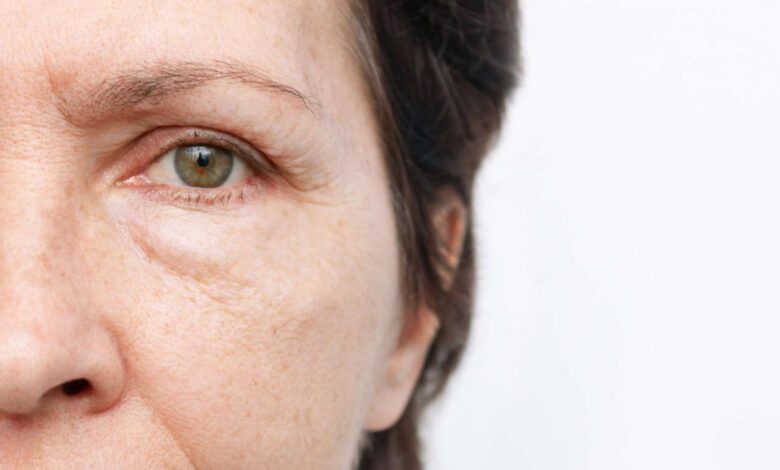
Sleep Deprivation Puffy Eyes, Reasons & Fixes
Can not sleeping enough cause eyes to swell reasons and management tips – Sleep Deprivation: Puffy Eyes, Reasons & Fixes – Ever woken up looking like you wrestled a badger? Those puffy eyes after a sleepless night aren’t just aesthetically unappealing; they’re a clear sign your body’s crying out for rest. This post dives deep into why lack of sleep leads to swollen eyes, exploring the underlying physiological mechanisms, and offering practical management tips to help you look – and feel – your best.
We’ll cover everything from lymphatic drainage to hormonal imbalances and even explore when those puffy peepers might signal something more serious. Get ready to unlock the secrets to brighter, less swollen eyes!
Insufficient Sleep and Eye Swelling
Insufficient sleep doesn’t just leave you feeling tired; it can also manifest physically, often in the form of puffy eyes. This isn’t simply a cosmetic issue; it’s a direct consequence of physiological changes within the body triggered by sleep deprivation. Understanding the underlying mechanisms helps us appreciate the importance of prioritizing sufficient rest.
The Physiological Link Between Sleep Deprivation and Fluid Retention
Sleep deprivation disrupts the body’s delicate fluid balance. When we sleep, our bodies work to repair and restore themselves, including regulating fluid distribution. Lack of sleep interferes with this process, leading to increased fluid retention, particularly in areas with loose connective tissue like the face and around the eyes. This retention manifests as puffiness or swelling. The body’s natural mechanisms for managing fluid are less efficient during sleep deprivation, resulting in a buildup of fluid in these susceptible areas.
The Lymphatic System’s Role in Fluid Drainage and the Impact of Sleep Disruption
The lymphatic system plays a crucial role in removing excess fluid and waste products from the body’s tissues. This system relies on gentle muscle contractions and movement to effectively pump lymphatic fluid. During sleep, these contractions continue, supporting lymphatic drainage. However, insufficient sleep can impair lymphatic function, slowing down the drainage of fluid from the face and contributing to the swelling around the eyes.
A lack of movement and prolonged periods of inactivity, often associated with sleep deprivation, further hinders this process.
The Influence of Different Sleep Stages on Fluid Balance
Different sleep stages influence fluid balance in subtle but important ways. Deep sleep, characterized by slow-wave activity, is crucial for bodily restoration and repair, including fluid regulation. Insufficient deep sleep reduces the body’s capacity to efficiently manage fluid distribution, increasing the likelihood of fluid retention. Conversely, REM sleep, while vital for cognitive functions, doesn’t directly impact fluid balance as significantly as deep sleep.
Puffy eyes from lack of sleep? It’s often due to fluid retention, worsened by poor circulation. Interestingly, eye health is linked to overall well-being; did you know that research suggests, as explored in this article can eye test detect dementia risk in older adults , eye exams might even offer clues about dementia risk? Getting enough sleep is crucial for managing eye puffiness, so prioritize those Zzz’s for better health all around!
Therefore, a balanced sleep cycle encompassing adequate amounts of both REM and deep sleep is essential for maintaining optimal fluid balance.
Hormonal Influences on Eye Swelling After Insufficient Sleep
Hormonal fluctuations play a significant role in fluid retention. Cortisol, a stress hormone, is released in higher amounts during periods of sleep deprivation. Elevated cortisol levels can contribute to increased fluid retention, exacerbating eye swelling. Other hormones involved in fluid regulation may also be affected by sleep disruption, further contributing to this symptom. For instance, disruptions in the circadian rhythm, which regulates hormonal release, can influence the body’s ability to maintain fluid homeostasis.
The interplay of these hormonal factors makes sufficient sleep crucial for preventing fluid retention and eye swelling.
Identifying Contributing Factors Beyond Sleep
Puffy eyes aren’t always a sign of a late night. While lack of sleep is a common culprit, several other factors can contribute to periorbital edema (the medical term for swelling around the eyes). Understanding these contributing factors is crucial for effective management and addressing the underlying cause. This means looking beyond your bedtime routine to identify potential medical conditions, environmental triggers, and medication side effects.
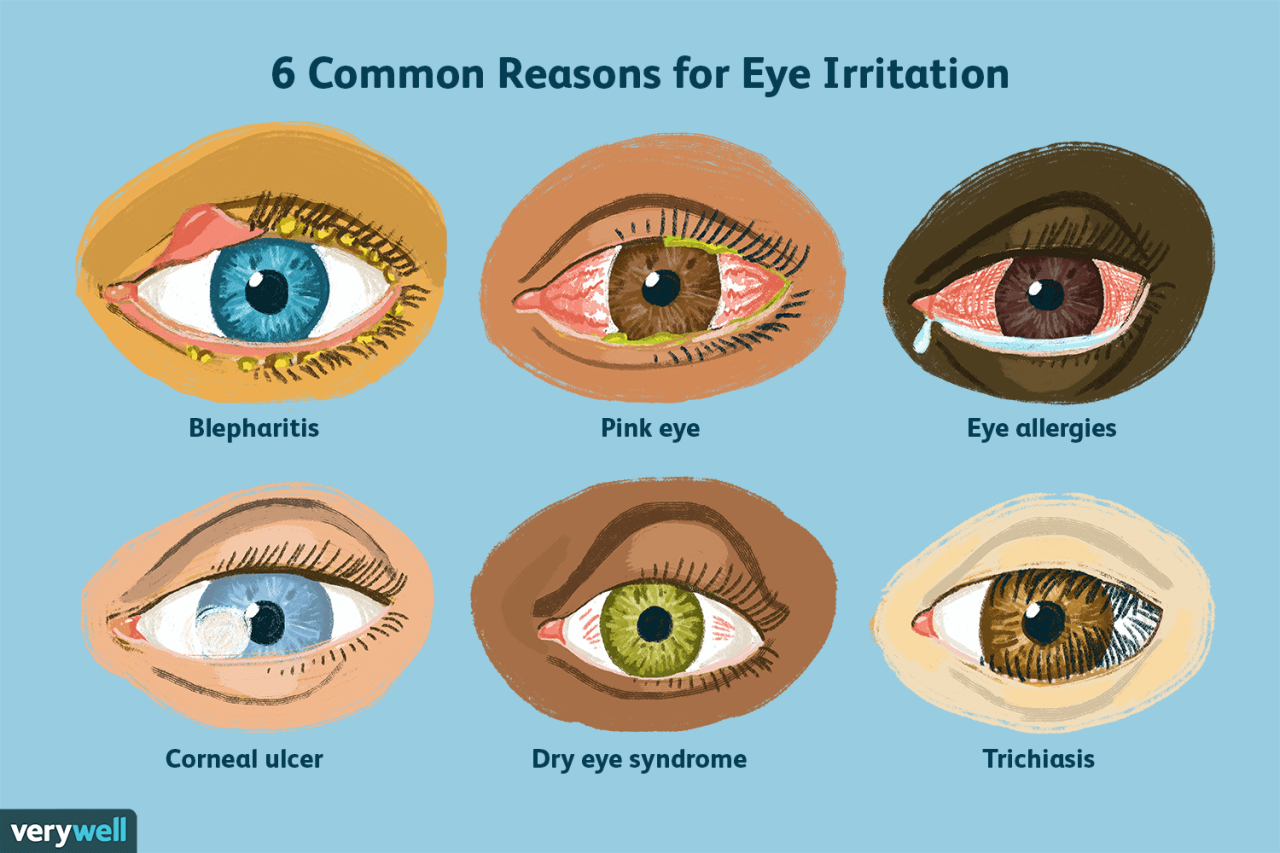
Medical Conditions Causing Eye Swelling
Many medical conditions can cause eye swelling independently of sleep patterns. It’s important to consult a doctor if you experience persistent or unexplained eye swelling, as it can indicate a serious underlying health issue. The following table summarizes some common conditions:
| Condition | Symptoms | Potential Causes | Treatment |
|---|---|---|---|
| Conjunctivitis (Pink Eye) | Redness, itching, discharge, swelling of the eyelids | Viral, bacterial, or allergic infection | Antibiotics (bacterial), antihistamines (allergic), artificial tears |
| Blepharitis | Inflammation of the eyelids, redness, crusting, swelling | Bacterial infection, skin conditions (e.g., seborrheic dermatitis, rosacea) | Warm compresses, eyelid hygiene, antibiotics (if bacterial) |
| Orbital Cellulitis | Severe swelling, redness, pain around the eye, fever, vision changes | Bacterial infection of the tissues surrounding the eye | Intravenous antibiotics |
| Allergic Reactions | Itching, redness, swelling, watery eyes | Exposure to allergens (e.g., pollen, pet dander, dust mites) | Antihistamines, avoidance of allergens |
| Kidney Disease | Facial swelling (including periorbital edema), fatigue, shortness of breath | Fluid buildup due to impaired kidney function | Dialysis, medication to manage fluid balance |
| Heart Failure | Facial swelling (including periorbital edema), shortness of breath, fatigue | Fluid retention due to impaired heart function | Medication to improve heart function and manage fluid balance |
Allergies and Eye Swelling
Allergic reactions are a frequent cause of eye swelling, often accompanied by itching, redness, and watery eyes. Differentiating allergic swelling from sleep-deprivation swelling is key. Allergic swelling tends to be accompanied by other allergy symptoms like sneezing, runny nose, and itchy throat. Sleep deprivation-related swelling is usually less itchy and is often more pronounced in the morning, gradually subsiding throughout the day.
Environmental Factors Exacerbating Eye Swelling
Environmental factors can significantly contribute to or worsen eye swelling. Exposure to pollutants, such as smoke and dust, can irritate the eyes and lead to inflammation. Dehydration can also exacerbate swelling as fluid retention increases. Extreme temperatures, both hot and cold, can also affect the delicate skin around the eyes, leading to puffiness.
Medications Contributing to Periorbital Edema
Certain medications can list periorbital edema as a side effect. Examples include some blood pressure medications (calcium channel blockers), steroids, and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). If you suspect a medication is causing your eye swelling, consult your doctor before discontinuing it; they can help determine alternative treatment options.
Lack of sleep? Puffy eyes are a common consequence, often due to fluid retention. Managing this involves prioritizing sleep, staying hydrated (surprisingly!), and using cold compresses. It’s all about self-care, much like the proactive approach Karishma Mehta took, as detailed in this article about her egg freezing journey: karishma mehta gets her eggs frozen know risks associated with egg freezing.
Prioritizing your well-being, whether it’s sleep or fertility planning, is key to feeling your best. Remember those cold compresses for those puffy eyes!
Management Strategies for Eye Swelling
Source: verywellhealth.com
Insufficient sleep is a common culprit behind puffy eyes, but thankfully, there are several effective strategies to manage and reduce this issue. Addressing both the root cause (sleep deprivation) and the symptom (swelling) is key to achieving long-term relief. This involves improving your sleep hygiene and employing various home remedies and readily available products.
Puffy eyes from lack of sleep? It’s often due to fluid retention, worsened by dehydration. Managing this means prioritizing sleep, but also considering your diet! Check out this article on are women and men receptive of different types of food and game changing superfoods for women for insights into nutrition and its impact on overall health, including how it can affect your body’s fluid balance.
Remember, a healthy diet, along with sufficient sleep, can make a big difference in reducing those pesky under-eye bags.
Improving Sleep Hygiene: A Step-by-Step Guide
Consistent, high-quality sleep is paramount for reducing eye puffiness. The following steps Artikel a practical approach to improving your sleep hygiene:
- Establish a Regular Sleep Schedule: Go to bed and wake up around the same time each day, even on weekends, to regulate your body’s natural sleep-wake cycle.
- Create a Relaxing Bedtime Routine: Wind down an hour or two before bed with calming activities like reading, taking a warm bath, or listening to soothing music. Avoid screen time during this period.
- Optimize Your Sleep Environment: Ensure your bedroom is dark, quiet, and cool. Invest in comfortable bedding and consider using blackout curtains or earplugs if necessary.
- Get Regular Exercise: Physical activity can improve sleep quality, but avoid intense workouts close to bedtime.
- Review Your Diet and Hydration: Limit caffeine and alcohol intake, especially in the evening. Ensure you’re adequately hydrated throughout the day, but avoid excessive fluid consumption close to bedtime.
- Address Underlying Medical Conditions: If you suspect an underlying medical condition might be affecting your sleep, consult your doctor.
Effective Home Remedies for Reducing Eye Swelling
Several simple home remedies can help alleviate eye puffiness. Remember to always use gentle pressure and avoid rubbing your eyes, as this can worsen the swelling.
- Cold Compresses: Apply a cool, damp washcloth or a bag of frozen peas (wrapped in a cloth) to your eyelids for 10-15 minutes. The cold constricts blood vessels, reducing inflammation.
- Cucumber Slices: The coolness and slight astringent properties of cucumber can soothe puffy eyes. Place thin cucumber slices over your closed eyelids for about 10-15 minutes.
- Tea Bags: Used, chilled tea bags (especially chamomile or green tea) can provide relief. The tannins in tea have anti-inflammatory properties. Place the cooled tea bags on your closed eyelids for 10-15 minutes.
- Potato Slices: Similar to cucumbers, chilled potato slices can help reduce swelling due to their cooling effect and potential anti-inflammatory properties. Apply for 10-15 minutes.
The Benefits and Mechanism of Cold Compresses
Cold compresses are a highly effective and readily available method for reducing eye swelling. The cold temperature causes vasoconstriction, meaning the blood vessels in the area narrow. This reduces blood flow to the swollen area, minimizing inflammation and consequently, reducing the puffiness. The reduced blood flow also helps to decrease fluid retention, further contributing to the reduction in swelling.
The immediate cooling sensation also provides soothing relief.
Over-the-Counter Eye Creams and Gels
Many over-the-counter eye creams and gels are formulated to reduce puffiness and dark circles. These products often contain ingredients like caffeine, hyaluronic acid, or retinol, which can help improve circulation, reduce fluid retention, and boost collagen production. Always check the ingredients list and choose a product suitable for your skin type. Remember that results may vary, and it’s important to be patient and consistent with use.
When to Seek Professional Medical Advice
Source: health.com
Persistent eye swelling, even if seemingly minor, can sometimes signal a more serious underlying health issue. Ignoring persistent symptoms can lead to delays in treatment and potentially worsen the condition. It’s crucial to understand when to seek professional medical attention to ensure prompt and appropriate care.Eye swelling that doesn’t improve after a few days, or worsens despite home remedies, warrants a visit to a healthcare professional.
This is particularly important if the swelling is accompanied by other symptoms, which can indicate a more complex medical situation.
Warning Signs Requiring Medical Attention
It’s important to be aware of certain warning signs that suggest a need for immediate medical attention. These signs often indicate a more serious underlying condition than simple sleep deprivation.
- Sudden onset of severe eye swelling, especially if it’s unilateral (affecting only one eye).
- Eye swelling accompanied by pain, redness, blurred vision, or changes in vision.
- Swelling that is accompanied by fever, headache, or nausea.
- Eye swelling that is accompanied by difficulty breathing or swallowing.
- Persistent eye swelling that doesn’t respond to home remedies or over-the-counter treatments after several days.
- Eye swelling that is accompanied by skin changes such as rash, blistering, or discoloration around the eyes.
Situations Where Eye Swelling May Indicate a Serious Underlying Condition
Eye swelling can be a symptom of various serious conditions. For example, severe allergies can cause significant periorbital edema (swelling around the eyes). Furthermore, certain infections, such as cellulitis (a bacterial skin infection), or orbital cellulitis (infection of the tissues surrounding the eye), can present with pronounced eye swelling. Less common but equally serious conditions like thyroid eye disease (Graves’ ophthalmopathy) can also cause significant eye swelling.
In some cases, kidney disease or heart failure can manifest as swelling around the eyes. Finally, certain medications can trigger eye swelling as a side effect.
Appropriate Specialists and Diagnostic Tests, Can not sleeping enough cause eyes to swell reasons and management tips
The type of specialist you should consult depends on the suspected cause of the eye swelling.
- Ophthalmologist: An ophthalmologist is an eye doctor who can examine your eyes thoroughly, looking for signs of infection, inflammation, or other eye-related problems. They are the primary specialists for eye swelling related to ocular issues.
- Allergist: If allergies are suspected, an allergist can perform allergy testing to identify triggers and recommend appropriate treatment.
- Primary Care Physician (PCP): Your PCP is often the first point of contact and can assess your overall health and refer you to the appropriate specialist if necessary.
- Endocrinologist: If thyroid problems are suspected, an endocrinologist can conduct tests to assess thyroid function.
- Nephrologist: A nephrologist specializes in kidney diseases and may be consulted if kidney-related issues are suspected.
Diagnostic tests may include a complete eye examination, allergy testing, blood tests (to assess kidney function, thyroid function, or detect infections), imaging studies (such as CT scans or MRI scans to assess the structures around the eye), and sometimes a biopsy of the affected tissue to identify the underlying cause. The specific tests ordered will depend on the suspected cause of the eye swelling and the individual’s medical history.
Illustrative Examples of Eye Swelling
Eye swelling, or periorbital edema, can manifest in various ways depending on its underlying cause. Understanding the different presentations can help in identifying the potential culprit, whether it’s lack of sleep, an allergic reaction, or a more serious medical condition. The following examples illustrate three distinct scenarios.
Sleep Deprivation-Induced Eye Swelling
Imagine Sarah, a 28-year-old graphic designer, who consistently pulls all-nighters to meet deadlines. She’s been averaging only four hours of sleep per night for the past month. Her eyes appear puffy and slightly pale, with a soft, almost doughy texture. The swelling is most prominent around the lower eyelids, creating a noticeable bagginess. The skin itself isn’t particularly red or irritated.
Her sleep habits are erratic, often interrupted by caffeine consumption to push through her work. She has no known allergies and reports no other significant medical history. In this case, the eye swelling is a direct consequence of sleep deprivation, leading to fluid retention in the tissues surrounding the eyes.
Allergic Reaction-Induced Eye Swelling
Next, consider Mark, a 35-year-old teacher with a known pollen allergy. During peak pollen season, his eyes become significantly swollen, itchy, and red. The swelling is more pronounced in the upper eyelids, causing them to feel heavy and tight. The skin appears inflamed and slightly darker in color than usual. The texture is taut, almost shiny, due to the underlying inflammation.
He reports significant itching and watery eyes, accompanied by sneezing and a runny nose. His medical history includes seasonal allergies, successfully managed with antihistamines in the past. This scenario clearly demonstrates the characteristic features of allergic conjunctivitis, leading to significant periorbital swelling.
Medical Condition-Induced Eye Swelling
Finally, let’s look at the case of Emily, a 60-year-old retired nurse who recently experienced sudden, severe swelling around both eyes. The swelling is significant, extending beyond the eyelids and into the surrounding facial tissues. The skin is taut and shiny, with a pale, almost translucent appearance. The swelling developed rapidly and is accompanied by significant discomfort and a feeling of tightness.
Emily’s medical history includes hypertension and mild kidney disease. In this scenario, the eye swelling could be indicative of a more serious medical condition, such as kidney failure or an underlying heart problem causing fluid retention, necessitating immediate medical attention. The rapid onset and severity of the swelling distinguish this case from the previous examples.
Outcome Summary
So, next time you’re tempted to sacrifice sleep for another episode of your favorite show, remember the potential consequences for your appearance and overall well-being. Prioritizing sleep hygiene is crucial not just for feeling your best, but also for looking your best. While occasional puffiness is normal, persistent swelling warrants a trip to the doctor. Remember, a well-rested you is a healthier, happier, and definitely less puffy you! Now go get some sleep!
General Inquiries: Can Not Sleeping Enough Cause Eyes To Swell Reasons And Management Tips
Can I use makeup to hide puffy eyes caused by lack of sleep?
While makeup can temporarily mask puffiness, it’s not a long-term solution. Addressing the underlying sleep deprivation is key.
Are there specific foods that can worsen eye swelling?
Salty foods and alcohol can contribute to fluid retention, potentially worsening eye puffiness. A balanced diet is always recommended.
How long does it typically take for eye swelling from sleep deprivation to subside?
Usually, getting a good night’s sleep will significantly reduce swelling within a day or two. However, this depends on the severity and other contributing factors.
Can allergies cause eye swelling that looks similar to sleep deprivation swelling?
Yes, both can cause puffiness. Allergic reactions often involve itchiness and redness, which are less common with sleep deprivation swelling.
