Surprise Billing Arbitration Resume Pause
Surprise billing arbitration resume pause: Whoa, hold on a minute! The recent pause on surprise medical bill arbitration has sent shockwaves through the healthcare system, leaving patients and providers alike wondering what’s next. This unexpected halt has created a whirlwind of uncertainty, sparking debates about patient protection, provider reimbursements, and the very future of how we handle those unexpected, jaw-dropping medical bills.
Let’s dive into the complexities and explore the potential fallout.
This post will dissect the impact of this pause, exploring arguments for and against it, examining alternative dispute resolution methods, analyzing legislative responses, and ultimately considering the path forward for resolving surprise medical bills. We’ll look at real-world scenarios, explore the ethical dilemmas, and consider the perspectives of patients, providers, and policymakers.
The Impact of the Surprise Billing Arbitration Resume Pause
The recent pause in surprise billing arbitration presents a significant challenge to the healthcare system, potentially jeopardizing the progress made in protecting patients from unexpected medical bills. This pause introduces uncertainty and risk for both patients and providers, potentially reversing the positive trends observed since the implementation of arbitration processes. The consequences, both short-term and long-term, warrant careful consideration.
Consequences of Pausing Surprise Billing Arbitration
Halting the arbitration process directly impacts the resolution of billing disputes between patients, providers, and insurers. Patients are left vulnerable to potentially exorbitant out-of-network charges, while providers face delays in receiving payments and increased administrative burdens. The pause also creates a chilling effect on the willingness of providers to participate in networks, potentially leading to reduced access to care for patients.
Without a functioning arbitration system, disputes may drag on for extended periods, leading to escalating costs and financial distress for all parties involved. This situation is reminiscent of the pre-arbitration era, where patients frequently faced unpredictable and substantial medical bills, often leading to financial hardship and difficulty accessing necessary care.
Short-Term Effects on Patients
In the short term, the pause will likely lead to an increase in surprise medical bills for patients. Patients may face unexpected and substantial charges from out-of-network providers, even for services received within in-network facilities. This could result in delayed or forgone necessary medical care due to financial constraints. Patients might also experience increased stress and anxiety related to the uncertainty surrounding their medical bills, potentially impacting their overall health and well-being.
For example, a patient undergoing emergency treatment might receive a bill far exceeding their expectations, creating a significant financial burden and emotional distress.
Long-Term Effects on Patients
The long-term effects of the pause could be even more detrimental. The lack of a reliable mechanism for resolving billing disputes could lead to a decrease in access to care, particularly for vulnerable populations. Patients may delay or avoid necessary medical care due to fear of incurring unexpected costs, potentially leading to worse health outcomes. This could disproportionately affect low-income individuals and those with pre-existing conditions, exacerbating existing health disparities.
The pause on surprise billing arbitration is a bit of a wild card, right? It makes you wonder about the bigger picture of healthcare reform. This is especially true considering the CMS just launched a new primary care Medicare model ACO, as detailed in this article: cms launches primary care medicare model aco. Hopefully, these changes, along with the eventual resolution of the arbitration pause, will lead to more affordable and accessible care for everyone.
The cumulative effect of numerous unresolved billing disputes could result in significant financial strain for many families, leading to long-term financial instability.
Effects on Healthcare Providers, Surprise billing arbitration resume pause
The pause also presents significant challenges for healthcare providers. Providers might face increased administrative costs associated with managing billing disputes and negotiating directly with insurers. This could lead to reduced profitability and potentially impact the ability of providers to offer a wide range of services. The uncertainty surrounding payment could also affect provider recruitment and retention, particularly in areas with limited access to care.
For instance, a small, independent practice might struggle to absorb the costs associated with resolving numerous billing disputes without a functioning arbitration system, potentially impacting their ability to remain in operation.
Comparison to Previous Periods Without Arbitration
The current situation bears a striking resemblance to the pre-arbitration era, characterized by a lack of transparency and accountability in medical billing. Patients were frequently left to navigate complex billing processes and negotiate with insurers independently, often with unsatisfactory results. This led to widespread patient dissatisfaction and financial hardship. The absence of a robust dispute resolution mechanism resulted in increased litigation and a general lack of trust between patients, providers, and insurers.
The current pause risks a return to this chaotic and inequitable system.
Impact on a Specific Patient Group: Emergency Room Patients
Consider a group of low-income individuals requiring emergency room care. These patients often lack the resources to navigate complex billing systems and are particularly vulnerable to surprise billing. Without a functioning arbitration system, they are more likely to face exorbitant out-of-network charges that they cannot afford. This could lead to delayed or forgone necessary follow-up care, resulting in poorer health outcomes and increased healthcare costs in the long run.
This scenario highlights the significant vulnerability of certain patient populations when surprise billing arbitration mechanisms are not in place.
Arguments For and Against the Pause: Surprise Billing Arbitration Resume Pause
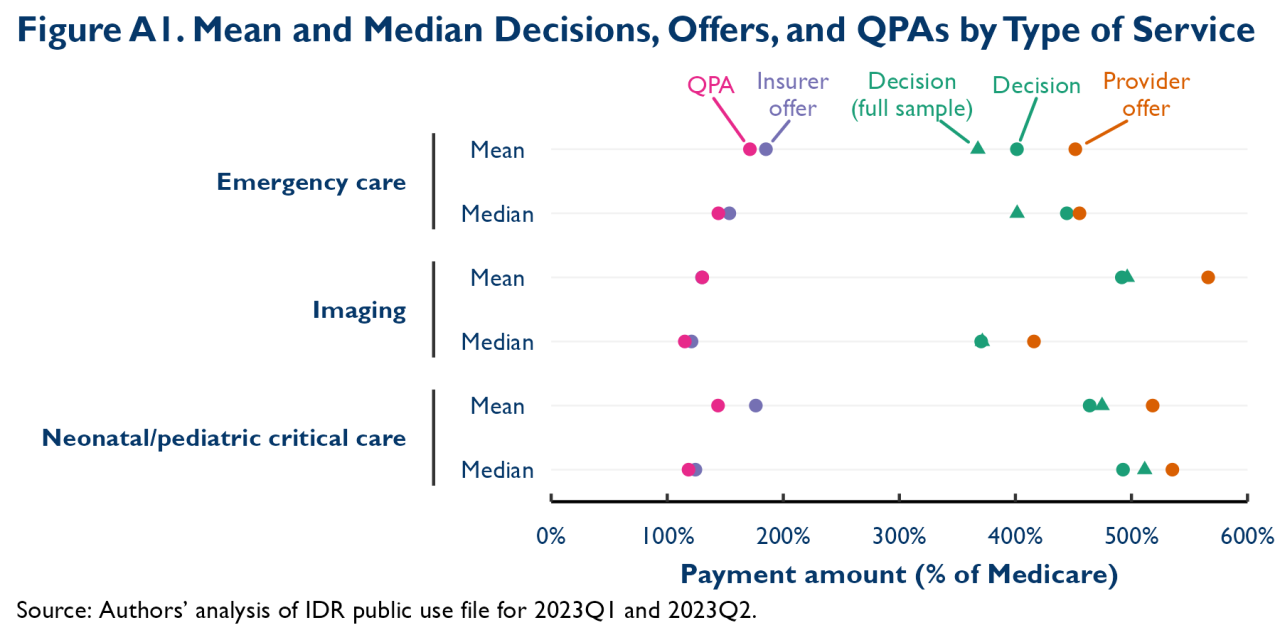
Source: brookings.edu
The recent pause on surprise billing arbitration has sparked considerable debate within the healthcare industry. Understanding the arguments for and against this pause is crucial to evaluating its overall impact on patients, providers, and insurers. This section will delve into the various perspectives, highlighting supporting and opposing evidence, and analyzing the ethical considerations involved.
Stakeholder Positions and Their Arguments
The surprise billing arbitration pause affects numerous stakeholders, each with their own vested interests and perspectives. Patients, naturally, desire affordable and predictable healthcare costs. Providers, particularly out-of-network physicians, worry about reduced reimbursement rates and the potential impact on their practices. Insurers seek to control costs and ensure fair pricing for their members. The government aims to balance patient protection with the stability of the healthcare system.
These diverse interests often clash, making the debate complex.
Arguments Supporting the Pause
Proponents of the pause argue that it provides an opportunity to assess the effectiveness and fairness of the existing arbitration system. Concerns have been raised about the potential for bias in arbitration decisions, leading to inconsistent reimbursement rates and potentially higher costs for patients. Some argue that the pause allows for a more thorough review of the rules and processes, ensuring a more equitable system moving forward.
Furthermore, the pause might allow for the development of more transparent and efficient dispute resolution mechanisms. A potential argument is that the existing system isn’t truly protecting consumers as intended, necessitating a temporary halt to allow for improvements.
Arguments Against the Pause
Opponents of the pause highlight the potential negative consequences for patients caught in disputes with out-of-network providers. The delay in resolving billing disputes could lead to increased financial burdens for patients, potentially impacting their access to care. Providers also express concern about delayed payments, potentially jeopardizing their financial stability. Insurers, while advocating for cost control, might also face challenges in managing claims during the pause.
The disruption to the established system could create uncertainty and inefficiency, negatively impacting all stakeholders.
Ethical Considerations of the Pause
The ethical implications of the pause center on the balance between patient protection and the overall functioning of the healthcare system. A prolonged pause might disproportionately affect vulnerable populations, who may be less able to navigate complex billing disputes or absorb unexpected costs. Furthermore, the pause raises questions about fairness and equity, particularly concerning the potential impact on out-of-network providers who may face financial hardship due to delayed payments.
The ethical dilemma lies in finding a solution that protects patients from excessive costs without unduly burdening providers.
Summary of Arguments in Table Format
| Argument | Supporting Evidence | Opposing Evidence | Overall Assessment |
|---|---|---|---|
| Need for System Review | Concerns about bias in arbitration, inconsistent reimbursement rates. | Potential for increased patient costs and provider financial hardship during the pause. | Requires careful consideration of potential benefits against risks. |
| Protection of Vulnerable Patients | Delayed resolution of disputes could disproportionately affect vulnerable populations. | A revised system could ultimately better protect patients in the long run. | A critical ethical consideration requiring mitigation strategies. |
| Ensuring Provider Financial Stability | Delayed payments could jeopardize the financial stability of out-of-network providers. | A more efficient system could lead to fairer and more timely payments. | Balancing patient protection with provider viability is crucial. |
| Promoting Transparency and Efficiency | A pause allows for development of more transparent and efficient dispute resolution mechanisms. | The pause itself introduces temporary inefficiency and uncertainty. | A potential long-term benefit, but requires careful management of short-term consequences. |
Alternative Dispute Resolution Mechanisms

Source: healthleadersmedia.com
The pause on surprise billing arbitration highlights the need for effective and accessible alternative dispute resolution (ADR) mechanisms. While arbitration has been a central focus, other methods offer potential advantages and disadvantages, impacting patient access to care in various ways. Exploring these alternatives is crucial to designing a system that balances patient protection with provider participation.The current system, even with the arbitration pause, leaves many patients vulnerable to unexpected medical bills.
Several alternative approaches exist, each with its own set of benefits and drawbacks. Understanding these nuances is critical to building a more robust and equitable system for resolving surprise medical billing disputes.
Mediation
Mediation involves a neutral third party facilitating communication between the patient and the provider to reach a mutually agreeable resolution. Unlike arbitration, mediation doesn’t result in a binding decision; the parties retain control over the outcome. This process emphasizes collaboration and compromise, potentially leading to faster and less adversarial resolutions.
- Pros: Less adversarial than arbitration, preserves the relationship between patient and provider, potentially faster and cheaper than arbitration.
- Cons: Success depends on the willingness of both parties to cooperate, may not be effective in cases with significant power imbalances, may not provide a binding solution.
Mediation’s impact on patient access to care is largely positive. By fostering cooperation, it can prevent strained relationships that might hinder future care. However, its reliance on mutual agreement could disadvantage patients who lack bargaining power. For example, a patient with a complex medical condition might be less able to negotiate effectively with a large healthcare system.
Independent Medical Review
Independent Medical Review (IMR) involves an independent physician reviewing the medical necessity and appropriateness of the services provided. This review typically focuses on the clinical aspects of the care, rather than the billing dispute itself. The IMR physician’s opinion can then be used to inform the resolution of the billing dispute.
- Pros: Focuses on the clinical aspects of care, providing a medically informed assessment, can help to clarify whether services were medically necessary.
- Cons: Can be costly and time-consuming, the IMR physician’s decision may not be binding, may not address all aspects of the billing dispute.
IMR can improve patient access to care by ensuring that only medically necessary services are billed. This could prevent patients from incurring unnecessary expenses, thereby making healthcare more affordable. However, the process itself can be slow, potentially delaying resolution of the billing issue.
Negotiation
Direct negotiation between the patient and the provider, possibly with the assistance of patient advocates or consumer protection agencies, is the most straightforward approach. This method relies on the parties’ willingness to compromise and reach a mutually acceptable agreement.
- Pros: Simple, inexpensive, and potentially fast, empowers patients to take control of the situation.
- Cons: Requires active participation from both parties, success depends on the willingness of both parties to compromise, may not be effective in cases with significant power imbalances.
Negotiation can positively affect patient access to care by offering a quick and low-cost resolution. However, its success depends heavily on the patient’s ability to advocate for themselves and negotiate effectively, potentially disadvantaging vulnerable populations. For example, a patient who is unfamiliar with medical billing practices might find it difficult to negotiate effectively with a healthcare provider.
Detailed Description: Independent Medical Review
Independent Medical Review (IMR) offers a structured approach to resolving disputes over the medical necessity of services. A neutral physician, chosen from a pre-approved panel and with expertise in the relevant specialty, reviews the patient’s medical records and relevant documentation. They assess whether the services billed were medically necessary and appropriate given the patient’s condition. The IMR physician’s decision is often, but not always, binding, depending on the specific state or payer regulations.
For example, in some states, the IMR physician’s decision is final and binding for the payer, while in others, it’s merely a recommendation. The process typically involves submitting the necessary documentation to the review organization, which then assigns a physician to conduct the review. The physician’s report is then provided to all parties involved, providing a medically-informed perspective on the billing dispute.
The process can take several weeks, depending on the complexity of the case and the availability of the reviewing physician.
Legislative and Regulatory Responses
The fight against surprise medical billing has moved beyond the negotiation table and into the legislative arena. Laws are being crafted and implemented at both the state and federal levels, each with its own approach to tackling this pervasive problem. The effectiveness of these interventions varies significantly, highlighting the complexities involved in balancing patient protection with the interests of healthcare providers.
The Role of Legislation in Addressing Surprise Billing
Legislation plays a crucial role in establishing clear rules and regulations regarding surprise medical billing. Laws can define what constitutes a surprise bill, mandate transparency in pricing and provider networks, and establish mechanisms for resolving billing disputes. Effective legislation needs to be comprehensive, addressing issues like out-of-network emergency services, ancillary services provided by out-of-network providers in in-network facilities, and the balance billing practices employed by providers.
Without clear legislative guidance, patients remain vulnerable to unexpected and often exorbitant medical bills. Furthermore, legislation provides a framework for enforcement, allowing for penalties against providers who engage in abusive billing practices.
Potential Impact of Different Legislative Approaches
Different legislative approaches have varying impacts on patients, providers, and insurers. Some laws focus on price regulation, setting limits on what out-of-network providers can charge. Others utilize arbitration or independent dispute resolution (IDR) mechanisms to determine fair reimbursement rates. Price regulation might offer more immediate relief to patients but could potentially stifle competition among providers or lead to reduced access to care if providers withdraw from networks.
Conversely, arbitration-based approaches may be more complex to implement but could offer a more equitable and sustainable solution in the long term by fostering negotiation and compromise. The impact also depends on the specific design of the arbitration process, such as the selection of arbitrators and the criteria used for determining reimbursement. For example, a system that heavily favors insurers could lead to unfair reimbursement rates for providers, while a system that favors providers could lead to higher costs for patients.
Potential Regulatory Hurdles to Implementing Alternative Solutions
Implementing alternative solutions like arbitration or IDR faces several regulatory hurdles. These include establishing clear guidelines for the arbitration process, ensuring impartiality and transparency, and dealing with the potential for administrative burdens and costs. The design of the arbitration system is crucial; a poorly designed system could lead to delays, increased costs, or unfair outcomes. Moreover, effective enforcement mechanisms are essential to ensure compliance by all stakeholders.
Resistance from providers who might see these solutions as detrimental to their financial interests can also present a significant challenge. Finally, ensuring that the chosen alternative dispute resolution mechanisms are accessible to all patients, regardless of their socioeconomic status or geographic location, is another key hurdle.
Examples of Successful and Unsuccessful Legislative Interventions
Several states have implemented different approaches to surprise billing, with varying degrees of success. New York’s approach, for example, which involves a relatively stringent form of price regulation, has been credited with reducing patient out-of-pocket costs. Conversely, states with more flexible arbitration systems have seen mixed results, with some experiencing a reduction in disputes while others struggle with implementation challenges.
International examples, like those in some European countries with universal healthcare systems, offer further insight. These systems often have different regulatory frameworks and approaches, providing valuable comparative data. For instance, the success of these systems is often linked to strong regulatory oversight and enforcement mechanisms.
Comparison of Different Legislative Approaches
| Legislation | Key Features | Potential Benefits | Potential Drawbacks |
|---|---|---|---|
| Price Regulation (e.g., New York) | Sets maximum allowable charges for out-of-network services. | Directly reduces patient out-of-pocket costs. | Potential for reduced provider participation in networks; potential for limiting provider choice for patients. |
| Independent Dispute Resolution (IDR) (e.g., some states) | Uses an independent third party to determine fair reimbursement rates. | Potentially more equitable than price regulation; can foster negotiation and compromise. | Complexity of implementation; potential for delays and increased administrative costs; outcomes may vary depending on the specifics of the IDR process. |
| Transparency and Disclosure Requirements | Mandates providers to disclose pricing and network information upfront. | Empowers patients to make informed choices; reduces uncertainty about costs. | May not fully address the problem of surprise bills if providers still bill out-of-network; enforcement can be challenging. |
Patient Advocacy and Consumer Protection
The recent pause on surprise billing arbitration highlights the crucial role of patient advocacy and consumer protection in the healthcare system. Patients are often caught in the middle of disputes between providers and insurers, leaving them vulnerable to unexpected and substantial financial burdens. Effective advocacy, coupled with informed patient strategies, is essential to mitigate these risks and ensure fair treatment.
The Role of Patient Advocacy Groups in Influencing Policy
Patient advocacy groups play a vital role in shaping healthcare policy related to surprise billing. These organizations, representing the interests of patients and consumers, engage in lobbying efforts, public awareness campaigns, and collaborations with policymakers to advocate for legislation that protects patients from unexpected medical bills. Their influence stems from their ability to mobilize public opinion, provide expert testimony, and offer data-driven insights into the impact of surprise billing on patients’ lives and the healthcare system as a whole.
For example, groups like the Consumer Federation of America have been instrumental in pushing for stronger consumer protections in the healthcare market. Their research and advocacy efforts have helped to inform and shape legislation at both the state and federal levels.
Strategies Patients Can Employ to Protect Themselves from Surprise Billing
Several proactive steps can significantly reduce the risk of surprise medical bills. Before receiving care, patients should verify their insurance coverage, including understanding their in-network and out-of-network benefits. This includes clarifying which providers and facilities are within their network and what their cost-sharing responsibilities will be for out-of-network care. Patients should also obtain a pre-service estimate of costs whenever possible, particularly for elective procedures or hospitalizations.
Furthermore, it’s crucial to review all medical bills meticulously for accuracy and to promptly dispute any charges that seem incorrect or unexpected. Finally, understanding the appeals process with both the provider and insurer is essential for resolving billing discrepancies.
The surprise billing arbitration pause is a significant development, impacting patient access to care. It’s interesting to consider this in light of the recent news about Walmart Health’s closure; reading the article on despite Walmart Health’s closure, the company healthcare destination Scott Bowman makes you wonder about the future of retail healthcare and how it might affect the ongoing debate around surprise billing.
Ultimately, the pause on arbitration could have unforeseen consequences for patients navigating the complexities of healthcare costs.
Examples of Successful Patient Advocacy Efforts
The passage of the No Surprises Act in the United States is a significant example of successful patient advocacy. Driven by years of lobbying and public awareness campaigns by patient advocacy groups, this legislation established a process for resolving disputes over surprise medical bills, providing patients with crucial protection against unexpected costs. State-level initiatives, such as those in California and New York, which implemented similar protections prior to the federal law, demonstrate the impact of targeted advocacy efforts at the state level.
These successful examples highlight the power of coordinated action by patient advocacy groups in bringing about meaningful policy changes.
The Importance of Transparency in Healthcare Billing
Transparency in healthcare billing is paramount to protecting patients from surprise bills. Clear and easily understandable billing statements, readily available cost information for services, and straightforward explanations of insurance coverage are crucial for empowering patients to make informed decisions. When patients have access to this information, they are better equipped to negotiate with providers and insurers, to identify potential billing errors, and to avoid unexpected costs.
This transparency promotes a more equitable and patient-centered healthcare system.
A Visual Representation of the Patient Journey and Potential Points of Vulnerability to Surprise Billing
Imagine a flowchart. The patient journey begins with a need for medical care (e.g., illness, injury, elective procedure). The first branching point is choosing a provider: in-network or out-of-network. Choosing an out-of-network provider immediately increases the risk of surprise billing. The next step is receiving care.
This is followed by receiving the bill. Here, another branching point appears: the bill is understandable and within expectations, or it contains unexpected charges (surprise billing). If it contains unexpected charges, the patient enters a process of dispute resolution, which can be lengthy and complex, potentially involving arbitration or negotiation with both the provider and the insurance company.
This process is represented by a loop that shows the possibility of the dispute being resolved or remaining unresolved. Finally, the journey ends with either a resolved bill or an outstanding debt. Each branching point in this flowchart represents a potential point of vulnerability to surprise billing. The lack of transparency and clarity at each step significantly increases the likelihood of a patient encountering a surprise medical bill.
The Future of Surprise Billing Resolution
The recent pause on surprise billing arbitration offers a critical juncture to reassess the effectiveness of current resolution mechanisms and chart a course towards a more sustainable and patient-centric system. The long-term implications of this pause, coupled with ongoing debates about cost containment and access to care, necessitate a proactive and collaborative approach to shaping the future of surprise billing resolution.
Predictions for Future Surprise Billing Resolution Mechanisms
Several trends suggest a shift towards more streamlined and transparent processes. We can expect increased reliance on advanced data analytics to identify and predict potential surprise billing scenarios, allowing for proactive interventions. This could involve real-time price transparency tools integrated into electronic health records (EHRs) or patient portals, giving individuals greater control and understanding of their healthcare costs before receiving services.
Furthermore, the development of standardized billing codes and improved communication between providers and insurers will likely play a significant role in reducing the occurrence of surprise bills in the first place. The ongoing expansion of value-based care models, which incentivize quality over quantity, could also indirectly mitigate the problem by fostering greater cooperation between providers and payers. For example, bundled payments for specific procedures could eliminate the potential for unanticipated charges from different providers involved in the same episode of care.
Long-Term Impacts of the Pause on the Healthcare System
The pause on arbitration has provided valuable data on the effectiveness of the existing system. Analysis of this data, including claims data and patient feedback, can inform the design of a more efficient and equitable resolution process. However, a prolonged pause could also lead to increased uncertainty for both providers and patients. Providers may face greater financial risk if they are unable to resolve disputes effectively, potentially leading to higher costs for patients or reduced access to care.
Conversely, patients could experience delays in receiving necessary treatment while disputes are resolved through alternative mechanisms, highlighting the need for a timely and efficient resolution system. For instance, the initial implementation of the No Surprises Act experienced some growing pains; learning from these experiences is vital to avoid similar issues in the future.
Key Challenges in Addressing Surprise Billing Moving Forward
One significant challenge is ensuring equitable reimbursement for providers while protecting patients from unexpected costs. Finding a balance that avoids shifting costs onto patients or unduly penalizing providers remains a complex task. Furthermore, the complexity of healthcare billing and coding presents a significant hurdle. Streamlining these processes and improving data standardization are crucial steps towards preventing surprise billing altogether.
The pause on surprise billing arbitration is a significant development, especially considering the rising healthcare costs. This is further highlighted by the sheer increase in Medicare spending on GLP-1 medications for weight loss, as detailed in this insightful KFF report: medicare glp1 spending weight loss kff. Understanding these cost drivers is crucial as we navigate the future of surprise billing and healthcare affordability.
The arbitration pause gives us time to consider these broader financial implications.
Another key challenge lies in ensuring transparency and accessibility for all stakeholders, particularly for patients who may lack the resources or understanding to navigate complex billing systems. A user-friendly and accessible system is vital to empower patients to advocate for themselves.
The Need for Collaboration Among Stakeholders
Effective surprise billing resolution requires a collaborative approach involving patients, providers, insurers, and policymakers. Open communication and shared responsibility are essential for creating a system that is both efficient and equitable. For example, establishing a multi-stakeholder working group could facilitate the development of consensus-based solutions, ensuring that all perspectives are considered. This collaborative approach could also help to build trust and improve communication between providers and insurers, reducing the likelihood of disputes arising in the first place.
This collaborative approach is critical, as a fragmented approach will only exacerbate existing problems.
Potential Framework for a Future Surprise Billing Resolution System
A future system should prioritize transparency, efficiency, and patient protection. This could involve a multi-tiered approach, starting with proactive measures to prevent surprise billing, such as enhanced price transparency tools and standardized billing practices. For disputes that do arise, a streamlined and accessible arbitration or mediation process should be available, with clear guidelines and timelines to ensure timely resolution.
Independent review boards, composed of experts from various healthcare sectors, could provide impartial oversight and ensure fairness. Regular evaluation and adjustments based on data analysis would be crucial for continuous improvement and adaptation to changing healthcare dynamics. This framework would emphasize proactive prevention, transparent processes, and equitable outcomes for all parties involved.
Final Review
Source: allzonems.com
The pause on surprise billing arbitration is far from a simple issue; it’s a complex web of competing interests and ethical considerations. While the short-term effects are already being felt, the long-term consequences remain uncertain. Ultimately, finding a solution that protects patients from crippling debt while ensuring fair compensation for providers requires a collaborative effort from all stakeholders. The journey towards a more transparent and equitable healthcare billing system is a long one, but the pause serves as a stark reminder of the urgency and importance of finding a sustainable solution.
FAQ
What happens to patients with pending arbitration cases?
The status of pending cases varies depending on the specific jurisdiction and the details of the pause. Some cases might be delayed, while others might require renegotiation or alternative dispute resolution methods.
How does this pause affect provider income?
The pause can negatively impact provider income, especially for those who frequently encounter surprise billing situations. Without arbitration, they might face difficulties in negotiating fair reimbursement rates.
Are there any legal challenges to the pause?
It’s likely that legal challenges will arise, depending on the specifics of the pause and how it impacts various stakeholders. The legal landscape is complex and will evolve as the situation unfolds.
What are the chances of the pause being lifted soon?
The timeline for lifting the pause is uncertain and depends on various factors, including ongoing negotiations, legislative actions, and legal challenges. It’s a dynamic situation with no guaranteed timeframe.