Whooping Cough Deaths Hit Record High Understanding the Danger
Whooping cough deaths hit record high in us know what makes this infection so dangerous – Whooping cough deaths hit a record high in the US, and it’s terrifying. This isn’t just a “kids’ cough”; it’s a serious infection that can be deadly, especially for infants. We’ll dive into why this seemingly common illness has become so dangerous, exploring the severity of the infection, vulnerable populations, and what we can do to prevent future tragedies.
This post will cover the brutal realities of whooping cough, from its characteristic symptoms and devastating complications to the factors driving this alarming surge in deaths. We’ll look at effective treatment and prevention strategies, discuss the challenges we face in controlling outbreaks, and explore what the future holds in the fight against this deadly disease. Get ready for a deep dive into the world of pertussis – it’s more complicated than you think.
The Severity of Whooping Cough
Whooping cough, also known as pertussis, is a highly contagious respiratory infection caused by the bacterium Bordetella pertussis. While often dismissed as a childhood illness, its severity, especially in infants, is tragically underestimated, leading to significant morbidity and mortality. Understanding the mechanisms of the disease and its varied presentations across different age groups is crucial for effective prevention and management.
Mechanisms of Severe Illness in Infants
Infants are particularly vulnerable to severe whooping cough due to their underdeveloped immune systems and smaller airways. The bacteria produce toxins that damage the respiratory tract, causing inflammation and swelling. This inflammation can lead to severe coughing fits, which can cause vomiting, exhaustion, and even apnea (cessation of breathing), a life-threatening condition in infants. The intense coughing can also lead to hypoxia (lack of oxygen) and potentially brain damage due to reduced oxygen supply.
Furthermore, the weakened state of the infant following infection increases their susceptibility to secondary bacterial infections like pneumonia.
Characteristic Symptoms of Whooping Cough
Whooping cough typically progresses through three distinct stages. The first is the catarrhal stage, lasting 1-2 weeks, characterized by mild cold-like symptoms such as runny nose, sneezing, low-grade fever, and a mild cough. This stage is often misdiagnosed as a common cold. The second stage is the paroxysmal stage, where the characteristic “whooping” cough develops. This involves severe, repetitive coughing fits, often followed by a high-pitched “whoop” sound during inhalation as the child struggles to breathe.
These fits can be extremely distressing and exhausting. The final stage is the convalescent stage, where the frequency and severity of the coughing gradually decrease, although it can persist for several weeks or even months.
Case Studies Illustrating Severity and Outcomes
One case study involved a 2-month-old infant who presented with severe coughing fits, apnea, and cyanosis (bluish discoloration of the skin due to lack of oxygen). The infant required hospitalization, oxygen therapy, and respiratory support. While the infant ultimately recovered, the experience highlighted the potentially life-threatening nature of whooping cough in this age group. Another case involved a 6-year-old child who experienced prolonged coughing, but without the characteristic whoop.
This illustrates that the classic “whoop” sound isn’t always present, making diagnosis challenging. This child recovered fully with antibiotic treatment. These examples illustrate the broad spectrum of disease severity, from mild to life-threatening.
Symptom Comparison Across Age Groups, Whooping cough deaths hit record high in us know what makes this infection so dangerous
| Age Group | Symptoms | Severity | Complications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Infants (<1 year) | Apnea, cyanosis, poor feeding, vomiting, exhaustion | Often severe, potentially life-threatening | Pneumonia, seizures, brain damage, death |
| Children (1-10 years) | Paroxysmal coughing fits, whooping sound (often present), vomiting | Variable, ranging from mild to severe | Pneumonia, ear infections, dehydration |
| Adults (11+ years) | Persistent cough, fatigue, occasional paroxysms, less severe whooping | Generally less severe than in infants and children | Pneumonia, rib fractures from coughing |
Vulnerable Populations and Risk Factors
Whooping cough, or pertussis, while preventable through vaccination, disproportionately affects certain populations, leading to severe illness and even death. Understanding these vulnerable groups and the contributing factors is crucial for effective public health strategies. This section will delve into the specific populations at highest risk, the role of vaccination rates, and the influence of pre-existing health conditions.
Populations Most Vulnerable to Severe Whooping Cough
Infants, particularly those younger than six months, are the most vulnerable to severe pertussis. Their immature immune systems haven’t fully developed the ability to fight off the infection, and they are too young to receive the full course of the DTaP vaccine. Pregnant women are also at increased risk, both for themselves and for their unborn children. Infection during pregnancy can lead to premature birth, low birth weight, and even stillbirth.
Furthermore, older adults, whose immunity may wane over time, are also at higher risk of severe complications. Their weakened immune systems may struggle to combat the infection effectively. Finally, individuals with compromised immune systems due to underlying health conditions, such as HIV/AIDS or those undergoing chemotherapy, are extremely susceptible to severe whooping cough.
The Role of Vaccination Rates in Whooping Cough Severity and Frequency
Low vaccination rates directly correlate with increased whooping cough outbreaks and severity. When a significant portion of a population is unvaccinated (or has inadequate vaccine coverage), it creates a breeding ground for the bacteria to spread easily. This phenomenon, known as herd immunity, is compromised, allowing the disease to circulate widely and potentially affect even those who are vaccinated.
For example, areas with low DTaP vaccination rates among children have seen a resurgence of pertussis outbreaks, with a greater number of hospitalizations and deaths, particularly among infants.
Impact of Underlying Health Conditions on Whooping Cough Severity
Pre-existing health conditions can significantly worsen the severity of whooping cough. For instance, individuals with respiratory conditions like asthma or cystic fibrosis are at higher risk of developing severe respiratory complications from pertussis, including pneumonia and respiratory failure. Similarly, those with compromised immune systems are more susceptible to severe infections and prolonged illness. The added burden of whooping cough on already weakened systems can lead to life-threatening complications.
Heart conditions can also be exacerbated by the intense coughing fits associated with whooping cough, leading to increased cardiac strain and potential heart failure.
Progression of Whooping Cough Infection in a Vulnerable Individual
This flowchart illustrates the potential progression of a whooping cough infection in a vulnerable individual, such as an infant.[Imagine a flowchart here. The flowchart would begin with “Exposure to Pertussis Bacteria.” This would lead to “Incubation Period (7-10 days),” followed by “Catarrhal Stage (1-2 weeks): Runny nose, mild cough.” This then leads to “Paroxysmal Stage (several weeks): Severe coughing fits, ‘whooping’ sound, vomiting.” This stage branches into two possibilities: “Recovery (with appropriate treatment and care)” and “Complications (pneumonia, seizures, encephalopathy, death).” The “Complications” branch would lead to “Hospitalization and Intensive Care.” The “Recovery” branch would lead to “Gradual improvement of symptoms.”]
Treatment and Prevention Strategies
Whooping cough, or pertussis, is a serious bacterial infection, and tackling it requires a multi-pronged approach encompassing effective treatment and robust preventative measures. While antibiotics can help manage the illness, vaccination remains the cornerstone of prevention, alongside public health initiatives to control outbreaks.
Medical Treatments for Whooping Cough
Treatment for whooping cough primarily focuses on antibiotics, such as azithromycin, erythromycin, or clarithromycin. These medications aim to reduce the duration and severity of the illness, primarily by limiting the spread of the bacteria. Early treatment is crucial, especially for infants and young children who are most vulnerable to severe complications. However, antibiotics are most effective in the early stages of infection, before the characteristic whooping cough develops.
Once the characteristic cough has started, the antibiotics’ impact on the duration of the illness is less significant. Furthermore, antibiotics do not eliminate the possibility of long-term complications, such as pneumonia or seizures. Supportive care, including managing symptoms like coughing and dehydration, is also a vital part of treatment.
Vaccination Strategies for Whooping Cough
Several vaccination strategies are employed to combat whooping cough. The most common is the DTaP vaccine, which protects against diphtheria, tetanus, and pertussis. This vaccine is typically given in a series of shots to infants and children, with boosters administered later in childhood and adulthood. The acellular pertussis (aP) vaccines used in DTaP are generally safer and produce fewer side effects than the older whole-cell pertussis vaccines.
Another vaccine, Tdap, is designed for adolescents and adults and provides a booster dose of protection against pertussis. The efficacy of these vaccines varies over time, requiring booster shots to maintain sufficient immunity. While generally safe and highly effective, some individuals may experience mild side effects such as soreness at the injection site, fever, or irritability. Rarely, more serious adverse events may occur.
The safety profile of these vaccines is continuously monitored and reassessed.
Public Health Measures to Prevent Whooping Cough Outbreaks
Effective public health strategies are essential in preventing and controlling whooping cough outbreaks. These include maintaining high vaccination rates among infants, children, and adolescents, to create herd immunity. Prompt diagnosis and treatment of cases, including contact tracing to identify and vaccinate close contacts of infected individuals, is also critical. Public awareness campaigns educating the public about the disease, its symptoms, and the importance of vaccination, can significantly improve preventative measures.
Implementing robust surveillance systems to track whooping cough cases and identify outbreaks allows for timely intervention and resource allocation. Finally, ensuring access to vaccination for all populations, regardless of socioeconomic status or insurance coverage, is crucial for achieving broad protection.
Comparative Analysis of Vaccination Rates and Whooping Cough Incidence
To illustrate the effectiveness of vaccination, consider a hypothetical bar graph. The X-axis represents different regions (Region A, Region B, Region C), and the Y-axis shows both vaccination rates (as a percentage) and whooping cough incidence rates (cases per 100,000 population). Let’s assume:Region A: 90% vaccination rate, 5 cases per 100,000 population.Region B: 70% vaccination rate, 15 cases per 100,000 population.Region C: 50% vaccination rate, 30 cases per 100,000 population.This hypothetical data demonstrates a clear inverse relationship: higher vaccination rates are associated with lower whooping cough incidence rates.
This highlights the critical role of vaccination in controlling the spread of pertussis. Real-world data from various public health agencies confirms this trend consistently.
The Impact of the Record High Death Toll
Source: bwbx.io
The recent surge in whooping cough deaths in the US represents a significant public health crisis, demanding a thorough understanding of its contributing factors and consequences. This alarming increase necessitates a comprehensive analysis of the underlying causes, demographic trends, and the broader societal and economic ramifications. Understanding these factors is crucial for developing and implementing effective prevention and control strategies.The record-high number of whooping cough deaths is a complex issue stemming from a confluence of factors.
Decreased vaccination rates, particularly among infants too young to be fully vaccinated, have played a major role. The waning immunity of older populations, coupled with the emergence of circulating strains less susceptible to existing vaccines, further complicates the situation. Additionally, limited access to healthcare, particularly in underserved communities, can hinder timely diagnosis and treatment, leading to more severe outcomes.
Finally, inadequate public health surveillance and communication can impede effective response efforts.
Statistical Overview of Whooping Cough Deaths
Analyzing whooping cough mortality data reveals concerning trends. While precise figures fluctuate yearly depending on reporting and data collection methods, a clear upward trend in recent years is evident. Infants under one year of age consistently represent the most vulnerable group, experiencing the highest mortality rates. Geographic disparities also exist, with some states consistently reporting higher incidence and mortality rates than others, often correlating with lower vaccination coverage rates in those areas.
Temporal trends often show cyclical patterns, with periodic increases in cases and deaths followed by periods of relative decline, highlighting the need for ongoing vigilance and proactive public health interventions. For example, a significant spike in cases might be observed in a particular region following a period of reduced vaccination efforts.
Societal and Economic Impacts of Increased Whooping Cough Mortality
The increased mortality rate from whooping cough carries significant societal and economic burdens. The loss of young lives is devastating to families and communities, creating profound emotional and psychological distress. Healthcare costs associated with hospitalization, intensive care, and long-term care for survivors are substantial, placing a strain on both families and the healthcare system. Lost productivity due to illness and caregiving responsibilities also contributes to the economic impact.
Furthermore, outbreaks can disrupt schools and childcare facilities, impacting workforce participation and overall societal function. For example, the closure of a school due to a whooping cough outbreak can result in significant financial losses for families and the school district.
Timeline of Significant Events and Policy Changes
A review of historical data reveals a complex interplay of events and policies impacting whooping cough control. The introduction of the pertussis vaccine in the mid-20th century significantly reduced the incidence of the disease. However, the emergence of vaccine-associated side effects, coupled with misinformation campaigns, led to decreased vaccination rates in certain populations. Subsequent efforts focused on improving vaccine safety and efficacy, as well as public education campaigns to address vaccine hesitancy.
More recently, the development of newer, acellular pertussis vaccines has aimed to improve efficacy and reduce side effects. Ongoing research and surveillance are critical for tracking disease trends, identifying emerging strains, and adapting prevention and control strategies accordingly. For instance, the introduction of a booster dose for adolescents and adults reflects a shift in understanding the waning immunity of older populations and the need for ongoing protection.
Emerging Challenges and Future Directions: Whooping Cough Deaths Hit Record High In Us Know What Makes This Infection So Dangerous
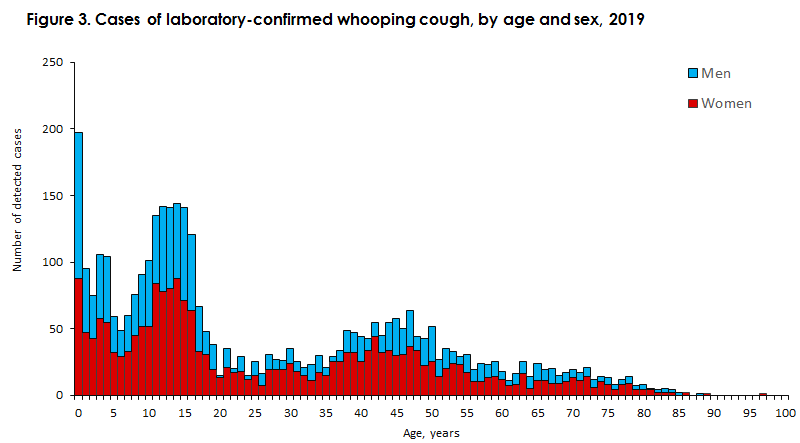
Source: ssi.dk
The recent record high in whooping cough deaths underscores the urgent need to address persistent challenges hindering effective control of this preventable disease. While vaccines and antibiotics exist, their effectiveness is hampered by several factors, creating a complex landscape requiring innovative solutions and collaborative efforts. The path forward necessitates a multi-pronged approach encompassing improved vaccine strategies, enhanced surveillance, targeted public health initiatives, and a renewed focus on antibiotic stewardship.
Vaccine Hesitancy and its Impact on Herd Immunity
Vaccine hesitancy, fueled by misinformation and distrust in scientific consensus, significantly undermines the effectiveness of vaccination programs. This reluctance to vaccinate children leaves vulnerable populations unprotected and compromises herd immunity, allowing the pertussis bacterium to circulate more freely and increasing the risk of outbreaks, particularly among infants who are too young to be fully vaccinated. The consequences of this are clearly seen in the recent surge in cases and deaths.
For example, communities with low vaccination rates often experience significantly higher incidence rates of whooping cough compared to those with high vaccination rates. Addressing vaccine hesitancy requires robust public health campaigns that promote accurate information, build trust in healthcare providers, and effectively counter misinformation through credible sources.
Antibiotic Resistance in Pertussis Bacteria
The increasing prevalence of antibiotic-resistant strains of
- Bordetella pertussis*, the bacterium responsible for whooping cough, poses a significant threat to treatment efficacy. Overuse and misuse of antibiotics have driven the selection and spread of resistant strains, making treatment more challenging and potentially leading to prolonged illness, increased complications, and higher mortality rates. The emergence of macrolide-resistant
- B. pertussis* strains, for example, necessitates the exploration of alternative treatment strategies and a more judicious use of antibiotics. This highlights the critical need for responsible antibiotic stewardship programs.
Future Research Directions for Whooping Cough Control
Several avenues of research hold promise for improving whooping cough prevention, treatment, and control. This includes the development of more effective and longer-lasting vaccines, potentially incorporating novel antigens or delivery systems. Research into the development of new antibiotics effective against resistant strains ofB. pertussis* is crucial. Further investigation into the factors contributing to the persistence of the bacteria in the environment and its transmission dynamics can inform more effective public health interventions.
Finally, advanced epidemiological modeling can aid in predicting and mitigating outbreaks.
The Role of Public Health Campaigns and Education
Effective public health campaigns are essential in combating whooping cough. These campaigns should focus on accurate and accessible information regarding the disease, its severity, and the importance of vaccination. Targeting specific at-risk populations, such as pregnant women and parents of young children, is crucial to maximize impact. Educational programs should also emphasize the importance of prompt diagnosis and treatment, as well as the responsible use of antibiotics.
A multi-media approach, utilizing social media, community outreach, and collaboration with healthcare providers, can effectively reach a wider audience.
Recommendations for Healthcare Professionals and Policymakers
A coordinated effort from healthcare professionals and policymakers is critical to address the challenges posed by whooping cough. This includes:
- Strengthening vaccination programs by improving vaccine uptake through targeted educational campaigns and addressing vaccine hesitancy.
- Implementing robust surveillance systems to track outbreaks and monitor antibiotic resistance patterns.
- Promoting responsible antibiotic use through stewardship programs to mitigate the development and spread of resistant strains.
- Investing in research and development of new vaccines and treatments.
- Enhancing public health infrastructure to support effective outbreak response and prevention strategies.
Ending Remarks

Source: cbsnewsstatic.com
The record-high number of whooping cough deaths in the US serves as a stark reminder of the ongoing threat this preventable disease poses. While effective vaccines and treatments exist, the challenges of vaccine hesitancy and antibiotic resistance highlight the need for sustained public health efforts, improved vaccination rates, and ongoing research. Understanding the severity of whooping cough, identifying vulnerable populations, and implementing comprehensive prevention strategies are crucial to protecting our communities and preventing future tragedies.
Let’s work together to ensure that no more lives are lost to this preventable disease.
Common Queries
What is the incubation period for whooping cough?
The incubation period for whooping cough is typically 7-10 days, but it can range from 5 to 21 days.
How long is a person contagious with whooping cough?
A person is most contagious during the catarrhal stage (before the characteristic cough develops), but can remain contagious for several weeks after the cough begins, particularly if untreated.
Is whooping cough treatable with antibiotics?
Yes, antibiotics can shorten the duration and severity of whooping cough, but they are most effective when given early in the course of the illness. They may not significantly reduce the severity of the paroxysmal cough.
Can whooping cough be prevented?
Yes, vaccination is the most effective way to prevent whooping cough. The DTaP vaccine is highly effective and recommended for children, and the Tdap vaccine is recommended for adolescents and adults.