Transforming Payer Operations Through Real-Time Clinical Data Exchange
Transforming payer operations through real time clinical data exchange – Transforming payer operations through real-time clinical data exchange is revolutionizing healthcare. Imagine a world where claims are processed instantly, high-risk patients are identified proactively, and care coordination is seamless. This isn’t science fiction; it’s the promise of real-time data integration, offering unprecedented opportunities to improve efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance the overall patient experience. This post delves into the exciting possibilities and practical considerations of this transformative shift.
The current healthcare system often struggles with fragmented data, leading to delays in claims processing, inaccurate reimbursements, and inefficient care management. Real-time data exchange, however, offers a solution by connecting disparate systems and providing payers with a holistic view of patient health information. This allows for faster, more accurate claims adjudication, improved risk stratification, and better care coordination – ultimately leading to significant cost savings and improved patient outcomes.
The Current State of Payer Operations
The healthcare payer landscape is currently grappling with significant challenges. Rising healthcare costs, increasing regulatory complexity, and the ever-growing demand for higher quality care are putting immense pressure on payers to optimize their operations and improve efficiency. This necessitates a fundamental shift in how they manage data and interact with providers and patients.The traditional methods employed by payers for data exchange are often slow, inefficient, and prone to errors.
This outdated infrastructure significantly impacts their ability to effectively manage costs, improve care quality, and meet the evolving needs of the healthcare system.
Challenges in Managing Healthcare Costs and Quality
Payers face a constant struggle to balance the need to control costs with the imperative to provide high-quality care. The fragmented nature of healthcare data, with information siloed across various systems and providers, makes it incredibly difficult to gain a comprehensive view of a patient’s health journey. This lack of a holistic perspective hinders accurate risk stratification, leading to inefficient resource allocation and potentially suboptimal care.
For example, a payer might unknowingly cover redundant or unnecessary procedures for a patient because they lack a complete picture of the patient’s prior treatments and diagnoses across different healthcare facilities. This results in unnecessary expenses and potentially compromised patient outcomes. Furthermore, the lack of real-time data makes it difficult to identify and intervene in high-risk situations proactively.
Limitations of Traditional Data Exchange Methods
Traditional data exchange methods, such as fax machines and batch processing, are slow, cumbersome, and prone to errors. These methods often involve manual data entry, which is time-consuming, expensive, and susceptible to human error. The delay in data transmission can significantly impact claim processing times, leading to delayed reimbursements for providers and increased administrative costs for payers. Moreover, the lack of standardization in data formats further complicates the process, making it difficult to integrate data from different sources.
For instance, a payer might receive claims in various formats from different providers, requiring significant manual effort to reconcile and process them. This process also creates a bottleneck in the system, increasing processing times and potential for errors.
Impact of Inefficient Data Flow on Claim Processing and Provider Reimbursements
Inefficient data flow directly translates to longer claim processing times and delayed reimbursements for providers. This can lead to strained relationships between payers and providers, negatively impacting the overall quality of care. Delayed reimbursements can also cause financial hardship for providers, potentially leading to reduced access to care for patients. The financial burden imposed by inefficient systems is significant, impacting both payer profitability and provider solvency.
Consider a scenario where a provider submits a claim and waits several weeks or even months to receive payment due to the payer’s inefficient claim processing system. This delay can cause cash flow problems for the provider, potentially affecting their ability to invest in new equipment, hire staff, or maintain their operations.
Hindrances to Proactive Care Management and Risk Stratification
The absence of real-time clinical data significantly hinders payers’ ability to engage in proactive care management and accurate risk stratification. Without access to up-to-the-minute information on patient conditions and treatment plans, payers are unable to identify high-risk individuals who require targeted interventions. This lack of insight prevents timely interventions, potentially leading to adverse health outcomes and increased healthcare costs.
For example, a payer might not be aware of a patient’s deteriorating health condition until after a hospital admission, missing opportunities for preventative care and reducing the effectiveness of managing chronic conditions. This inability to proactively manage care leads to increased hospital readmissions and higher overall healthcare expenses.
Real-Time Clinical Data Exchange
The current state of payer operations, as we’ve discussed, is often hampered by information silos and delayed data exchange. This leads to inefficiencies, increased costs, and suboptimal patient care. Real-time clinical data exchange offers a powerful solution, transforming how payers interact with providers and manage patient health. By integrating real-time data streams, payers can achieve unprecedented levels of accuracy, efficiency, and proactive patient management.
Improved Claim Adjudication Accuracy
Real-time access to clinical data dramatically improves the accuracy of claim adjudication. Instead of relying on potentially outdated or incomplete information submitted after the fact, payers can instantly verify the medical necessity of services, ensuring that claims are processed correctly and payments are made efficiently. This eliminates delays caused by manual verification and reduces the number of denied or delayed claims, leading to smoother workflows and improved provider satisfaction.
For example, a real-time system could instantly cross-reference a claim for a specific procedure with the patient’s electronic health record (EHR), verifying the diagnosis and confirming the procedure’s appropriateness based on established medical guidelines. This eliminates the need for lengthy manual reviews and potential delays.
Proactive Identification of High-Risk Patients
Real-time data allows payers to proactively identify patients at high risk of adverse health events. By analyzing data streams from various sources – including EHRs, wearables, and claims data – payers can develop predictive models to identify individuals who are likely to experience hospital readmissions, require emergency care, or develop chronic conditions. This enables timely interventions, such as targeted case management, preventative care programs, and personalized outreach, reducing healthcare costs and improving patient outcomes.
For instance, a payer might identify a patient with a history of heart failure who is exhibiting signs of worsening symptoms through their connected wearable device. Immediate intervention could prevent a potentially costly hospital readmission.
Improved Care Coordination and Reduced Hospital Readmissions
Real-time data exchange facilitates seamless care coordination among providers, improving communication and reducing redundancies. When all stakeholders have access to a unified view of the patient’s medical history and current condition, they can make more informed decisions and avoid unnecessary testing or treatments. This improved collaboration is especially effective in reducing hospital readmissions, a significant cost driver in healthcare.
For example, a patient discharged from the hospital after a heart attack can have their progress monitored in real-time. If their vital signs indicate a deterioration, the care team can intervene immediately, preventing a potentially life-threatening situation and avoiding a costly readmission.
Cost Savings Associated with Real-Time Data Integration
| Area of Improvement | Cost Savings Mechanism | Estimated Annual Savings (per 10,000 members) | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Claim Adjudication | Reduced manual processing, fewer denied claims | $50,000 – $100,000 | Faster processing of claims, fewer appeals |
| High-Risk Patient Identification | Reduced hospital readmissions, preventative care | $100,000 – $250,000 | Proactive interventions preventing costly hospital stays |
| Care Coordination | Improved communication, reduced redundant tests | $25,000 – $75,000 | More efficient use of resources, fewer unnecessary procedures |
| Fraud Detection | Early identification of suspicious claims | $10,000 – $30,000 | Prevention of fraudulent billing practices |
Technological Infrastructure for Real-Time Data Exchange
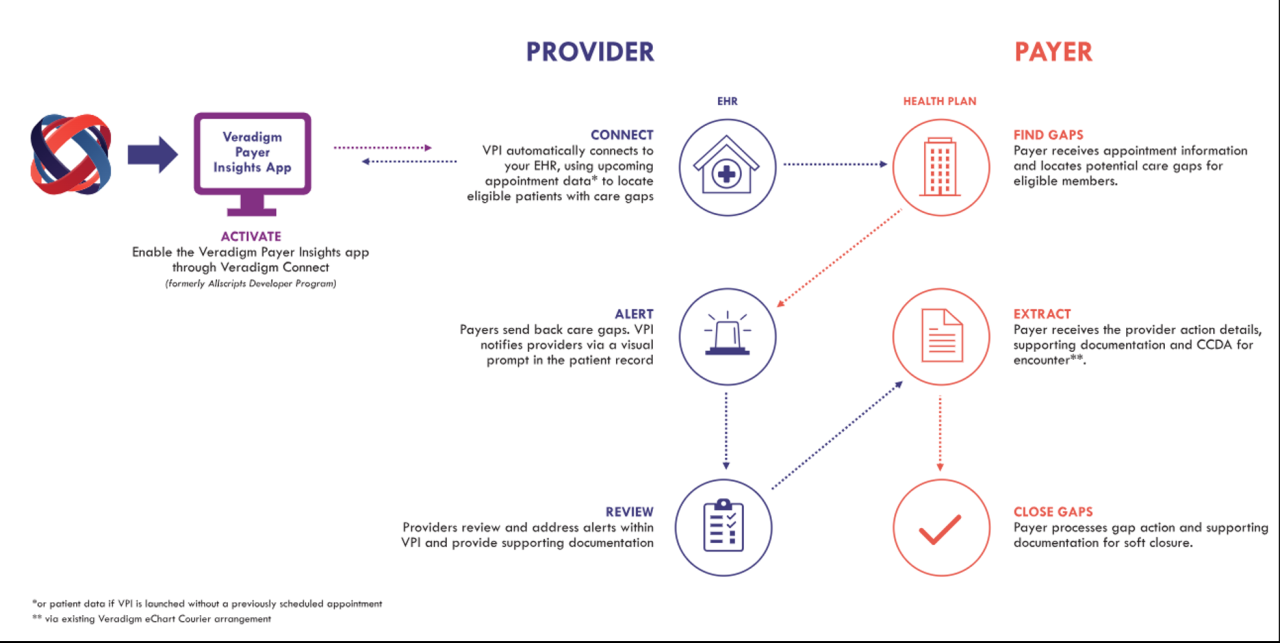
Source: veradigm.com
Building a system for real-time clinical data exchange requires a robust technological foundation. This involves selecting the right technologies, designing an appropriate architecture, and implementing stringent security measures to protect sensitive patient information. The complexity of this undertaking necessitates a careful and strategic approach.
Real-time clinical data exchange is revolutionizing payer operations, streamlining claims processing and improving care coordination. This efficiency is crucial for large healthcare systems like AdventHealth, especially considering the recent news of AdventHealth CEO Terry Shaw’s retirement , a transition that will undoubtedly impact their strategic direction. Ultimately, the seamless flow of data will be key for AdventHealth’s continued success under new leadership, ensuring efficient payer interactions and better patient outcomes.
Key Technologies Enabling Real-Time Data Exchange
Several key technologies are essential for facilitating the seamless and secure exchange of clinical data in real time. These technologies work in concert to ensure data integrity, interoperability, and patient privacy.
- FHIR (Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources): FHIR is a standard for exchanging electronic health information. Its RESTful API approach allows for easy integration with various systems and promotes interoperability between different healthcare platforms. This simplifies the process of data exchange significantly.
- APIs (Application Programming Interfaces): APIs act as the communication bridge between different systems. They allow applications to request and receive data from other applications, facilitating real-time data flow. Well-designed APIs are crucial for efficient data exchange within the payer ecosystem.
- Blockchain Technology: While less prevalent currently in mainstream payer operations, blockchain offers potential for enhancing data security and transparency. Its decentralized and immutable nature could improve the auditability and trustworthiness of data exchange processes, though significant implementation challenges remain.
Data Exchange Architectures for Payer Operations
The choice of data exchange architecture significantly impacts the efficiency and scalability of the system. Different architectures offer varying levels of flexibility, security, and complexity.
Real-time clinical data exchange is revolutionizing payer operations, streamlining processes and improving care coordination. The potential impact on healthcare policy is huge, especially considering the news that rfk jr clears key hurdle on path to hhs secretary , a position that will heavily influence the future of healthcare technology adoption. This makes the efficient exchange of clinical data even more crucial for navigating the evolving regulatory landscape and maximizing payer efficiency.
- Point-to-Point Integration: This involves direct connections between individual systems. While simple to implement for a small number of systems, it becomes increasingly complex and difficult to manage as the number of systems grows. It lacks scalability and can be challenging to maintain.
- Centralized Hub-and-Spoke Architecture: A central hub acts as an intermediary, receiving data from various sources and distributing it to different destinations. This architecture offers improved scalability and manageability compared to point-to-point integration. However, it introduces a single point of failure.
- Decentralized Mesh Network: In this architecture, systems communicate directly with each other without a central hub. This enhances resilience and reduces the risk of single points of failure. However, it increases complexity in terms of management and security.
Security and Privacy Considerations for Real-Time Data Exchange
Handling sensitive patient data in real time demands robust security and privacy measures. Breaches can have severe consequences, including financial penalties, reputational damage, and erosion of patient trust.
Implementing strong encryption protocols (e.g., TLS/SSL) for data transmission is crucial. Access control mechanisms, such as role-based access control (RBAC), should be implemented to restrict access to sensitive data based on user roles and responsibilities. Regular security audits and penetration testing are necessary to identify and mitigate vulnerabilities. Compliance with regulations such as HIPAA (in the US) and GDPR (in Europe) is paramount.
Revamping payer operations hinges on real-time clinical data exchange, allowing for faster, more accurate claims processing. This is where innovations like those highlighted in this article on the ai most exciting healthcare technology center connected medicine UPMC become incredibly relevant. Their advancements in connected medicine directly impact the efficiency and accuracy of this data flow, ultimately streamlining the entire payer process and improving patient care.
Implementing a Real-Time Data Exchange System
Implementing a real-time data exchange system is a multi-stage process requiring careful planning and execution.
- Needs Assessment and Planning: Define specific requirements, identify stakeholders, and establish clear goals and objectives for the system.
- Technology Selection and Architecture Design: Choose appropriate technologies and design a suitable architecture based on the needs assessment.
- System Development and Integration: Develop and integrate the various components of the system, including data sources, APIs, and security measures.
- Testing and Validation: Thoroughly test the system to ensure functionality, security, and compliance with regulations.
- Deployment and Monitoring: Deploy the system and continuously monitor its performance and security.
Impact on Different Payer Stakeholders: Transforming Payer Operations Through Real Time Clinical Data Exchange

Source: medium.com
Real-time clinical data exchange dramatically reshapes the payer landscape, impacting various stakeholders in profound ways. The immediate and ongoing benefits extend far beyond simple efficiency gains, leading to a more coordinated, cost-effective, and patient-centric healthcare system. Let’s explore how this transformation affects key players.
Impact on Providers
The shift to real-time data exchange offers significant advantages for healthcare providers. Improved communication channels, streamlined administrative processes, and faster reimbursements are just a few of the key improvements. This ultimately allows providers to focus more on patient care and less on administrative burdens.
- Improved Communication and Collaboration: Real-time access to patient data enables seamless communication between providers, specialists, and payers, reducing delays and improving care coordination.
- Faster Payments and Reduced Administrative Burden: Automated claims processing and reduced paperwork significantly accelerate payment cycles, freeing up valuable time and resources for providers.
- Enhanced Care Coordination: Access to a complete and up-to-date patient record allows providers to make more informed decisions, leading to better treatment plans and improved patient outcomes.
Impact on Patients
For patients, real-time data exchange translates into a more personalized, efficient, and effective healthcare experience. Improved care coordination and access to their own health data empower patients to actively participate in their care.
- Improved Care Coordination: Real-time data sharing ensures that all healthcare providers have access to the same information, preventing medical errors and improving the overall quality of care.
- Personalized Medicine: Access to comprehensive patient data allows for more tailored treatment plans, leading to better health outcomes and a more personalized healthcare experience.
- Increased Patient Engagement: Patients can access their own health data and actively participate in their care, leading to greater satisfaction and improved health outcomes.
- Reduced Medical Errors: Real-time data exchange helps to eliminate discrepancies and inconsistencies in patient records, minimizing the risk of medical errors.
Impact on Payer Administrators
Payer administrators also benefit significantly from real-time data exchange. The improvements in efficiency and cost reduction are substantial, leading to a more sustainable and efficient healthcare system.
- Improved Efficiency and Reduced Costs: Automated claims processing and reduced manual intervention lead to significant cost savings and increased operational efficiency.
- Enhanced Fraud Detection: Real-time data analysis allows for the early detection of fraudulent claims, reducing financial losses for payers.
- Better Risk Management: Access to real-time data enables payers to identify and manage high-risk patients more effectively, leading to better health outcomes and reduced costs.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: Real-time data analytics provides payers with valuable insights into healthcare trends, allowing them to make more informed decisions about resource allocation and benefit design.
Case Studies and Best Practices
Real-time clinical data exchange is transforming payer operations, but successful implementation requires careful planning and execution. Learning from those who have paved the way is crucial for avoiding pitfalls and maximizing benefits. This section explores successful implementations, challenges overcome, and best practices for data governance, security, and interoperability.
Successful Implementations of Real-Time Data Exchange, Transforming payer operations through real time clinical data exchange
Several payers have successfully integrated real-time clinical data exchange into their operations, leading to significant improvements in efficiency and care quality. For example, a large national health insurer partnered with a major electronic health record (EHR) vendor to create a secure, HIPAA-compliant platform for exchanging data. This allowed them to automate prior authorization processes, reducing turnaround times from days to minutes and freeing up staff for higher-value tasks.
Another payer leveraged real-time data to identify high-risk patients proactively, enabling timely interventions and preventing costly hospital readmissions. This resulted in a demonstrable reduction in healthcare costs and improved patient outcomes. These examples highlight the potential for significant return on investment (ROI) when real-time data exchange is implemented effectively.
Overcoming Challenges in Implementing Real-Time Data Exchange Systems
Implementing real-time clinical data exchange isn’t without its hurdles. Many organizations struggle with data integration challenges, requiring significant upfront investment in infrastructure and personnel. Interoperability issues, stemming from the diverse range of EHR systems and data formats used across the healthcare landscape, are a frequent obstacle. Data security and privacy concerns are paramount, demanding robust security measures to protect sensitive patient information.
Finally, effective change management is crucial to ensure buy-in from all stakeholders, including clinicians, administrative staff, and IT professionals. Organizations that have successfully navigated these challenges often emphasize strong project management, collaborative partnerships, and a phased implementation approach, allowing for iterative improvements and adjustments along the way.
Best Practices for Data Governance, Security, and Interoperability in Real-Time Data Exchange
Effective data governance is paramount for ensuring the accuracy, reliability, and security of exchanged data. This includes establishing clear data ownership, defining data quality standards, and implementing robust data validation processes. Security measures must be comprehensive, encompassing encryption, access controls, and regular security audits to protect sensitive patient information. Achieving interoperability requires adherence to established standards, such as HL7 FHIR, and the adoption of standardized data formats to facilitate seamless data exchange between different systems.
Furthermore, ongoing monitoring and evaluation of the system’s performance are crucial to identify and address potential issues promptly.
Visual Representation of a Successful Real-Time Data Exchange Workflow
Imagine a visual flowchart. It begins with a patient undergoing a medical procedure, with their clinical data instantly captured by the EHR system. This data is then securely transmitted, via a dedicated, encrypted pathway, to the payer’s system. The payer’s system automatically processes the data, triggering pre-programmed rules and workflows. For instance, prior authorization is granted or denied based on the clinical data received in real-time.
This decision is then communicated back to the provider, again instantly. The entire process is automated, transparent, and secure, resulting in a streamlined and efficient workflow that improves both patient care and operational efficiency. Finally, the data is stored securely and is accessible for reporting and analytics, allowing the payer to track key performance indicators (KPIs) and identify areas for further improvement.
Future Trends and Considerations

Source: idhnet.org
The rapid evolution of technology and the increasing emphasis on value-based care are reshaping the landscape of payer operations. Real-time clinical data exchange, while already transformative, is poised for even greater impact as new technologies emerge and regulatory frameworks adapt. Understanding these future trends and potential challenges is crucial for payers seeking to optimize their operations and improve patient outcomes.
Emerging Technologies and Their Applications
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are rapidly transforming healthcare, and their application to real-time clinical data exchange promises significant advancements. AI algorithms can analyze vast datasets to identify patterns and predict future health events, enabling payers to proactively manage risk and personalize interventions. For example, AI could analyze real-time data from wearable devices and electronic health records (EHRs) to identify individuals at high risk of developing chronic conditions, allowing for timely interventions to prevent costly hospitalizations.
ML models can also be used to optimize claims processing, detect fraud, and improve the accuracy of risk adjustment models. These technologies offer the potential to significantly enhance efficiency, accuracy, and cost-effectiveness of payer operations.
Barriers to Widespread Adoption
Despite the significant potential benefits, several barriers hinder the widespread adoption of real-time clinical data exchange. Interoperability challenges remain a significant hurdle, with different healthcare systems often using incompatible data formats and standards. Data security and privacy concerns are also paramount, requiring robust security measures to protect sensitive patient information. Furthermore, the significant upfront investment required for implementing new technologies and integrating them with existing systems can be a deterrent for some payers.
Finally, a lack of standardized processes and workflows for handling real-time data can create operational challenges. Overcoming these barriers requires collaborative efforts across the healthcare ecosystem, including payers, providers, technology vendors, and regulators.
The Evolving Regulatory Landscape
The regulatory landscape surrounding healthcare data exchange is constantly evolving. Regulations such as HIPAA in the United States and GDPR in Europe aim to protect patient privacy and ensure data security. However, these regulations can also create complexities for data sharing. Future regulations may focus on promoting interoperability and data standardization while maintaining strong privacy protections. Payers must stay abreast of these evolving regulations and adapt their data exchange practices accordingly to ensure compliance.
The increasing focus on data transparency and patient access to their own health information will also influence the development of new regulations and standards.
Future Developments in Data Standards and Interoperability
The lack of standardized data formats and interoperability protocols remains a major obstacle to widespread adoption of real-time clinical data exchange. However, ongoing efforts are underway to develop and implement more robust standards, such as FHIR (Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources). FHIR offers a flexible and standardized approach to exchanging healthcare data, facilitating seamless integration between different systems. Future developments in data standards will likely focus on improving semantic interoperability, ensuring that data is not only exchanged but also interpreted consistently across different systems.
This will require collaborative efforts among stakeholders to develop common vocabularies and ontologies for representing healthcare information. Increased adoption of standardized APIs and cloud-based solutions will also further enhance interoperability.
Last Point
The journey towards transforming payer operations through real-time clinical data exchange is not without its challenges. However, the potential benefits – from streamlined workflows and reduced administrative burdens to improved patient care and cost savings – are too significant to ignore. By embracing innovative technologies, addressing security and privacy concerns, and fostering collaboration across the healthcare ecosystem, payers can unlock the full potential of real-time data and usher in a new era of efficiency and effectiveness in healthcare delivery.
The future of payer operations is undeniably connected, and real-time data exchange is the key.
Quick FAQs
What are the biggest security risks associated with real-time clinical data exchange?
The biggest risks include unauthorized access, data breaches, and ensuring compliance with HIPAA and other relevant regulations. Robust security measures, including encryption, access controls, and regular audits, are crucial.
How can payers ensure data interoperability in a real-time environment?
Standardization through the use of interoperability frameworks like FHIR is key. Payers also need to invest in robust integration engines and APIs to connect different systems.
What is the return on investment (ROI) for implementing real-time data exchange?
ROI varies depending on the specific implementation, but potential savings come from reduced administrative costs, improved claim accuracy, fewer readmissions, and better risk management. A thorough cost-benefit analysis is crucial before implementation.
What are some common obstacles to implementing real-time data exchange?
Common obstacles include legacy system limitations, lack of interoperability, data governance challenges, resistance to change within organizations, and the high initial investment costs.