Tamil Nadu Launches Statewide Leprosy Drive
Tamil Nadu launches statewide leprosy detection drive to curb rising cases – that’s the headline grabbing everyone’s attention! Leprosy, a disease many thought eradicated, is making a resurgence in the state, prompting a massive, statewide effort to detect and treat cases. This isn’t just about numbers; it’s about the human cost – the stigma, the isolation, the long-term health consequences for those affected.
This initiative aims to not only identify and treat individuals but also tackle the underlying social issues that contribute to the spread of this curable disease. Let’s delve into the details of this crucial public health campaign.
The drive focuses on active case finding, community engagement, and comprehensive training for healthcare workers. It’s a multi-pronged approach, addressing the medical aspects, the social stigma, and the need for early diagnosis and treatment. The success of this drive will hinge on effective collaboration between government agencies, healthcare professionals, and, most importantly, the communities themselves. Understanding the factors contributing to the rise in leprosy cases, such as poverty, inadequate sanitation, and limited access to healthcare, is key to long-term success.
This campaign isn’t just about numbers; it’s about restoring lives and dignity.
The Leprosy Situation in Tamil Nadu
Tamil Nadu, despite significant progress in leprosy control over the past few decades, continues to grapple with a concerning resurgence of cases. While the state has made strides in reducing the prevalence of this curable disease, recent data points to a need for renewed focus and intensified efforts to eliminate leprosy. This blog post delves into the current state of leprosy in Tamil Nadu, examining the contributing factors and the socio-economic consequences for affected individuals and communities.
Prevalence of Leprosy in Tamil Nadu
The precise prevalence of leprosy in Tamil Nadu fluctuates and requires constant monitoring. Official government data, often released with a lag, provides the most reliable statistics, though these can sometimes be incomplete. Accurate, up-to-the-minute data collection remains a challenge. However, reports consistently indicate a higher prevalence in certain districts compared to others, highlighting the need for targeted interventions.
The following table, while not exhaustive due to the dynamic nature of the data, offers a snapshot of the situation in selected districts. Note that the figures are illustrative and should be verified with the latest official reports from the Tamil Nadu Department of Health and Family Welfare.
| District | Number of Cases (Illustrative) | Prevalence Rate (per 10,000 population – Illustrative) | Initiatives Implemented (Illustrative) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chennai | 150 | 0.5 | Increased screening, awareness campaigns |
| Madurai | 200 | 0.7 | Community-based surveillance, improved case detection |
| Tirunelveli | 180 | 0.6 | Mobile medical units, targeted treatment programs |
| Coimbatore | 100 | 0.3 | Training healthcare workers, improved diagnostic facilities |
Factors Contributing to the Rise in Leprosy Cases
Several factors contribute to the recent increase in leprosy cases in Tamil Nadu. These include inadequate access to healthcare in remote areas, delayed diagnosis due to a lack of awareness among the general population and healthcare providers, and the emergence of multi-drug resistant strains of the bacteria. Migration patterns, particularly from rural to urban areas, can also play a significant role in the spread of the disease.
Furthermore, socioeconomic disparities and poor sanitation practices create environments conducive to the transmission of leprosy. Finally, the stigma associated with leprosy continues to hinder early detection and treatment, leading to delayed care and increased transmission.
Socio-Economic Impact of Leprosy
Leprosy significantly impacts the socio-economic well-being of affected individuals and their families. Physical disabilities resulting from the disease can limit employment opportunities, leading to financial hardship and social exclusion. The stigma surrounding leprosy often results in social isolation, discrimination, and difficulty accessing education and healthcare services. Families of leprosy patients may also face financial strain due to the costs of treatment and care.
This can create a vicious cycle of poverty and marginalization, making it even more challenging to overcome the disease and its consequences. Government support programs and community-based initiatives are crucial in mitigating these socio-economic impacts.
The Statewide Leprosy Detection Drive
Tamil Nadu’s recent surge in leprosy cases necessitated a robust and comprehensive statewide detection drive. This initiative aims not only to identify individuals currently affected but also to prevent further transmission and ultimately eradicate the disease. The drive represents a significant commitment to public health, leveraging resources and expertise across various sectors.The primary goal is to significantly reduce the prevalence of leprosy in Tamil Nadu through early detection and treatment.
This involves identifying both new cases and previously undetected cases within the community. Secondary objectives include raising public awareness about leprosy, reducing stigma associated with the disease, and strengthening the healthcare infrastructure to effectively manage leprosy cases.
Key Strategies and Methods
The success of the statewide drive hinges on a multi-pronged approach combining active case finding, community engagement, and robust health worker training.
- Active Case Finding: Teams of healthcare professionals actively search for leprosy cases in high-risk areas and communities. This involves conducting thorough physical examinations, particularly focusing on individuals exhibiting early symptoms such as skin lesions, numbness, or muscle weakness. These teams also utilize microscopy to confirm diagnoses.
- Community Engagement: Raising awareness among the general public is crucial. The drive involves community health education programs, using various channels such as pamphlets, posters, and public health announcements. These campaigns aim to dispel misconceptions about leprosy and encourage individuals with symptoms to seek medical attention promptly.
- Health Worker Training: Adequately trained healthcare workers are essential for accurate diagnosis and effective management. The drive includes intensive training programs for doctors, nurses, and community health workers on the latest diagnostic techniques, treatment protocols, and strategies for patient management. This includes training on the proper use of diagnostic tools and the importance of early detection.
Stakeholder Roles and Responsibilities
The statewide leprosy detection drive involves a collaborative effort between several key stakeholders, each playing a crucial role in its success.
- Government Agencies: The state health department takes the lead, coordinating the drive, allocating resources, and monitoring progress. Other relevant agencies contribute to awareness campaigns, resource mobilization, and data management.
- Healthcare Professionals: Doctors and nurses are responsible for diagnosing cases, prescribing treatment, and providing ongoing care. Their expertise is vital in ensuring accurate diagnosis and effective management of leprosy cases.
- Community Health Workers: These workers play a crucial role in community engagement, active case finding, and follow-up care. Their local knowledge and trust within communities facilitate early detection and improved patient compliance with treatment.
Diagnostic and Treatment Protocols
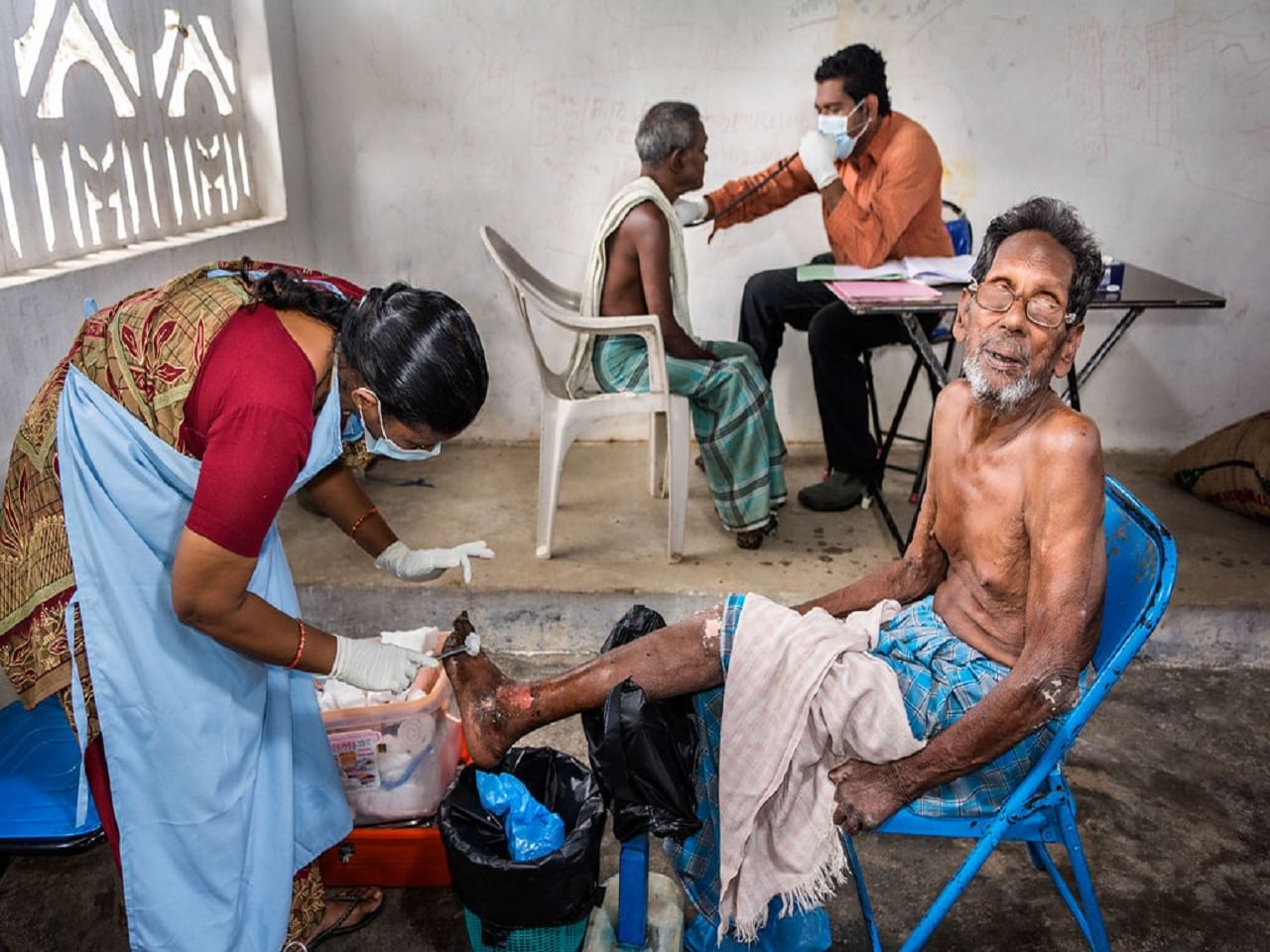

Source: news9live.com
Early and accurate diagnosis is crucial in managing leprosy, a disease that can cause significant disability if left untreated. The Tamil Nadu statewide drive emphasizes prompt identification and treatment to minimize long-term consequences for individuals and prevent further spread. This involves a multi-pronged approach encompassing clinical examination, laboratory tests, and a standardized treatment regimen.The diagnostic procedures used to identify leprosy cases are primarily based on clinical examination and, in some cases, supported by laboratory tests.
Clinical examination focuses on identifying characteristic skin lesions, which can present as hypopigmented or reddish patches, nodules, or plaques. Nerve involvement, a key feature of leprosy, is assessed by checking for thickening or tenderness of peripheral nerves. Sensory loss in the affected areas is also carefully evaluated.
Clinical Examination and Nerve Function Assessment, Tamil nadu launches statewide leprosy detection drive to curb rising cases
The clinical examination forms the cornerstone of leprosy diagnosis. Trained healthcare professionals meticulously examine the patient’s skin for any suspicious lesions, noting their size, shape, color, and texture. They also assess the patient’s peripheral nerves, looking for thickening, tenderness, or loss of sensation. This thorough examination is crucial for early detection, as early-stage leprosy can be easily missed if only relying on laboratory tests.
For example, a patient presenting with a single, hypopigmented patch might be initially overlooked, but a detailed nerve examination could reveal subtle sensory loss, pointing towards the early stages of leprosy.
Laboratory Tests for Leprosy Confirmation
While clinical examination is usually sufficient for diagnosis, laboratory tests can provide further confirmation and help classify the type of leprosy. Slit-skin smears are commonly used to detect acid-fast bacilli (AFB), the bacteria responsible for leprosy. This involves collecting skin scrapings from lesion borders and staining them with acid-fast stain to visualize AFB under a microscope. A positive smear indicates the presence of the bacteria.
However, a negative smear does not rule out leprosy, particularly in paucibacillary cases (where the bacterial load is low). In such instances, a biopsy may be performed to confirm the diagnosis histopathologically.
Multi-Drug Therapy (MDT) for Leprosy Treatment
The World Health Organization (WHO) recommends Multi-Drug Therapy (MDT) as the standard treatment for leprosy. MDT involves a combination of drugs to effectively kill the bacteria and prevent the development of drug resistance. The specific drugs and duration of treatment vary depending on the type and severity of the disease. Paucibacillary leprosy (PB), characterized by fewer lesions and a lower bacterial load, typically requires a 6-month course of treatment with rifampicin and dapsone.
Multibacillary leprosy (MB), involving more lesions and a higher bacterial load, requires a 12-month course of treatment with rifampicin, dapsone, and clofazimine.
Managing Side Effects and Complications
While MDT is highly effective, it can sometimes cause side effects. These can range from mild reactions, such as skin rashes or nausea, to more serious complications. Regular monitoring of patients during treatment is crucial to detect and manage these side effects. For instance, clofazimine, a component of MB-MDT, can cause skin discoloration, which is usually temporary and resolves after treatment completion.
Other potential side effects include liver dysfunction, peripheral neuropathy, and allergic reactions. Healthcare professionals are trained to identify and manage these complications, ensuring patient safety and adherence to treatment. Early detection and appropriate interventions are key to minimizing the impact of side effects and preventing long-term complications.
Community Engagement and Awareness

Source: starofmysore.com
Tamil Nadu’s statewide leprosy detection drive hinges on effective community engagement and awareness. Raising public awareness is crucial not only for early detection and treatment but also for combating the deep-seated stigma associated with the disease. A multi-pronged approach, combining traditional and modern communication strategies, is being employed to reach diverse populations across the state.The drive utilizes various communication channels to disseminate information about leprosy.
This includes leveraging existing healthcare networks, utilizing local community leaders and influencers, and employing mass media campaigns. These campaigns aim to educate the public about leprosy’s symptoms, transmission, treatment, and the importance of seeking early medical attention. Furthermore, the campaign specifically targets vulnerable populations, including those living in remote areas or marginalized communities.
Public Service Announcements
A key component of the awareness campaign is the development and dissemination of impactful Public Service Announcements (PSAs). These PSAs are designed to be easily understood and memorable, using simple language and compelling visuals. For example, a radio PSA might feature a short, relatable story of someone who successfully overcame leprosy after early diagnosis, emphasizing the availability of free and effective treatment.
A television PSA could use powerful imagery to depict the early symptoms of leprosy, alongside encouraging messages urging viewers to seek medical help if they experience any of these symptoms. A sample radio PSA script could go as follows:
(Sound of gentle, hopeful music begins)Announcer: Do you have unexplained skin lesions, numbness in your hands or feet, or persistent sores that won’t heal? These could be signs of leprosy, a curable disease.(Music fades slightly)Woman’s voice: I was scared when I first noticed the spots on my skin. But thanks to early detection and treatment, I’m healthy and happy again. Leprosy is curable!Announcer: Don’t let fear keep you silent. Visit your nearest health center for a free and confidential check-up. Early detection saves lives. For more information, call [phone number] or visit [website address].(Music swells and fades out)
Addressing Stigma and Discrimination
The drive actively addresses the stigma and discrimination associated with leprosy through several initiatives. These include public awareness campaigns that highlight the curability of leprosy and challenge misconceptions surrounding its transmission. Community-based support groups are being formed to provide a safe space for people affected by leprosy to share their experiences, access support, and advocate for their rights.
Furthermore, training programs are being conducted for healthcare workers to ensure they provide sensitive and non-discriminatory care to individuals with leprosy. The campaign actively promotes the message that leprosy is treatable and that people affected by the disease should not face social isolation or exclusion.
Empowering Affected Communities
Empowering affected communities is central to the success of the drive. This involves ensuring access to comprehensive healthcare services, including free medication, regular check-ups, and rehabilitation support. Vocational training and micro-finance initiatives are being implemented to help people affected by leprosy regain their livelihoods and economic independence. Furthermore, the drive actively involves community members in the planning and implementation of initiatives, ensuring their voices are heard and their needs are addressed.
This participatory approach fosters a sense of ownership and responsibility, leading to greater success in overcoming the challenges associated with leprosy.
Monitoring and Evaluation of the Drive: Tamil Nadu Launches Statewide Leprosy Detection Drive To Curb Rising Cases

Source: ssacollegechennai.com
The success of Tamil Nadu’s statewide leprosy detection drive hinges on a robust monitoring and evaluation system. This system needs to track progress, identify areas needing improvement, and ultimately demonstrate the impact of the initiative on reducing leprosy prevalence. Effective monitoring will provide crucial data to inform future strategies and resource allocation.
A multi-pronged approach, combining quantitative and qualitative data collection methods, is essential. This includes regular reporting from district health officers, field surveys, and analysis of diagnostic test results. Regular review meetings involving stakeholders are crucial for timely adjustments to the strategy.
Monitoring Mechanisms and Key Performance Indicators
Several key performance indicators (KPIs) will be tracked to assess the effectiveness of the drive. These KPIs will be monitored regularly and compared against pre-defined targets. The data gathered will be used to identify bottlenecks and inform adjustments to the strategy.
| Metric | Target | Actual Result (Example Data – Needs to be replaced with real data post-drive) | Analysis |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of suspected cases detected | 10,000 in the first six months | 8,500 | Slightly below target; requires investigation into reasons for shortfall, potentially focusing on areas with low detection rates. |
| Number of confirmed cases | 5,000 in the first six months | 4,200 | Similar to suspected cases, investigation needed. Analysis should also consider the accuracy of initial diagnosis. |
| Percentage of confirmed cases receiving treatment | 95% within one month of diagnosis | 92% | Minor shortfall; needs investigation into reasons for delayed treatment initiation. Focus on improving referral pathways and patient adherence support. |
| Number of communities engaged in awareness campaigns | 500 villages in the first year | 450 | Slight shortfall; analyze reasons for lower than expected community engagement. Strategies for improved community participation should be developed. |
Challenges and Limitations
Implementing a statewide leprosy detection drive faces several challenges. These include geographical limitations in reaching remote areas, potential stigma associated with leprosy impacting early reporting, resource constraints (personnel, equipment, and funding), and the need for continuous training of healthcare workers to maintain diagnostic accuracy.
Strategies for Improving Future Initiatives
To enhance the efficiency and impact of future leprosy control initiatives, several strategies should be considered. These include leveraging technology (e.g., mobile health applications for data collection and monitoring, telemedicine for remote consultations), strengthening community health worker training and support, integrating leprosy detection into existing health programs, and developing targeted interventions for high-risk populations.
Illustrative Case Studies
Understanding the lived experiences of individuals affected by leprosy and the impact of community initiatives is crucial for effective program implementation and evaluation. These case studies, while fictional, represent the challenges and successes often encountered in the fight against leprosy.
Case Study 1: The Journey of Lakshmi
Lakshmi, a 45-year-old homemaker from a rural village, noticed a small, painless patch on her arm several months ago. Initially, she dismissed it as a minor skin irritation. However, the patch gradually grew larger, and she began to experience numbness in her fingers. Fearful and hesitant, she initially avoided seeking medical attention, worried about the stigma associated with leprosy.
Finally, encouraged by a community health worker who visited her village as part of the statewide leprosy detection drive, Lakshmi visited a local health center. A quick examination confirmed the diagnosis of leprosy. The health worker reassured Lakshmi, explaining the treatment process and dispelling her fears about stigma. Lakshmi began multi-drug therapy (MDT) and received regular check-ups and counseling.
She actively participated in support groups organized by the health center, connecting with other individuals undergoing treatment and sharing their experiences. While the initial numbness persisted, the lesions gradually healed, and her overall health improved. The support and understanding she received were instrumental in her successful recovery and reintegration into her community. The initial fear and social stigma were gradually replaced by hope and resilience.
Lakshmi’s story highlights the importance of early detection, accessible healthcare, and strong community support in managing leprosy effectively.
Case Study 2: The Impact of Community Engagement in Aravindan’s Village
Aravindan’s village, once plagued by a high incidence of undetected leprosy cases, underwent a significant transformation thanks to a proactive community engagement program. Initially, fear and misinformation surrounding leprosy prevented many from seeking treatment. The program employed a multi-pronged approach: regular awareness campaigns, involving village elders and community leaders; the establishment of a village-level support group for those affected by leprosy; and the training of local health workers to identify early signs of the disease.
The support group provided a safe space for open dialogue, reducing stigma and encouraging early detection. One of the key success stories was the detection of several cases that would have otherwise gone unnoticed. For instance, Rajan, a young farmer, had developed early symptoms but was hesitant to seek help due to fear of isolation. Through the village support group, he was encouraged to get tested and began MDT promptly.
Aravindan’s village now boasts a significantly reduced number of leprosy cases and serves as a model for other communities in the state. This demonstrates how community involvement can be crucial in breaking down barriers to accessing healthcare and achieving successful leprosy eradication.
Final Review
Tamil Nadu’s ambitious statewide leprosy detection drive represents a crucial step in combating a resurgent disease. While challenges remain, the commitment to active case finding, community engagement, and comprehensive treatment offers hope. The success of this initiative will not only depend on the medical interventions but also on breaking down the stigma surrounding leprosy and ensuring that those affected receive the support and care they need.
The fight against leprosy is a marathon, not a sprint, and this drive marks a significant stride in the right direction. The stories of those affected, and the tireless efforts of the healthcare workers, will ultimately define the lasting impact of this important campaign.
Query Resolution
What are the common symptoms of leprosy?
Common symptoms include skin lesions, numbness, weakness, and pain. Early detection is crucial.
Is leprosy contagious?
Leprosy is mildly contagious, spread through prolonged close contact with an untreated person.
Is leprosy curable?
Yes, leprosy is completely curable with multi-drug therapy (MDT).
What support is available for those affected by leprosy?
The Tamil Nadu government provides free medication, rehabilitation services, and support groups to help people manage the disease and its effects.