TEFCA Goes Live Health Data Sharing Interoperability
TEFCA goes live health data sharing interoperability! This is HUGE news for healthcare. For years, we’ve struggled with fragmented health data, making patient care less efficient and more prone to errors. Imagine a world where your doctor in one state instantly has access to your complete medical history from another – that’s the promise of TEFCA. This new nationwide network aims to revolutionize how we share health information, improving coordination, reducing costs, and ultimately, saving lives.
This post dives into what TEFCA is, how it works, and what it means for the future of healthcare.
We’ll explore the technical aspects, the potential benefits for patients, and the challenges that lie ahead. We’ll also look at how TEFCA compares to previous attempts at interoperability and what makes this initiative different. Get ready for a deep dive into the exciting world of seamless health data exchange!
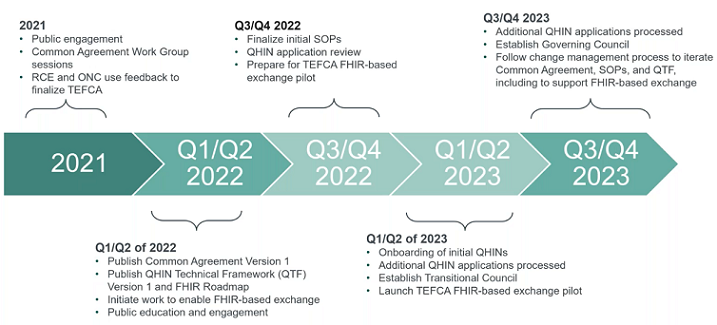
TEFCA’s Go-Live
Source: healthitanswers.net
The launch of the Trusted Exchange Framework and Common Agreement (TEFCA) marks a pivotal moment for nationwide health data exchange. For years, the fragmented nature of healthcare data systems has hindered efficient care coordination and created significant administrative burdens. TEFCA aims to solve this by establishing a common, nationwide framework for secure health information exchange, paving the way for a more interconnected and patient-centric healthcare system.TEFCA’s implementation promises significant improvements in interoperability across the healthcare landscape.
By providing a consistent set of rules and technical specifications, it facilitates seamless data sharing between disparate health information systems. This will ultimately improve the quality of care, reduce medical errors, and enhance patient safety.
Improved Healthcare Processes and Reduced Administrative Burdens
TEFCA will streamline numerous healthcare processes. For example, imagine a patient transferring from a hospital to a rehabilitation center. With TEFCA, their medical records can be easily and securely transferred, eliminating the need for manual chart reviews and reducing delays in care. Similarly, providers can access a patient’s complete medical history regardless of where they received care, enabling more informed decision-making and personalized treatment plans.
This will also drastically reduce the time and resources spent on administrative tasks like faxing and phone calls, freeing up valuable time for patient care. The reduction in administrative overhead is expected to translate into significant cost savings for healthcare organizations. A specific example could be a large hospital system reducing its administrative staff hours dedicated to record retrieval by 20% due to TEFCA’s automated data exchange.
Comparison of TEFCA with Previous Methods, Tefca goes live health data sharing interoperability
Prior to TEFCA, health information exchange relied heavily on disparate, often incompatible systems. This resulted in a patchwork of solutions with limited interoperability and significant challenges in data sharing. The following table compares key features of TEFCA with a previous, more fragmented approach, represented here by a hypothetical system named “Legacy System.”
| Feature | TEFCA | Legacy System |
|---|---|---|
| National Scope | Nationwide, consistent framework | Regional, varying standards and agreements |
| Interoperability | High, using common technical specifications | Low, significant variations in systems and data formats |
| Security | Robust security standards and protocols | Variable security measures, potential vulnerabilities |
| Governance | Centralized governance through the Common Agreement | Decentralized, often informal agreements |
Technical Aspects of TEFCA Interoperability
TEFCA’s (Trusted Exchange Framework and Common Agreement) go-live marks a significant step towards nationwide health information exchange. But the success of this ambitious project hinges on a robust and secure technical architecture. Understanding the underlying technology is crucial to appreciating both its potential and its limitations. This section delves into the technical intricacies of TEFCA, exploring its architecture, security measures, and potential challenges.
TEFCA Network Architecture and Core Components
TEFCA’s architecture is based on a federated model, meaning it connects various Qualified Health Information Networks (QHINs) rather than creating a single, monolithic system. This decentralized approach promotes interoperability while allowing individual QHINs to maintain their unique operational characteristics. The core components include the Common Agreement, which sets the standards for data exchange; the Qualified Health Information Networks (QHINs), which act as the communication hubs; and the Trust Framework, which ensures secure and reliable data transmission.
The system relies on a combination of technologies, including HL7 FHIR (Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources) for data exchange and various security protocols to protect sensitive information. This architecture enables a flexible and scalable solution capable of adapting to the evolving needs of the healthcare industry.
Security Measures in TEFCA
Protecting patient health information (PHI) is paramount. TEFCA employs a multi-layered security approach encompassing technical, administrative, and physical safeguards. These measures include robust authentication and authorization mechanisms to verify the identity of users and systems accessing the network. Data encryption, both in transit and at rest, is essential to prevent unauthorized access. Regular security audits and vulnerability assessments are conducted to identify and mitigate potential risks.
Furthermore, the Common Agreement mandates adherence to stringent privacy and security standards, such as HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) regulations, ensuring compliance with existing legal frameworks. The use of digital signatures and audit trails enhances accountability and transparency within the system.
Challenges Related to Data Standardization and Compatibility
While TEFCA aims for seamless interoperability, challenges remain. One significant hurdle is the diversity of existing health information systems and data formats. Achieving true interoperability requires consistent data standardization across different healthcare organizations. This necessitates the adoption of common data models and terminologies. Variations in clinical workflows and practices can also impact compatibility.
Addressing these issues requires ongoing collaboration among stakeholders, including healthcare providers, technology vendors, and regulatory bodies, to promote the widespread adoption of standardized data formats and practices. The successful implementation of TEFCA will rely heavily on consistent application of the standards and ongoing refinement based on practical experience.
The TEFCA going live for health data sharing is a huge step forward, but it also highlights the vulnerabilities in the system. Consider the recent impact of the cyberattack on Elevance Health, as reported in this article: elevance health earnings q1 change cyberattack medicaid medicare advantage , which underscores the need for robust security measures alongside improved interoperability.
Ultimately, TEFCA’s success hinges on addressing these security concerns to protect patient data while enabling seamless information exchange.
Hypothetical Scenario: Secure Data Sharing Using TEFCA
Imagine Dr. Smith at Community Hospital needs to share a patient’s radiology report with Dr. Jones at a specialist clinic. Both hospitals are connected to different QHINs participating in the TEFCA network. Dr.
Smith, using a TEFCA-compliant application, initiates a secure data request, specifying the required information and the recipient (Dr. Jones). The request is routed through the relevant QHINs, using secure communication channels and adhering to established security protocols. The system verifies the identities of both Dr. Smith and Dr.
Jones through appropriate authentication methods. The radiology report, encrypted and digitally signed, is then securely transferred to Dr. Jones’s system. Dr. Jones can then access the report, confident in its authenticity and integrity, all while maintaining compliance with HIPAA and other relevant regulations.
This scenario highlights the potential of TEFCA to streamline clinical workflows and improve patient care.
TEFCA’s Role in Improving Patient Care

Source: ehealthexchange.org
TEFCA, the Trusted Exchange Framework and Common Agreement, promises a revolution in healthcare by fostering seamless interoperability between different health information systems. This improved data sharing has the potential to significantly enhance patient care, leading to better health outcomes and a more efficient healthcare system. The benefits extend far beyond simple data transfer; they touch upon the very core of how healthcare is delivered and experienced.Improved data sharing, facilitated by TEFCA, offers several key advantages for patients.
It enables a more holistic view of a patient’s health history, allowing providers to make more informed decisions. This leads to better coordinated care, reduced medical errors stemming from duplicated tests or conflicting medication prescriptions, and ultimately, improved patient safety. Imagine a scenario where a patient’s allergy to penicillin is readily available to every doctor, nurse, and pharmacist involved in their care – preventing potentially life-threatening reactions.
Better Coordinated Care and Reduced Medical Errors
The fragmented nature of the current healthcare system often leads to delays and inconsistencies in care. Patients frequently find themselves repeating their medical history to multiple providers, leading to frustration and potential for errors. TEFCA’s nationwide network enables providers to access a comprehensive view of a patient’s medical record, including lab results, imaging reports, and medication history. This eliminates the need for repeated data entry and ensures that all providers are working with the most up-to-date information, reducing the risk of medical errors and improving the overall quality of care.
For instance, a patient with a complex medical history undergoing surgery would benefit greatly from all their specialists having access to a complete and current record, minimizing the chances of complications arising from overlooked details.
Facilitating New Healthcare Applications and Services
TEFCA’s infrastructure creates a fertile ground for the development of innovative healthcare applications and services. By providing a secure and standardized method for data exchange, TEFCA empowers developers to create tools that leverage patient data to improve health outcomes. This could include applications for remote patient monitoring, personalized medicine, population health management, and predictive analytics. For example, an app could analyze patient data to identify individuals at high risk for developing certain conditions, allowing for early intervention and preventative measures.
Another application could facilitate virtual consultations, improving access to care for patients in remote areas.
TEFCA Use Cases Across Various Healthcare Settings
The impact of TEFCA extends across a wide range of healthcare settings. The ability to securely share data will improve efficiency and coordination in various areas.
- Hospitals: Improved care coordination between different departments within a hospital, seamless transfer of patient information between inpatient and outpatient settings, and efficient discharge planning.
- Clinics: Enhanced communication between primary care physicians and specialists, leading to better management of chronic conditions and reduced hospital readmissions.
- Pharmacies: Reduced medication errors through access to complete medication histories, improved medication reconciliation, and better identification of potential drug interactions.
- Public Health Agencies: Facilitated tracking and management of outbreaks, improved surveillance of chronic diseases, and better targeting of public health interventions.
- Research Institutions: Secure and ethical access to de-identified patient data for research purposes, accelerating medical breakthroughs and improving the development of new treatments.
Empowering Patients with Greater Control Over Their Health Information
TEFCA is not just about improving care coordination; it’s also about empowering patients. By providing patients with greater control over their health information, TEFCA fosters a more patient-centric healthcare system. Patients will have more control over which providers can access their data, and they can potentially access and manage their health information through patient portals and other tools.
This increased transparency and control can improve patient engagement and lead to better health outcomes. The ability to easily share their health information with new providers can streamline transitions of care and reduce administrative burdens.
The TEFCA launch for nationwide health data sharing is huge news, promising better patient care through seamless interoperability. However, this progress highlights the importance of competition, especially considering the FTC’s recent lawsuit against the Novant Health and Community Health Systems merger, as seen in this article: federal trade commission sues block novant health community health systems hospital acquisition.
Preventing monopolies is key to ensuring fair access to this improved data sharing network offered by TEFCA.
Challenges and Opportunities for TEFCA Adoption
TEFCA’s go-live marks a significant step towards nationwide health data interoperability, but widespread adoption faces considerable hurdles. Successfully navigating these challenges will determine TEFCA’s ultimate impact on patient care and the overall healthcare ecosystem. Addressing concerns around cost, complexity, and privacy is crucial for achieving broad participation and realizing the full potential of this groundbreaking initiative.
Cost Barriers to TEFCA Implementation
The initial investment required for TEFCA implementation can be substantial for healthcare providers, particularly smaller practices and rural hospitals with limited IT budgets. This includes costs associated with software upgrades, staff training, and ongoing maintenance. To mitigate this, a phased implementation approach, offering tiered pricing models based on organizational size and capabilities, could be considered. Government subsidies or grants specifically targeted at smaller providers could also significantly alleviate financial burdens and encourage participation.
Furthermore, showcasing demonstrable return on investment through improved care coordination and reduced administrative costs can incentivize adoption. For example, a study could highlight how reduced duplicate testing resulting from better data access translates to cost savings.
Complexity of TEFCA Integration
Integrating TEFCA into existing healthcare IT infrastructure can be complex and time-consuming. Many healthcare providers use a variety of legacy systems that may not be easily compatible with TEFCA’s standards. This requires significant technical expertise and potentially substantial modifications to existing workflows. To address this, the development of standardized APIs and readily available integration tools can simplify the process.
Offering comprehensive technical support and training programs can also equip healthcare providers with the necessary skills and knowledge. Furthermore, the creation of a centralized resource hub with readily available documentation, troubleshooting guides, and case studies would aid in the implementation process. A successful example of such a resource would be a searchable knowledge base with FAQs, step-by-step guides, and video tutorials on common integration challenges.
The launch of TEFCA for streamlined health data sharing is a huge leap forward, promising to revolutionize healthcare. Imagine the possibilities – seamless access to patient records could be crucial in situations like the groundbreaking clinical trials now underway, as reported by this article on the FDA’s approval of pig kidney transplants in humans: fda approves clinical trials for pig kidney transplants in humans.
This kind of rapid data exchange, facilitated by TEFCA, will be essential for monitoring and managing such complex procedures. Ultimately, TEFCA’s interoperability will be a game-changer for future medical advancements.
Data Privacy and Security Concerns in TEFCA
Concerns regarding data privacy and security are paramount. Healthcare providers must ensure compliance with HIPAA and other relevant regulations while participating in TEFCA. Robust security measures, including encryption, access controls, and audit trails, are essential to protect sensitive patient information. To address these concerns, transparent and comprehensive data governance policies should be established and readily available. Regular security audits and penetration testing should be conducted to identify and mitigate potential vulnerabilities.
Furthermore, public education campaigns emphasizing TEFCA’s security protocols and patient data protection measures can help alleviate anxieties. Examples of such measures could include clear explanations of data encryption methods used and the processes in place to handle data breaches.
Government Regulations and Industry Standards in Facilitating TEFCA Adoption
Government regulations play a crucial role in shaping TEFCA adoption. Clear and consistent regulatory frameworks that support interoperability while ensuring data privacy are essential. Industry standards, developed collaboratively by stakeholders, can provide a common foundation for TEFCA implementation. Government incentives, such as tax credits or grants, can encourage adoption, especially for smaller providers. Mandates for data exchange in specific clinical scenarios can also drive participation.
For example, regulations could mandate the use of TEFCA for the exchange of critical patient information during emergencies or transitions of care. The alignment of existing regulatory frameworks with TEFCA’s standards will be key to ensuring smooth integration and minimizing compliance burdens.
Equitable Access to TEFCA Benefits
Ensuring equitable access to TEFCA’s benefits across diverse healthcare settings and populations requires a multifaceted approach. This includes providing targeted support to underserved communities and addressing digital health literacy disparities. Outreach programs focused on educating providers and patients about TEFCA’s benefits and addressing potential barriers are critical. Financial assistance programs can help providers in underserved areas overcome cost barriers to implementation.
Furthermore, culturally competent training materials and technical support in multiple languages are necessary to ensure inclusive participation. For instance, a successful program could involve partnering with community health organizations to provide training and support to providers serving specific populations, tailoring the approach to address the unique needs of those communities.
The Future of Health Data Sharing with TEFCA
TEFCA’s go-live marks a pivotal moment, not just for US healthcare interoperability, but for the global landscape. Its success will redefine how health data is shared, accessed, and utilized, paving the way for a more efficient, patient-centric, and cost-effective healthcare system. The future implications are vast and transformative.
A Vision for Post-TEFCA Health Data Sharing in the US
With TEFCA fully operational, we can anticipate a dramatic shift towards seamless data exchange. Imagine a future where a patient’s complete medical history – from allergies and medications to lab results and imaging reports – is readily accessible to any authorized provider, regardless of the healthcare system they belong to. This will eliminate redundant testing, reduce medical errors stemming from incomplete information, and foster better coordinated care.
The potential for improved population health management is also significant, allowing for more effective public health initiatives and proactive interventions. Real-world examples like improved management of chronic conditions like diabetes, where consistent data sharing enables better monitoring and preventative care, illustrate the potential impact.
TEFCA as a Global Model for Interoperability
TEFCA’s architecture and implementation strategy offer a compelling blueprint for other nations grappling with interoperability challenges. Its common, nationwide framework for secure data exchange can be adapted and customized to fit different healthcare systems and regulatory environments. Countries like Canada, with its own complex healthcare landscape, could benefit immensely from studying TEFCA’s approach, specifically its focus on common technical standards and governance frameworks.
Successful international adoption could lead to significant improvements in global healthcare collaboration and the exchange of best practices.
Long-Term Impact of TEFCA on Healthcare Costs, Quality, and Patient Outcomes
The long-term effects of TEFCA are projected to be substantial. Reduced medical errors due to improved data access will translate to lower healthcare costs. More effective care coordination will lead to better patient outcomes, potentially reducing hospital readmissions and improving overall health. Improved preventative care, facilitated by readily available data, will further contribute to better health outcomes and cost savings.
While quantifying these impacts precisely is challenging, we can look to early adopters of similar initiatives for clues. Studies showing reductions in healthcare spending and improved patient satisfaction in regions with robust health information exchange programs support the projected benefits of TEFCA.
Infographic: The Evolution of Health Data Sharing with TEFCA
This infographic depicts the transformation of health data sharing, showcasing the pre-TEFCA landscape, the TEFCA implementation phase, and the envisioned future.
- Panel 1: Pre-TEFCA Landscape (Image Description): A chaotic scene depicting isolated data silos represented by different colored boxes, with arrows indicating sporadic and difficult data exchange. Text overlay: “Fragmented Data, Limited Interoperability.”
- Panel 2: TEFCA Implementation (Image Description): A central hub (representing the TEFCA network) connects various healthcare organizations (represented by boxes of different colors), with clear, streamlined data flows. Text overlay: “TEFCA Connecting the Healthcare Ecosystem.”
- Panel 3: The Future with TEFCA (Image Description): A smooth, efficient network of interconnected data points, highlighting seamless data exchange and improved patient outcomes (represented by icons of healthy individuals and reduced healthcare costs). Text overlay: “Seamless Data Exchange, Improved Patient Care.”
- Timeline (Image Description): A horizontal timeline showing the progression from the pre-TEFCA era to the fully implemented future, with key milestones marked along the way.
- Key Metrics (Image Description): A small graph or chart showing projected improvements in healthcare costs, patient satisfaction, and other relevant metrics, illustrating the quantitative impact of TEFCA.
Final Thoughts: Tefca Goes Live Health Data Sharing Interoperability

Source: dhinsights.org
The launch of TEFCA marks a significant turning point in healthcare. While challenges remain in terms of adoption and standardization, the potential benefits are immense. The ability to share health data seamlessly across the country promises to improve patient care, reduce costs, and foster innovation. The future of healthcare is interconnected, and TEFCA is paving the way. Stay tuned as we continue to monitor the progress and impact of this groundbreaking initiative.
It’s an exciting time to be in healthcare!
Question & Answer Hub
What does TEFCA stand for?
TEFCA stands for Trusted Exchange Framework and Common Agreement.
How secure is TEFCA?
TEFCA employs robust security measures to protect patient health information, including encryption and strong authentication protocols. Specific details are available on the TEFCA website.
Will TEFCA be available to all healthcare providers?
The goal is for widespread adoption, but participation will depend on individual provider decisions and their ability to meet the technical requirements. Phased rollout is anticipated.
What if my provider isn’t using TEFCA yet?
Adoption will take time. Contact your provider to inquire about their plans for TEFCA integration. You can also advocate for wider adoption within your healthcare system.