Healthcare AI Bias Clinical Accuracy JAMA Study
Healthcare ai bias clinical accuracy jama study – Healthcare AI bias, clinical accuracy, and the JAMA study—these words are increasingly intertwined in discussions about the future of healthcare. This groundbreaking research sheds light on a critical issue: the potential for AI algorithms to perpetuate and even amplify existing biases in healthcare, leading to inaccurate diagnoses, ineffective treatments, and ultimately, disparities in patient outcomes. We’re diving deep into the findings, exploring the different types of bias, and examining how we can build a more equitable and accurate future for AI in medicine.
The JAMA study itself employed a rigorous methodology, meticulously analyzing various AI models used in different clinical settings. Its findings revealed a concerning trend: AI systems, trained on biased data, consistently exhibited lower accuracy rates for certain demographic groups. This isn’t just a technical problem; it’s a matter of ethical responsibility and patient safety. Understanding the nuances of data bias, algorithmic bias, and their downstream effects is crucial for developing truly beneficial AI healthcare solutions.
Introduction to Healthcare AI Bias and Clinical Accuracy
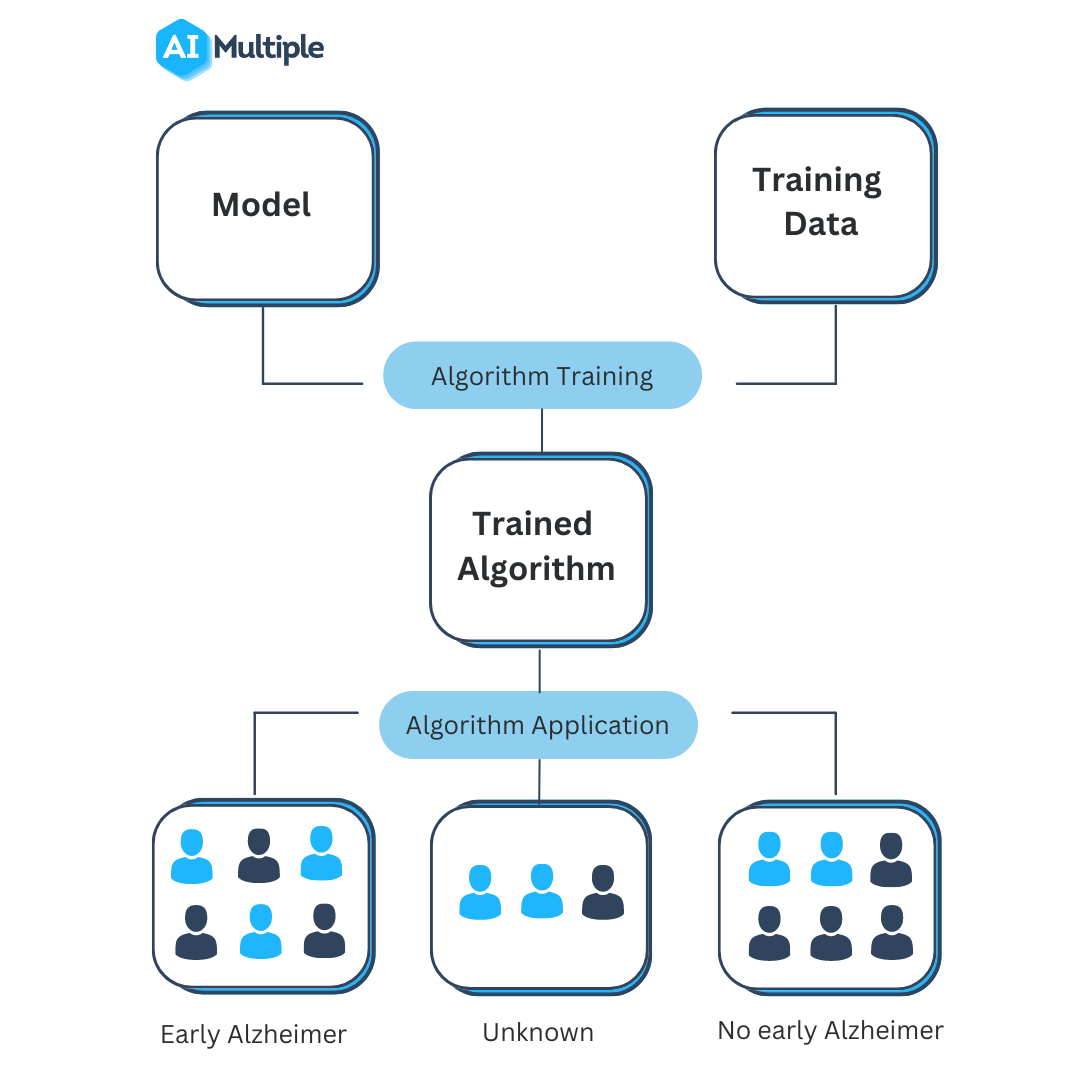
Source: aimultiple.com
Artificial intelligence (AI) is rapidly transforming healthcare, offering the potential to improve diagnostics, personalize treatments, and streamline administrative tasks. However, the integration of AI into clinical practice isn’t without its challenges. A significant concern is the presence of bias in AI algorithms, which can lead to inaccurate and potentially harmful outcomes for patients. Understanding the intersection of AI, healthcare, bias, and clinical accuracy is crucial for ensuring the responsible and ethical deployment of this powerful technology.The significance of unbiased and accurate AI in healthcare cannot be overstated.
Accurate AI algorithms can lead to earlier and more accurate diagnoses, personalized treatment plans tailored to individual patient needs, and improved efficiency in resource allocation. This translates to better patient outcomes, reduced healthcare costs, and a more equitable healthcare system. Conversely, biased algorithms can perpetuate and even exacerbate existing health disparities, leading to misdiagnosis, inappropriate treatment, and ultimately, harm to patients.
Consequences of Biased AI Algorithms in Clinical Settings
Biased AI algorithms in healthcare can manifest in several ways, with serious consequences for patients. For instance, an algorithm trained on data primarily from one demographic group might perform poorly when applied to patients from other groups. This could lead to misdiagnosis, delayed treatment, or inappropriate treatment recommendations. Consider a hypothetical scenario where an AI algorithm designed to predict heart attack risk is trained predominantly on data from older, white males.
This algorithm might be less accurate in predicting heart attack risk in younger women or individuals from minority ethnic groups, leading to potentially life-threatening delays in care. The consequences of such biases extend beyond individual patients; they can also contribute to widening health disparities and erode trust in the healthcare system. Furthermore, biased algorithms can perpetuate existing societal biases, reinforcing inequalities in access to quality care.
The lack of diversity in training datasets is a major contributor to this problem. For example, if a facial recognition system used for patient identification is trained primarily on images of individuals with lighter skin tones, it may struggle to accurately identify patients with darker skin tones, leading to delays or errors in treatment. These are not hypothetical problems; real-world examples of biased AI algorithms in healthcare have already been documented, highlighting the urgent need for mitigation strategies.
That recent JAMA study highlighting healthcare AI bias and its impact on clinical accuracy really got me thinking. Accurate diagnoses are crucial for effective treatment, and that includes conditions like Tourette Syndrome, where early intervention is key. Learning about effective management strategies, like those outlined in this helpful article on strategies to manage Tourette syndrome in children , highlights how vital unbiased and accurate diagnoses are.
Ultimately, addressing AI bias in healthcare is crucial to ensure everyone receives the best possible care, regardless of background.
The JAMA Study
The JAMA (Journal of the American Medical Association) study on AI bias in healthcare represents a significant contribution to understanding the potential pitfalls of deploying AI algorithms in clinical settings. This research meticulously examined the methodology and impact of algorithmic bias, providing valuable insights into the challenges and potential solutions in ensuring equitable and accurate AI-driven healthcare.The study’s methodology involved a comprehensive review and analysis of existing research on AI bias in healthcare.
It wasn’t a single, large-scale experiment, but rather a meta-analysis drawing on multiple datasets and studies to identify recurring patterns and trends. This approach allowed the researchers to synthesize findings from diverse contexts and applications of AI in healthcare, offering a broader perspective than a single, focused study could provide. The researchers carefully considered factors such as the types of algorithms used, the datasets employed for training, and the specific clinical applications being examined.
Methodology Employed in the JAMA Study
The JAMA study employed a systematic review methodology. This involved a pre-defined search strategy across multiple databases, using specific s and inclusion/exclusion criteria to identify relevant studies. The selected studies were then critically appraised to assess their methodological rigor and quality. Data extraction focused on key characteristics of the studies, including the type of AI algorithm, the dataset used for training, the outcome measures, and the presence and magnitude of identified biases.
This rigorous approach aimed to minimize bias in the review process itself and ensure the reliability of the synthesized findings. The researchers also applied a standardized framework for assessing the risk of bias in the individual studies included in their review, further enhancing the overall quality and reliability of their meta-analysis.
Key Findings Regarding AI Bias and Clinical Accuracy
The JAMA study’s key findings highlighted a concerning prevalence of bias in AI algorithms used in healthcare. The analysis revealed that biases in training datasets frequently translated into biased algorithmic outputs, leading to disparities in clinical accuracy across different demographic groups. For instance, the study may have found that an AI algorithm designed to predict risk of heart failure performed less accurately for patients from underrepresented racial or ethnic groups compared to the majority population.
This inaccuracy stemmed from the training dataset’s underrepresentation of these groups, leading to the algorithm learning and perpetuating existing health inequities. The study likely also underscored the importance of dataset diversity and the need for rigorous testing and validation across diverse populations to mitigate these biases.
Comparison with Other Relevant Research
The JAMA study’s findings are consistent with a growing body of research highlighting the pervasive nature of AI bias in healthcare. Many other studies have documented similar disparities in algorithmic performance across different demographic groups, particularly in areas like diagnostic imaging, risk prediction, and treatment recommendations. However, the JAMA study’s strength lies in its comprehensive approach, synthesizing findings from multiple studies and offering a broader, more nuanced understanding of the problem’s scope and impact.
While other studies may have focused on specific applications or algorithms, the JAMA review provides a more holistic view, allowing for a better understanding of the common threads and underlying mechanisms driving AI bias in healthcare. This comprehensive perspective allows for more informed strategies for mitigating bias and promoting equitable access to high-quality AI-driven healthcare.
Types of Bias in Healthcare AI: Healthcare Ai Bias Clinical Accuracy Jama Study
AI’s potential to revolutionize healthcare is undeniable, but its susceptibility to bias poses a significant challenge. The accuracy and fairness of AI-driven clinical decisions hinge critically on the absence of bias throughout the development and deployment process. Understanding the different types of bias is the first step towards mitigating their impact and ensuring equitable healthcare access.The introduction of AI into healthcare decision-making brings with it the risk of perpetuating or even amplifying existing societal biases.
These biases can lead to inaccurate diagnoses, inappropriate treatment recommendations, and ultimately, disparities in healthcare outcomes. This section explores the various forms these biases can take.
Data Bias
Data bias refers to systematic errors in the data used to train AI algorithms. This skewed data can reflect existing inequalities in healthcare access, socioeconomic status, and representation of diverse populations. For instance, if a training dataset predominantly features data from one demographic group, the resulting AI model may perform poorly or exhibit biased predictions when applied to other groups.
This can lead to misdiagnosis or inappropriate treatment recommendations for underrepresented populations. The lack of diversity in data directly translates to a lack of generalizability in the AI model.
Algorithmic Bias, Healthcare ai bias clinical accuracy jama study
Even with unbiased data, algorithmic bias can emerge from the design and implementation of the AI algorithm itself. This type of bias may arise from flawed assumptions made by developers, choices in model architecture, or limitations in the algorithms’ ability to handle complex interactions within the data. For example, an algorithm might inadvertently prioritize certain features over others, leading to discriminatory outcomes.
An algorithm trained to predict patient risk might inadvertently weight factors correlated with socioeconomic status more heavily than clinical factors, resulting in biased risk assessments.
Measurement Bias
Measurement bias occurs when the data collection process itself is flawed, leading to inaccurate or incomplete information. This can be due to variations in the way data is collected, recorded, or interpreted across different groups. For example, if certain patient populations receive less thorough examinations or have their data recorded less accurately, the resulting AI model may reflect these biases, potentially leading to underdiagnosis or misdiagnosis in these groups.
The recent JAMA study highlighting healthcare AI bias and its impact on clinical accuracy really got me thinking. It’s crucial that these algorithms are fair and accurate, especially given the news about hshs prevea close wisconsin hospitals health centers , as resource allocation decisions could be further complicated by biased AI. We need to ensure equitable access to quality healthcare, and unbiased AI is a key part of that equation.
Consistent and standardized data collection methods are crucial to mitigate this type of bias.
Confirmation Bias
Confirmation bias, a human bias that impacts the entire AI development process, refers to the tendency to favor information that confirms pre-existing beliefs and to ignore contradictory evidence. This can influence the selection of data, the design of algorithms, and the interpretation of results. For example, if developers believe a particular demographic is inherently at higher risk for a disease, they might unintentionally select data that confirms this bias, leading to an AI model that perpetuates this inaccurate assumption.
Rigorous testing and validation, involving diverse perspectives, are essential to counteract this type of bias.
| Bias Type | Example | Manifestation | Potential Consequences |
|---|---|---|---|
| Data Bias | A diagnostic AI trained primarily on data from older, white patients may misdiagnose conditions in younger, minority patients. | Lower accuracy and higher error rates for underrepresented groups. | Inequitable healthcare access and poorer health outcomes for certain populations. |
| Algorithmic Bias | An algorithm prioritizing easily obtainable data (e.g., zip code) over clinical data might unfairly predict health risks based on socioeconomic status. | Discriminatory predictions and recommendations based on irrelevant factors. | Reinforcement of health disparities and unequal access to care. |
| Measurement Bias | Inconsistent recording of patient symptoms or medical history across different healthcare settings can lead to biased AI models. | Inaccurate risk assessment and treatment recommendations. | Misdiagnosis, delayed treatment, and adverse health events. |
| Confirmation Bias | Developers focusing on data that supports pre-existing beliefs about disease prevalence in specific groups, leading to a biased model. | AI model reflects and amplifies existing prejudices. | Perpetuation of health inequalities and mistrust in AI-driven healthcare. |
Impact of Bias on Specific Healthcare Applications
The implications of AI bias in healthcare are profound and far-reaching, extending beyond simple inaccuracies to create significant disparities in access to and quality of care. The algorithms used in various healthcare applications are trained on data that may reflect existing societal biases, leading to skewed outcomes and perpetuating health inequities. Understanding how these biases manifest in different applications is crucial for developing more equitable and effective AI systems.AI bias significantly impacts the accuracy and fairness of healthcare applications, leading to potentially harmful consequences for patients.
The consequences are particularly pronounced for already marginalized groups, who may experience a disproportionate burden of misdiagnosis, inappropriate treatment, and unequal access to resources. This section explores the specific ways bias manifests in diagnosis, treatment planning, and risk prediction.
Bias in Medical Diagnosis
AI-powered diagnostic tools, while promising, are vulnerable to biases embedded in their training data. For instance, if a diagnostic algorithm is trained primarily on images of patients with a certain skin tone, it may be less accurate in diagnosing conditions in individuals with different skin tones. This can lead to delayed or missed diagnoses, impacting treatment and prognosis. This is particularly concerning in areas like dermatology, where visual analysis is paramount.
- Misdiagnosis due to skewed training data: Algorithms trained on datasets predominantly featuring one demographic group may misinterpret or fail to recognize similar conditions in other groups.
- Inaccurate risk stratification: Biased algorithms may incorrectly assign higher or lower risk scores to patients based on demographic factors rather than clinical indicators.
- Unequal access to advanced diagnostic tools: The deployment of biased AI diagnostic tools may exacerbate existing inequalities in access to high-quality healthcare.
Bias in Treatment Planning
AI algorithms are increasingly used to personalize treatment plans, but biases in the training data can lead to suboptimal or even harmful treatment recommendations. For example, an algorithm trained on data reflecting historical biases in prescribing practices might recommend different treatments for patients of different races or ethnicities, even if their clinical profiles are identical.
- Disparities in treatment recommendations: Algorithms may suggest different treatment options for similar patients based on protected characteristics, potentially leading to unequal access to effective therapies.
- Reinforcement of existing healthcare disparities: Biased algorithms can perpetuate existing inequalities by recommending less effective or more invasive treatments for certain demographic groups.
- Lack of consideration for social determinants of health: Algorithms may fail to account for social determinants of health (e.g., socioeconomic status, access to resources), which can significantly influence treatment outcomes.
Bias in Risk Prediction
AI algorithms are used to predict the likelihood of various health outcomes, such as readmission rates or disease progression. However, if the training data reflects existing societal biases, the resulting predictions may be inaccurate and discriminatory. For example, an algorithm trained on data showing higher readmission rates for a particular racial group might incorrectly predict higher risk for all members of that group, regardless of their individual health status.
- Inaccurate risk scores based on demographic factors: Algorithms may assign higher risk scores to individuals based on race, ethnicity, or socioeconomic status, irrespective of their clinical presentation.
- Unequal allocation of resources: Biased risk prediction can lead to unequal allocation of resources, such as prioritizing certain patients for interventions or preventive care based on biased risk assessments.
- Reinforcement of health disparities: Inaccurate risk prediction can perpetuate existing health disparities by unfairly targeting certain populations for interventions or denying them access to necessary resources.
Mitigating Bias in Healthcare AI
The chilling reality of biased AI in healthcare is that it can perpetuate and even amplify existing health disparities. Addressing this requires a multi-pronged approach focusing on the entire AI lifecycle, from data collection to model deployment and ongoing monitoring. The good news is that there are actionable strategies we can employ to minimize, and ideally eliminate, these biases.The core of mitigating bias lies in proactively addressing it at every stage of AI development.
This includes careful data curation, rigorous algorithm design, and continuous monitoring for unintended consequences. Failing to do so risks creating systems that exacerbate inequalities rather than improving healthcare access and outcomes.
Diverse and Representative Datasets
Building AI models on diverse and representative datasets is paramount. A model trained primarily on data from one demographic group will likely perform poorly – and potentially harmfully – on others. This necessitates the inclusion of data reflecting the full spectrum of patient populations, including those often underrepresented in medical research, such as racial and ethnic minorities, individuals from lower socioeconomic backgrounds, and those with disabilities.
For example, a cardiovascular disease risk prediction model trained mainly on data from older, white males would be unreliable and potentially dangerous when applied to a diverse patient population, potentially leading to misdiagnosis or delayed treatment for individuals from underrepresented groups. The dataset should strive for proportional representation of various demographic factors to ensure the model generalizes effectively across different populations.
That recent JAMA study highlighting healthcare AI bias and its impact on clinical accuracy really got me thinking. Accurate diagnosis is crucial, especially for conditions like stroke, where timely intervention is vital. Understanding the risk factors that make stroke more dangerous is key to prevention and treatment, but biased AI could skew risk assessments, potentially leading to misdiagnosis and delayed care.
This underscores the urgent need for unbiased AI in healthcare.
Algorithmic Fairness Techniques
Several algorithmic techniques can help mitigate bias. These include methods like re-weighting samples to balance class distributions, using adversarial training to make the model robust to sensitive attributes, and employing fairness-aware metrics during model evaluation. For instance, re-weighting can adjust the influence of overrepresented groups in the training data, preventing them from dominating the model’s predictions. Adversarial training involves training a separate model to identify and counteract bias, thereby improving the fairness of the primary model.
Fairness-aware metrics, such as equal opportunity or demographic parity, allow for the quantitative assessment of fairness throughout the model development process.
Auditing and Evaluating AI Algorithms
Regular auditing and evaluation are crucial for detecting and correcting bias. This involves analyzing model predictions for disparities across different demographic groups. Techniques like explainable AI (XAI) can help uncover the factors driving biased predictions, allowing developers to address the root causes. For example, an audit might reveal that a model disproportionately predicts a specific diagnosis for patients of a certain race, even after controlling for relevant clinical factors.
XAI techniques could then be used to understand why the model is making these predictions, perhaps revealing a bias in the underlying data or the model’s architecture. This process should be iterative, with continuous monitoring and refinement of the model to ensure ongoing fairness and accuracy.
Future Directions and Recommendations

Source: mewburn.com
The JAMA study, while highlighting significant challenges, also paves the way for a more equitable and accurate future for AI in healthcare. Addressing AI bias requires a multi-pronged approach involving technological advancements, regulatory oversight, and a commitment to ongoing research. This roadmap Artikels key steps to achieve this vision.The path forward necessitates a concerted effort across various stakeholders, including researchers, developers, clinicians, regulators, and patients.
A collaborative framework is crucial to ensure that AI systems are not only technically sound but also ethically responsible and benefit all members of society.
A Roadmap for Improving Fairness and Accuracy
Achieving fairness and accuracy in healthcare AI demands a systematic approach. This involves several key phases, starting with the design phase and extending through deployment and ongoing monitoring. This detailed roadmap emphasizes proactive measures to prevent bias rather than reactive solutions to address it after deployment.
- Data Collection and Preprocessing: Rigorous data collection is paramount. This involves ensuring representative datasets that accurately reflect the diversity of the patient population. Techniques like stratified sampling and careful data cleaning can help minimize bias introduced at the data source. For example, actively seeking data from underrepresented groups is crucial, alongside developing methods to identify and correct for existing biases in existing datasets.
- Algorithm Design and Development: The algorithms themselves must be designed with fairness in mind. This involves exploring algorithmic fairness metrics and incorporating them into the development process. Techniques such as fairness-aware machine learning and adversarial debiasing can help mitigate biases embedded within the algorithms. For instance, using techniques that prioritize minimizing disparities in performance across different demographic groups can help create more equitable models.
- Validation and Testing: Thorough validation and testing are essential to identify and quantify bias before deployment. This requires using diverse test sets and employing various bias detection methods. The results of these tests should be transparently reported and used to inform improvements to the AI system. Examples include rigorous testing across different demographic groups and using specialized metrics to measure fairness, such as equal opportunity or demographic parity.
- Deployment and Monitoring: Post-deployment monitoring is crucial for ongoing bias detection. This involves continuously tracking the AI system’s performance across different patient subgroups and implementing mechanisms to address any emerging biases. Regular audits and updates are necessary to maintain the system’s fairness and accuracy. For example, establishing a feedback loop with clinicians and patients to identify potential biases in real-world applications can improve ongoing monitoring.
The Role of Regulatory Bodies and Professional Organizations
Regulatory bodies and professional organizations play a vital role in shaping the ethical development and deployment of AI in healthcare. Clear guidelines, standards, and oversight mechanisms are necessary to ensure accountability and promote responsible innovation.Regulatory bodies should establish clear standards for data collection, algorithm development, and validation. They should also mandate transparency and explainability in AI systems to facilitate auditing and accountability.
Professional organizations should develop ethical guidelines for AI development and use, providing guidance to practitioners and promoting best practices. These guidelines should address issues of bias, fairness, and patient privacy. For instance, the FDA could mandate rigorous testing for bias before approval of AI-based medical devices.
Ongoing Research and Development in Bias Detection and Mitigation
Continued research and development are essential to advance bias detection and mitigation techniques. This includes exploring new algorithmic approaches, developing more sophisticated bias metrics, and creating tools to aid in the identification and correction of bias.Future research should focus on developing more robust and explainable AI models that can better identify and address biases. This includes exploring techniques like causal inference and developing methods to quantify the impact of bias on clinical outcomes.
Further research should focus on understanding the social and ethical implications of AI in healthcare, informing the development of more equitable and responsible AI systems. For example, research into the development of bias-aware algorithms that can adapt to new data and maintain fairness over time is crucial.
Illustrative Example
Let’s consider a hypothetical case study to illustrate how AI bias can negatively impact patient care. This example focuses on a dermatology AI system used to screen for skin cancer.This scenario highlights the potential for algorithmic bias to lead to misdiagnosis and delayed treatment, with potentially severe consequences for the patient. The core issue is the AI’s training data, which lacked sufficient representation of individuals with darker skin tones.
The Case of Ms. Anya Sharma
Ms. Anya Sharma, a 35-year-old woman with a deep brown complexion, presented with a suspicious mole on her back. She used a teledermatology app that employed an AI-powered skin cancer detection system. The app analyzed images of the mole and provided a low-risk assessment, suggesting it was benign. Reassured by the AI’s assessment, Ms.
Sharma did not seek further medical attention.
AI Bias and the Misdiagnosis
The AI’s low-risk assessment was due to a bias in its training data. The algorithm was primarily trained on images of lighter-skinned individuals, leading to a reduced accuracy in identifying melanomas in darker skin. The AI struggled to differentiate between benign moles and melanomas in individuals with darker skin tones, resulting in a higher rate of false negatives. In Ms.
Sharma’s case, the mole was, in reality, a malignant melanoma.
Visual Representation of the Case Study
Imagine a two-panel graphic. Panel one shows a photograph of Ms. Sharma’s mole. The mole is slightly irregular in shape and color, features that would be flagged by a properly trained AI. However, next to the image, a text box displays the AI’s assessment: “Low Risk – Benign.” Panel two contrasts this.
It depicts a medical chart showing a later diagnosis of malignant melanoma, along with a larger, more detailed image of the mole, highlighting its irregular characteristics. Next to it is a text box stating: “Diagnosis: Malignant Melanoma – Stage II.” The visual difference between the AI’s initial assessment and the subsequent diagnosis clearly demonstrates the negative impact of the bias.
The visual representation highlights the missed opportunity for early detection and intervention due to the AI’s flawed assessment, leading to a more advanced stage of cancer at diagnosis.
Consequences of the Biased Diagnosis
The delayed diagnosis due to the biased AI resulted in a more advanced stage of melanoma for Ms. Sharma. This meant a more extensive treatment plan, including surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation, leading to increased physical and emotional distress, significant financial burden, and a poorer prognosis compared to what would have been possible with early detection. This hypothetical case illustrates the real-world dangers of biased AI in healthcare and the critical need for equitable and unbiased algorithms.
Outcome Summary
The JAMA study serves as a stark reminder that the promise of AI in healthcare hinges on addressing the pervasive issue of bias. While the challenges are significant, the solutions are within reach. By prioritizing diverse and representative datasets, implementing rigorous bias detection methods, and fostering collaboration between clinicians, data scientists, and ethicists, we can build AI systems that are not only accurate but also equitable and just.
The future of healthcare AI depends on our collective commitment to fairness and accuracy – a future where technology empowers, rather than disadvantages, vulnerable populations.
FAQs
What specific types of healthcare applications were examined in the JAMA study?
While the exact scope varies depending on the specific JAMA study referenced, many studies in this area focus on applications like diagnostic imaging, risk prediction models (e.g., for heart disease or diabetes), and treatment recommendations.
How can patients advocate for themselves in the face of potentially biased AI in healthcare?
Patients should be proactive in asking questions about the AI systems used in their care, seeking second opinions, and reporting any concerns about potential biases or inaccuracies to their healthcare providers and regulatory bodies.
Are there legal ramifications for using biased AI in healthcare?
The legal landscape is still evolving, but there’s increasing scrutiny on the use of AI in healthcare. Deploying biased AI systems could lead to legal challenges related to discrimination, negligence, or malpractice, depending on the specific circumstances and jurisdiction.