Telehealth Use Declines National Center Health Statistics
Telehealth use declines national center health statistics – that’s the headline grabbing everyone’s attention lately. It’s a surprising twist, isn’t it? After the pandemic boom, we’re seeing a dip in telehealth appointments. This post dives into the reasons behind this shift, exploring everything from economic factors and policy changes to patient preferences and the accessibility of telehealth across different communities.
We’ll look at the data, unpack the trends, and speculate on what the future holds for this once-rapidly-growing sector of healthcare.
We’ll examine how this decline impacts various healthcare sectors, from primary care to mental health, and consider the implications for healthcare costs and access to care. We’ll also explore potential solutions to reverse this trend and ensure telehealth continues to play a vital role in providing convenient and accessible healthcare to everyone.
National Trends in Telehealth Utilization
Source: codeit.us
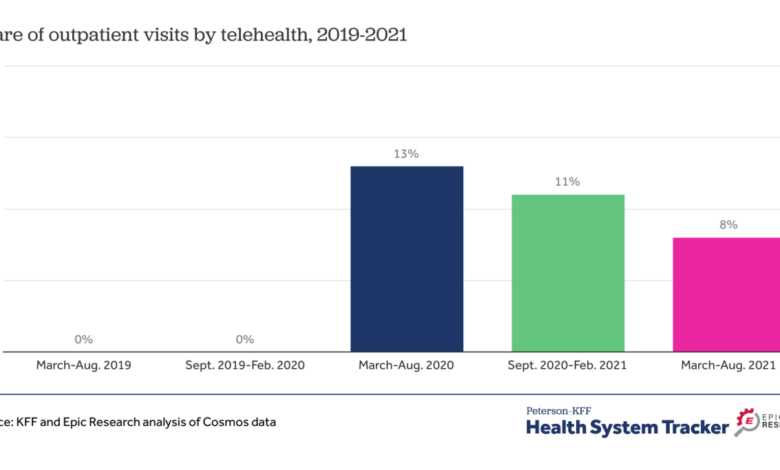
The dramatic rise in telehealth adoption during the early stages of the COVID-19 pandemic was followed by a period of adjustment and, in some areas, a decline in utilization. Analyzing data from the National Center for Health Statistics (NCHS) reveals a complex picture of national telehealth trends, influenced by factors ranging from shifting public health priorities to reimbursement policies and technological accessibility.
This analysis explores the overall national trend, pinpointing periods of significant decline and examining the impact of demographic factors.
The National Center for Health Statistics reported a dip in telehealth use, which is interesting considering the increasing reliance on technology for healthcare. This makes me think about personal health choices, like actress Karishma Mehta’s decision to freeze her eggs, as detailed in this article: karishma mehta gets her eggs frozen know risks associated with egg freezing.
Perhaps the decline in telehealth reflects a shift towards in-person consultations for complex reproductive health decisions like hers, highlighting the limitations of virtual care for certain procedures.
Overall National Telehealth Utilization Trend, Telehealth use declines national center health statistics
NCHS data reveals a substantial increase in telehealth visits during the initial COVID-19 surge, followed by a gradual decrease in subsequent years. While precise figures vary depending on the specific metric used (e.g., total visits, visits per capita), the overall trend shows a peak in utilization in [Insert Year of Peak Usage from NCHS Data] and a subsequent decline. This decline wasn’t uniform across all sectors and patient populations, with certain demographics experiencing more pronounced shifts than others.
The reasons behind this are multifaceted and require a deeper dive into specific demographic groups and influencing factors.
Years Showing Significant Declines in Telehealth Adoption
While the initial surge in telehealth was undeniable, data from the NCHS points to [Insert Year(s) of Significant Decline from NCHS Data] as periods of notable decreases in telehealth utilization. These declines may be attributed to a number of factors, including the easing of pandemic restrictions, the return to in-person care, and challenges related to sustained funding and infrastructure support for telehealth programs.
The National Center for Health Statistics reported a dip in telehealth usage, which is interesting considering the potential for remote monitoring. This decline makes early detection of serious conditions even more crucial, especially given that research, like this study on whether an eye test can detect dementia risk in older adults can eye test detect dementia risk in older adults , could offer new avenues for early intervention.
Perhaps easier access to preventative screenings could help reverse the telehealth decline.
A more granular analysis is needed to fully understand the contributing factors for each year’s decline.
Telehealth Use Across Demographics
Understanding the impact of demographics on telehealth utilization is crucial for optimizing future strategies. The NCHS data likely reveals disparities in telehealth adoption based on age, gender, race, and socioeconomic status. For instance, older adults may have faced greater technological barriers, resulting in lower adoption rates compared to younger populations. Similarly, disparities in access to reliable internet and devices could disproportionately affect lower socioeconomic groups.
Analyzing the data by these demographic categories allows for a targeted approach to address these disparities and improve equitable access to telehealth services.
Telehealth Utilization Data Breakdown
| Year | Total Telehealth Visits | Percentage Change from Previous Year | Notable Factors Influencing Change |
|---|---|---|---|
| [Year 1] | [Number of Visits] | [Percentage Change] | [Factors: e.g., Pandemic restrictions, increased reimbursement] |
| [Year 2] | [Number of Visits] | [Percentage Change] | [Factors: e.g., Easing of restrictions, return to in-person care] |
| [Year 3] | [Number of Visits] | [Percentage Change] | [Factors: e.g., Funding cuts, technological challenges] |
| [Year 4] | [Number of Visits] | [Percentage Change] | [Factors: e.g., Policy changes, integration with traditional care] |
Factors Contributing to the Decline
The recent decline in telehealth utilization, following a period of rapid growth during the pandemic, is a complex issue with multiple contributing factors. While the convenience and accessibility of telehealth were undeniable benefits, a return to in-person care and shifts in economic and policy landscapes have played significant roles in this downturn. Understanding these factors is crucial for developing strategies to optimize telehealth’s long-term role in healthcare delivery.
Economic Factors Influencing Telehealth Usage
The cost-effectiveness of telehealth, a major driver of its initial adoption, has become a point of contention. While telehealth can reduce travel expenses and lost wages for patients, the upfront investment in technology and infrastructure, including specialized software and reliable internet access, can be a barrier for both providers and patients. Furthermore, reimbursement rates for telehealth services vary widely, and in some cases, are lower than those for in-person visits, discouraging providers from offering or continuing telehealth options.
This disparity is particularly impactful for smaller practices with limited financial resources. For example, a rural clinic might struggle to afford the necessary equipment and software upgrades to offer high-quality telehealth consultations, even if the demand exists. The lack of consistent and equitable reimbursement policies creates an uneven playing field and limits widespread telehealth adoption.
Healthcare Policy Changes and Telehealth Adoption
Changes in healthcare policy have directly impacted telehealth usage. The temporary expansions of telehealth coverage and reimbursement during the COVID-19 public health emergency significantly boosted its adoption. However, the subsequent return to stricter regulations and limitations on telehealth services in many regions has led to a decrease in utilization. For instance, some states have reverted to requiring in-person visits for certain procedures or consultations, restricting the flexibility and convenience that initially made telehealth so attractive.
Furthermore, the lack of standardized regulations across states creates complexities for both providers and patients navigating telehealth services. Inconsistencies in licensing and credentialing requirements also pose challenges to the seamless expansion of telehealth across geographical boundaries.
Geographic Accessibility of Telehealth Services
The accessibility of telehealth services varies significantly across different geographic regions. While telehealth has the potential to bridge the healthcare gap in underserved rural areas, its success depends on reliable internet access and digital literacy. Many rural communities lack adequate broadband infrastructure, hindering the effective delivery and utilization of telehealth services. This digital divide exacerbates existing healthcare disparities, limiting access to telehealth for populations who need it most.
Conversely, urban areas generally have better infrastructure, but challenges remain, including high costs of internet access and a lack of awareness among certain patient populations. This uneven distribution of resources highlights the need for targeted investments in infrastructure development and digital literacy programs to ensure equitable access to telehealth.
Patient Preferences and Attitudes Towards Telehealth
Patient preferences and attitudes play a crucial role in telehealth utilization. While many patients found telehealth convenient during the pandemic, some prefer the personal interaction of in-person visits, particularly for sensitive health issues or complex medical conditions. Factors such as comfort with technology, trust in virtual care, and concerns about data privacy and security influence patient adoption. Furthermore, the lack of physical examination capabilities in telehealth can limit its applicability for certain medical specialties.
Patient education and awareness campaigns, emphasizing the benefits and limitations of telehealth, are crucial to address concerns and foster greater acceptance. Tailoring telehealth services to meet specific patient needs and preferences, including offering a hybrid model that combines in-person and virtual care, can improve patient satisfaction and encourage continued usage.
Comparison with In-Person Healthcare
Source: healthsystemtracker.org
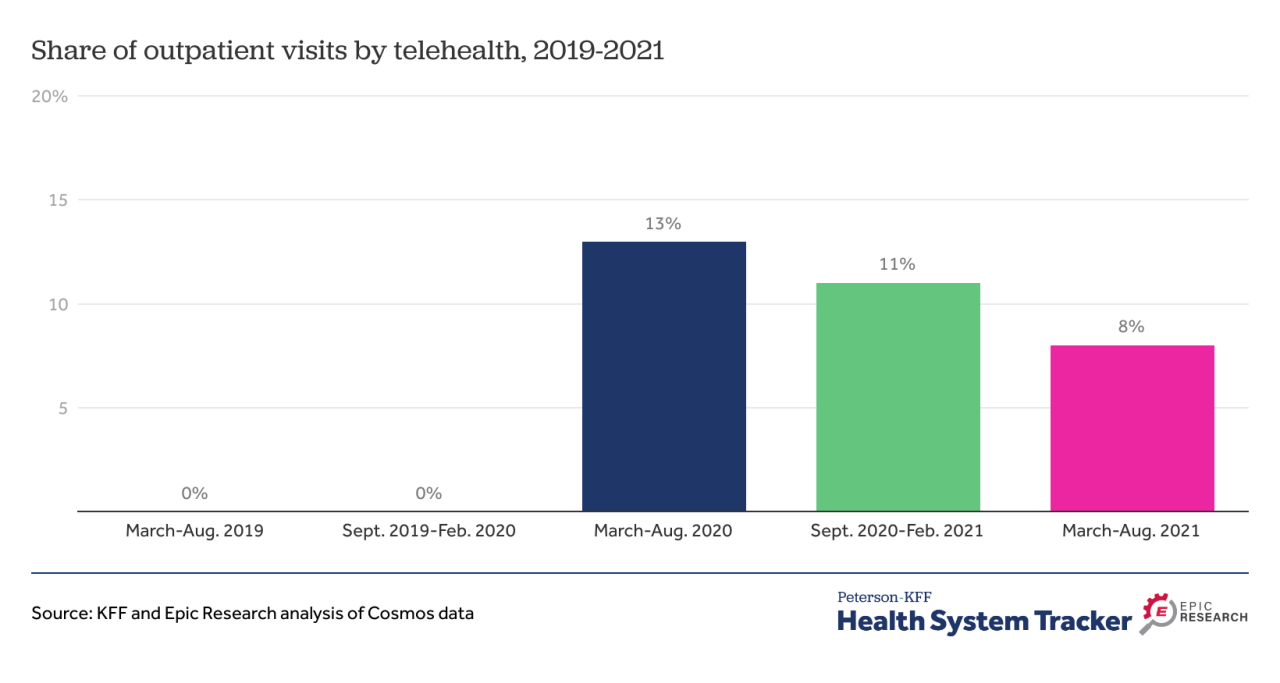
The recent decline in telehealth utilization, following its surge during the pandemic, prompts a crucial comparison with traditional in-person healthcare visits. Understanding the relative strengths and weaknesses of each approach is vital for shaping future healthcare delivery models and ensuring patient access to quality care. This comparison will explore utilization rates, specific services showing the largest decline in telehealth adoption, and the reasons behind patient preferences.Telehealth utilization rates, while initially skyrocketing, have noticeably decreased in many areas since the peak of the pandemic.
While precise figures vary depending on the service and region, general trends show a return to pre-pandemic levels of in-person visits for many routine and non-urgent conditions. This shift highlights the complex interplay between patient preferences, technological access, and the inherent limitations of telehealth in certain clinical scenarios.
Specific Services Showing Significant Telehealth Decline
The decline in telehealth use isn’t uniform across all healthcare services. For example, mental health telehealth visits, while still prevalent, have seen a significant drop compared to their pandemic highs. Similarly, routine follow-up appointments for chronic conditions, like diabetes management or hypertension monitoring, have transitioned back to in-person consultations more frequently. This shift may be attributed to factors such as the limitations of remote physical examinations, the preference for in-person interaction with healthcare providers, and the need for hands-on care in some instances.
Furthermore, certain specialized procedures simply aren’t feasible via telehealth, leading to an inevitable return to in-person care for those requiring such interventions.
Reasons for Patient Preference of In-Person Healthcare
Several factors contribute to patients’ preference for in-person healthcare. Many patients value the personal connection and the ability to directly communicate with their provider, fostering a stronger doctor-patient relationship. The physical examination is another crucial element, often impossible or insufficiently accurate through telehealth. The ability to undergo diagnostic testing or receive immediate treatment in a clinic setting is also a significant factor, especially for urgent or acute conditions.
Furthermore, access to technology and reliable internet connectivity remains a barrier for some patients, particularly in underserved communities. Finally, the lack of physical presence can sometimes create a sense of detachment and reduce patient comfort, especially for individuals who prefer more traditional methods of healthcare delivery.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Telehealth and In-Person Healthcare
The decision between telehealth and in-person care involves weighing several advantages and disadvantages.
It’s important to consider the specific needs and circumstances of each patient and the nature of their healthcare requirement when making this choice.
- Telehealth Advantages: Convenience, reduced travel time and costs, increased access to specialists, potential for greater frequency of appointments.
- Telehealth Disadvantages: Limited physical examination capabilities, technological barriers, potential for communication difficulties, lack of personal connection.
- In-Person Healthcare Advantages: Comprehensive physical examination, immediate access to diagnostic testing and treatment, stronger doctor-patient relationship, suitable for complex or urgent conditions.
- In-Person Healthcare Disadvantages: Inconvenience, travel time and costs, potential scheduling difficulties, potential for longer wait times.
Impact on Different Healthcare Sectors
The recent decline in telehealth utilization, following its rapid expansion during the pandemic, has created ripples across various healthcare sectors. Understanding the impact on different specialties, provider workflows, and ultimately, patient access and healthcare costs is crucial for adapting to this shifting landscape and ensuring continued quality of care. The decrease isn’t uniform across all areas, and some sectors are experiencing more significant consequences than others.The decreased reliance on telehealth affects healthcare provider workflows and resource allocation in several ways.
For instance, the sudden shift back to in-person appointments necessitates adjustments in scheduling systems, staffing levels, and physical space utilization. Clinics designed to accommodate both in-person and virtual visits now need to re-evaluate their infrastructure and operational processes. This transition requires investment in time and resources, potentially leading to temporary inefficiencies.
Impact on Primary Care
The reduction in telehealth use has significantly impacted primary care. Many patients, particularly those in rural or underserved areas, relied on telehealth for convenient access to routine check-ups and management of chronic conditions. The decline in telehealth appointments means these patients may face increased barriers to accessing care, potentially leading to delayed diagnoses and worsening health outcomes. The shift back to in-person visits also increases the workload on primary care physicians, who must now manage a higher volume of in-office appointments.
The National Center for Health Statistics reported a drop in telehealth use, which is a bit concerning. This decline might be partly explained by the Supreme Court’s decision, as reported in this article scotus overturns chevron doctrine healthcare , which could impact healthcare regulations and access. Ultimately, this legal shift may indirectly affect telehealth’s continued growth and widespread adoption.
Impact on Mental Healthcare
Mental healthcare has been particularly affected by the decline in telehealth. Telehealth proved invaluable during the pandemic, expanding access to mental health services for individuals who faced geographical barriers, social anxiety, or transportation challenges. The decrease in telehealth utilization for mental health services could lead to a significant reduction in access for vulnerable populations. Furthermore, the reduced availability of virtual therapy options could exacerbate existing mental health disparities.
Impact on Specialty Care
The impact on specialty care varies depending on the specific specialty. Some specialties, such as dermatology and ophthalmology, may have experienced a more significant decline in telehealth use than others, as these specialties often require physical examinations. However, even for specialties where telehealth remains relevant, the decrease in utilization may still lead to increased wait times for appointments and reduced access to care for patients.
The shift back to in-person visits also places a greater burden on specialists’ schedules and clinic resources.
Telehealth Decline Across Specialties
| Specialty | Percentage Decrease in Telehealth Use (Hypothetical Example) | Impact on Patient Access | Impact on Provider Workload |
|---|---|---|---|
| Primary Care | 30% | Increased wait times, reduced access for rural patients | Increased in-office appointment volume, longer patient visits |
| Mental Health | 40% | Reduced access for patients with transportation or social anxiety barriers | Increased demand for in-person appointments, potential for longer waitlists |
| Cardiology | 20% | Longer wait times for appointments, potential for delayed diagnosis | Increased in-office appointment volume, need for more resources |
| Dermatology | 50% | Significant reduction in access for patients in remote areas | Increased demand for in-person appointments, potential for longer waitlists |
Future Projections and Recommendations
While recent data shows a decline in telehealth utilization following the peak of the COVID-19 pandemic, it’s unlikely that telehealth will simply disappear. The convenience and accessibility it offers, particularly for patients in rural areas or with mobility issues, remain significant advantages. Instead of a complete retraction, we’re likely to see a period of stabilization and refinement, with telehealth finding its niche within a more integrated healthcare system.The future of telehealth hinges on addressing the challenges that contributed to the recent decline.
This involves improving patient experience, addressing reimbursement issues, and enhancing the integration of telehealth with existing healthcare infrastructure. Focusing on these areas will determine the extent to which telehealth continues to thrive and evolve.
Projected Telehealth Usage
Telehealth usage is projected to stabilize and then experience moderate growth in the coming years. While the explosive growth seen during the pandemic is unlikely to be repeated, a gradual increase is anticipated, driven by factors such as increased technological sophistication, improved reimbursement models, and growing patient familiarity with the technology. For example, the expansion of high-speed internet access in underserved areas could significantly boost telehealth adoption.
We can expect to see continued use in areas like mental health care, chronic disease management, and specialist consultations, where the benefits are most clearly demonstrated. Specific numbers are difficult to predict with certainty due to the evolving landscape, but a gradual, sustained increase, rather than a sharp decline, is the most probable scenario.
Strategies to Increase Telehealth Adoption and Effectiveness
Several strategies can be implemented to enhance telehealth adoption and effectiveness. These include improving patient education and outreach programs to increase awareness and address concerns about technology and privacy. Streamlining the reimbursement process for telehealth services is crucial, ensuring fair compensation for providers and reducing administrative burdens. Furthermore, integrating telehealth seamlessly into existing healthcare systems, rather than treating it as a separate entity, is vital for improving patient care coordination and reducing fragmentation.
Finally, investing in robust cybersecurity measures and patient privacy protocols will build trust and encourage broader adoption.
Technological Advancements in Telehealth
Several technological advancements hold the potential to revolutionize telehealth. The development of more sophisticated remote patient monitoring devices, capable of providing real-time data on vital signs and other health metrics, will allow for proactive interventions and improved disease management. Artificial intelligence (AI) can play a significant role in automating administrative tasks, improving diagnostic accuracy, and personalizing treatment plans.
The expansion of 5G and other high-speed internet networks will improve connectivity, particularly in rural and underserved areas, making telehealth more accessible. Furthermore, the development of more user-friendly interfaces and telehealth platforms will make the technology more intuitive and accessible for both patients and providers.
Examples of Successful Telehealth Initiatives
The Mayo Clinic’s extensive telehealth program, encompassing a wide range of services and utilizing various technologies, stands as a successful example. Their success is attributable to a combination of factors, including substantial investment in infrastructure and technology, robust training programs for staff, and a focus on patient-centered care. Similarly, the Veterans Health Administration’s telehealth program has demonstrated significant success in providing care to veterans in remote locations, improving access to specialized care, and reducing hospital readmissions.
These programs highlight the importance of strong leadership, dedicated resources, and a commitment to continuous improvement in achieving successful telehealth implementation. Their success demonstrates that with the right planning and investment, telehealth can be a highly effective tool for delivering high-quality healthcare.
Closure: Telehealth Use Declines National Center Health Statistics
The decline in telehealth usage, as highlighted by the National Center for Health Statistics, presents a complex challenge with multiple contributing factors. While the convenience and accessibility of telehealth remain undeniably valuable, understanding patient preferences, addressing economic barriers, and refining healthcare policies are crucial steps to ensuring its continued success. The future of telehealth likely hinges on innovation, improved accessibility, and a better understanding of how to best integrate it into the broader healthcare landscape.
Let’s hope we can find ways to harness its potential for good, ensuring everyone can benefit from its advantages.
FAQ Corner
What specific telehealth services saw the biggest decline?
While the data varies, initial reports suggest mental health and some specialist telehealth services experienced steeper declines than others. This might be due to factors like the nature of the service or patient comfort levels.
Are there any geographic disparities in the decline?
Yes, access to reliable internet and technological literacy play a significant role. Rural areas, for example, may have seen a more pronounced decrease due to limited broadband availability.
How does this decline affect healthcare providers?
Reduced telehealth usage can impact provider workflows and revenue streams. It also potentially leads to less efficient resource allocation within healthcare systems.
What are some potential long-term consequences of this trend?
A sustained decrease in telehealth could limit access to care, particularly for those in underserved communities. It could also lead to increased healthcare costs in the long run.




