
What is Xanthelasma Know Symptoms, Causes, Treatment
What is xanthelasma know symptoms causes treatment – What is xanthelasma? Know symptoms, causes, and treatment – that’s what we’re diving into today! These yellowish, slightly raised bumps near your eyelids might seem insignificant, but they can actually be a sign of underlying health issues, primarily related to high cholesterol. Understanding xanthelasma, from its appearance to its treatment options, is key to managing your overall well-being.
We’ll explore the different ways these lesions present themselves, what causes them, and what you can do about them, so you can feel informed and empowered.
Xanthelasma palpebrarum, to give it its proper name, typically appears as small, flat, yellowish plaques on or around the eyelids. While they’re usually painless and harmless in themselves, they often serve as a visual indicator of elevated cholesterol levels or other lipid disorders. We’ll delve into the details of its appearance, location, and the various medical conditions that might be linked to its presence.
We’ll also cover the spectrum of treatment options, from minimally invasive procedures to more involved approaches, helping you understand the best course of action depending on your individual circumstances.
What is Xanthelasma?
Xanthelasma palpebrarum, often shortened to xanthelasma, might sound intimidating, but it’s essentially a benign skin condition. Think of it as a collection of cholesterol-rich deposits that appear just beneath the surface of your skin. While not usually a cause for serious concern, it’s important to understand what it looks like and what might cause it.Xanthelasma Lesion Appearance and Location
So, you’re wondering, “What is xanthelasma? Know symptoms, causes, treatment?” It’s those yellowish cholesterol deposits around your eyelids. Understanding the underlying lipid issues is crucial, as high cholesterol is one of the risk factors that make stroke more dangerous , a serious health concern. Therefore, addressing xanthelasma might be a part of a broader strategy to improve overall cardiovascular health.
Getting those levels checked is key to preventing more serious complications down the line.
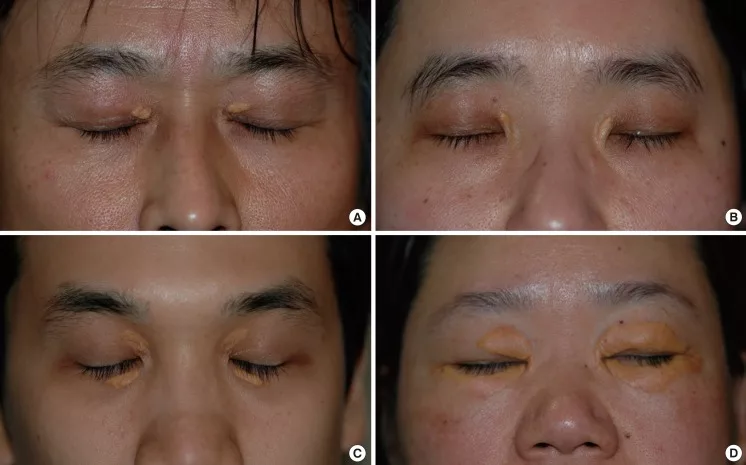
Xanthelasma Lesion Appearance
Xanthelasma lesions typically present as small, flat, yellowish plaques or bumps. They can vary in size, from tiny specks to larger patches, and often have a slightly raised texture. The color is usually a pale yellow, sometimes described as a butter-yellow or even slightly orange. The lesions are usually soft and smooth to the touch and are generally not painful or itchy.
Importantly, their appearance is often symmetrical, meaning they tend to appear on both eyelids simultaneously.
Xanthelasma Lesion Location
Xanthelasma lesions are almost exclusively found on the eyelids, specifically in the inner corners near the bridge of the nose. They rarely appear elsewhere on the body. This localized appearance is a key characteristic that helps distinguish xanthelasma from other skin conditions. While it’s possible to have xanthelasma on only one eyelid, it’s far more common to see them on both.
Comparison of Xanthelasma with Similar Skin Conditions
Understanding the differences between xanthelasma and other skin conditions is crucial for accurate diagnosis. The following table highlights key distinctions:
| Condition | Appearance | Location | Common Causes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Xanthelasma | Flat, yellowish plaques; soft, smooth texture | Inner corners of eyelids | High cholesterol, dyslipidemia |
| Miliaria (Heat Rash) | Small, raised bumps; often itchy | Various body areas, especially skin folds | Excessive sweating, blocked sweat ducts |
| Seborrheic Keratosis | Warty, raised lesions; often brown or black | Face, trunk, scalp | Aging, genetics |
| Syringoma | Small, flesh-colored or yellowish papules | Eyelids, armpits, groin | Genetics, hormonal changes |
Symptoms of Xanthelasma
Xanthelasma palpebrarum, while often visually noticeable, doesn’t always present with significant symptoms beyond its appearance. Understanding the typical presentation and variations is crucial for appropriate management and addressing any potential underlying health concerns.Xanthelasma typically manifests as yellowish, slightly raised plaques or lesions on the eyelids, most commonly near the inner corner (medial canthus). Their appearance is usually the primary, and often only, symptom.
Appearance and Size Variations
The size and number of xanthelasma lesions vary significantly between individuals. They can range from small, barely perceptible spots to larger plaques that may cover a substantial portion of the eyelid. Multiple lesions are common, sometimes appearing bilaterally (on both eyelids). The color is generally a pale yellow, but it can occasionally appear more orange or even slightly brown depending on factors such as the depth of the lesion and individual skin tone.
Larger lesions might appear more prominent and potentially cause a slight cosmetic concern for some individuals.
Location and Distribution, What is xanthelasma know symptoms causes treatment
While predominantly located on the eyelids, xanthelasma can occasionally appear in other areas of the face or body, although this is less common. The vast majority of cases, however, involve the eyelids, typically affecting the upper or lower lids, or both. The lesions are usually found close to the inner corner of the eye, but can extend outward along the eyelid margin.
Asymptomatic Nature of Xanthelasma
Many individuals with xanthelasma experience no symptoms other than the visible lesions themselves. The plaques are typically painless and do not cause itching, burning, or any other discomfort. This asymptomatic nature is a key characteristic of the condition. The absence of any other symptoms often leads to delayed medical attention, with many individuals seeking consultation only for cosmetic reasons.
Situations Warranting Medical Attention
While xanthelasma itself is generally benign, its presence can sometimes indicate underlying health issues, particularly those related to lipid metabolism. Medical attention is warranted when:
- Xanthelasma appears suddenly or rapidly increases in size.
- The individual experiences other symptoms, such as fatigue, abdominal pain, or jaundice, which could suggest underlying liver disease or other metabolic disorders.
- The individual has a family history of high cholesterol or other lipid disorders.
- There is concern about the cosmetic impact of the lesions.
In these situations, a medical professional can perform blood tests to assess lipid levels and other relevant markers to determine the underlying cause and recommend appropriate management strategies. Early detection and management of any underlying conditions are crucial to prevent potential complications.
Causes of Xanthelasma: What Is Xanthelasma Know Symptoms Causes Treatment
Xanthelasma palpebrarum, those yellowish plaques that appear on the eyelids, aren’t just a cosmetic concern; they’re a sign that something’s happening beneath the skin’s surface. Understanding the causes is crucial for appropriate management and addressing any underlying health issues. While the exact mechanisms aren’t fully understood, several factors contribute to their development.The most significant link is to elevated levels of lipids, specifically cholesterol and triglycerides, in the blood.
So, you’re researching xanthelasma – those yellowish bumps near your eyelids. Understanding the symptoms, causes, and treatment options is key, but managing related conditions is also important. For example, if a child in your family has Tourette Syndrome, learning effective management strategies is crucial, and I found this article incredibly helpful: strategies to manage Tourette syndrome in children.
Returning to xanthelasma, remember that early diagnosis and treatment can often improve the cosmetic impact.
These fats accumulate within specialized cells called macrophages in the skin, leading to the formation of these visible deposits. This isn’t to say everyone with high cholesterol will develop xanthelasma, but it’s a strong contributing factor. The accumulation isn’t simply a spillover; it’s a complex process involving the metabolism and uptake of lipids by skin cells.
High Cholesterol and Xanthelasma
High cholesterol, particularly high LDL (“bad”) cholesterol, is strongly associated with xanthelasma. The plaques are essentially collections of cholesterol and other lipids within the skin. When LDL cholesterol levels remain chronically elevated, the body’s ability to process and remove these lipids from the bloodstream becomes overwhelmed. This excess cholesterol then deposits in various areas of the body, including the eyelids, manifesting as xanthelasma.
Effective management of high cholesterol often leads to a reduction in the size or even disappearance of existing xanthelasma. A person with a family history of high cholesterol and xanthelasma might have a higher predisposition.
Other Risk Factors for Xanthelasma
Beyond high cholesterol, other factors can increase the risk of developing xanthelasma. These include genetic predispositions, certain metabolic disorders like diabetes, and obesity. Individuals with conditions affecting lipid metabolism, such as familial hypercholesterolemia (a genetic disorder causing high cholesterol), are at a significantly higher risk. Lifestyle factors like poor diet, lack of exercise, and smoking can also indirectly contribute by increasing cholesterol levels.
Xanthelasma Across Age Groups
While xanthelasma can occur at any age, its prevalence increases with age. This is partly due to the cumulative effects of lifestyle choices and the natural changes in lipid metabolism that occur as we age. In younger individuals, the presence of xanthelasma often points to a more significant underlying lipid disorder or genetic predisposition, requiring thorough investigation. Older adults, however, may develop xanthelasma as a consequence of age-related changes in lipid metabolism, even without overtly high cholesterol levels.
Therefore, the underlying causes need to be considered within the context of the individual’s age and overall health profile.
Treatment Options for Xanthelasma

Source: ytimg.com
Xanthelasma palpebrarum, those yellowish plaques that can appear on your eyelids, might be a cosmetic concern, but choosing the right treatment depends on several factors. The size, number, and location of the lesions, as well as your personal preferences and overall health, all play a role in determining the best approach. Let’s explore the various treatment options available.
Minimally Invasive Treatment Options
Several minimally invasive procedures offer a less aggressive approach to xanthelasma removal, often with quicker recovery times compared to surgical options. These are generally suitable for smaller lesions and individuals seeking less extensive treatment.
- Chemical Cautery: This involves applying a chemical solution, such as trichloroacetic acid (TCA) or other agents, directly to the xanthelasma. This causes the lesion to be destroyed and eventually slough off.
- Pros: Relatively simple, quick procedure, often performed in a doctor’s office.
- Cons: Potential for scarring, hypopigmentation (lighter skin), or hyperpigmentation (darker skin), multiple treatments may be necessary, risk of infection.
- Cryotherapy: This technique uses freezing temperatures (liquid nitrogen) to destroy the xanthelasma. The lesion freezes, causing cell death and eventual removal.
- Pros: Relatively quick, minimally invasive, can be performed in a doctor’s office.
- Cons: Potential for scarring, blistering, hypopigmentation or hyperpigmentation, may require multiple treatments.
- Laser Treatment: Different types of lasers, such as CO2 or erbium:YAG lasers, can be used to ablate (remove) the xanthelasma. The laser energy vaporizes the lesion.
- Pros: Precise removal, minimal bleeding, often good cosmetic results.
- Cons: Potential for scarring, pigmentation changes, risk of infection, can be more expensive than other minimally invasive options.
Surgical Treatment Options
Surgical excision is a more invasive option, generally reserved for larger or more numerous lesions, or when other methods have failed. This usually requires local anesthesia and may involve some downtime for recovery.
- Surgical Excision: This involves the complete surgical removal of the xanthelasma with a scalpel. The surgeon will make an incision to remove the lesion and then close the wound with sutures.
- Pros: Complete removal of the lesion, often good cosmetic results (with proper surgical technique).
- Cons: More invasive, requires local anesthesia, potential for scarring, longer recovery time, risk of infection, higher cost than minimally invasive options.
Decision-Making Flowchart for Xanthelasma Treatment
Imagine a flowchart. It would begin with a central question: “What are the size and number of xanthelasma lesions?” Branches would then lead to:* Small, single lesion: Options presented would be chemical cautery, cryotherapy, or laser treatment. Further branching would consider patient preference for minimal invasiveness and cost.
Multiple or large lesions
So you’re wondering, “What is xanthelasma? Know symptoms, causes, treatment?” It’s those yellowish bumps near your eyelids, often linked to high cholesterol. Managing this involves understanding your diet, and that’s where this article comes in: are women and men receptive of different types of food and game changing superfoods for women , which can significantly impact cholesterol levels.
Dietary changes, as highlighted in the link, are crucial in treating xanthelasma, alongside other medical interventions your doctor might recommend.
Patient factors (age, health, etc.) This would influence the choice, with older or less healthy individuals possibly being more inclined towards less invasive options.The flowchart would conclude with a recommended treatment based on the patient’s individual circumstances and lesion characteristics. This is a simplified representation; a proper clinical decision would involve a thorough examination and discussion with a dermatologist or qualified medical professional.
Visual Representation of Xanthelasma
Understanding the visual characteristics of xanthelasma is crucial for accurate self-assessment and effective communication with healthcare professionals. While a picture is worth a thousand words, a detailed description can be equally helpful in visualizing these skin lesions. This section provides a comprehensive description to aid in understanding their appearance.Xanthelasma lesions typically present as yellowish, slightly raised plaques. Their color ranges from a pale yellow, almost cream-colored, to a deeper, more intense yellow, sometimes with an orange tint.
The texture is generally smooth and waxy, almost like a thin layer of solidified butter or beeswax pressed against the skin. The lesions themselves are soft to the touch and usually do not cause any pain or discomfort.
Typical Xanthelasma Lesion Description
A typical xanthelasma lesion is often oval or elongated in shape, although they can also be round or irregular. Size varies considerably, ranging from a few millimeters to several centimeters in diameter. Larger lesions may be composed of several smaller, coalescing plaques. The borders of a xanthelasma lesion are usually well-defined, but not sharply demarcated; they tend to blend somewhat subtly into the surrounding skin.
The surface is typically smooth and flat, though in some cases, very slight irregularities or a slightly bumpy texture might be present. Lesions are usually found on or near the eyelids, often symmetrically on both sides.
Progression of Xanthelasma: A Visual Timeline
An illustration depicting the progression of xanthelasma could begin with a very early stage showing a tiny, barely perceptible yellowish spot, perhaps only a millimeter or two in diameter. This initial lesion would have a smooth, slightly raised surface and indistinct borders, almost blending seamlessly with the surrounding skin. The next stage could show a small, well-defined, oval-shaped plaque, perhaps 3-5 millimeters in diameter, exhibiting a more pronounced yellowish color and a slightly more elevated surface.
The borders are more clearly defined but still relatively smooth. A more advanced stage might depict several of these plaques merging together to form a larger, irregular lesion, possibly several centimeters in length. The color in this advanced stage might be more intense, and the overall texture could appear slightly more irregular or bumpy, although still generally smooth.
The final stage could show a large, confluent mass of yellowish plaques covering a significant portion of the eyelid. The color might appear slightly more varied, with some areas appearing slightly darker or more orange than others. Throughout the progression, the lesions would remain generally soft and non-painful to the touch.
Last Word
Source: sehathub.com
So, while those little yellowish bumps might seem like a minor cosmetic concern, understanding xanthelasma provides a window into your overall health. By recognizing the symptoms, exploring the potential causes, and knowing the treatment options available, you can take proactive steps to manage your health and well-being. Remember, consulting with a healthcare professional is crucial for accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment.
Don’t hesitate to seek medical advice if you notice any suspicious skin lesions or have concerns about your cholesterol levels. Taking charge of your health is always the best approach!
Clarifying Questions
Can xanthelasma be prevented?
While there’s no guaranteed prevention, maintaining healthy cholesterol levels through diet and exercise significantly reduces your risk.
Does xanthelasma ever go away on its own?
Rarely. While sometimes they may appear to shrink slightly, they usually persist without treatment.
Are there any home remedies for xanthelasma?
While some home remedies are touted, there’s no scientific evidence to support their effectiveness. Always consult a doctor before trying any alternative treatments.
Is xanthelasma contagious?
No, xanthelasma is not contagious.
