What is Ambient Clinical Intelligence and How is it Transforming Healthcare?
What is ambient clinical intelligence and how is it transforming healthcare? That’s the big question, and honestly, the answer is both fascinating and a little mind-blowing. Imagine a healthcare system that anticipates your needs before you even know you have them, a world where technology seamlessly weaves into the fabric of patient care, proactively identifying risks and optimizing treatment.
That’s the promise of Ambient Clinical Intelligence (ACI), and it’s already starting to reshape how we approach health and wellness.
ACI isn’t just another tech buzzword; it’s a fundamental shift in how we utilize data and technology within healthcare. By passively collecting and analyzing data from various sources – think wearables, electronic health records (EHRs), and even simple sensor data within a hospital room – ACI systems can provide real-time insights to clinicians, enabling faster diagnoses, more personalized treatment plans, and ultimately, better patient outcomes.
This goes beyond traditional clinical decision support systems; ACI is about creating an intelligent environment that supports and enhances human expertise.
Defining Ambient Clinical Intelligence (ACI)
Ambient Clinical Intelligence (ACI) represents a significant leap forward in healthcare technology, moving beyond traditional reactive systems to a more proactive and integrated approach. Unlike older systems, ACI doesn’t require explicit user interaction to function; it operates in the background, seamlessly collecting and analyzing data to provide insights and support clinical decision-making. This subtle yet powerful shift transforms how healthcare professionals interact with technology and, ultimately, how they care for patients.ACI’s core concept revolves around the continuous, unobtrusive monitoring and analysis of clinical data within the healthcare environment.
Ambient clinical intelligence is revolutionizing healthcare by providing real-time insights, improving patient care, and boosting efficiency. This is particularly crucial in areas like labor and delivery, where timely interventions are vital, as highlighted by the challenges faced by rural hospitals, which you can read more about in this insightful article on Rural Hospitals Labor Delivery &.
Ultimately, ACI’s ability to analyze vast amounts of data could help bridge the care gap and improve outcomes for mothers and newborns, even in underserved areas.
It leverages advancements in artificial intelligence, machine learning, and sensor technology to create a context-aware system that anticipates needs and offers timely, relevant information. This differs from traditional clinical decision support systems (CDSS), which typically rely on explicit user queries and often present information in a fragmented manner. ACI, on the other hand, strives for seamless integration and proactive assistance.
Key Components and Functionalities of ACI Systems
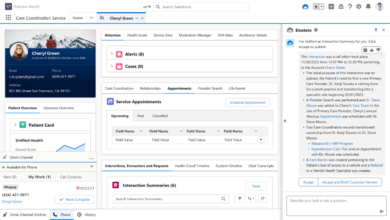
ACI systems typically comprise several interconnected components working in harmony. These include sophisticated data acquisition modules, integrating information from electronic health records (EHRs), wearable sensors, medical devices, and even environmental monitoring systems. Powerful AI algorithms then process this vast amount of data in real-time, identifying patterns, predicting potential complications, and flagging critical events. The system’s output is often presented through intuitive interfaces, such as voice assistants or augmented reality overlays, ensuring ease of access and usability for healthcare professionals.
Crucially, ACI systems are designed to be adaptable and learn from past experiences, constantly refining their accuracy and efficiency. Key functionalities include real-time patient monitoring, predictive analytics for risk stratification, automated alerts for critical events, and personalized treatment recommendations.
Real-World Applications of ACI in Healthcare Settings, What is ambient clinical intelligence and how is it transforming healthca
ACI’s potential applications are vast and rapidly expanding. In intensive care units (ICUs), ACI can continuously monitor vital signs, detect early signs of sepsis or respiratory distress, and alert the medical team proactively. In operating rooms, ACI can provide surgeons with real-time information about a patient’s physiological state, assisting in making informed decisions during complex procedures. In outpatient clinics, ACI can help streamline workflows, automate administrative tasks, and provide personalized recommendations for preventive care.
For example, an ACI system might flag a patient’s elevated blood pressure weeks before their scheduled appointment, prompting earlier intervention and potentially preventing a more serious health event. The applications extend beyond specific settings; ACI can be used to optimize resource allocation, improve patient flow, and reduce medical errors across the entire healthcare system.
Comparison of ACI with Other Healthcare Technologies
The following table contrasts ACI with other prominent healthcare technologies, highlighting their unique functionalities, benefits, and limitations.
| Technology | Functionality | Benefits | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ambient Clinical Intelligence (ACI) | Continuous, unobtrusive monitoring and analysis of clinical data; proactive alerts and recommendations. | Improved patient outcomes, reduced medical errors, enhanced efficiency. | High initial investment cost, data privacy concerns, reliance on robust infrastructure. |
| Telehealth | Remote patient monitoring, virtual consultations, remote diagnostics. | Increased access to care, improved convenience, reduced healthcare costs. | Digital literacy barriers, technological limitations, potential for misdiagnosis. |
| Electronic Health Records (EHRs) | Centralized storage and management of patient medical information. | Improved care coordination, reduced medical errors, enhanced data accessibility. | Data interoperability issues, high implementation costs, potential for data breaches. |
ACI’s Impact on Clinical Workflow: What Is Ambient Clinical Intelligence And How Is It Transforming Healthca
Ambient Clinical Intelligence (ACI) isn’t just a technological advancement; it’s a paradigm shift in how healthcare professionals interact with data and each other. Its seamless integration into existing workflows promises to revolutionize efficiency, reduce burnout, and ultimately, improve patient care. By passively collecting and analyzing data, ACI proactively assists clinicians, freeing them from tedious tasks and allowing them to focus on what truly matters: their patients.ACI integrates into existing clinical workflows by subtly embedding itself within the existing technological landscape.
Instead of requiring clinicians to actively input data into separate systems, ACI passively gathers information from electronic health records (EHRs), medical devices, and even voice interactions. This data is then processed using sophisticated algorithms to identify patterns, predict potential complications, and provide real-time alerts and suggestions to the care team. For example, if a patient’s vital signs indicate a potential deterioration, ACI might proactively alert the nurse and physician, allowing for timely intervention.
This proactive approach minimizes the risk of overlooking critical information buried within large datasets.
ACI’s Enhancement of Clinical Efficiency and Workload Reduction
The potential for ACI to improve efficiency and reduce workload is substantial. Imagine a scenario where a physician no longer needs to manually review hundreds of pages of patient records to identify relevant information. ACI can quickly summarize key findings, highlighting critical details and presenting them in a concise, easily digestible format. This frees up valuable time for direct patient interaction, reducing physician burnout and allowing for more focused, higher-quality care.
Similarly, nurses can benefit from automated reminders for medication administration, reducing the risk of medication errors and freeing them to focus on patient needs. Studies have shown that even small reductions in administrative tasks can significantly improve job satisfaction and reduce burnout among healthcare professionals. One example is a hospital implementing ACI to automate chart reviews, resulting in a 20% reduction in physician administrative time.
ACI’s Improvement of Communication and Collaboration
ACI significantly enhances communication and collaboration among healthcare teams. By centralizing relevant patient information and providing real-time updates, ACI fosters a more coordinated and informed approach to patient care. For instance, if a patient’s condition changes, ACI can automatically notify all relevant members of the care team, ensuring everyone is aware of the situation and can contribute to the best course of action.
This real-time information sharing minimizes delays, prevents miscommunication, and promotes a more cohesive approach to treatment. Moreover, ACI can facilitate seamless communication between different departments, such as radiology and cardiology, by automatically sharing relevant images and reports.
Illustrative Comparison of Clinical Workflows
The following illustrates a typical clinical workflow with and without ACI integration: Without ACI:[Diagram Description: A flowchart showing a linear process. It begins with “Patient Admission,” followed by “Nurse Assessment,” “Physician Review of Charts,” “Diagnostic Testing,” “Physician Orders,” “Treatment,” and finally “Discharge Planning.” Each step involves manual data entry and transfer between different systems, implying potential delays and information silos.] With ACI:[Diagram Description: A flowchart showing a more integrated and streamlined process.
It begins with “Patient Admission,” and then branches into parallel processes where ACI simultaneously collects data from multiple sources (vital signs, EHRs, diagnostic tests). This data is analyzed in real-time, generating alerts and recommendations for the care team (nurse and physician). These alerts trigger immediate responses, leading to more timely interventions. The flowchart then converges back to “Treatment” and “Discharge Planning,” indicating a faster and more efficient process.
The key difference is the presence of a central ACI system facilitating data flow and providing proactive alerts, thereby significantly reducing delays and improving communication.]
Data Sources and Analytics in ACI
Source: imagekit.io
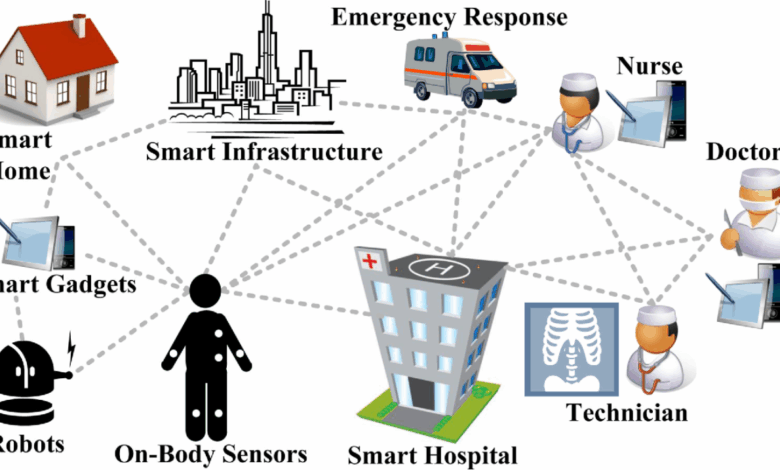
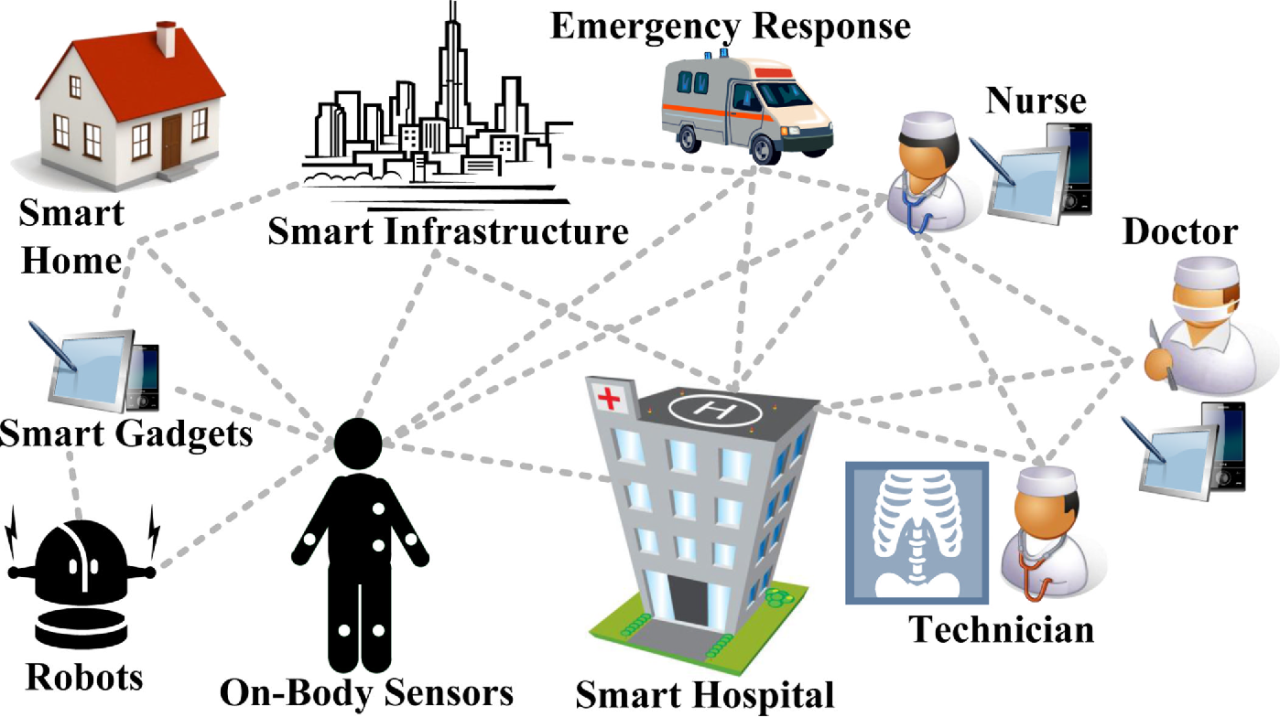
Ambient Clinical Intelligence (ACI) systems rely on a rich tapestry of data sources to build their understanding of the patient journey and clinical environment. The power of ACI lies not just in the volume of data collected, but in the sophisticated analytics applied to extract meaningful insights and support better decision-making. This section delves into the types of data used, the analytical techniques employed, and the associated privacy and security considerations.The diverse nature of data sources fueling ACI systems is a key element in their effectiveness.
These systems integrate information from disparate sources, creating a holistic view of the patient. The integration process itself presents considerable technical challenges, but the resulting comprehensive view significantly enhances the accuracy and utility of the insights generated.
Data Sources Utilized by ACI Systems
ACI systems draw on a wide range of data sources to paint a complete picture of a patient’s health and care. These sources often include structured and unstructured data, requiring advanced techniques to integrate and analyze them effectively. Effective integration of these diverse data types is crucial for the success of ACI systems.
- Electronic Health Records (EHRs): EHRs are the cornerstone of ACI data, providing structured information on patient demographics, medical history, diagnoses, medications, lab results, and vital signs. This structured data is relatively easy to process computationally.
- Wearable Sensors: Devices like smartwatches and fitness trackers contribute continuous streams of physiological data, including heart rate, activity levels, sleep patterns, and even ECG readings. This data provides valuable insights into a patient’s daily life and can detect subtle changes indicative of health issues.
- Imaging Data: Medical images from X-rays, CT scans, MRIs, and ultrasounds provide crucial visual information. ACI systems can analyze these images using computer vision techniques to identify anomalies, track disease progression, and assist in diagnosis.
- Clinical Notes and Documentation: Free-text clinical notes, physician reports, and other unstructured data offer rich contextual information. Natural language processing (NLP) techniques are crucial for extracting meaningful information from these sources.
- Laboratory Data: Comprehensive lab results, including blood tests, urine analysis, and other diagnostic tests, contribute quantitative data points for monitoring patient health and detecting potential problems.
Advanced Analytics Techniques in ACI
The sheer volume and variety of data collected by ACI systems necessitate the use of advanced analytics techniques to extract meaningful insights. These techniques enable pattern recognition, predictive modeling, and real-time decision support.
- Machine Learning (ML): ML algorithms are widely used for pattern recognition in medical data, identifying correlations between different variables and predicting future health outcomes. For example, ML models can predict the likelihood of hospital readmission based on patient history and current health status.
- Deep Learning (DL): DL, a subset of ML, is particularly effective in analyzing unstructured data like medical images and clinical notes. Convolutional neural networks (CNNs) can identify subtle anomalies in medical images with high accuracy, aiding in early disease detection.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): NLP techniques are used to extract clinically relevant information from unstructured text data, such as physician notes and discharge summaries. This information can be used to improve clinical decision-making and enhance patient care.
- Predictive Modeling: ACI systems use predictive models to anticipate potential health risks and optimize treatment strategies. For example, a predictive model might identify patients at high risk of developing sepsis based on their vital signs and lab results, allowing for early intervention.
Data Privacy and Security Concerns in ACI
The extensive use of patient data in ACI systems raises significant privacy and security concerns. Robust measures are crucial to protect sensitive information and ensure compliance with regulations like HIPAA.
- Data breaches: Unauthorized access to patient data can have serious consequences, potentially leading to identity theft, financial loss, and reputational damage. Robust cybersecurity measures are essential to prevent breaches.
- Data anonymization and de-identification: While anonymizing data can mitigate privacy risks, it’s important to ensure that the anonymization techniques used are effective and do not compromise the utility of the data for research or clinical purposes.
- Informed consent: Patients must be fully informed about how their data will be used and have the opportunity to provide informed consent. Transparency and patient control over their data are critical.
- Compliance with regulations: ACI systems must comply with relevant data privacy and security regulations, such as HIPAA in the United States and GDPR in Europe. This requires careful consideration of data governance and compliance procedures.
ACI and Patient Care
Ambient Clinical Intelligence (ACI) holds immense potential to revolutionize patient care, moving beyond reactive treatment to proactive, personalized interventions. By seamlessly integrating data from various sources and applying advanced analytics, ACI empowers healthcare providers to deliver more effective and efficient care, ultimately leading to improved patient outcomes and enhanced safety.ACI’s ability to analyze vast amounts of data allows for a deeper understanding of individual patient needs and preferences.
This understanding is crucial for creating truly personalized treatment plans, moving away from a “one-size-fits-all” approach. Furthermore, ACI can significantly improve patient engagement by providing timely, relevant information and facilitating clear communication between patients and their care teams.
Improved Patient Outcomes and Safety
The benefits of ACI extend to numerous aspects of patient care. By providing real-time insights into a patient’s condition, ACI enables quicker identification of potential complications, facilitating prompt intervention and reducing the risk of adverse events. For example, ACI can detect subtle changes in vital signs that might indicate an impending deterioration, allowing healthcare professionals to take preemptive action.
Early warning systems powered by ACI can drastically reduce hospital readmission rates and improve overall patient safety. The proactive nature of ACI allows for a shift from crisis management to preventative care, significantly improving patient outcomes.
Personalized Treatment Plans and Enhanced Patient Engagement
ACI facilitates personalized medicine by tailoring treatment plans to individual patient characteristics, including genetics, lifestyle, and medical history. For instance, ACI can analyze a patient’s genomic data to predict their response to specific medications, enabling doctors to prescribe the most effective treatment with minimal side effects. Moreover, ACI can empower patients by providing them with access to their own health data and educational resources, promoting a more active role in their own care.
This enhanced patient engagement fosters better adherence to treatment plans and leads to improved health outcomes. Imagine a system that sends personalized reminders about medication schedules, provides educational materials tailored to the patient’s condition, and facilitates direct communication with their healthcare provider – this is the power of ACI in patient engagement.
Early Disease Detection and Preventative Care
ACI’s analytical capabilities are invaluable for early disease detection. By identifying patterns and anomalies in patient data, ACI can flag individuals at high risk of developing certain conditions, allowing for early intervention and preventative measures. For example, ACI can analyze electronic health records, wearable sensor data, and imaging results to detect subtle signs of heart disease, cancer, or diabetes long before they manifest as overt symptoms.
This proactive approach can significantly improve patient prognosis and reduce healthcare costs associated with managing advanced disease.
- Reduced hospital readmissions: ACI’s early warning systems identify potential complications, enabling timely intervention and preventing readmissions.
- Improved medication adherence: Personalized reminders and educational resources provided by ACI enhance patient engagement and medication compliance.
- Enhanced diagnostic accuracy: ACI’s analytical capabilities aid in early disease detection, leading to more timely and effective treatment.
- Reduced medical errors: Real-time alerts and decision support systems minimize human error and improve the safety of care.
- More efficient workflow for clinicians: ACI automates tasks, freeing up clinicians to focus on direct patient care.
Challenges and Future Directions of ACI
Ambient Clinical Intelligence, while promising a revolution in healthcare, faces significant hurdles in its implementation and widespread adoption. Successfully navigating these challenges will be crucial to realizing ACI’s full potential and ensuring its ethical and equitable deployment across diverse healthcare settings. This section explores the key obstacles and promising avenues for future development.
Implementation and Scaling Challenges
Deploying ACI systems effectively requires addressing several critical issues. Firstly, the sheer volume and heterogeneity of healthcare data present a major challenge. Integrating data from disparate sources – electronic health records (EHRs), wearable devices, imaging systems, and more – requires robust interoperability standards and sophisticated data integration platforms. Secondly, the computational demands of processing and analyzing this massive dataset are substantial, necessitating high-performance computing infrastructure and efficient algorithms.
Thirdly, the need for comprehensive data security and privacy protocols is paramount. Protecting sensitive patient information from unauthorized access and breaches is crucial for maintaining trust and compliance with regulations like HIPAA. Finally, successful implementation necessitates significant investment in infrastructure, training, and ongoing maintenance, posing a financial burden for healthcare organizations, particularly smaller ones. The successful scaling of ACI will depend on addressing these challenges through collaborative efforts involving technology providers, healthcare institutions, and regulatory bodies.
Ambient clinical intelligence is revolutionizing healthcare by analyzing massive datasets to provide real-time insights. This data-driven approach is incredibly powerful, and its potential is amplified by advancements like the widespread adoption of digital twins, as explored in this fascinating study: study widespread digital twins healthcare. Ultimately, the integration of these technologies promises a future where personalized, proactive healthcare becomes the norm, thanks to the insights gleaned from ambient clinical intelligence.
Ethical Considerations in ACI
The use of ACI raises several important ethical considerations. Bias in algorithms is a significant concern. If the data used to train ACI systems reflects existing biases in healthcare, the resulting system may perpetuate or even amplify these inequalities, leading to disparities in care. For example, an algorithm trained primarily on data from a specific demographic group might not accurately predict outcomes for other groups.
Maintaining patient privacy and data security is another critical ethical issue. ACI systems process vast amounts of sensitive patient data, requiring robust security measures to prevent unauthorized access and breaches. Transparency and explainability of ACI algorithms are also crucial. Healthcare professionals need to understand how ACI systems arrive at their recommendations to ensure responsible use and avoid unintended consequences.
Finally, the potential for job displacement due to automation needs careful consideration, requiring strategies for retraining and reskilling healthcare workers. Addressing these ethical considerations requires a multidisciplinary approach involving clinicians, ethicists, policymakers, and technology developers.
Future Trends and Advancements in ACI
The future of ACI holds immense potential. Advancements in artificial intelligence, particularly in areas like natural language processing and machine learning, will enable more sophisticated and accurate analysis of clinical data. This will lead to improved diagnostic accuracy, personalized treatment plans, and more efficient workflow optimization. The integration of ACI with other emerging technologies, such as the Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) and virtual reality (VR), will further enhance its capabilities.
IoMT devices will provide a continuous stream of patient data, allowing for proactive monitoring and intervention, while VR can be used for immersive training and simulation. Furthermore, the development of more robust and explainable AI models will increase trust and transparency. This will involve techniques such as incorporating human-in-the-loop systems and developing methods for explaining the reasoning behind AI-driven decisions.
Ambient clinical intelligence is revolutionizing healthcare by automating tasks and providing real-time insights. This is hugely impactful, and a great example is how Nuance integrates generative AI scribe with Epic EHRs , streamlining documentation and freeing up clinicians’ time. Ultimately, this kind of AI integration is a core component of what makes ambient clinical intelligence so transformative for the future of patient care.
A Hypothetical Future Scenario
Imagine a future hospital where ACI is seamlessly integrated into every aspect of care. Physicians use smart glasses equipped with ACI to access a patient’s complete medical history, real-time physiological data, and predictive analytics during rounds. The system flags potential complications, suggests optimal treatment strategies, and alerts the physician to any inconsistencies or overlooked details. Nurses utilize ACI-powered tools to automate administrative tasks, freeing up time for direct patient care.
The system proactively monitors patients’ vital signs, alerting staff to any concerning changes. Predictive analytics identify patients at high risk of readmission, enabling proactive interventions to prevent hospital readmissions. Personalized treatment plans are generated based on a patient’s unique genetic profile, lifestyle, and medical history, ensuring optimal outcomes. The entire system is secure, transparent, and ethically designed, ensuring patient privacy and data security while enhancing the quality and efficiency of healthcare delivery.
This is not merely a technological advancement; it’s a fundamental transformation of how healthcare is delivered, prioritizing patient-centered care and improving outcomes for all.
Case Studies of ACI Implementation

Source: ytimg.com
Ambient Clinical Intelligence (ACI) is no longer a futuristic concept; it’s being implemented in real-world healthcare settings, transforming how care is delivered. Examining successful ACI implementations provides valuable insights into its benefits and challenges. The following case studies illustrate the diverse applications and outcomes of ACI across different healthcare environments.
ACI Implementation in a Large Urban Hospital
A major urban hospital implemented an ACI system integrating data from electronic health records (EHRs), wearable sensors, and imaging systems. The system used machine learning algorithms to predict patient deterioration, enabling proactive interventions. This resulted in a 15% reduction in hospital readmissions within 30 days and a 10% decrease in average length of stay. The system also facilitated more efficient staffing allocation by predicting patient needs and workload fluctuations.
Challenges included data integration complexities and the need for extensive staff training on the new system. The hospital’s experience highlights the potential for ACI to significantly improve operational efficiency and patient outcomes, but also underscores the importance of careful planning and robust change management.
ACI in a Rural Primary Care Clinic
A rural primary care clinic implemented a simpler ACI system focusing on chronic disease management. The system used data from EHRs and patient-reported outcomes to identify patients at high risk of exacerbation of conditions like diabetes and hypertension. The system then provided clinicians with personalized alerts and recommendations for preventative care. This resulted in improved patient engagement, better adherence to medication regimens, and a reduction in emergency room visits.
The relatively smaller scale of the implementation made it easier to manage and integrate into existing workflows. The success of this case study demonstrates that ACI can be beneficial even in resource-constrained settings, emphasizing the adaptability of the technology.
ACI in Home Healthcare
A home healthcare agency integrated ACI into its telehealth platform. The system used data from wearable sensors, remote patient monitoring devices, and patient-reported data to monitor patients’ vital signs and activity levels. The system alerted clinicians to significant changes, enabling timely interventions and preventing hospital readmissions. This improved patient safety and satisfaction while reducing the overall cost of care.
The challenges included ensuring data privacy and security, and managing the technical aspects of remote monitoring. This case study showcases ACI’s potential to expand access to high-quality care for patients in their homes.
Comparison of Case Studies
The three case studies illustrate the versatility of ACI across different healthcare settings. While the urban hospital focused on broad-scale predictive analytics and operational efficiency, the rural clinic emphasized chronic disease management and patient engagement. The home healthcare agency concentrated on remote patient monitoring and proactive interventions. Despite differing implementations, all three experienced positive outcomes, demonstrating ACI’s ability to improve patient care and operational efficiency across diverse contexts.
However, challenges related to data integration, staff training, and data security remain consistent across all implementations, highlighting the need for careful planning and robust infrastructure.
Summary of ACI Implementation Case Studies
| Setting | Implementation Details | Results |
|---|---|---|
| Large Urban Hospital | Integrated system using EHRs, wearables, and imaging; predictive analytics for patient deterioration | 15% reduction in readmissions, 10% decrease in length of stay, improved staffing efficiency |
| Rural Primary Care Clinic | System focusing on chronic disease management using EHRs and patient-reported outcomes; personalized alerts and recommendations | Improved patient engagement, better medication adherence, reduced ER visits |
| Home Healthcare Agency | ACI integrated into telehealth platform; remote patient monitoring using wearables and patient-reported data | Improved patient safety and satisfaction, reduced cost of care |
Final Wrap-Up
Source: amazonaws.com
The integration of Ambient Clinical Intelligence into healthcare is still in its early stages, but the potential is undeniable. As ACI systems become more sophisticated and data security concerns are addressed, we can expect to see even more dramatic transformations in patient care. From proactive disease management to personalized medicine and streamlined workflows, ACI is poised to revolutionize how we deliver and experience healthcare, creating a future where technology empowers both clinicians and patients to achieve optimal health outcomes.
The journey is just beginning, and it’s one I’m incredibly excited to follow.
Clarifying Questions
What are the biggest challenges in implementing ACI?
Data privacy and security are major concerns. Ensuring interoperability between different systems and overcoming resistance to adopting new technologies are also significant hurdles.
How does ACI differ from telehealth?
Telehealth focuses on remote patient monitoring and virtual consultations. ACI is broader, encompassing data analysis and proactive insights from various sources, not just remote patient data.
Is ACI replacing doctors?
Absolutely not! ACI is a tool to augment the capabilities of healthcare professionals, empowering them to make better, faster decisions, not replacing their expertise and judgment.
What are the ethical considerations surrounding ACI?
Bias in algorithms, data privacy violations, and the potential for misuse of sensitive patient information are key ethical considerations.