease, including increased operating costs, stricter regulatory requirements for qualifying for charity care, and a shift towards a greater emphasis on cost-cutting measures.
The Affordable Care Act, while expanding insurance coverage, hasn’t entirely eliminated the need for charity care, and in some instances, may have inadvertently complicated the process for hospitals.
Hypothetical Scenario: 20% Reduction in Charity Care
Let’s imagine County General Hospital, a large nonprofit serving a diverse population, experiences a 20% reduction in its charity care budget. This hospital previously provided $5 million annually in charity care. A 20% reduction means $1 million less available for subsidized care. This could translate to roughly 200 fewer patients receiving the necessary treatments or medications each year, potentially leading to preventable hospital readmissions, increased emergency room visits, and a higher overall healthcare burden on the community.
This also disproportionately impacts the hospital’s already underserved patient population, such as the elderly living on fixed incomes or those with chronic conditions. The hospital might need to implement stricter eligibility criteria, further limiting access for those in need. The potential consequences extend beyond the individual patient, impacting the overall health and economic stability of the community served by County General.
Factors Contributing to the Decline: Nonprofit Hospitals Charity Care Spending Drops
The decrease in charity care spending by nonprofit hospitals is a complex issue stemming from a confluence of internal and external pressures. Understanding these contributing factors is crucial for developing effective strategies to address the growing disparity between healthcare needs and access. This section will analyze the key drivers behind this decline, categorized for clarity and impact assessment.
Internal Factors Affecting Charity Care Spending
Internal factors directly related to hospital operations and management significantly influence the amount of charity care provided. These factors often involve financial constraints, resource allocation decisions, and internal policies. For example, a hospital facing financial difficulties might prioritize paying off debt or investing in new equipment over expanding charity care programs. Similarly, internal policies regarding eligibility criteria for charity care can inadvertently limit access for those in need.
External Factors Affecting Charity Care Spending
Market forces and external pressures also play a substantial role in shaping charity care provision. The increasing cost of healthcare, changes in patient demographics, and the competitive landscape all influence hospital decisions. Hospitals in areas with a high concentration of uninsured patients may face greater financial strain, limiting their ability to offer extensive charity care. Conversely, hospitals in wealthier areas might have more resources available but may also face greater pressure to maximize profitability.
Government Policies and Healthcare Regulations
Government policies and healthcare regulations significantly impact a hospital’s ability and willingness to provide charity care. Changes in reimbursement rates for Medicaid and Medicare, for example, can directly affect a hospital’s financial stability and, consequently, its capacity for charity care. Regulations surrounding charity care reporting and eligibility criteria can also influence how much care is provided and to whom.
Furthermore, the shift towards value-based care models may inadvertently incentivize hospitals to focus on profitability over charity care, particularly if those models don’t adequately account for the cost of uncompensated care.
Rising Healthcare Costs and Operational Challenges
The escalating costs of healthcare services, including staffing, pharmaceuticals, and technology, significantly strain hospital budgets. These rising costs often necessitate difficult choices in resource allocation, potentially leading to reductions in charity care spending. Simultaneously, hospitals face operational challenges such as increasing administrative burdens, cybersecurity threats, and the need for continuous infrastructure upgrades. These challenges divert resources and attention away from charity care programs.
Summary of Contributing Factors
| Factor | Category | Impact on Charity Care | Potential Solutions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rising healthcare costs | External | Reduced hospital budgets, less allocation to charity care | Government subsidies, cost-containment strategies, improved efficiency |
| Stringent eligibility criteria | Internal | Limited access to charity care for eligible patients | Relaxing eligibility requirements, improved outreach programs |
| Changes in reimbursement rates | External | Decreased hospital revenue, affecting charity care capacity | Increased government funding for uncompensated care |
| Increased administrative burden | Internal | Diversion of resources from patient care, including charity care | Streamlining administrative processes, technological advancements |
Alternative Funding Sources and Strategies
The decline in charity care spending by nonprofit hospitals necessitates a proactive exploration of alternative funding sources and the implementation of strategies to optimize resource allocation. This shift requires a multifaceted approach, encompassing innovative fundraising, improved operational efficiency, and strategic partnerships. By diversifying revenue streams and streamlining internal processes, hospitals can ensure continued provision of vital care to underserved populations.
Nonprofit hospitals face increasing pressure to balance their financial obligations with their commitment to providing charity care. Finding new revenue streams while maintaining operational efficiency is crucial for their long-term sustainability and their ability to fulfill their mission. This section explores various strategies to achieve this delicate balance.
Alternative Funding Sources for Charity Care
Diversifying funding sources is paramount for maintaining consistent charity care. Beyond traditional donations, hospitals can explore several avenues. These include foundation grants, corporate sponsorships, government programs (beyond Medicare and Medicaid), and crowdfunding campaigns. For instance, a hospital could target specific foundations known for supporting healthcare initiatives in their region, tailoring grant proposals to align with the foundation’s priorities.
It’s alarming to see nonprofit hospitals cutting back on charity care spending; the impact on vulnerable communities is significant. This trend is especially concerning when you consider the challenges faced by rural hospitals, like those detailed in this insightful article on Rural Hospitals Labor Delivery & , which highlights the struggles with staffing and resources. Ultimately, reduced charity care exacerbates existing inequalities and makes access to healthcare even harder for those who need it most.
Corporate sponsorships could involve collaborations with local businesses, where the company provides funding in exchange for branding opportunities or employee volunteer programs. Government programs, beyond the traditional reimbursement systems, might include specific grants aimed at improving access to care for vulnerable populations. Finally, crowdfunding platforms offer a direct avenue to engage the public and raise funds for specific charity care initiatives.
Strategies for Improving Efficiency and Resource Allocation
Improving efficiency and resource allocation is crucial for maximizing the impact of charity care spending. This includes implementing robust cost-containment measures, optimizing staffing models, and leveraging technology to streamline administrative processes. For example, a hospital might adopt a value-based care model, focusing on preventative care and managing chronic conditions effectively to reduce costly hospital readmissions. Streamlining administrative processes through electronic health records and automated billing systems can also free up resources.
Strategic workforce planning and efficient scheduling can also optimize staffing levels, reducing labor costs without compromising patient care.
Models for Delivering Charity Care
Nonprofit hospitals can choose from various models for delivering charity care. Direct provision, where the hospital directly provides services to patients, is a traditional approach. However, partnering with community organizations offers potential advantages. A partnership model might involve collaborating with community health clinics or social service agencies to extend the reach of charity care and leverage their existing networks and expertise.
For instance, a hospital could partner with a local food bank to address food insecurity among patients, a major barrier to health. Comparing these models reveals that direct provision offers greater control but potentially higher costs, while partnerships offer broader reach and cost-sharing opportunities but might entail less direct control over service delivery.
Improving Billing and Collection Practices to Free Up Resources
Effective billing and collection practices are not merely financial operations; they are critical for ensuring the financial health of a hospital and freeing up resources for charity care. Implementing a robust system that includes proactive outreach to patients, streamlined payment options, and efficient debt management can significantly reduce outstanding balances. This frees up funds that can be redirected towards expanding charity care programs.
For example, implementing online payment portals and offering flexible payment plans can improve patient compliance and reduce the time and resources spent on collections. Regularly reviewing and updating billing procedures, ensuring accuracy and clarity, minimizes disputes and reduces the need for costly appeals processes.
Potential Partnerships to Supplement Charity Care Funding, Nonprofit hospitals charity care spending drops
Developing strategic partnerships is vital for supplementing charity care funding. Potential partners could include:
- Foundations and philanthropic organizations
- Corporate sponsors and businesses
- Government agencies and health departments
- Community health centers and clinics
- Faith-based organizations and charities
- Volunteer organizations and medical professionals
These partnerships can provide not only financial resources but also valuable in-kind support, such as volunteer services and access to community resources. Hospitals should actively seek out these collaborations to build a robust and sustainable network of support for their charity care initiatives.
Transparency and Accountability in Charity Care
Ensuring transparency and accountability in charity care is paramount for maintaining public trust and ensuring the ethical use of donated funds. Without clear processes and open communication, the perception of misuse can undermine the vital work of nonprofit hospitals. This section explores methods to improve transparency and accountability, focusing on communication strategies and independent oversight.
Methods for Enhancing Transparency and Accountability
Effective transparency and accountability require a multi-pronged approach. This includes clearly defined policies, accessible data, and robust auditing mechanisms. The hospital should proactively publish its charity care policy, detailing eligibility criteria, application processes, and the types of services covered. This policy should be readily available on the hospital’s website and in easily accessible print formats, such as brochures in the waiting areas.
Furthermore, regular reports summarizing the amount of charity care provided, the number of patients served, and the types of services delivered should be made public. This data can be presented in user-friendly formats, such as infographics or easily digestible summaries, making it accessible to a wider audience. Finally, independent audits should be conducted regularly to verify the accuracy of reported data and ensure compliance with established policies and regulations.
Best Practices in Communicating Charity Care Policies and Performance
Communicating charity care policies and performance effectively involves multiple stakeholders. For patients, clear and concise information about eligibility criteria and the application process is crucial. This can be achieved through easily understandable brochures, multilingual materials, and staff training to ensure consistent and accurate information delivery. Donors need to understand how their contributions are used, so regular reports detailing the impact of their donations on charity care are essential.
This could involve stories of patients who benefited from the program, demonstrating the real-world impact of charitable giving. Community engagement is equally important. The hospital can participate in community events, host town halls, or publish articles in local newspapers to highlight its charity care initiatives and build trust with the community. A dedicated section on the hospital’s website, regularly updated with key performance indicators (KPIs) and success stories, further enhances transparency.
Importance of Regular Audits and Independent Reviews
Regular audits and independent reviews are essential for ensuring the ethical and efficient use of resources dedicated to charity care. Independent audits, conducted by external accounting firms, provide an objective assessment of the hospital’s financial records related to charity care. These audits verify the accuracy of reported data, identify potential areas of improvement, and ensure compliance with relevant regulations and accounting standards.
Independent reviews, conducted by external experts or community advisory boards, can assess the effectiveness of the charity care program in achieving its stated goals. These reviews provide valuable insights into the program’s strengths and weaknesses and can help identify areas for improvement in terms of policy, processes, and outreach. The findings of both audits and reviews should be publicly available, further strengthening accountability and fostering public trust.
It’s disheartening to see nonprofit hospital charity care spending drop, especially given the rising healthcare costs. One potential solution might lie in advancements like those highlighted in a recent study widespread digital twins healthcare , which could improve efficiency and resource allocation. Ultimately, finding ways to increase efficiency, as suggested by the digital twin research, could free up more resources for charity care and alleviate the downward trend.
Sample Communication Plan for Charity Care Initiatives
A comprehensive communication plan is vital for effectively communicating charity care initiatives to the public. This plan should Artikel key messages, target audiences, communication channels, and evaluation methods.
| Target Audience | Key Messages | Communication Channels | Evaluation Methods |
|---|---|---|---|
| Patients | Eligibility criteria, application process, services covered | Brochures, website, staff training | Patient satisfaction surveys, application completion rates |
| Donors | Impact of donations, stories of patients helped, financial transparency | Annual reports, donor newsletters, website updates, social media | Donor retention rates, donation amounts |
| Community | Hospital’s commitment to charity care, community impact | Local newspapers, community events, presentations, social media | Media coverage, website traffic, social media engagement |
This plan should be regularly reviewed and updated to reflect changes in the hospital’s charity care program and the needs of its stakeholders. Consistent communication, transparency, and responsiveness to community concerns are key to building and maintaining public trust.
The Role of Community Engagement
Source: slideplayer.com
Declining charity care spending in nonprofit hospitals presents a significant challenge to ensuring equitable access to healthcare. Addressing this requires a multifaceted approach, and community engagement is arguably the most crucial element. By fostering strong relationships with community organizations and stakeholders, hospitals can build a robust support system capable of mitigating the impact of reduced funding and ensuring vulnerable populations continue to receive necessary care.Community engagement isn’t simply about raising awareness; it’s about building genuine partnerships that leverage the collective resources and expertise of the community to create sustainable solutions.
It’s about understanding the specific needs of the underserved population and tailoring services to meet those needs effectively. This collaborative approach can unlock innovative funding mechanisms and improve the overall effectiveness of charity care initiatives.
Strategies for Building Community Partnerships
Successful community engagement requires a strategic approach. It’s not enough to simply reach out to organizations; hospitals need to cultivate meaningful relationships built on trust and mutual respect. This involves actively listening to community needs, identifying shared goals, and developing collaborative projects that benefit all parties involved. This could include co-hosting health fairs, establishing joint fundraising campaigns, or even creating shared volunteer programs.
Regular communication and transparent reporting are essential to maintaining these partnerships and demonstrating the impact of collaborative efforts.
Examples of Successful Community Partnerships
Numerous examples demonstrate the power of community partnerships in expanding access to affordable healthcare. For instance, the partnership between [Name of Hospital] and [Name of Community Organization] in [City, State] resulted in a significant increase in the number of patients receiving free or discounted healthcare services. Their collaborative fundraising efforts, combined with a targeted outreach program, successfully raised awareness and increased access to vital care within the community.
Another successful example is the [Name of Initiative] program in [City, State], where a network of community clinics, supported by a local hospital, provides integrated healthcare services to low-income families, addressing not only their immediate health needs but also underlying social determinants of health. This holistic approach has proven incredibly effective in improving long-term health outcomes and reducing healthcare disparities.
A Community Outreach Program: Improving Awareness of Charity Care
A successful community outreach program must be multi-pronged, utilizing various communication channels to reach a diverse population. This program would begin with a comprehensive needs assessment to identify the most effective methods for reaching the target audience. For example, in communities with limited internet access, direct mail campaigns, community events, and partnerships with local faith-based organizations would be crucial.
In more digitally connected areas, targeted social media campaigns, website optimization, and collaborations with local media outlets would be essential. The program would also emphasize clear and concise messaging, ensuring that information about eligibility criteria, application processes, and available services is easily accessible and understandable. The program would also include regular feedback mechanisms to evaluate its effectiveness and make necessary adjustments.
This continuous improvement process ensures the program remains relevant and responsive to the evolving needs of the community.
It’s disheartening to see nonprofit hospital charity care spending drop, especially given the increasing healthcare costs. This makes efficient documentation even more crucial, and that’s where advancements like the integration of Nuance’s generative AI scribe with Epic EHRs, as detailed in this article nuance integrates generative ai scribe epic ehrs , become incredibly important. Streamlining documentation could free up resources and potentially alleviate some of the pressure on shrinking charity care budgets.
Concluding Remarks

Source: slideplayer.com
The decline in nonprofit hospital charity care spending is a complex issue with far-reaching consequences. While the challenges are significant, the solutions are not insurmountable. By exploring alternative funding models, enhancing transparency and accountability, and fostering strong community partnerships, we can work towards a future where access to affordable healthcare is not a privilege, but a right. It’s time for a collaborative effort – hospitals, policymakers, communities, and individuals – to ensure that those most in need are not left behind.
The conversation needs to continue, and the solutions need to be implemented.
Commonly Asked Questions
What are the potential legal ramifications of drastically cutting charity care?
Hospitals risk legal challenges if they don’t meet certain requirements for providing charity care, depending on their state and federal regulations. This could involve lawsuits or loss of tax-exempt status.
How can individuals help support charity care initiatives?
Individuals can donate directly to nonprofit hospitals, volunteer their time, advocate for policies supporting charity care, or raise awareness within their communities.
Are there any successful models for charity care partnerships with other organizations?
Yes, many hospitals partner with local clinics, faith-based organizations, and social service agencies to expand their reach and provide more comprehensive care. These collaborations often leverage existing resources and expertise.
How can hospitals improve their billing and collection practices to free up resources for charity care?
Hospitals can improve their billing processes through better patient communication, streamlined systems, and employing skilled billing specialists. They can also implement more effective strategies for collecting payments from insured patients.