
Telehealth Mental Health Medicare Access Bill Reintroduced Senate
Telehealth Mental Health Medicare Access Bill Reintroduced Senate – that headline alone sparked a firestorm of discussion! This bill, aiming to expand access to crucial mental healthcare services for Medicare beneficiaries, is back in the Senate. It promises a significant shift in how millions access mental health support, particularly those in rural areas or facing other barriers.
But will it truly deliver on its promises, or will it face the same hurdles as previous attempts? Let’s delve into the details and see what’s at stake.
This reintroduction signifies a renewed push to address a critical gap in our healthcare system. The bill aims to broaden telehealth coverage under Medicare, making mental health services more accessible and affordable for seniors. We’ll examine the specifics of the bill, its potential impact on both patients and providers, and the ongoing debate surrounding its feasibility and cost.
Bill Overview and History
The reintroduction of the telehealth mental health Medicare access bill in the Senate represents a significant step towards expanding access to crucial mental healthcare services for seniors. This legislation aims to address persistent disparities in access to care, particularly for those living in rural areas or facing mobility challenges. Its history reflects a long-standing effort to leverage telehealth technology to improve mental health outcomes for Medicare beneficiaries.The bill’s key provisions focus on broadening the scope of telehealth services covered under Medicare Part B.
This includes expanding the types of mental health professionals who can provide telehealth services, increasing the number of telehealth sessions covered, and potentially removing geographic restrictions on telehealth visits. The aim is to ensure that Medicare beneficiaries have access to a wider range of mental health professionals and convenient methods of receiving care, regardless of their location.
Legislative History and Timeline
This bill builds upon previous attempts to expand telehealth access for mental health services under Medicare. Several versions of similar legislation have been introduced in previous congressional sessions, each building on the successes and addressing the shortcomings of its predecessors. While previous versions enjoyed bipartisan support, they ultimately failed to pass into law due to various factors, including procedural hurdles and competing legislative priorities.A timeline of significant events might include: [Year]
- Initial introduction of a similar bill in the House; [Year]
- Senate version introduced; [Year]
- Bill passes the House; [Year]
- Senate committee hearings; [Year]
- Bill fails to advance in the Senate; [Year]
- Reintroduction of a revised bill in the House; [Year]
Current Senate reintroduction. (Note
These years are placeholders and should be replaced with actual dates from reliable sources such as the Congressional Record or official government websites.)
Comparison with Similar Legislation
Several states have already enacted legislation expanding telehealth access for mental health services, offering valuable insights and potential models for the federal bill. For example, [State A] passed a law [describe the law’s key features], while [State B] adopted a different approach by [describe the law’s key features]. These state-level experiences provide data on the effectiveness and challenges associated with expanding telehealth access, informing the design and potential impact of the federal legislation.
At the federal level, other bills related to telehealth access have been passed, focusing on broader healthcare access, but the specific focus on mental health services for Medicare beneficiaries distinguishes this bill. A comparative analysis of these laws and their outcomes would highlight both successes and challenges to inform the current bill’s design and implementation.
Impact on Medicare Beneficiaries: Telehealth Mental Health Medicare Access Bill Reintroduced Senate
This bill, if passed, would significantly alter the landscape of mental healthcare access for millions of Medicare beneficiaries. Currently, many face significant barriers to receiving timely and convenient mental healthcare, particularly those in rural areas or those with limited mobility. The expansion of telehealth services promises to alleviate these challenges and improve the overall mental health of this vulnerable population.The proposed legislation aims to increase access to mental healthcare services by expanding Medicare’s coverage of telehealth services.
This means more Medicare beneficiaries will have the option of receiving mental health treatment remotely, via video conferencing or other digital platforms. This shift could be particularly transformative for those who struggle with transportation, live in geographically isolated areas, or have physical limitations that make in-person appointments difficult.
Increased Access for Rural and Underserved Populations, Telehealth mental health medicare access bill reintroduced senate
The benefits of increased telehealth access are especially pronounced for rural and underserved populations. These communities often experience significant shortages of mental health professionals, resulting in longer wait times, limited treatment options, and reduced access to specialized care. Telehealth offers a solution by connecting patients with providers who may be located hundreds of miles away, eliminating geographical barriers to care.
For example, a rural resident with depression could receive therapy from a specialist in a larger city without the need for extensive travel, saving time, money, and reducing the burden of transportation. This increased access can lead to earlier intervention, improved treatment adherence, and ultimately, better mental health outcomes.
Challenges and Barriers to Implementation
Despite the potential benefits, several challenges and barriers to implementation exist. Digital literacy and access to reliable internet connectivity remain significant hurdles for some beneficiaries. Older adults, in particular, may require additional training and support to effectively utilize telehealth platforms. Moreover, ensuring equitable access for those with limited technological resources, such as low-income individuals or those living in areas with poor internet infrastructure, will require careful planning and investment in digital equity initiatives.
Concerns regarding data privacy and security also need to be addressed to ensure patient confidentiality and trust in the system. Finally, the integration of telehealth into existing healthcare systems requires careful coordination and collaboration between providers, payers, and technology companies.
Hypothetical Case Study: Mrs. Eleanor Vance
Consider Mrs. Eleanor Vance, an 80-year-old Medicare beneficiary living in a remote rural area. She suffers from anxiety and depression, but the nearest mental health clinic is a two-hour drive away, a journey that is increasingly difficult due to her arthritis. Prior to the passage of this bill, Mrs. Vance had limited access to mental healthcare.
Under the new legislation, however, she can now access virtual therapy sessions with a qualified provider via video conferencing. This eliminates the need for extensive travel, allowing her to receive regular treatment from the comfort of her home. The improved access to care leads to a significant improvement in her mental health, allowing her to maintain her independence and improve her quality of life.
This scenario highlights the transformative potential of expanded telehealth access for vulnerable Medicare beneficiaries.
The reintroduction of the telehealth mental health Medicare access bill to the Senate is fantastic news, offering crucial support for those needing care. It’s amazing to see advancements in other areas too, like the groundbreaking news that the FDA has approved clinical trials for pig kidney transplants in humans, as reported by this article. This kind of innovation highlights the power of medical progress, and hopefully, similar breakthroughs will soon impact mental healthcare access, further strengthening the impact of the Senate bill.
Financial Implications and Cost Analysis
The reintroduction of the telehealth mental health Medicare access bill presents a complex financial picture. Understanding the projected costs, funding mechanisms, and potential long-term savings is crucial for evaluating its feasibility and impact. This analysis examines the various financial aspects of expanding telehealth access for Medicare beneficiaries.The bill’s implementation necessitates a significant financial investment, encompassing various cost categories.
These costs need to be carefully considered against the potential benefits, such as improved access to care and reduced overall healthcare expenditures. A comprehensive cost-benefit analysis is essential to determine the bill’s long-term fiscal viability.
Cost Breakdown and Funding Sources
The estimated costs associated with implementing this bill are multifaceted. They include increased reimbursement rates for telehealth services, investments in technological infrastructure (both for providers and beneficiaries), training for healthcare professionals on telehealth platforms, and administrative costs associated with the expansion of the program. Funding sources could include a combination of increased Medicare premiums, reallocation of existing Medicare funds, and potentially, additional federal appropriations.
The specific allocation of funds would depend on the final version of the bill and subsequent budget negotiations.
| Cost Category | Estimated Cost (in billions USD) | Funding Source | Projected Savings (in billions USD) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Increased Reimbursement Rates | $5-10 | Increased Medicare Premiums, Reallocation of Existing Funds | $2-5 (reduced hospital readmissions, ER visits) |
| Technological Infrastructure Upgrades | $2-4 | Federal Appropriations, Private Sector Investment | $1-3 (improved efficiency, reduced travel costs) |
| Provider Training and Support | $1-2 | Federal Grants, Professional Organizations | $0.5-1 (improved care quality, reduced medical errors) |
| Administrative Costs | $0.5-1 | Medicare Administrative Account | $0.25-0.5 (streamlined processes, reduced paperwork) |
Note: These are estimates, and the actual costs and savings may vary depending on various factors, including adoption rates, technological advancements, and the specific design of the program. For example, the projected savings on hospital readmissions are based on studies showing a correlation between improved access to mental healthcare and a reduction in hospital readmissions, particularly among older adults.
Similar studies support the projected savings in reduced emergency room visits and improved care quality. These figures are illustrative and should be considered as preliminary estimations. Further detailed analysis would be needed for a more precise projection.
Cost-Benefit Analysis and Long-Term Savings
While the initial implementation costs are substantial, the projected long-term savings in healthcare expenditures could significantly outweigh these costs. Improved access to mental healthcare through telehealth is expected to lead to better management of chronic conditions, reduced hospitalizations, fewer emergency room visits, and overall improved health outcomes. These improvements could translate into substantial savings for the Medicare system and potentially the broader healthcare system.
For instance, a reduction in hospital readmissions alone could generate significant cost savings, given the high cost of hospital care. Similarly, preventing avoidable emergency room visits could lead to considerable cost savings. The long-term benefits extend beyond financial savings and include improved quality of life for Medicare beneficiaries. A comprehensive cost-benefit analysis should consider both the direct and indirect costs and benefits of expanding telehealth access.
The reintroduction of the telehealth mental health Medicare access bill in the Senate is fantastic news! Access to timely care is crucial, especially for conditions like Tourette Syndrome, which often benefit from early intervention. For parents seeking support, learning effective management strategies is key, and I highly recommend checking out this helpful resource on strategies to manage Tourette Syndrome in children.
Hopefully, expanded telehealth access will make these vital services more readily available to families across the country.
Provider Perspectives and Preparedness
Source: carecloud.com
The reintroduction of the telehealth mental health Medicare access bill presents a complex landscape for mental health providers, filled with both exciting opportunities and significant challenges. The potential expansion of telehealth services under Medicare could dramatically alter their practices, requiring adaptation and strategic planning to effectively leverage the benefits while mitigating potential drawbacks. This section explores the provider perspective, highlighting the hurdles and advantages, and outlining preparatory steps for successful integration of expanded telehealth services.The bill’s impact on provider practices will vary significantly depending on factors such as specialty, practice size, existing telehealth infrastructure, and patient demographics.
Larger practices with established telehealth programs may find the transition relatively smoother, while smaller, rural practices may face greater challenges in terms of technological upgrades and workforce training. However, even established providers will need to adjust their workflows and billing processes to accommodate the changes brought about by increased Medicare reimbursement for telehealth services.
Provider Challenges in Adapting to Expanded Telehealth
Providers face several key challenges in adapting to the expanded telehealth services proposed by the bill. These include the need for robust technological infrastructure, including reliable high-speed internet access and secure telehealth platforms compliant with HIPAA regulations. Furthermore, there are concerns about the potential for increased administrative burden related to telehealth billing and documentation, as well as the need for additional training to effectively deliver care via telehealth.
The potential for increased patient volume also necessitates careful consideration of staffing levels and appointment scheduling. Finally, maintaining the quality of care and addressing potential equity concerns related to access and digital literacy amongst patients are crucial. For example, a rural psychiatrist may need to invest in improved internet connectivity and additional training for their staff to manage the increase in telehealth appointments.
A solo practitioner may find the administrative burden of telehealth billing particularly challenging.
Opportunities Presented by Expanded Telehealth Access
Despite the challenges, the bill also presents significant opportunities for mental health providers. Expanded access to telehealth can significantly increase the reach of mental healthcare services, particularly in underserved rural and geographically isolated communities. This could lead to improved patient outcomes and reduced healthcare disparities. Furthermore, telehealth offers the potential for increased efficiency and flexibility, allowing providers to see more patients and offer more convenient appointment times.
The increased reimbursement rates offered under the bill could also enhance the financial viability of providing mental healthcare services, particularly for providers serving vulnerable populations. For instance, a therapist specializing in trauma could reach a broader patient base through telehealth, offering their services to individuals who might otherwise face significant barriers to access.
Steps for Providers to Prepare for Expanded Telehealth Services
To effectively prepare for expanded telehealth services, providers should take several key steps. This includes:
- Assess current technological infrastructure: Evaluate the existing technology and identify areas needing upgrades or improvements to ensure HIPAA compliance and optimal telehealth functionality. This might include investing in high-speed internet, secure video conferencing platforms, and electronic health record (EHR) systems with robust telehealth capabilities.
- Develop or update telehealth policies and procedures: Establish clear guidelines for telehealth appointments, including patient consent, technical troubleshooting, and handling emergencies. These policies should address issues of confidentiality, data security, and patient privacy.
- Train staff on telehealth platforms and procedures: Provide comprehensive training to all staff members involved in delivering telehealth services. This should include instruction on the use of telehealth technology, billing procedures, and patient communication strategies.
- Review and update billing and coding practices: Familiarize themselves with the updated Medicare reimbursement guidelines for telehealth services and adjust their billing processes accordingly.
- Address potential equity concerns: Develop strategies to ensure equitable access to telehealth services for all patients, regardless of their technological literacy or socioeconomic status. This might include providing technical assistance, offering alternative communication methods, and addressing potential language barriers.
Resources and Support Systems for Providers
Several resources and support systems can assist providers in adapting to the changes brought about by expanded telehealth services.
- Professional organizations: Organizations like the American Psychological Association (APA) and the American Psychiatric Association (APA) offer resources, guidance, and advocacy related to telehealth.
- Telehealth technology vendors: Numerous vendors provide telehealth platforms, technical support, and training services.
- Government agencies: Agencies like the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) provide information and guidance on Medicare reimbursement for telehealth services.
- Consultants and training programs: Specialized consultants and training programs offer assistance with telehealth implementation, billing, and compliance.
Technological Considerations and Infrastructure
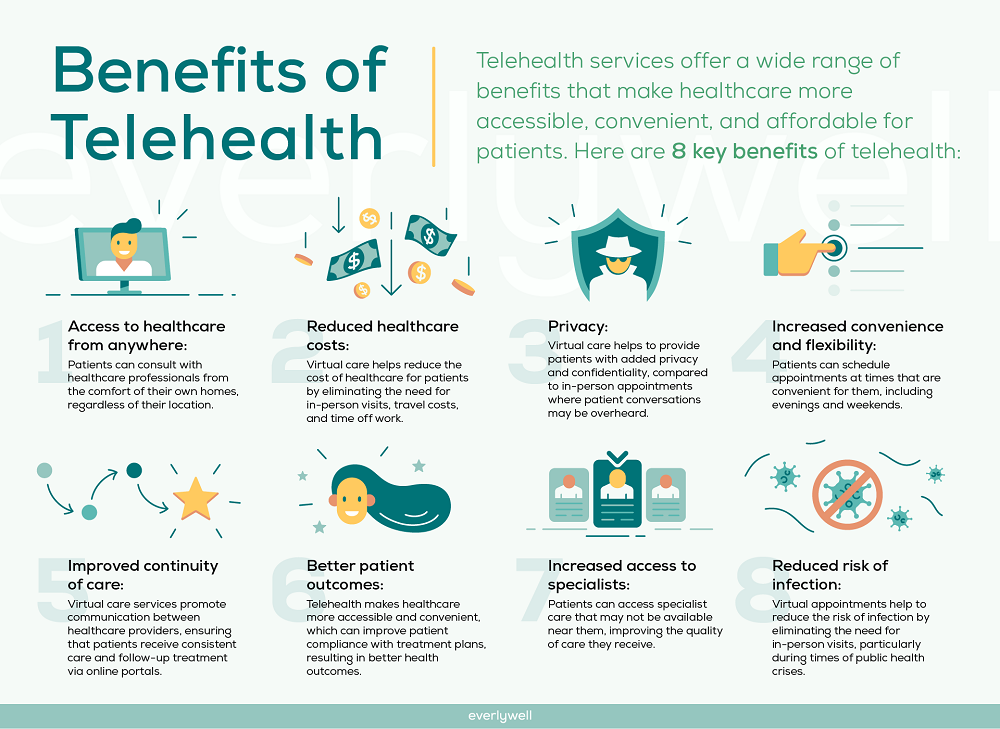
Source: ctfassets.net
The successful implementation of a Medicare telehealth mental healthcare expansion hinges critically on robust technological infrastructure. This infrastructure must be capable of handling the increased demand for remote mental health services while ensuring patient privacy and data security. Without adequate technological support, the bill’s aims of improved access and quality of care will be significantly hampered.The necessary technological infrastructure encompasses several key components, impacting both providers and beneficiaries.
This includes reliable high-speed internet access, secure video conferencing platforms, electronic health record (EHR) systems compatible with telehealth, and robust cybersecurity measures. Furthermore, the infrastructure must be designed to accommodate diverse technological proficiency levels among both patients and providers.
Internet Access and Digital Literacy
Reliable and affordable high-speed internet access is paramount for successful telehealth. Many Medicare beneficiaries, particularly those in rural or underserved areas, lack access to broadband internet. Similarly, digital literacy—the ability to effectively use technology—varies significantly across the population. Some beneficiaries may struggle to navigate telehealth platforms or utilize necessary technologies. The digital divide, therefore, poses a significant barrier to equitable access to telehealth mental healthcare services.
For example, a recent study showed that 20% of rural Medicare beneficiaries lack reliable broadband, significantly hindering their ability to participate in telehealth appointments. This disparity highlights the need for targeted investments in broadband infrastructure and digital literacy training programs.
Patient Privacy and Data Security
Protecting patient privacy and data security is crucial in telehealth. The transmission of sensitive health information requires robust security measures to prevent breaches and unauthorized access. Compliance with regulations like HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) is essential. Telehealth platforms must employ encryption, secure data storage, and strong authentication protocols to safeguard patient data. For instance, a telehealth platform utilizing end-to-end encryption would ensure that only the provider and patient can access the conversation, minimizing the risk of data breaches.
The bill should explicitly address these security requirements and mandate compliance with relevant regulations to ensure patient confidentiality.
Addressing Technological Barriers in the Bill
The reintroduced bill should explicitly address the technological challenges to telehealth expansion. This includes provisions for funding investments in broadband infrastructure, particularly in underserved areas. Furthermore, the bill should allocate resources for digital literacy training programs to empower beneficiaries to effectively utilize telehealth services. It should also include stipulations for telehealth platforms to meet stringent security and privacy standards, ensuring compliance with HIPAA and other relevant regulations.
Finally, the bill could incentivize providers to adopt and utilize telehealth technologies through financial reimbursements or other support mechanisms. Addressing these technological considerations will be crucial to ensure the success of the telehealth expansion for Medicare beneficiaries seeking mental healthcare.
Potential for Policy Changes and Future Directions

Source: selecthub.com
This telehealth mental health Medicare access bill, while a significant step forward, presents opportunities for refinement and expansion. Analyzing potential amendments, considering future legislative possibilities, and examining successful models from other jurisdictions can inform its evolution and maximize its impact on beneficiaries. The following sections delve into these crucial areas.
Potential Bill Amendments and Modifications
Several amendments could enhance the bill’s effectiveness and reach. These modifications aim to address potential shortcomings and expand access to a broader range of beneficiaries. For example, expanding the types of mental health professionals covered under the bill could improve access in underserved areas. Similarly, addressing concerns about data privacy and security through stricter regulations could increase patient trust and adoption.
Future Legislation Building Upon the Bill
This bill could serve as a foundation for future legislation focused on telehealth mental health. Future acts could address issues such as integrating telehealth into primary care settings, creating standardized reimbursement rates for telehealth services across all states, and developing comprehensive training programs for providers on the effective use of telehealth technology. The success of this bill will likely influence the scope and ambition of future legislative efforts in this area.
For example, we could see legislation addressing the digital divide and ensuring equitable access for all Medicare beneficiaries, regardless of their technological literacy or geographic location.
Successful Telehealth Mental Health Initiatives in Other Jurisdictions
Several jurisdictions have implemented successful telehealth mental health initiatives that could inform the direction of this bill. For instance, Oregon’s telehealth expansion program demonstrated the effectiveness of integrating telehealth into rural healthcare systems. This initiative increased access to mental healthcare in underserved communities and improved patient outcomes. Similarly, Vermont’s focus on integrating telehealth into its existing mental health system showcased a comprehensive approach that can be replicated in other states.
These models highlight the importance of considering the unique context of each jurisdiction when designing and implementing telehealth programs.
Table of Potential Policy Changes
| Proposed Change | Rationale | Potential Impact | Challenges |
|---|---|---|---|
| Expand the range of covered mental health professionals to include licensed clinical social workers (LCSWs) and marriage and family therapists (MFTs). | Increase access to care, particularly in areas with shortages of psychiatrists and psychologists. | Improved access to care for a wider range of beneficiaries; potentially increased costs. | Ensuring adequate oversight and quality control for a broader range of providers. |
| Implement stricter data privacy and security regulations for telehealth platforms. | Protect patient confidentiality and address concerns about data breaches. | Increased patient trust and adoption of telehealth services; potentially higher costs for providers. | Balancing patient privacy with the need for interoperability and data sharing. |
| Provide funding for telehealth infrastructure development in underserved areas. | Address the digital divide and ensure equitable access to care for all Medicare beneficiaries. | Improved access to care in rural and underserved areas; reduced health disparities. | Securing funding and coordinating with existing infrastructure initiatives. |
| Develop standardized reimbursement rates for telehealth mental health services across all states. | Reduce disparities in reimbursement rates and promote equity in access to care. | Improved access to care and financial stability for providers; simplified billing and administration. | Negotiating agreements with multiple stakeholders and ensuring adequate funding. |
Ethical Considerations and Patient Safety
The expansion of telehealth mental healthcare, while offering significant benefits, necessitates a careful consideration of ethical implications and robust safety measures to protect patients. The unique aspects of virtual care introduce new challenges that require proactive solutions to ensure ethical practice and high-quality care. This section will explore key ethical concerns and highlight strategies to mitigate risks and maintain the integrity of the patient-provider relationship.
The reintroduction of the telehealth mental health Medicare access bill in the Senate is a huge step forward, especially considering the current healthcare landscape. The news that Steward Health Care secured financing to avoid bankruptcy, as reported on this site , highlights the financial pressures on healthcare systems. This makes expanded access to affordable mental healthcare, like that proposed in the bill, even more critical for patients.
Potential Ethical Concerns in Telehealth Mental Healthcare
Several ethical concerns arise in telehealth mental healthcare delivery. These include issues related to informed consent, confidentiality, accessibility, and the potential for misdiagnosis or inadequate treatment due to limitations in the virtual setting. For instance, ensuring a patient’s comprehension of the limitations of telehealth, particularly regarding the absence of physical examination, is crucial. Similarly, the potential for technology failures, impacting the continuity of care, needs to be addressed proactively.
The challenge of accurately assessing a patient’s mental state solely through a video screen also requires careful consideration and appropriate training for providers. Furthermore, access disparities based on technological literacy or internet availability need to be acknowledged and mitigated.
Ensuring Patient Safety and Quality of Care in Telehealth Settings
Maintaining patient safety and high-quality care in telehealth requires a multi-pronged approach. This involves rigorous adherence to established clinical guidelines, appropriate provider training in telehealth modalities, and robust technological infrastructure. The use of standardized protocols for assessment and treatment, incorporating elements of risk stratification, is essential. Regular quality assurance measures, including audits of telehealth sessions and patient feedback mechanisms, are crucial to identify and address potential deficiencies.
Additionally, clear protocols for managing emergencies and crises, including established referral pathways to in-person care, are necessary. Consideration must also be given to the integration of telehealth services with existing mental health care systems to ensure seamless transitions of care. For example, a patient experiencing a severe suicidal crisis via telehealth would require immediate referral to an emergency room or crisis hotline.
Informed Consent and Patient Autonomy in Telehealth
Informed consent is paramount in telehealth mental healthcare. It’s not just about obtaining a signature; it requires a thorough explanation of the treatment process, including its limitations, risks, and potential benefits, in a language the patient understands. Patients need to be fully aware of the technological aspects of the telehealth platform, including data security measures and potential risks associated with technology failures.
Autonomy means respecting the patient’s right to make informed decisions about their care, including the choice to discontinue treatment at any time. The process of obtaining informed consent in telehealth should be documented meticulously, reflecting the patient’s understanding and agreement. This includes clearly outlining the limitations of the technology and the potential for disruptions to service. For instance, the provider should explain what will happen if the internet connection fails mid-session.
Best Practices for Maintaining Patient Confidentiality and Data Security in Telehealth
Maintaining patient confidentiality and data security is critical in telehealth. Strict adherence to HIPAA regulations and other relevant privacy laws is mandatory.
- Utilize HIPAA-compliant telehealth platforms that encrypt data both in transit and at rest.
- Implement robust password protection and multi-factor authentication for all user accounts.
- Train staff on data security protocols and HIPAA regulations.
- Establish clear policies for data storage, access, and disposal.
- Conduct regular security audits and vulnerability assessments.
- Develop a comprehensive incident response plan to address data breaches or security incidents.
- Educate patients about data security measures and their rights regarding their health information.
- Ensure that all telehealth equipment and software are regularly updated with the latest security patches.
Conclusion
The reintroduction of the Telehealth Mental Health Medicare Access Bill in the Senate offers a beacon of hope for improved mental healthcare access. While challenges remain – financial considerations, technological hurdles, and provider preparedness – the potential benefits for millions of Medicare beneficiaries are undeniable. The success of this bill hinges not only on legislative maneuvering but also on collaborative efforts among policymakers, healthcare providers, and technology innovators.
The journey ahead is complex, but the potential impact on the lives of countless individuals makes this a fight worth fighting.
Question Bank
What are the main criticisms of the bill?
Critics raise concerns about the bill’s cost, potential for fraud, the need for robust cybersecurity measures, and ensuring equitable access for all beneficiaries, regardless of technological literacy or internet availability.
How does this bill differ from previous attempts?
This version may include refinements based on lessons learned from previous iterations, potentially addressing earlier shortcomings in areas like provider reimbursement or technological infrastructure requirements. Specific differences would need to be examined based on the bill’s text.
What support systems are available for providers adopting telehealth?
Many organizations offer training, technical assistance, and financial incentives to help providers transition to telehealth. Specific resources vary by state and federal programs.
Will this bill impact private insurance coverage of telehealth mental health services?
Directly, no. This bill focuses solely on Medicare coverage. However, its success could influence private insurers to expand their own telehealth benefits.





