
What Do High and Low Creatinine Reveal? Signs to Identify Them
What do high and low creatinine reveal and signs to identify them? That’s the burning question we’re tackling today! Creatinine, a byproduct of muscle metabolism, offers a fascinating window into our kidney health and overall well-being. Understanding its fluctuations – whether soaring high or dipping low – is crucial for preventative care and managing potential health issues.
This journey into the world of creatinine will unravel the mysteries behind its levels and equip you with the knowledge to understand what your body is trying to tell you.
We’ll explore the science behind creatinine production and excretion, examining the common causes of both high (hypercreatininemia) and low (hypocreatininemia) levels. We’ll delve into the symptoms associated with each, looking at how different medical conditions can manifest. Importantly, we’ll also discuss how lifestyle factors, like diet and hydration, play a significant role in maintaining healthy creatinine levels. Get ready to become your own creatinine detective!
Creatinine
Creatinine is a chemical waste product produced by your muscles as a byproduct of creatine metabolism. Understanding creatinine levels is crucial for assessing kidney function, as it’s primarily filtered out of the blood by the kidneys and excreted in urine. Fluctuations in creatinine levels can signal underlying health issues, highlighting the importance of regular monitoring, particularly for individuals with pre-existing kidney conditions or risk factors.Creatinine Production and ExcretionCreatinine is formed in the body through the breakdown of creatine phosphate, a molecule essential for energy production in muscle cells.
The rate of creatinine production is largely dependent on muscle mass; individuals with more muscle mass tend to produce more creatinine. Once produced, creatinine enters the bloodstream and is transported to the kidneys. The kidneys efficiently filter creatinine from the blood, with the vast majority being excreted in the urine. A small amount of creatinine is also eliminated through the gastrointestinal tract.
This continuous process of production and excretion maintains a relatively stable level of creatinine in the blood under normal conditions.Creatinine Levels in BloodA blood creatinine test measures the amount of creatinine present in a blood sample. The results are typically expressed in milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL) or micromoles per liter (µmol/L). Normal creatinine levels vary slightly depending on factors such as age, sex, and muscle mass.
Generally, for adults, a normal range is considered to be between 0.7 and 1.3 mg/dL for men and 0.6 and 1.1 mg/dL for women. However, these are just guidelines, and individual ranges can differ. Elevated creatinine levels, often referred to as hypercreatininemia, usually indicate impaired kidney function, while significantly low levels may suggest muscle wasting or other underlying conditions.
Precise interpretation of creatinine levels always requires consideration of the individual’s overall health status and other clinical factors. For example, a creatinine level of 2.0 mg/dL in a young, athletic individual might be less concerning than the same level in an elderly person with a history of heart disease.
High Creatinine Levels (Hypercreatininemia)

Source: renaltracker.com
High creatinine levels, or hypercreatininemia, indicate that your kidneys aren’t filtering waste products from your blood as efficiently as they should. This isn’t necessarily a sign of immediate danger, but it’s a crucial indicator that warrants medical attention and investigation to determine the underlying cause. Understanding the potential causes and associated symptoms is vital for timely diagnosis and management.
Causes of Elevated Creatinine Levels
Several factors can contribute to elevated creatinine levels. These range from acute, temporary issues to chronic, long-term conditions affecting kidney function. It’s important to note that a single high creatinine reading doesn’t automatically diagnose kidney disease; further testing is always necessary.
Medical Conditions Associated with High Creatinine
High creatinine is often linked to various medical conditions directly impacting kidney health or indirectly affecting kidney function. These conditions can significantly impair the kidneys’ ability to filter waste, leading to a buildup of creatinine in the blood. Examples include chronic kidney disease (CKD), acute kidney injury (AKI), diabetic nephropathy (kidney damage due to diabetes), and glomerulonephritis (inflammation of the glomeruli, the filtering units in the kidneys).
Additionally, certain medications and muscle damage can also contribute to elevated creatinine levels.
Symptoms of High Creatinine
The symptoms associated with high creatinine levels often depend on the underlying cause and the severity of kidney dysfunction. In many cases, early-stage hypercreatininemia might be asymptomatic, meaning you won’t experience any noticeable symptoms. However, as kidney function declines, you might experience symptoms such as fatigue, nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite, swelling in the legs, ankles, and feet (edema), shortness of breath, changes in urination (increased or decreased frequency, foamy urine), muscle cramps, and persistent itching.
It’s crucial to remember that these symptoms are not exclusive to high creatinine and can be associated with many other health problems.
Comparison of Hypercreatininemia Causes
The following table compares different causes of hypercreatininemia, highlighting their associated symptoms, treatment approaches, and prognosis. Remember that this is a simplified overview, and individual experiences can vary greatly. Always consult a healthcare professional for accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment.
| Cause | Symptoms | Treatment | Prognosis |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) | Fatigue, edema, decreased urine output, nausea, anemia | Blood pressure management, medication to slow disease progression, dialysis or kidney transplant in advanced stages | Varies depending on stage and treatment; early diagnosis and management improves prognosis |
| Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) | Sudden decrease in urine output, fatigue, nausea, vomiting, edema | Treatment of underlying cause, dialysis if necessary, supportive care | Varies depending on cause and severity; many recover fully, but some may develop CKD |
| Diabetic Nephropathy | Similar to CKD, often with symptoms related to diabetes (e.g., thirst, frequent urination) | Blood sugar control, blood pressure management, medication to protect kidneys | Depends on blood sugar control and progression of kidney damage; can lead to end-stage renal disease |
| Glomerulonephritis | Edema, high blood pressure, blood in urine, fatigue | Treatment of underlying cause (e.g., infection), corticosteroids or other immunosuppressants | Varies depending on the cause and severity; some recover fully, while others develop CKD |
| Rhabdomyolysis (muscle breakdown) | Muscle pain, weakness, dark urine | Fluid replacement, dialysis if necessary | Generally good with prompt treatment; severe cases can lead to AKI |
Low Creatinine Levels (Hypocreatininemia): What Do High And Low Creatinine Reveal And Signs To Identify Them
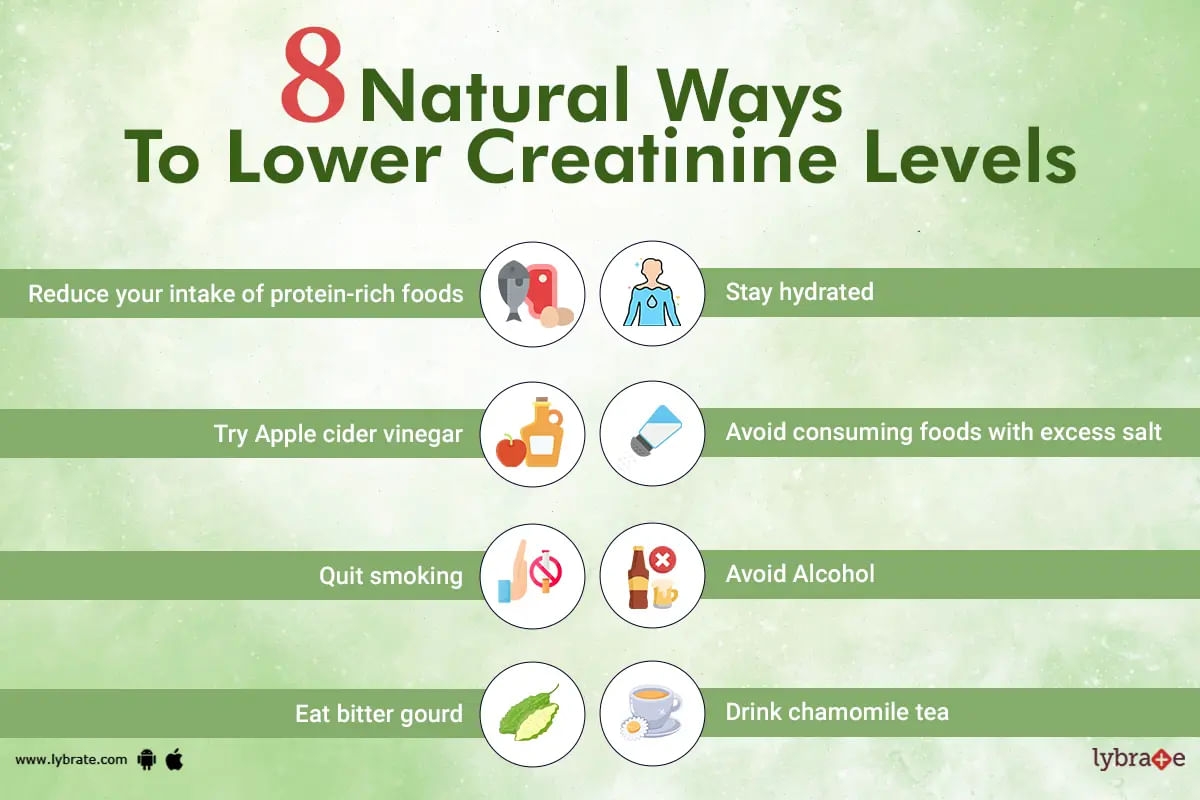
Source: lybrate.com
Low creatinine levels, also known as hypocreatininemia, indicate that your kidneys are not filtering creatinine from your blood as efficiently as they should. While high creatinine is often a cause for concern, low creatinine can also signal underlying health issues, though it’s less common. It’s important to understand that a low creatinine reading alone doesn’t necessarily mean something is wrong; it needs to be interpreted in the context of your overall health and other test results.Low creatinine levels aren’t usually associated with noticeable symptoms.
This is because creatinine is a byproduct of muscle metabolism, and its levels are influenced by a variety of factors, some of which may not cause any noticeable physical effects. The detection of low creatinine typically occurs during routine blood tests conducted for other reasons.
Causes of Low Creatinine Levels
Low creatinine can result from reduced muscle mass, decreased creatinine production, or increased creatinine excretion. Several conditions and situations can contribute to this. For instance, individuals with significantly low muscle mass, such as those with muscle-wasting diseases or those who are severely malnourished, will naturally produce less creatinine. Similarly, certain medications can impact creatinine production or excretion.
Conditions Leading to Low Creatinine, What do high and low creatinine reveal and signs to identify them
Several medical conditions can lead to low creatinine levels. Examples include:* Muscle wasting diseases: Conditions like muscular dystrophy or severe cachexia (extreme weight loss and muscle wasting) can significantly reduce muscle mass, resulting in lower creatinine production. Imagine a patient with advanced muscular dystrophy; their reduced muscle mass directly translates to less creatinine being produced.* Malnutrition or starvation: Severe malnutrition or prolonged starvation drastically reduces muscle mass, leading to decreased creatinine production.
A person surviving on minimal calories for an extended period, for example, might exhibit this.* Pregnancy: During pregnancy, creatinine levels often decrease, primarily due to an increase in glomerular filtration rate (GFR), the rate at which the kidneys filter blood. This is a normal physiological change during pregnancy and not necessarily indicative of a problem.* Liver disease: While less directly related, severe liver disease can indirectly influence creatinine levels through its impact on overall metabolism and muscle function.
The liver plays a crucial role in many metabolic processes, and its dysfunction can have ripple effects.* Certain medications: Some medications, such as some antibiotics and certain chemotherapy drugs, can affect creatinine production or excretion. The specific effects vary depending on the drug.
Factors Influencing Creatinine Levels
It’s crucial to understand that several factors can influence creatinine levels, making interpretation of a single low reading complex. These factors should always be considered when evaluating creatinine results.
- Age: Creatinine levels tend to be lower in older adults due to decreased muscle mass.
- Sex: Men generally have higher creatinine levels than women due to higher muscle mass.
- Race: There can be slight variations in creatinine levels based on ethnicity.
- Diet: A diet low in protein can lead to lower creatinine levels.
- Physical activity: Highly active individuals may have higher creatinine levels.
Interpreting Creatinine Test Results
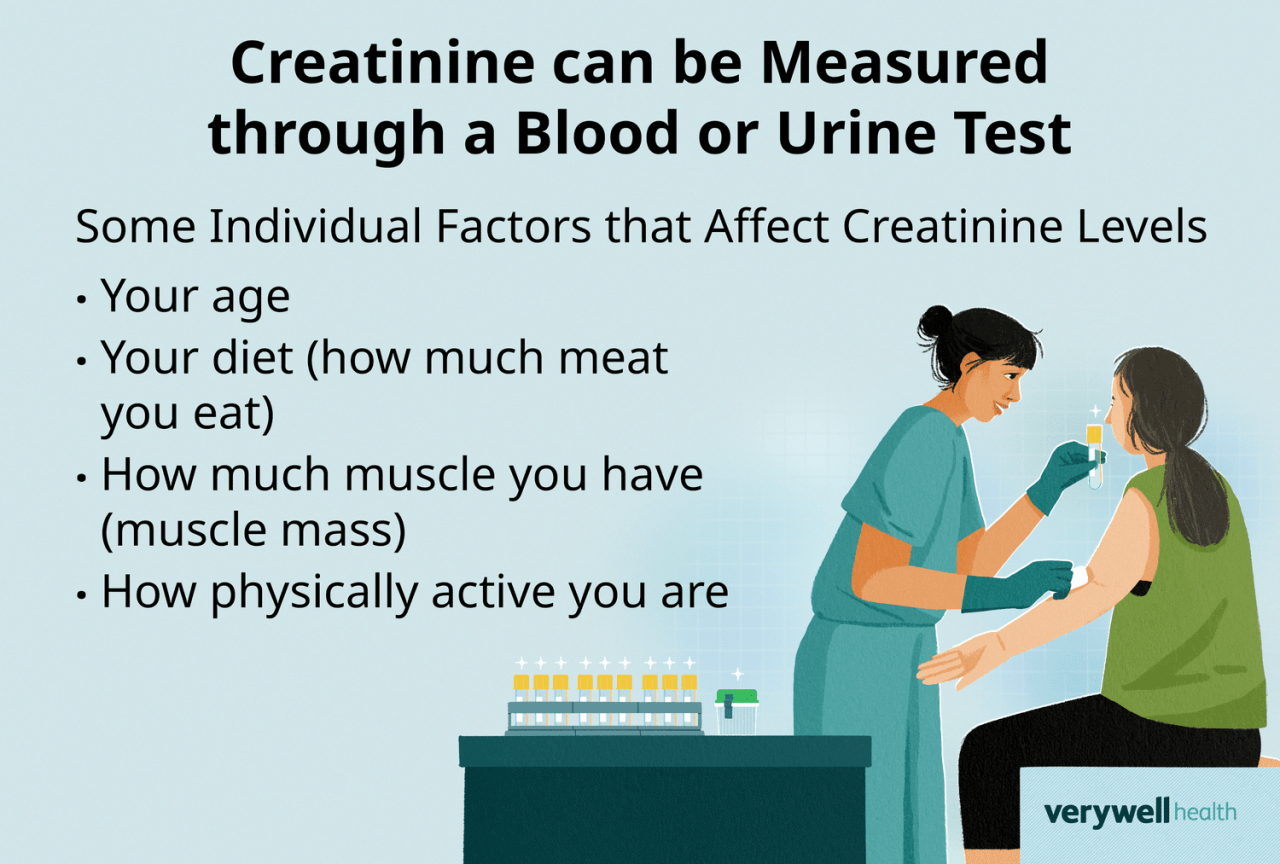
Understanding creatinine levels is crucial for assessing kidney function. Creatinine, a waste product of muscle metabolism, is filtered by the kidneys and excreted in urine. Elevated or decreased creatinine levels can indicate underlying kidney issues or other health problems. This section will delve into how creatinine tests are performed and interpreted, considering variations based on age and gender, and highlighting factors that can influence test accuracy.Creatinine tests are performed using a simple blood sample.
The lab then measures the amount of creatinine present in the blood, typically expressed in milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL) or micromoles per liter (µmol/L). Interpretation of these results involves comparing the measured level to established reference ranges, which vary depending on factors like age, sex, and muscle mass. Higher creatinine levels generally suggest reduced kidney function, while lower levels might point to reduced muscle mass or other less common conditions.
However, it’s important to remember that creatinine levels alone aren’t a definitive diagnosis; they’re one piece of the puzzle in assessing kidney health.
Creatinine Levels and Kidney Function
The relationship between creatinine levels and kidney function is indirect but significant. Healthy kidneys efficiently filter creatinine from the blood. When kidney function declines (e.g., due to chronic kidney disease), less creatinine is filtered, leading to a buildup of creatinine in the blood and thus a higher serum creatinine level. The estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR), a calculated value that estimates how well the kidneys are filtering blood, is often used in conjunction with creatinine levels to assess kidney function.
A low eGFR, often calculated using creatinine levels, age, and gender, indicates impaired kidney function. For example, a 70-year-old with a serum creatinine of 1.5 mg/dL might have a significantly lower eGFR than a 30-year-old with the same creatinine level because age is a factor in eGFR calculation.
Creatinine Test Interpretation Across Age and Gender
Reference ranges for creatinine vary significantly across age and gender. Men typically have higher creatinine levels than women due to generally greater muscle mass. Muscle mass is a key factor influencing creatinine production. Older adults may also have slightly higher creatinine levels, but this isn’t always indicative of kidney problems. It’s essential that clinicians consider these factors when interpreting creatinine test results.
Understanding creatinine levels is crucial; high levels might signal kidney problems, while low levels can indicate muscle issues. Sometimes, managing unrelated health concerns is key, like in children with Tourette Syndrome, where effective strategies are vital for their well-being. For insights into managing this condition, check out this helpful resource on strategies to manage Tourette syndrome in children.
Returning to creatinine, consistent monitoring and recognizing symptoms like fatigue or swelling are important for early intervention.
A creatinine level considered high in a young woman might be within the normal range for an older man. Clinicians use age- and gender-specific reference ranges to interpret results accurately. For example, a creatinine level of 1.2 mg/dL might be considered normal for a young woman but elevated for a young man.
Factors Affecting Creatinine Test Accuracy
Several factors can influence the accuracy of creatinine tests. It’s crucial to consider these when interpreting results.
- Dehydration: Dehydration concentrates creatinine in the blood, leading to falsely elevated readings.
- Muscle Mass: Individuals with significantly reduced muscle mass (e.g., due to muscle wasting diseases or malnutrition) may have lower creatinine levels, even with normal kidney function.
- Diet: A high-protein diet can temporarily increase creatinine levels.
- Medications: Certain medications can interfere with creatinine metabolism or excretion, affecting test results.
- Race: Some studies suggest slight variations in creatinine levels across different racial groups, though this is a complex and debated area.
- Laboratory Variations: Differences in laboratory methods and equipment can lead to slight variations in results.
Creatinine and Muscle Mass
Source: verywellhealth.com
Creatinine, a byproduct of creatine metabolism in muscle tissue, has a direct and significant relationship with muscle mass. Understanding this connection is crucial for accurate interpretation of creatinine test results, as muscle mass significantly influences both creatinine production and excretion. Higher muscle mass generally leads to higher creatinine levels, while lower muscle mass results in lower levels. This isn’t simply a correlation; it’s a fundamental aspect of creatinine’s physiology.Creatinine production and excretion are intrinsically linked to muscle mass.
Larger muscles contain more creatine, leading to a higher rate of creatinine production. This increased production necessitates a corresponding increase in creatinine excretion through the kidneys. Conversely, individuals with less muscle mass produce less creatinine, resulting in lower levels in the blood. The kidneys, however, maintain a relatively consistent rate of creatinine clearance, regardless of muscle mass, unless renal function is impaired.
Therefore, the creatinine level reflects the balance between production (influenced by muscle mass) and excretion (influenced primarily by kidney function).
Creatinine Levels and Muscle Mass Variations
Interpreting creatinine levels requires considering the individual’s muscle mass. A high creatinine level in a bodybuilder might be within the normal range for their high muscle mass, whereas the same level in a sedentary individual could indicate potential kidney problems. Similarly, a low creatinine level in a frail elderly person might be expected due to age-related muscle loss (sarcopenia), while the same level in a younger, healthy individual might warrant further investigation.
The key is to assess creatinine in the context of the individual’s overall health, age, sex, and muscle mass.
Examples of Muscle Mass Impact on Creatinine Interpretation
Consider a 25-year-old male bodybuilder with a high creatinine level. This might not be indicative of kidney disease if his high creatinine reflects his significantly increased muscle mass. Conversely, a 70-year-old woman with a low creatinine level might have a normal result considering age-related muscle loss. A young athlete with a low creatinine level, however, might indicate a need for further testing to rule out conditions affecting muscle mass or kidney function.
These examples highlight the necessity of considering individual factors when interpreting creatinine levels. Clinicians often use estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) calculations, which incorporate creatinine levels and other factors like age and sex, to provide a more accurate assessment of kidney function. This helps account for the variations in creatinine levels based on muscle mass.
Identifying High vs. Low Creatinine
Creatinine levels in the blood provide valuable insights into kidney function and muscle mass. Understanding the clinical signs associated with both high and low creatinine is crucial for accurate diagnosis and appropriate management. While a simple blood test measures creatinine levels, the clinical picture helps paint a more complete picture of the underlying condition.
Clinical Presentation of High Creatinine (Hypercreatininemia)
High creatinine levels, or hypercreatininemia, often manifest with symptoms related to the underlying cause, rather than directly from the elevated creatinine itself. The symptoms are often subtle in the early stages and can be easily missed. However, as kidney function deteriorates, more pronounced symptoms emerge. These symptoms are not specific to high creatinine and can be associated with many other conditions.
Therefore, a blood test is essential for confirmation.
Understanding creatinine levels is crucial for kidney health; high levels often signal kidney damage, while low levels can indicate muscle problems or malnutrition. It’s fascinating how seemingly unrelated health markers can connect – for instance, research suggests that eye exams might offer clues about dementia risk, as explored in this insightful article: can eye test detect dementia risk in older adults.
Returning to creatinine, consistent monitoring and recognizing symptoms like fatigue or swelling are key to maintaining kidney health.
Clinical Presentation of Low Creatinine (Hypocreatininemia)
Low creatinine levels, or hypocreatininemia, typically indicate reduced muscle mass. This can be a consequence of various conditions, including malnutrition, muscle wasting diseases (like muscular dystrophy), or severe illness. The visible signs are predominantly related to muscle loss, such as noticeable muscle atrophy, weakness, and fatigue. However, it is important to note that low creatinine alone does not definitively diagnose a specific condition; further investigation is always necessary.
Visual Representations of High and Low Creatinine
There is no visual representation of creatinine levels directly observable in a person. Creatinine is measured through a blood test, and the result is a numerical value. However, we can visualize theeffects* of high and low creatinine. High creatinine might be indirectly visualized by imagining a patient exhibiting signs of kidney disease, such as edema (swelling in the legs and ankles) due to fluid retention, or pale skin indicative of anemia, a common complication of kidney failure.
Conversely, a person with low creatinine might show visibly reduced muscle mass, with thinner limbs and a less defined musculature compared to individuals with a similar build and age. These are not definitive signs but illustrative examples.
Diagnostic Procedures for Confirming Creatinine Levels
The primary method for confirming creatinine levels is a simple blood test. A blood sample is drawn, and the creatinine concentration is measured in a laboratory using automated analyzers. This is a routine and widely available test. To determine the cause of abnormally high or low creatinine, further investigations are often necessary. These might include urine tests (to assess kidney function more comprehensively), imaging studies (such as ultrasound or CT scan of the kidneys), and muscle biopsies (if muscle wasting is suspected).
The specific additional tests will depend on the patient’s clinical presentation and the suspected underlying cause.
Lifestyle Factors and Creatinine Levels
Creatinine levels, while primarily reflecting kidney function, are also significantly influenced by various lifestyle choices. Understanding these factors can be crucial in interpreting creatinine test results and making informed decisions about health and wellness. Dietary habits, physical activity, and hydration all play a role in maintaining healthy creatinine ranges.Diet’s Impact on Creatinine Production and ExcretionDietary protein intake is a major determinant of creatinine production.
Creatinine is a byproduct of creatine metabolism, and creatine is found predominantly in muscle tissue. A diet high in protein, especially red meat, leads to increased creatine intake and subsequently higher creatinine production. Conversely, a diet low in protein will generally result in lower creatinine levels. However, it’s important to note that this relationship is not linear, and other factors, like muscle mass, also contribute.
For example, a highly trained athlete on a high-protein diet might have higher creatinine levels than a sedentary individual on a moderate-protein diet due to the athlete’s larger muscle mass.
Lifestyle Choices and Creatinine
Several lifestyle factors beyond diet influence creatinine levels. Intense physical activity, for instance, can temporarily elevate creatinine levels due to increased muscle breakdown and creatine release. This increase is usually transient and returns to normal after the activity ceases. Conversely, prolonged periods of inactivity or muscle wasting conditions can lead to lower creatinine levels. Similarly, certain medications, such as some antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs, can affect creatinine production or excretion, influencing the measured levels.
Understanding creatinine levels is crucial for kidney health; high levels signal potential damage, while low levels might indicate muscle problems. This is especially relevant given the exciting news that the FDA has approved clinical trials for pig kidney transplants in humans, as seen in this article: fda approves clinical trials for pig kidney transplants in humans. Such advancements highlight the importance of monitoring creatinine, a key indicator of kidney function, to ensure the success of these groundbreaking transplants.
It is crucial to consider these factors when interpreting creatinine results. For instance, a patient recovering from surgery might show lower creatinine levels due to reduced muscle mass and activity, and this shouldn’t be immediately interpreted as a kidney problem without considering the patient’s overall condition.
Hydration and Creatinine Excretion
Adequate hydration is essential for efficient creatinine excretion. The kidneys filter creatinine from the blood and excrete it in urine. Dehydration can reduce the kidneys’ ability to filter and excrete creatinine effectively, leading to an artificially elevated serum creatinine level. Conversely, sufficient fluid intake supports optimal kidney function and promotes efficient creatinine clearance. Therefore, maintaining a healthy hydration level is crucial for accurate creatinine readings and overall kidney health.
For example, a person experiencing dehydration due to prolonged illness or inadequate water intake may present with higher creatinine levels even if their kidney function is otherwise normal. Proper hydration helps prevent this false elevation.
Final Review
So, there you have it – a comprehensive look at the world of creatinine! Remember, understanding your creatinine levels is a key component of overall health awareness. While this information is empowering, it’s not a substitute for professional medical advice. If you have concerns about your creatinine levels, or experience any of the symptoms discussed, please consult your doctor for proper diagnosis and personalized guidance.
Taking proactive steps towards understanding your body is always a step in the right direction towards better health!
FAQ Insights
What is a normal creatinine level?
Normal creatinine levels vary depending on age, sex, and muscle mass. Your doctor will compare your results to the appropriate reference range.
Can diet affect my creatinine levels?
Yes, a diet high in protein can temporarily increase creatinine levels. Conversely, a very low protein diet can lead to lower levels.
How often should I get my creatinine levels checked?
The frequency of creatinine testing depends on your individual health status and risk factors. Your doctor will determine the appropriate schedule.
Are there any specific foods that can lower creatinine levels?
There aren’t specific foods that directly lower creatinine, but a balanced diet, including plenty of fruits and vegetables, supports overall kidney health.
