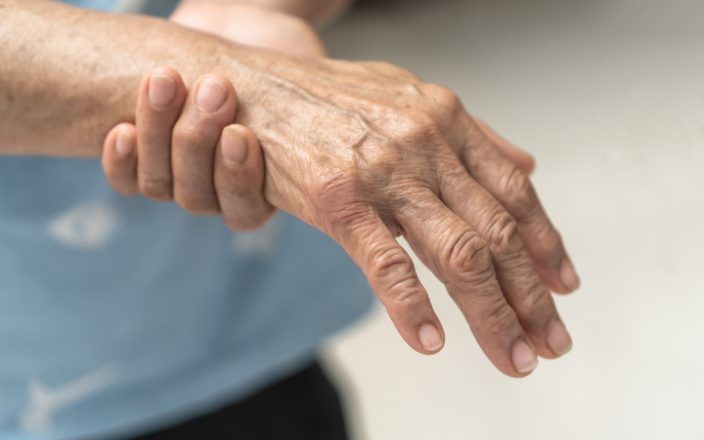

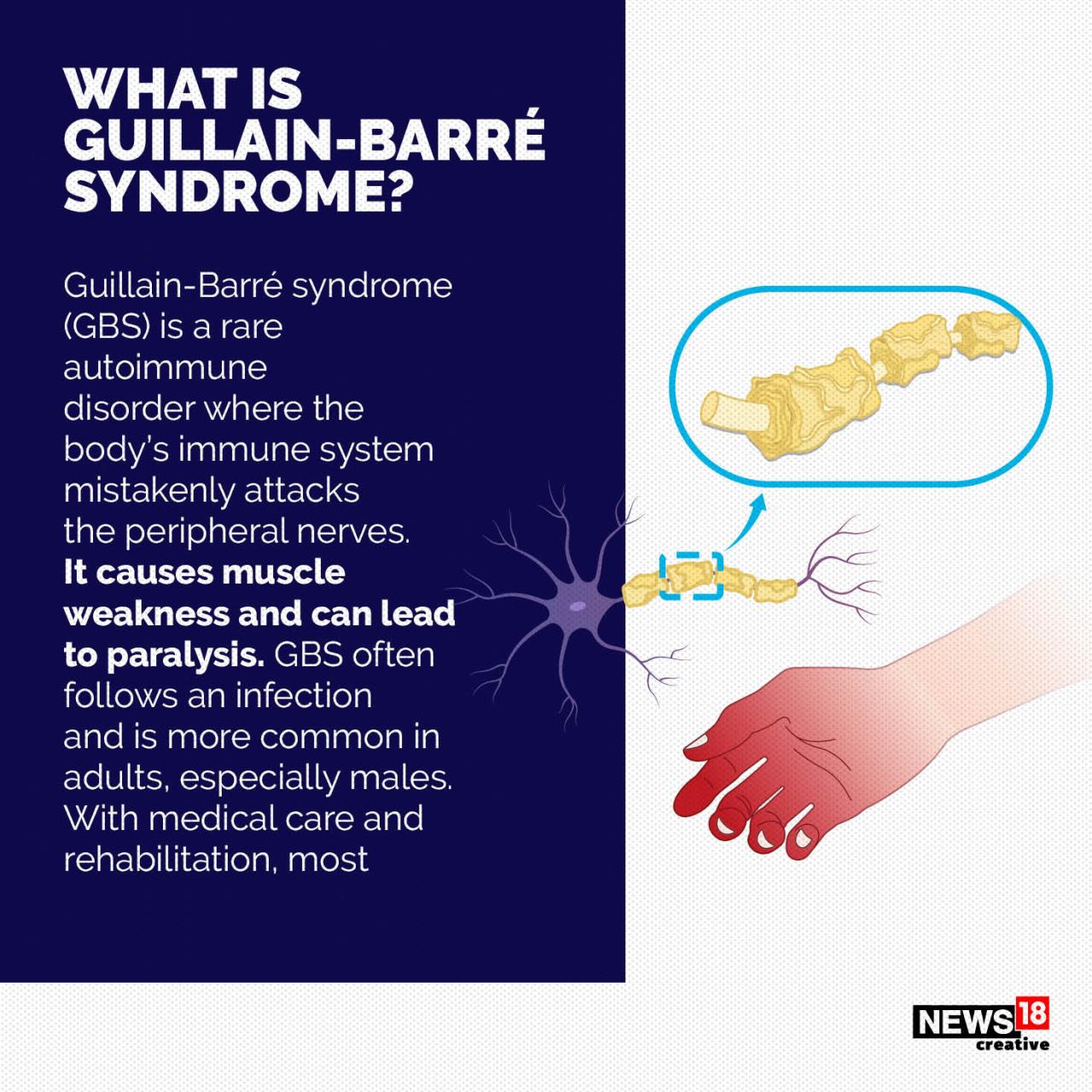
How Does Raw Chicken Trigger Guillain-Barré Syndrome?
How does raw chicken trigger guillain barre syndrome – How does raw chicken trigger Guillain-Barré syndrome? It’s a chilling question, and the answer lies in a tiny, often overlooked bacterium: Campylobacter. This common chicken contaminant can, in rare cases, trigger a devastating autoimmune response leading to Guillain-Barré syndrome (GBS), a condition where the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks its own nerves. Understanding the connection between raw chicken, Campylobacter, and GBS is crucial for protecting ourselves and our families.
The link isn’t direct; it’s a complex interplay of infection, immune response, and unfortunate circumstance. Campylobacter, often present on undercooked poultry, causes an infection that, in some individuals, triggers a cross-reactive immune response. Essentially, the body’s defenses, in fighting off Campylobacter, accidentally begin attacking the myelin sheath protecting nerves, resulting in the debilitating symptoms of GBS. While the risk is low, the consequences are severe, highlighting the importance of safe food handling practices.
Campylobacter and Guillain-Barré Syndrome
Campylobacteriosis, an infection caused by the bacteria
So, I was reading about how raw chicken, specifically contaminated with Campylobacter jejuni, can sometimes trigger Guillain-Barré syndrome – a scary thought! It got me thinking about other health scares, like Monali Thakur’s recent hospitalization, which highlights the importance of respiratory health; you can read more about it and preventative measures here: monali thakur hospitalised after struggling to breathe how to prevent respiratory diseases.
Proper food handling is key to avoiding bacterial infections, which, as we’ve seen, can have serious consequences far beyond just a tummy ache.
- Campylobacter jejuni*, is a leading cause of bacterial diarrhea worldwide. While most infections resolve without complications, a concerning association exists between
- Campylobacter* infection and the development of Guillain-Barré syndrome (GBS), a rare but serious autoimmune disorder affecting the nervous system. Understanding this link is crucial for both prevention and treatment strategies.
The precise mechanisms by which
- Campylobacter* infection triggers GBS remain under investigation, but the current understanding points towards a process of molecular mimicry.
- Campylobacter jejuni* possesses surface glycolipids that share structural similarities with gangliosides, components of the myelin sheath surrounding nerve cells. The immune system, in its attempt to fight the
- Campylobacter* infection, may mistakenly recognize these similar structures on nerve cells as foreign invaders. This leads to an autoimmune response, where the body’s own immune system attacks the myelin sheath, causing inflammation and nerve damage, ultimately resulting in the symptoms characteristic of GBS, such as muscle weakness and paralysis. This cross-reactivity between bacterial antigens and human neural tissues is a key component of the pathogenic process.
Studies Demonstrating the Association Between Campylobacter and GBS
Several studies have established a statistically significant association between antecedentCampylobacter* infection and the subsequent development of GBS. These studies, while varying in methodology and sample size, consistently support the link between the bacterial infection and the autoimmune disorder.
| Study | Year | Sample Size | Conclusion |
|---|---|---|---|
| Kusunoki et al. | 2000 | 107 GBS patients | Significantly higher prevalence of
|
| Hughes et al. | 2002 | 374 GBS patients | Demonstrated a strong association between
|
| Yuki et al. | 2001 | 110 GBS patients | Identified a significant association between
|
| Willison and Yuki | 2002 | Review article | Summarized evidence from numerous studies supporting the strong link between
|
Raw Chicken as a Source of Campylobacter
Campylobacter is a leading cause of bacterial foodborne illness worldwide, and raw chicken is a significant source of this bacteria. Understanding the prevalence of Campylobacter in poultry and the factors contributing to its presence is crucial for preventing illness. This knowledge empowers us to adopt safe food handling practices and significantly reduce the risk of infection.Campylobacter contamination in raw chicken is unfortunately widespread.
Studies consistently show high rates of contamination, with percentages often exceeding 80% in retail chicken samples. This high prevalence highlights the importance of rigorous hygiene practices throughout the entire chicken production chain, from farm to table. The exact percentage varies depending on factors such as geographical location, farming practices, and testing methodologies. However, the consistently high rates underscore the need for vigilance in handling raw poultry.
Factors Contributing to Campylobacter Contamination in Chicken
Campylobacter contamination of chicken occurs at various stages, from the farm to the processing plant and even during consumer handling. Several factors contribute to this pervasive problem.
On the farm, the presence of Campylobacter in the chicken’s environment can lead to colonization of the bird’s intestines. Stressful conditions for the birds, poor hygiene on the farm, and contaminated feed or water can increase the risk of contamination. During processing, cross-contamination can occur due to improper sanitation of equipment and surfaces. If contaminated carcasses come into contact with clean ones, the bacteria can easily spread.
So, I was reading about how Campylobacter bacteria in raw chicken can trigger Guillain-Barré syndrome – pretty scary stuff! It got me thinking about the complexities of our immune systems and how sometimes things go wrong. This is why news like the FDA approving clinical trials for pig kidney transplants in humans, fda approves clinical trials for pig kidney transplants in humans , is so fascinating; it shows how far we’ve come in understanding organ rejection and immune responses.
But back to that raw chicken – definitely worth cooking thoroughly!
The chilling process after slaughter, if not properly managed, can also facilitate the growth and survival of Campylobacter.
Finally, improper handling of raw chicken at home significantly increases the risk of contamination. This includes cross-contamination from raw chicken to other foods, utensils, and surfaces. Inadequate cooking temperatures can allow Campylobacter to survive, making the chicken unsafe to consume.
Safe Handling and Preparation of Raw Chicken
To minimize the risk of Campylobacter infection, meticulous attention to safe handling and preparation of raw chicken is paramount. Following these steps can significantly reduce your risk.
Implementing these practices is vital in preventing the spread of Campylobacter and reducing the risk of foodborne illness. Remember, even a small amount of raw chicken juice can contain millions of bacteria. Thorough cleaning and cooking are essential.
- Wash your hands thoroughly with soap and water for at least 20 seconds before and after handling raw chicken.
- Wash all surfaces, utensils, and cutting boards that have come into contact with raw chicken with hot, soapy water. Consider using a disinfectant solution as well.
- Avoid cross-contamination. Keep raw chicken separate from other foods during shopping, storage, and preparation.
- Cook chicken thoroughly to an internal temperature of 165°F (74°C) as measured by a food thermometer. This ensures that all Campylobacter bacteria are killed.
- Refrigerate raw chicken promptly at 40°F (4°C) or below. Do not leave it at room temperature for extended periods.
- Never consume raw or undercooked chicken.
Other Bacterial Contaminants in Raw Chicken and GBS
Source: cnbctv18.com
Raw chicken, unfortunately, isn’t just a potential vector for
- Campylobacter*; several other bacteria can contaminate it, some of which have been implicated, albeit less directly, in Guillain-Barré Syndrome (GBS). Understanding these other potential culprits is crucial for a complete picture of the risks associated with consuming undercooked poultry. While
- Campylobacter* remains the most strongly linked bacterial pathogen to GBS, exploring other possibilities enhances our understanding of this complex autoimmune disorder.
Several other bacteria frequently contaminate raw chicken and are known to cause foodborne illnesses. The relationship between these bacteria and GBS is less clear-cut than with
-Campylobacter*, often due to difficulties in establishing direct causal links and the complex interplay of genetic and environmental factors in GBS development. However, investigating these potential contributors is vital for comprehensive food safety and public health strategies.
Salmonella and GBS
Salmonella is another common bacterial contaminant of raw chicken. While primarily causing gastroenteritis, some studies suggest a possible, albeit weak, association between Salmonella infection and an increased risk of GBS. The mechanism, if any, is not fully understood, and the evidence is not as compelling as that for Campylobacter. It’s important to note that the majority of Salmonella infections do not lead to GBS, highlighting the complexity of this relationship.
Other Bacteria and the GBS Link
Beyond Campylobacter and Salmonella, other bacteria such as Escherichia coli ( E. coli), Clostridium perfringens, and various other species can contaminate raw chicken. However, a direct causal link between infection with these bacteria and GBS development remains largely unestablished. The research in this area is ongoing and faces significant challenges.
Challenges in Establishing Definitive Links
Pinpointing the precise role of specific bacterial contaminants in triggering GBS cases presents several significant hurdles. A crucial challenge lies in differentiating between the various factors that contribute to GBS. Many individuals with GBS have no identifiable preceding infection, making it difficult to isolate a specific bacterial culprit. Furthermore, the symptoms of GBS can be mimicked by other conditions, making diagnosis and attribution challenging.
Epidemiological studies, while informative, often struggle to establish definitive cause-and-effect relationships due to the complexities of the disease and the multitude of potential contributing factors.
- Difficulty in isolating a specific bacterial trigger in many GBS cases.
- The lack of a consistent, readily identifiable bacterial infection preceding all GBS cases.
- Challenges in differentiating GBS from other conditions with similar symptoms.
- The complexity of epidemiological studies in establishing definitive causal links.
- The potential for multiple contributing factors in GBS development, including genetic predisposition and environmental influences.
The Immune Response and GBS Development: How Does Raw Chicken Trigger Guillain Barre Syndrome
Source: pinimg.com
Guillain-Barré Syndrome (GBS) is a complex autoimmune disorder, and its development following a Campylobacter infection is a fascinating, albeit frightening, example of how our own immune system can turn against us. Understanding the immune response in this context is crucial to grasping the disease’s mechanism.The immune system, normally our body’s defense against foreign invaders, plays a paradoxical role in GBS.
While initially fighting off the Campylobacter bacteria, it can inadvertently trigger an autoimmune attack on the body’s own peripheral nerves. This misdirected response stems from a process called molecular mimicry.
Molecular Mimicry in GBS
Molecular mimicry is the key to understanding how Campylobacter infection can lead to GBS. Certain surface proteins on the Campylobacter bacteria share similar structures to proteins found on the surface of human nerve cells. This structural similarity is crucial. When the immune system mounts an attack against the bacterial proteins, some antibodies mistakenly recognize and bind to the similar proteins on the nerves.
This cross-reactivity is the foundation of the autoimmune response in GBS. Think of it like this: imagine a lock (a nerve cell protein) and two keys. One key (Campylobacter protein) fits perfectly, but a slightly different key (the antibody designed for the Campylobacter protein) also fits, albeit imperfectly, opening the lock (the nerve cell protein) and triggering an immune response.
This leads to inflammation and damage of the myelin sheath surrounding the nerves.
So, how does raw chicken trigger Guillain-Barré syndrome? It’s linked to Campylobacter bacteria, often found in undercooked poultry. Understanding food safety is crucial, especially considering how our bodies react differently to various foods; check out this interesting article on how are women and men receptive of different types of food and game changing superfoods for women , which highlights the importance of a balanced diet.
Proper food handling and preparation are key to preventing illnesses like Guillain-Barré, so always cook your chicken thoroughly!
The Autoimmune Attack on Nerves
Once the antibodies mistakenly bind to the nerve proteins, a cascade of events unfolds. The binding of these antibodies activates the complement system, a part of the innate immune system. This system further enhances inflammation, causing damage to the myelin sheath, the protective layer surrounding the nerves. This damage disrupts the efficient transmission of nerve signals, leading to the characteristic symptoms of GBS: weakness, numbness, and paralysis.
Macrophages, immune cells that engulf and destroy pathogens, are also recruited to the site of inflammation. However, in this autoimmune context, they contribute to further damage of the myelin and even the axons (the main part of the nerve cell). The inflammatory response itself, involving the release of various cytokines and other inflammatory mediators, contributes to the overall nerve damage and functional impairment observed in GBS patients.
The body, in its attempt to eliminate the perceived threat (the similar proteins on the nerve cells), ends up attacking and damaging its own nervous system. This ultimately results in the debilitating symptoms associated with Guillain-Barré Syndrome.
Risk Factors and Prevention Strategies
Understanding the factors that increase the risk of developing Guillain-Barré syndrome (GBS) after Campylobacter infection, primarily from consuming contaminated raw chicken, is crucial for effective prevention. This involves identifying individual vulnerabilities and implementing strategies at both the individual and public health levels. The goal is to minimize exposure to Campylobacter and, consequently, reduce the incidence of GBS.
Several factors can influence an individual’s susceptibility to GBS following Campylobacter infection. While not everyone who experiences Campylobacteriosis develops GBS, certain predispositions might increase the risk. It’s important to note that the exact mechanisms linking Campylobacter infection to GBS are still being researched, and the interplay of genetic and environmental factors is complex.
Individual Risk Factors for GBS Following Campylobacter Infection
While the precise reasons why some individuals develop GBS after Campylobacter infection and others don’t remain unclear, some factors seem to increase the risk. These are not definitive causes, but rather elements that may increase susceptibility.
- Genetics: A person’s genetic makeup might influence their immune response to Campylobacter. Some genetic variations may make individuals more prone to developing an autoimmune response that triggers GBS. Research is ongoing to pinpoint specific genes involved.
- Age: While GBS can occur at any age, there’s a slightly increased risk in older adults. This may be linked to age-related changes in the immune system.
- Pre-existing conditions: Individuals with underlying health issues, particularly those affecting the immune system, might be at a slightly higher risk. This isn’t a direct causal link but highlights the importance of overall health in managing infections.
- Previous Campylobacter infections: While rare, a history of Campylobacter infections might theoretically increase the risk of GBS in subsequent infections. This is an area requiring further research.
Preventative Measures to Reduce GBS Risk from Contaminated Raw Chicken, How does raw chicken trigger guillain barre syndrome
Implementing rigorous food safety practices at home is vital in reducing the risk of Campylobacter infection and, consequently, GBS. These steps minimize the chances of exposure to the bacteria.
- Thorough cooking: Ensure chicken is cooked to an internal temperature of 165°F (74°C) to kill Campylobacter bacteria. Use a food thermometer to verify.
- Handwashing: Wash hands thoroughly with soap and water before and after handling raw chicken, and after touching any surfaces that have come into contact with raw chicken.
- Safe food preparation: Avoid cross-contamination. Use separate cutting boards and utensils for raw chicken and other foods. Wash all surfaces thoroughly with hot, soapy water after contact with raw chicken.
- Refrigeration: Refrigerate raw chicken promptly at 40°F (4°C) or below. Do not leave it at room temperature for extended periods.
- Source selection: Choose chicken from reputable sources that adhere to strict food safety standards. Look for properly sealed packaging and ensure the “sell-by” date is not expired.
Public Health Strategies to Reduce Campylobacter Contamination
Reducing Campylobacter contamination in the chicken supply chain requires a multi-faceted approach involving various stakeholders, from farmers to processors and retailers. These strategies aim to minimize the bacterial load in chicken before it reaches consumers.
- Improved farm practices: Implementing better biosecurity measures on farms to reduce the initial presence of Campylobacter in poultry flocks.
- Enhanced processing techniques: Developing and implementing more effective processing methods to reduce Campylobacter contamination during the slaughter and packaging stages.
- Stricter regulatory oversight: Enhancing food safety regulations and monitoring to ensure compliance throughout the chicken supply chain. This includes regular testing and inspections.
- Consumer education: Educating consumers about safe food handling practices, particularly regarding the proper cooking of chicken and preventing cross-contamination.
- Research and development: Investing in research to develop new technologies and strategies to further reduce Campylobacter contamination in chicken production.
Closing Notes
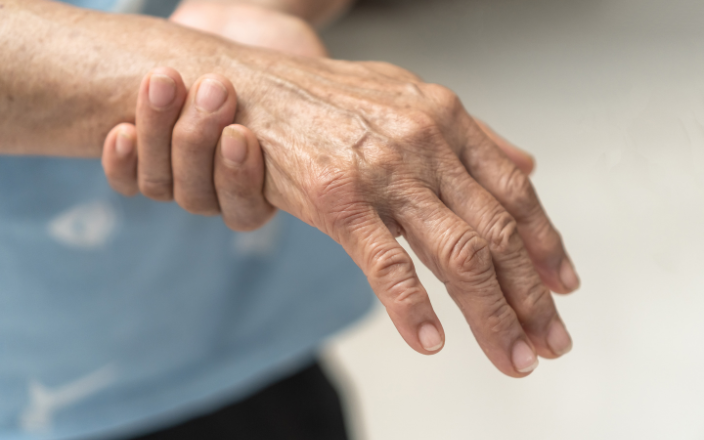

Source: avinews.com
So, while raw chicken isn’t a guaranteed path to Guillain-Barré syndrome, it’s a significant risk factor. The connection hinges on Campylobacter contamination and the body’s sometimes-erratic immune response. By diligently practicing safe food handling techniques, like thoroughly cooking chicken and maintaining proper hygiene, we can significantly minimize our exposure to this potentially dangerous bacterium and reduce the chances of this rare but serious complication.
Remember, food safety isn’t just about avoiding a tummy ache; it’s about protecting our long-term health.
FAQ Resource
What are the symptoms of Guillain-Barré syndrome?
Symptoms vary but often include weakness, tingling, numbness, and paralysis, typically starting in the feet and legs and progressing upwards.
Is Guillain-Barré syndrome always fatal?
No, it’s not always fatal. Many people recover fully, although recovery can take months or even years.
Can other foods besides chicken carry Campylobacter?
Yes, other poultry, undercooked meats, and unpasteurized milk can also harbor Campylobacter.
Are there specific groups of people more at risk?
While anyone can get GBS, some individuals, like those with weakened immune systems, may be at higher risk.
